Abstract
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) is an inherited group of rare, life-threatening disorders due to the defect in T cell development and function. Clinical manifestations are characterised by recurrent and severe bacterial, viral, and fungal opportunistic infections that start from early infancy period. Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is the treatment of choice. The pattern of inheritance of SCID may be X-linked or autosomal recessive. Though the diagnosis of SCID is usually established by flow cytometry-based tests, genetic diagnosis is often needed for genetic counselling, prognostication, and modification of pre-transplant chemotherapeutic agents. This review aims to highlight the genetic aspects of SCID.
Keywords: Adenosine deaminase, Flow cytometry, Genetics, Newborn screening, Severe combined immunodeficiency
Abbreviations
- SCID
Severe combined immunodeficiency
- RAG
Recombination activating genes
- TCR
T-cell receptor
- ZBD
Zinc-binding domain
- CTD
C terminal domain
- NBD
Nucleotide-binding domain
- PHD
Plant homeodomain
- CVID
Combined variable immunodeficiency
- NHEJ
Non-homologous end joining
- XRCC4
X-ray repair cross-complementing protein
- DNA-PK
DNA dependent protein kinase
- BRCT1
BRCA1 C terminus domain
- FAT
(FRAP) (FKBP12-rapamycin-associated protein)
- FATC
C-terminal of FAT domain
- RD
Reticular dysgenesis
- TREC
T-cell receptor excision circle
Introduction
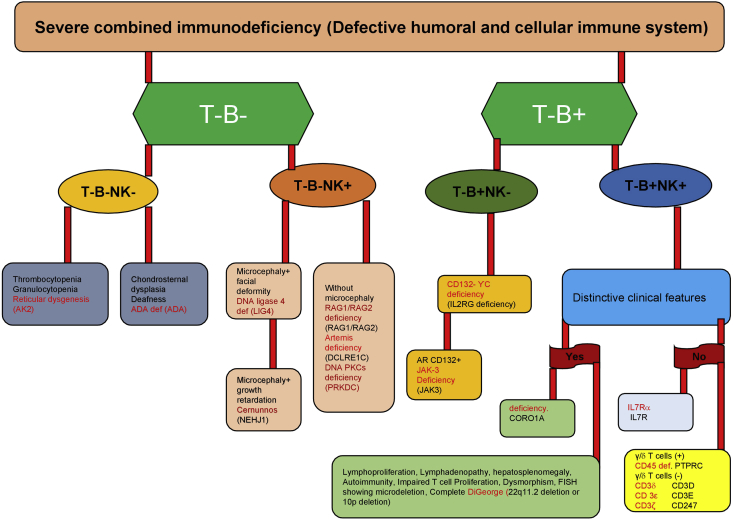
Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is a diverse group of potentially life-threatening disorders that results from an aberration in T cell development or function. The prognosis is grave if there is a delay in disease recognition and therapy. Most of them have an underlying genetic basis, which is not only crucial in identifying these disorders but also helps to tailor the management protocols accordingly. The incidence of SCID varies between 1 in 40,000 to 75,000 per live birth. Till date, more than 20 genetic defects have been described to result in SCID. Phenotypically, the broad classification of SCID includes T-B- SCID or T-B + SCID phenotypes based on B cell status and further sub-classified as per state of natural killer cells. Although the molecular diagnosis is readily available in individual centres worldwide, the phenotypic classification of SCID is helpful for the clinicians to narrow down on certain genetic defects [Table 1 & Fig. 1]. Table 2 classifies SCID based on pathogenic mechanisms.
Table 1.
Broad classification of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) based on flow cytometry.
| T-B + SCID | Genes | T-B- SCID | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL2R common gamma chain | IL2RG | Recombinase-activating genes 1 and 2 | RAG1/RAG2 |
| Janu kinase 3 | JAK3 | DNA cross-link repair enzyme 1c (Artemis) | DCLRE1C |
| IL7-RA Chain | IL7RA | DNA dependent protein kinase | PRKDC |
| IL2 RA CD25 deficiency | IL2R | Adenylate kinase (reticular dysgenesis) | AK2 |
| CD45(Protein tyrophospahtase receptor type C) | PTPRC | Adenosine deaminase | ADA |
| CD3-delta | CD3D | DNA Ligase 4 | LIG4 |
| CD3-Zeta | CD3ζ | Non-homologous end joining protein 1(Cernunnos) | NHEJ1 |
| CD3-Epsilon | CD3ε | ||
| Coronin 1A | CORO1A |
Figure 1.
Phenotypic classification of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID).
Table 2.
Classification of SCID on the basis of pathogenic mechanisms.
| Genotype | Function | Phenotype | Locus | Inheritance | Clinical features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Defective survival of haematopoietic precursors | |||||
| AK2 | Regulates the adenine nucleotide composition and catalyses the reversible transfer of phosphate groups | T–B–NK– | 1p35.1 | AR | Lymphopenia, hypoplasia of secondary lymphoid organs and thymus, multiple infections, profound neutropenia, hearing abnormality, thymic dystrophy |
| Toxic metabolite accumulation | |||||
| ADA | Component of the purine salvage pathway. Removes toxic metabolites and prevents inhibition of lymphoid cells | T–B–NK– | 20q13.11 | AR | Multiple recurrent opportunistic infections, hypoplasia, FTT, skeletal alterations |
| PNP | Reversibly catalyses the phosphorolysis of purine nucleosides | T–B + NK– | 14q11.2 | AR | Persistent opportunistic infections, autoimmune disorders |
| Cytokine signalling anomalies | |||||
| IL2RG | Required for the activation of JAK3 for intracellular signal transduction | T–B + NK– | Xq13.1 | XL | Recurrent multiple opportunistic infections (Pneumocystis jirovecii), failure to thrive, oral candidiasis, absent tonsils and lymph nodes |
| JAK3 | Tyrosine Kinase., essential to differentiate haematopoietic cells | T–B + NK– | 19p13.1 | AR | Protracted diarrhoea, failure to thrive, life-threatening opportunistic infections |
| IL7RA | Essential development of T-cell and activation of JAK3 kinase | T–B + NK+ | 5p13 IL7 | AR | Diarrhoea, persistent rotavirus gastroenteritis, weight loss, progressive cough, vomiting, poor appetite, failure to thrive |
| V(D)J recombination and problems in T-cell receptor | |||||
| RAG1 or RAG2 | Recombinases required for DNA recombination in B and T cell development | T–B–NK+ | 11p13 | AR | Apart from opportunistic infections, patients can also develop fetures of Omenn syndrome (hepatosplenomegaly, lymph node swelling, eczema, eosinophilia, elevated IgE) and granuloma formation |
| Artemis | DNA repair process during V(D)J recombination | T–B–NK+ | 10p | AR | |
| DNA PKcs | Repair of double-stranded DNA breaks and in the process of recombination | T–B–NK+ | 8q11.21 | AR | Recurrent oral candidiasis, lower respiratory tract infections, failure to thrive, growth failure, microcephaly, and seizures |
| NHEJI | DNA repair factor involved in the NHEJ pathway | T–B–NK+ | 2q35 | AR | Neural disorders, recurrent bacterial infections, microcephaly, growth retardation, bird-like face, increased radiosensitivity |
| LIG4 | Mediates V(D)J recombination and DSB repair through the NHEJ pathway | T–B–NK+ | 13q33.3 | AR | Microcephaly, facial dysmorphisms, retarded growth, neurological abnormalities, bone marrow failure, pancytopenia |
| TCR abnormalities | |||||
| CD45 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase essential for signal transduction | T–B + NK+ | 1q31-q32 | AR | Failure to thrive, diarrhoea, oral thrush, pneumonia, disseminated BCG infection |
| CD3δ | TCR/CD3 complex component, involved in signal transduction | T–B + NK+ | 11q23.3 | AR | Defective T-cell development and signal transduction |
| CD3ε | Part of TCR-CD3 complex, involved in T-cell development | T–B + NK+ | 11q23.3 | AR | Defective T-cell development, immunodeficiency |
| CD3ζ | Component of TCR-CD3 complex, important for antigen recognition to different signal-transduction pathways intracellularly | T–B + NK+ | 1q24.2 | AR | Erythroderma, protracted diarrhoea, pulmonary abscess, impaired immune response. |
| CORO 1A | Cell cycle progression, signal transduction, gene regulation and cell death | T–B–NK+ | 16p11.2 | AR | T cell lymphopenia, susceptibility to infection and immune dysregulation |
| Thymic abnormalities | |||||
| FOXNI | Required for thymic epithelial cell development, proliferation and terminal differentiation of TEC sublineages, T cell progenitor growth, and fate determination | T–/lowB + NK+ | 17q11.2 | AR | Hairlessness and athymia, Atrophic thymus, T-cell immunodeficiency, congenital alopecia, nail dystrophy |
| DiGeorge syndrome | Disorder due to microdeletion of chromosome 22 | T–B + NK+ | 22q11.2 | AD/Denovo | Psychiatric disorders, cardiac defects, immunodeficiency, facial malformations, hypocalcaemia, polydactyly |
V(D)J recombination and alterations in TCR
RAG1 and RAG2 deficiency
Recombinase-activating gene (RAG)- RAG1 and RAG2, are DNA recombinases that mediate DNA recombination process and ensure the somatic diversification of immunoglobulin and TCR genes during B-cell and T-cell development, respectively. The RAG1 gene has two exons that span 12,544 base pairs while RAG2 has two exons spanning 7092 base pairs, located on 11p13. The protein introduces double-stranded breaks in the DNA, allowing V(D), J rearrangements for antigen receptor diversity and specificity.1 In the absence of VDJ recombination, T cell undergoes apoptosis. Deficiency of either RAG1 or RAG2 causes T-B-NK + SCID and is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern.
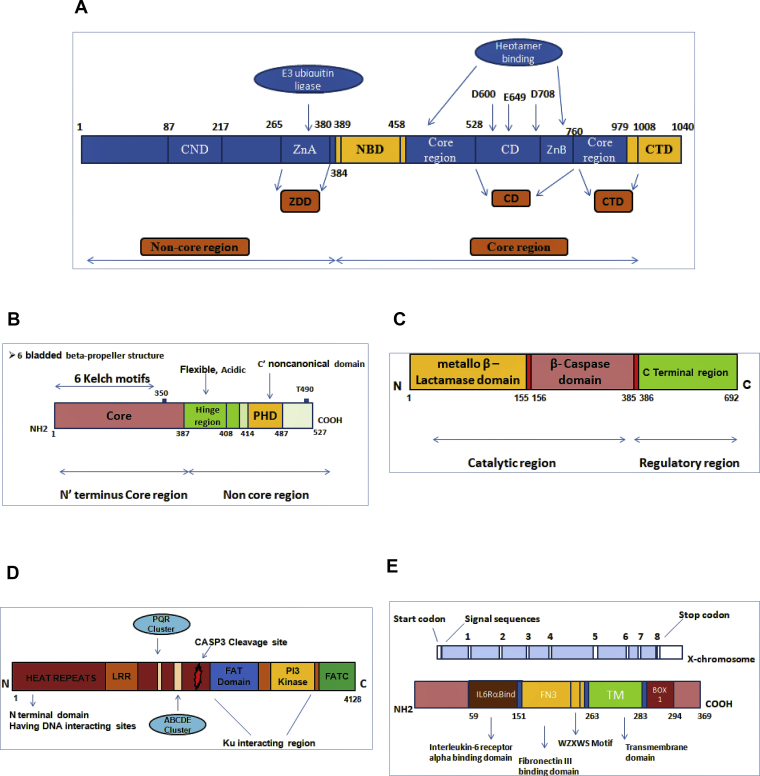
RAG1 gene consists of core and non-core region. The core part of RAG1 includes the nonamer-binding domain (NBD), a dimerisation domain, and DNA-binding domain, zinc-binding domain (ZBD), and the c-terminus domain (CTD) that is required for V(D)J recombination process (Fig. 2). The RAG2 protein consists of plant homeodomain (PHD) in its non-core region (Fig. 2). Maximum mutations (missense) are concentrated in the core part (ZBD) of RAG1 followed by NBD and CTD while remaining fall in non-core domain.2 Missense mutations in the core domain are commonly noted in RAG2 followed by nonsense and frameshift mutations.
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of SCID genes and their associated domains. (A)RAG1 gene showing core region domains as nonamer binding domain (NBD), a central domain and the C′ terminal domain. The non-core region have zinc dimerization domain (ZDD) having zinc finger A (ZFA), central non-core domain (CND). The three active site residues are shown by D600, D708 and E649. (B)RAG2 gene showing the 6-bladed beta-propeller structure in the N terminal core region. The non-core region shows acidic hinge region and plant homeodomain (PHD). (C)DCLRE1C gene (Artemis) showing three distinct regions belonging to Metallo-β−lactamase superfamily namely β-lactamase domain, β- CASP domain and C′ terminal domain. (D)PRKDC gene showing 5′ DNA interacting site, leucine-rich repeats, phosphorylation cluster. sites (PQR, ABCDE), helix-turn-helix repeats while FAT, FATC, PI3K kinase domains and caspase 3 cleavage site are present at C-terminal region. (E)IL2RG gene showing Interleukin-6 receptor alpha binding domain (IL6Ra-bind), fibronectin III binding domain (FN3), the WSXWS motif, transmembrane domain (TM), and Box 1 domain.
Genotype-phenotype correlation
A broad phenotypic spectrum of RAG deficiency highlights the need to test the pathogenicity of each RAG variants. A large number of algorithms is available to detect the pathogenicity of the RAG defects. A correlation has been found between recombination activity and the clinical phenotype in SCID patients.3
Clinical presentation of RAG defect ranges from classical SCID to hypomorphic forms. Autoimmunity is also widely reported in this type of SCID. Granuloma formation and Epstein Bar Virus related lymphomas have also been reported. An autoimmune phenomenon like cytopenia has been reported by Zago et al.4 Selective IgA deficiency has also been reported with RAG1 defect. Other clinical phenotypes described with RAG defects are chronic multifocal osteomyelitis, hyper IgM syndrome, CVID, and idiopathic CD4 lymphocytopenia.
One of the important clinical presentations of RAG defects is Omenn syndrome, characterized by significant expansion of activated oligoclonal T cells, erythroderma, diarrhoea, hepatosplenomegaly, generalized lymphadenopathy, hypereosinophilia, and elevated IgE levels. Patients with Omenn syndrome have normal or elevated CD3+ T cell counts, however, naïve T cell population (CD3+ 45RA + RO-) is grossly decreased.
DNA cross-link repair enzyme 1c (Artemis)
The Artemis gene (DCLRE1C) is a 78-kDa protein having 692 amino acids that span 56,665 base pairs and consists of 20 exons. The gene has three distinct regions belonging to metallo-β−lactamase superfamily with catalytic core domain constituted by the association of the b-lactamase homology domain and the b-CASP domain (Fig. 2).5, 6 The missense and in-frame deletion affects the highly conserved residues of the β-CASP domain, that abrogate complete protein expression.7, 8 Larger deletions in the exons (1–4) and a nonsense founder mutation results in loss function in DCLRE1C. However, hypomorphic mutations have also been reported in leaky SCID with residual protein function.
DCLRE1C encodes ARTEMIS, a nuclease which is single-stranded with- 5′-3′ exonuclease potential and endonuclease activity over 5′ and 3′ ends. It is essential for V(D)J rearrangement and for DNA repair. The gene enables end-joining and considered to be important for opening hairpin loops during V(D)J rearrangement.
Artemis deficiency causes early arrest in the maturation of T cells and B cell differentiation during early pre-B cell stage, resulting in T–B–NK + SCID.9 Artemis is regulated by DNA-PKcs and promotes its endonucleolytic activity. Artemis deficiency is also known as Athabascan SCID as it was initially reported from family speaking the Athabascan language. Patients with this form of SCID are sensitive to ionizing radiation and chemotherapeutic agents.10, 11
Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ1)
NHEJ1 consists of 8 exons spanning 1–299 amino acids and present on 2q35. It encodes the DNA repair factor required for end-joining process. The molecular defect in NHEJ1 results in an autosomal recessive form of T–B–NK + SCID. Somatic DNA rearrangement of V(D)J genes is important for the adaptive immune system. Double stranded breaks during V(D)J recombination is initiated by RAG genes and are finally repaired by NHEJ proteins.12 The DNA hairpin structures are then resolved and joined by DNA ligase IV in association with Cernunnos/XLF.13 Defects of the NHEJ pathway causes profound T and B cell lymphocytopenia and results in radiosensitive SCID. Autoimmunity is also reported in these patients.
NHEJ1 gene consists of globular head region (1–126 amino acids) required for XRCC4 interaction and a coiled-coil region (127–228 amino acid). Most of the mutations are reported in exon 2 followed by exon 5.14 Germline inactivating mutations have also been reported that results either in deleted protein or less active protein.15, 16, 17, 18, 19
DNA ligase IV
The gene encoding DNA ligase IV (LIG4) is present on the 13q33.3 chromosome. It is important for V(D)J recombination and DSB repair in an ATP-dependent reaction. The protein comprising of DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) and X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 4 (XRCC4) is required for NHEJ. DNA ligase IV deficiency is related to LIG4 syndrome, an autosomal disorder that results in T-B-NK + SCID with or without developmental disorder.20 Radiosensitivity, microcephaly, facial dysmorphisms, retarded growth, neurological abnormalities, bone marrow failure, and increased predisposition to malignancies are also seen.
LIG4 has an active site with conserved ligase domain (Lys 273) with DNA binding domain and adenylation domain at its 5′ end. While the 3′ end consists of homodimer XRCC4 interaction domain (743–800) having a tandem BRCA1 C-terminus domain (BRCT1) and BRCT2 region with a spacer region. XRCC4 binds with single ligase molecule and gets unwinded due to its coiled-coil conformation. The point mutations usually occur in the adenylation domain affecting the adenylate complex formation.21
DNA dependent protein kinase deficiency (DNAPKcs)
PRKDC, present on chromosome 8q11.21 has 86 exons that encode DNA-PKcs. The encoded protein is essential for nonhomologous end-joining of DNA during V(D)J recombination. DNA-PKcs regulates Artemis by phosphorylating it and forming a complex thus regulating V(D)J recombination.22, 23
The 5′ region of DNA-PKcs consists of the leucine zipper, PQR cluster, and ABCDE cluster (phosphorylation sites) while the 3′ region has PI3K like domain, FATC domain, helix-turn-helix motifs (HEAT) and FAT domains (Fig. 2).16 Hypomorphic mutations in the FAT domain of DNA-PKcs retards T and B development and cause T-B-NK + SCID, having autosomal recessive inheritance. In addition, PRKDC is responsible for AIRE transcriptional activity. A study reported deficiency of DNA PKCs in a Turkish girl who had increased sensitivity to radiation.24 Woodbine et al reported neurologic abnormalities due to a defect in PRKDC.2
Cytokine signalling abnormalities
IL2R common gamma chain deficiency
IL2RG located on Xq13.1 has 8 exons that span 4.2 Kb IL2RG encodes the common-gamma chain which is an important component of IL2R and binds to IL7, IL21, IL15, IL4, and IL-9. The gamma portion of IL2R is important for the development of T and NK cells through cytokines IL2 and IL15, respectively. Mutations of IL2RG results in X-linked form of SCID, T-B + NK- type. IL2RG consists of IL-6 receptor alpha binding domain (IL6Ra-bind), fibronectin III binding domain (FN3), the WSXWS motif, transmembrane domain (TM), and Box 1 domain (Fig. 2).25 Around 200 different pathogenic mutations in IL2RG have been reported.26 A large number of mutations are reported in exon 3 followed by exon 4 and exon 5. Missense and nonsense mutations comprise for about 48% of total mutations followed by insertion/deletion and splice site mutations.26 The alterations in the gene result in nonfunctional gamma chain thereby preventing the formation of protein. Mutations in IL2RG results in typical X-SCID with absent T and NK cells and functionally abnormal B cells. Hypomorphic IL2RG mutations result in milder symptoms and cause atypical X-SCID. Patients usually present with opportunistic infections, diarrhoea, prolonged fever, rash, pneumonia, and sepsis. The condition is lethal in the early phase of life until there is the reestablishment of the immune system by HSCT or gene therapy.
Janus kinase 3 deficiency
Gene for Janus kinase 3 (JAK3) is located on a 19p13.11 chromosome and it has 25 exons. It is non-receptor tyrosine-kinase present on immune cells and gets associated with the common-gamma chain of different cytokine receptors and results in activation of other kinases and STATs.27 JAK3 plays a pivotal role in cytokine receptor cell signalling. Exon 17–23 encodes the catalytic domain JH1 while the pseudokinase domain JH2 is encoded by exons 10–16. Exon 17 skipping results in frameshift mutations and formation of a stop codon that results in inactive protein.28 JAK3 deficiency constitutes around 6% of the total SCID patients and is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait. A large number of compound heterozygous mutations have been reported in JAK3 deficiency. Patients with JAK3 defect with missense mutations have been reported to have reduced JAK3 protein and atypical phenotype.
IL7RA deficiency
IL7RA consists of 8 exons and spans 23.2 Kb. The encoded protein is expressed on the lymphoid lineage and is required during T cell development during early stage and for proliferation and survival of T cells in the periphery. The IL-7R has an alpha chain (CD127) and a common γ chain that is required by various other cytokines including IL-2, IL-15, and IL-21. The domains in IL7R consist of the intracellular, transmembrane and extracellular domain. The 5′ terminus has a signal sequence, extracellular cysteine domain which is highly conserved, WSXWS motif, transmembrane domain (for cell signalling) while the 3′ region consists of serine and tyrosine containing domain and 3′ untranslated region.29 A large number of mutations in IL7RA was found in exon 2 followed by exon 4 and exon 5.30 Deficiency of ILR7 alpha causes T-B + NK + SCID, that accounts for around 10% of the total SCID patients.29 Omenn syndrome has also been reported with defects in IL7RA.31 Apart from opportunistic infections, autoimmunity has also been reported in this form of SCID.30, 31, 32, 33
Toxic metabolite accumulation
Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency
ADA is a 32 kb gene spanning 33,003 base pairs and has 12 exons located on 20q13.12 chromosome.34, 35 It encodes adenosine deaminase enzyme catalysing the removal of amino group from adenosine and deoxyadenosine, and converts to inosine and deoxyinosine, respectively in an irreversible manner. Deficiency of ADA causes accumulation of adenosine, deoxyadenosine, and 2′-O-methyladenosine resulting in lymphocyte apoptosis, causing the absence of T cell function. An absence of adenosine deaminase enzyme was initially identified by Giblett et al in the year 1972.36 Mutations in ADA are associated with T-B-NK- form of SCID that has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance. ADA deficiency is the most severe form of SCID and is known to occur in 15% of total SCID patients. Most of the mutations identified are deleterious missense mutations occurring in exon 4,5 and 7. In addition splice site mutations have also been observed.
‘Partial’ ADA deficiency has been reported in some individuals with reduced but not absent enzymatic activity in erythrocytes.37 Most of ADA deficient patients lack ADA enzyme activity while others have residual ADA activity. Santisteban et al reported a delayed onset of disease due to defects in ADA.38 Hirschhorn et al reported somatic mosaicism of an inherited mutation in the ADA gene due to in vivo reversion to normal form.39, 40 Therapeutic approaches include enzyme replacement therapy, early HSCT, or gene therapy.
Defective survival of haematopoietic precursors
AK2 deficiency
Adenylate kinase 2 gene is located on 1p35.1 chromosome having 9 exons. Adenylate kinases are involved in cellular and mitochondrial energy homeostasis. Mutation of the AK2 gene causes reticular dysgenesis (RD), an autosomal recessive disorder occurring in 2% of children with SCID.41 Deficiency of AK2 is associated with lack of innate and adaptive immunity. Single nucleotide substitution, frameshift mutations, and large intragenic deletions are reported in patients with RD.41, 42, 43, 44 Until now, 21 diverse types of recessive mutations have been reported.41
Reticular dysgenesis is the most serious type of SCID that is associated with absent granulocytes, lymphocytes, hypoplasia of the primary and secondary lymphoid organs and fatal septicemia within days after birth. It also leads to blockage of myeloid differentiation with normal erythrocytes and megakaryocytic maturation. Genetic testing confirms the diagnosis. HSCT is the most effective mode for treatment.
TCR abnormalities
CD45
CD45 gene is present on 1q31.3-q32 having 34 exons. CD45 is a type 1 glycoprotein expressed on all haematopoietic cells and their precursors excluding RBCs and platelets. CD45 is tyrosine phosphatase required for lymphocyte signalling.45 The encoded protein is important for regulation of kinases that is needed for signalling of T and B cell antigen receptor. Mutations in the CD45 gene cause T–B + NK + SCID phenotype, having autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. CD45 deficiency was first reported by Kung et al in a patient with a deletion on one allele and a single nucleotide change at the other.46
CD3D and CD3Z
T cell receptor consists of either αβ or γ/δ heterodimer and is linked to transmembrane proteins (gamma, delta, epsilon and zeta chain). The CD3 signalling is needed for late double negative T cell proliferation while T cell receptor is important for recognition of antigen and is involved in the signal transduction pathway. CD3δ subunit is important for the development of T cells.47 A defect in T cell receptor complex causes T-B + NK + SCID having autosomal recessive inheritance pattern.
CD3δ Deficiency
CD3δ is located on 11q23.3 chromosome and have 5 exons. CD3δ deficiency was first reported by Dadi et al.48 CD3δ is essential for both αβ and γδ positive T cell lineage development. The defect is associated with the complete arrest of T cell development and is more lethal as compared to ϒ and ζ chain deficiency.
CD3ε deficiency
CD3ε gene is present on 11q23 and has 9 exons. CD3ε is an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) and a component of CD3-TCR complex required for T cell signalling and T cell development. CD3ε is an essential component for transduction of the PreTα/TCRβ receptor survival and proliferation.49 CD3ε deficiency blocks T cell differentiation and typically causes T-B + NK + SCID inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern.
CD3Z SCID
CD3Z gene is located on 1q24.2 chromosome having 10 exons. It is an essential component of the TCR-CD3 complex and enables coupling of antigens to intracellular signal-transduction pathways. Mutations in this gene cause T–B + NK + phenotype with autosomal recessive inheritance pattern.50
Coronin-1A deficiency
Coronin1A is located on a 16p11.2 chromosome and has 12 exons. The encoded protein is 57 KD having 461 amino acids and is required for haemostasis of T lymphocytes. Coronin 1A and F actin cytoskeleton are important for chemotaxis and activation. Deficiency of Coronin 1A known to result in T-B + SCID with a normal sized thymus.51
Genetic diagnosis of SCID
Genetic confirmation in SCID is necessary for genetic counselling and antenatal testing. Moreover, radiosensitive forms of SCID are prone to develop increased toxicity to alkylator-based chemotherapeutic agents used in the conditioning regimen for HSCT.10, 11 Pre-transplant conditioning regimens are preferably avoided in patients with radiosensitive forms of SCID. Genetic diagnosis can be established by Sanger or Next-Generation sequencing (NGS). Many centres prefer to do a targeted exome panel by NGS in view of its advantage of short turnover time and simultaneous sequencing of multiple genes.
Newborn screening
Assessment of T cell receptor excision circles (TRECs) in the dried blood spots is an effective screening method developed in the United States for the identification of infants with SCID patients and other forms of T-cell lymphopenia. It allows us to screen newborns immediately after birth so as to reduce the chances of infection and other complications. Early diagnosis without infections is the goal behind the development of this newborn screening (NBS). By this method, infants with SCID could be identified and subjected to early definitive therapy such as HSCT or gene therapy. The TREC assay can be performed in Guthrie card dried blood spots that are used for the newborn screening. A real-time PCR method that causes amplification of DNA isolated from spots is used for the detection of TRECs that serve as a marker for naïve T cells. TRECs are the byproducts released during T cell receptor recombination process.52 TRECs counts are low or stable in patients with clonally expanded T cells as TRECS do not replicate during the division of T cells. Different countries use different methods and algorithms for TREC detection.53 Laboratory investigations and diagnostic follow-up are needed after a positive screen for determining the type of SCID. Assessment of kappa-receptor excision circles (KREC) allow identification of B cell lymphopenia and delayed-onset ADA SCID, however, its effectiveness still needs to be established. NBS has been successful in the last 10 years and has improved results on children born with SCID. However, normal TREC levels can be seen in defects of lymphocyte maturation beyond VDJ recombination steps such as ZAP70 defect and MHC class II deficiency. Late-onset ADA deficiency has also been reported to have normal levels of TREC.
Conclusion
SCID comprises of a group of inherited defects that results in impaired T cell development or function. Several genetic defects have been identified in SCID with different clinical phenotypes. Genetic diagnosis of SCID is essential for molecular confirmation of diagnosis, genetic counselling, and HSCT. Newborn screening for SCID and availability of easy access to HSCT services are the needs of the hour for successful early diagnosis and management.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Authorship statement
Rajni Kumrah; concept and design, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing: Pandiarajan Vignesh; concept and design, literature search, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing and manuscript review: Pratap Patra; concept and design, literature search: Ankita Singh; concept and design, literature search: Anjani Gummadi; concept and design, literature search, clinical studies and manuscript review: Poonam Saini; manuscript editing and manuscript review: Madhubala Sharma; manuscript editing and manuscript review: Anit Kaur; manuscript editing and manuscript review: Amit Rawat; concept and design, manuscript editing and manuscript review.
Footnotes
Peer review under responsibility of Chongqing Medical University.
References
- 1.Tasher D., Dalal I. The genetic basis of severe combined immunodeficiency and its variants. Appl Clin Genet. 2012;5:67–80. doi: 10.2147/TACG.S18693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Notarangelo L.D., Kim M.S., Walter J.E. Human RAG mutations: biochemistry and clinical implications. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16(4):234–246. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lee Y.N., Frugoni F., Dobbs K. A systematic analysis of recombination activity and genotype-phenotype correlation in human recombination-activating gene 1 deficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133(4):1099–1108. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.10.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zago C.A., Jacob C.M., de Albuquerque Diniz E.M. Autoimmune manifestations in SCID due to IL-7Rmutations: Omenn syndrome and cytopenias. Hum Immunol. 2014;75(7):662–666. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2014.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nicolas N., Moshous D., Cavazzana-Calvo M. A human severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) condition with increased sensitivity to ionizing radiations and impaired V(D)J rearrangements defines a new DNA recombination/repair deficiency. J Exp Med. 1998;188(4):627–634. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.4.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moshous D., Callebaut I., de Chasseval R. Artemis, a novel DNA double-strand break repair/V(D)J recombination protein, is mutated in human severe combined immune deficiency. Cell. 2001;105(2):177–186. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00309-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pannicke U., Honig M., Schulze I. The most frequent DCLRE1C (ARTEMIS) mutations are based on homologous recombination events. Hum Mutat. 2010;31:197–207. doi: 10.1002/humu.21168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pannicke U., Ma Y., Hopfner K.P. Functional and biochemical dissection of the structure-specific nuclease ARTEMIS. EMBO J. 2004;23:1987–1997. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schatz D.G., Swanson P.C. V(D) J recombination: mechanisms of initiation. Annu Rev Genet. 2011;45:167–202. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-110410-132552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Moshous D., Callebaut I., de Chasseval R. Artemis, a novel DNA double-strand break repair/V(D)J recombination protein, is mutated in human severe combined immune deficiency. Cell. 2001;105(2):177–186. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00309-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dvorak C.C., Cowan M.J. Radiosensitive severe combined immunodeficiency disease. Immunol Allergy Clin N AM. 2010;30(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2009.10.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Huang C.Y., Sharma G.G., Walker L.M. Defects in coding joint formation in vivo in developing ATM-deficient B and T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 2007;204(6):1371–1381. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ahnesorg P., Smith P., Jackson S.P. XLF interacts with the XRCC4-DNA ligase IV complex to promote DNA nonhomologous end-joining. Cell. 2006;124(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.12.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Woodbine L., Gennery A.R., Jeggo P.A. The clinical impact of deficiency in DNA non-homologous end-joining. DNA Repair (Amst) 2014;16:84–96. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.02.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Buck D., Moshous D., de Chasseval R. Severe combined immunodeficiency and microcephaly in siblings with hypomorphic mutations in DNA ligase IV. Eur J Immunol. 2006;36(1):224–235. doi: 10.1002/eji.200535401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Woodbine L., Gennery A.R., Jeggo P.A. The clinical impact of deficiency in DNA non-homologous end-joining. DNA Repair (Amst) 2014;16:84–96. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.02.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Du L., Peng R., Bjorkman A. Cernunnos influences human immunoglobulin class switch recombination and may be associated with B cell lymphomagenesis. J Exp Med. 2012;209(2):291–305. doi: 10.1084/jem.20110325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tilgner K., Neganova I., Singhapol C. Brief report: a human induced pluripotent stem cell model of Cernunnos deficiency reveals an important role for XLF in the survival of the primitive hematopoietic progenitors. Stem Cells. 2013;31(9):2015–2023. doi: 10.1002/stem.1456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dai Y., Kysela B., Hanakahi L.A. Nonhomologous end joining and V(D)J recombination require an additional factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(5):2462–2467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0437964100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.O'Driscoll M., Cerosaletti K.M., Girard P.M. DNA Ligase IV mutations identified in patients exhibiting developmental delay and immunodeficiency. Mol Cell. 2001;8(6):1175–1185. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00408-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Riballo E., Doherty A.J., Dai Y. Cellular and biochemical impact of a mutation in DNA ligase IV conferring clinical radiosensitivity. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(33):31124–31132. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103866200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Woodbine L., Neal J.A., Sasi N.K. PRKDC mutations in a SCID patient with profound neurological abnormalities. J Clin Investig. 2013;123(7) doi: 10.1172/JCI67349. 2969–2680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.van der Burg M., Weemaes C.M., Preijers F. B-cell recovery after stem cell transplantation of Artemis-deficient SCID requires elimination of autologous bone marrow precursor-B-cells. Haematologica. 2006;91(12):1705–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.van der Burg M., van Veelen L.R., Verkaik N.S. A new type of radiosensitive T-B-NK+ severe combined immunodeficiency caused by a LIG4 mutation. J Clin Investig. 2006;116(1):137–145. doi: 10.1172/JCI26121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jamal A., Upton J.E.M. IL2RG: a series of three novel mutations with clinical manifestations. LymphoSign J. 2016;3(3):111–118. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lim C.K., Abolhassani H., Appelberg S.K. IL2RG hypomorphic mutation: identification of a novel pathogenic mutation in exon 8 and a review of the literature. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2019;15:2. doi: 10.1186/s13223-018-0317-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gilmour K.C., Cranston T., Loughlin S. Rapid protein-based assays for the diagnosis of T-B+ severe combined immunodeficiency. Br J Haematol. 2001;112(3):671–676. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Barreiros L.A., Segundo G.R.S., Grumach A.S. A novel homozygous JAK3 mutation leading to T-B+NK– SCID in two Brazilian patients. Front Pediatr. 2018;6:230. doi: 10.3389/fped.2018.00230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Butte M.J., Haines C., Bonilla F.A. IL-7 receptor deficient SCID with a unique intronic mutation and post-transplant autoimmunity due to chronic GVHD. Clin Immunol. 2007;125(2):159–164. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2007.06.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rossberg S., Schwarz K., Meisel C. Delayed onset of (severe) combined immunodeficiency (S)CID (T-B+NK+): complete IL-7 receptor deficiency in a 22 months old girl. Klin Pädiatr. 2009;221(6):339–343. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1239537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Puel A., Leonard W.J. Mutations in the gene for the IL-7 receptor result in T(-)B(+)NK(+) severe combined immunodeficiency disease. Curr Opin Immunol. 2000;12(4):468–473. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(00)00122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yu G.P., Nadeau K.C., Berk D.R. Genotype, phenotype, and outcomes of nine patients with T-B+NK+SCID. Pediatr Transplant. 2011;15(7):733–741. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3046.2011.01563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Giliani S., Mori L., de Saint Basile G. Interleukin-7 receptor alpha (IL-7R alpha) deficiency: cellular and molecular bases. Analysis of clinical, immunological, and molecular features in 16 novel patients. Immunol Rev. 2005;203:110–126. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wilson D.K., Rudolph F.B., Quiocho F.A. Atomic structure of adenosine deaminase complexed with a transition-state analog: understanding catalysis and immunodeficiency mutations. Science. 1991;252(5010):1278–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.1925539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bradford K.L., Moretti F.A., Carbonaro-Sarracino D.A., Gaspar H.B., Kohn D.B. Adenosine deaminase (ADA)-Deficient severe combined immune deficiency (SCID): molecular pathogenesis and clinical manifestations. J Clin Immunol. 2017;37(7):626–637. doi: 10.1007/s10875-017-0433-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Giblett E.R., Anderson J.E., Cohen I. Adenosine deaminase deficiency in two patients with severely impaired cellular immunity. Lancet. 1972;2(7786):1067–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Arredondo-Vega F.X., Santisteban I., Richard E. Adenosine deaminase deficiency with mosaicism for a 'second-site suppressor' of a splicing mutation: decline in revertant T lymphocytes during enzyme replacement therapy. Blood. 2002;99(3):1005–1013. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.3.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Santisteban I., Arredondo-Vega F.X., Kelly S. Novel splicing, missense, and deletion mutations in seven adenosine deaminase-deficient patients with late/delayed onset of combined immunodeficiency disease. Contribution of genotype to phenotype. J Clin Investig. 1993;92(5):2291–2302. doi: 10.1172/JCI116833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hirschhorn R., Yang D.R., Israni A. Somatic mosaicism for a newly identified splice-site mutation in a patient with adenosine deaminase-deficient immunodeficiency and spontaneous clinical recovery. Am J Hum Genet. 1994;55(1):59–68. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hirschhorn R., Yang D.R., Puck J.M. Spontaneous reversion to normal of an inherited mutation in a patient with adenosine deaminase deficiency. Nat Genet. 1996;13(3):290–295. doi: 10.1038/ng0796-290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lagresle-Peyrou C., Six E.M., Picard C. Human adenylate kinase 2 deficiency causes a profound hematopoietic defect associated with sensorineural deafness. Nat Genet. 2009;41(1):106–111. doi: 10.1038/ng.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Pannicke U., Hönig M., Hess I. Reticular dysgenesis (aleukocytosis) is caused by mutations in the gene encoding mitochondrial adenylate kinase 2. Nat Genet. 2009;41(1):101–105. doi: 10.1038/ng.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Al-Zahrani D., Al-Ghonaium A., Al-Mousa H. Skeletal abnormalities and successful hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with reticular dysgenesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;132(4):993–996. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.04.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Henderson L.A., Frugoni F., Hopkins G. First reported case of Omenn syndrome in a patient with reticular dysgenesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131(4):1227–1230. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.07.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tchilian E.Z., Wallace D.L., Wells R.S. A deletion in the gene encoding the CD45 antigen in a patient with SCID. J Immunol. 2001;166(2):1308–1313. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.2.1308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kung C., Okumura M., Seavitt J.R. CD45-associated protein is not essential for the regulation of antigen receptor-mediated signal transduction. Eur J Immunol. 1999;29(12):3951–3955. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199912)29:12<3951::AID-IMMU3951>3.0.CO;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.de Saint Basile G., Geissmann F., Flori E. Severe combined immunodeficiency caused by deficiency in either the δ or the ε subunit of CD3. J Clin Investig. 2004;114(10):1512–1517. doi: 10.1172/JCI22588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Dadi H.K., Simon A.J., Roifman C.M. Effect of CD3 delta deficiency on maturation of alpha/beta and gamma/delta T-cell lineages in severe combined immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(19):1821–1828. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa031178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sommers C.L., Dejarnette J.B., Huang K. Function of CD3 epsilon-mediated signals in T cell development. J Exp Med. 2000;192(6):913–919. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.6.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rieux-Laucat F., Hivroz C., Lim A. Inherited and somatic CD3zeta mutations in a patient with T-cell deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(18):1913–1921. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa053750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Shiow L.R., Paris K., Akana M.C. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) associated with a coronin-1a mutation and a chromosome 16p11.2 deletion. Clin Immunol. 2009;131(1):24–30. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2008.11.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Puck J.M. Neonatal screening for severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) Curr Opin Pediatr. 2011;23(6):667–673. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0b013e32834cb9b0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kwan A., Abraham R.S., Currier R. Newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency in 11 screening programs in the United States. JAMA. 2014;312(7):729–738. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.9132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]