Fig. 1.
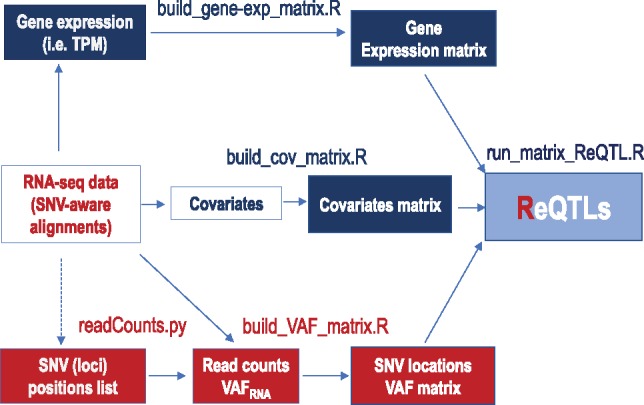
Major steps of the ReQTL analyses (differences from eQTL analysis are outlined in red). SNV-aware alignments are used to generate gene expression data; TPM values are quantile transformed and used to generate the gene expression matrix (exemplified by build_gene-exp_matrix.R). Lists of genomic positions can be built using any custom set of positions of interest (i.e. dbSNP). Alternatively, lists of genomic positions can be generated through variant call and subsequent retainment of the unique variant genomic loci across the sample set. At each genomic position in the list, the reference and variant number of RNA-seq reads are counted from the alignments and used to estimate VAFRNA in each individual sample from the set (https://github.com/HorvathLab/NGS/tree/master/readCounts). The VAFRNA estimations are used to build the VAF matrix (exemplified by build_VAF_matrix.R). Covariates can be accounted for by using approaches similar to the ones used in eQTL analyses. The three matrices are then used as input for Matrix eQTL (exemplified by run_matrix_ReQTL.R). (Color version of this figure is available at Bioinformatics online.)
