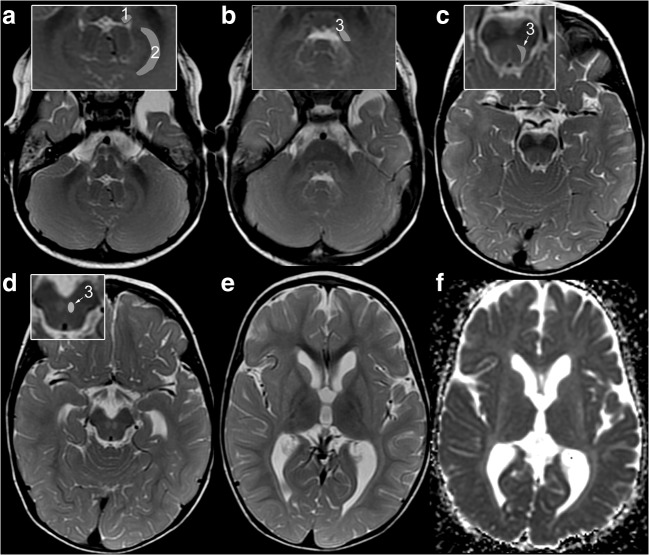
Fig. 2.
Characteristic MRI pattern of striatal variant of POLR3A-related disease. MRI in patient 1 at 1.5 years demonstrates the characteristic combination of atrophic, T2-hyperintense striatum ,and T2-hyperintense SCP (A-E: T2w; F: ADC-map; insets: 1 = ICP, 2 = peridentate white matter, 3 = SCP). a T2-hyperintensity of ICP (1) and peridentate white matter (2) are additional findings. b Further additional findings are T2-hyperintensity of tegmentum and intraparenchymal course of trigeminal nerve. T2-hyperintensity of SCP (3, insets in B-D) is seen along its course from the cerebellum (b), dorsal mesencephalon (c) to the decussation in the anterior mesencephalon (d). e, f: Homogeneous, mild, and symmetric T2-hyperintensity of the striatum with volume loss and increased diffusion. NB the lateral medullary lamina between pallidum and putamen is commonly seen at this age due to its relative T2-hyperintensity compared with pallidum and putamen; increased conspicuity is due to T2-hyperintensity of putamen (e)