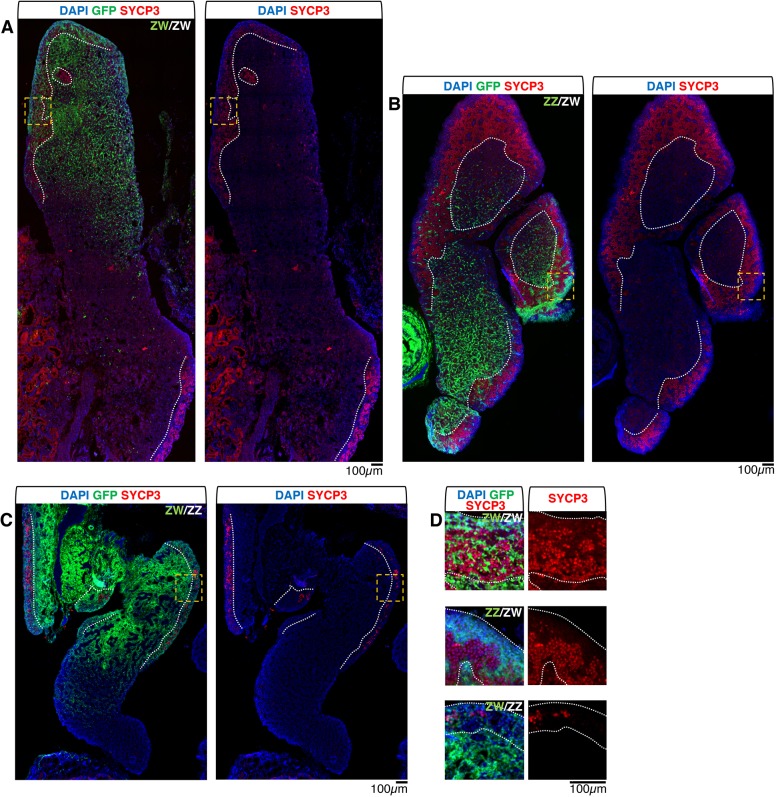
Fig. 5.
In mixed-sex gonadal chimeras ZZ somatic cells provide an adequate niche for progression of cortical germ cell into meiosis. (A-D) Sections from chimeric left gonads at D18 (HH44) immunostained for SYCP3 (red); donor cells are GFP positive (green); nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). (A) ZW donor into ZW host (ZW/ZW) control chimeric ovary; (B) ZZ donor into ZW host (ZZ/ZW); (C) ZW donor into ZZ host (ZW/ZZ); (D) high-magnification images of cortical areas (orange dashed boxes) from A-C (top to bottom, respectively). In ZW/ZW and in ZZ/ZW chimeric left ovaries, most cortical germ cells express SYCP3. In the ZW/ZZ chimeric left ovotestis, SYCP3 is expressed only in some cortical germ cells (see Fig. S3 for visualisation of the distribution of all the germ cells). The ZZ donor cortical somatic cells in the ZZ/ZW chimera provide an adequate niche for progression of germ cells into meiosis. Both ZW and ZZ cortical germ cells can progress into meiosis. However, in the ZW/ZZ ovotestis meiosis is compromised. White dotted line shows the cortex-medulla border.