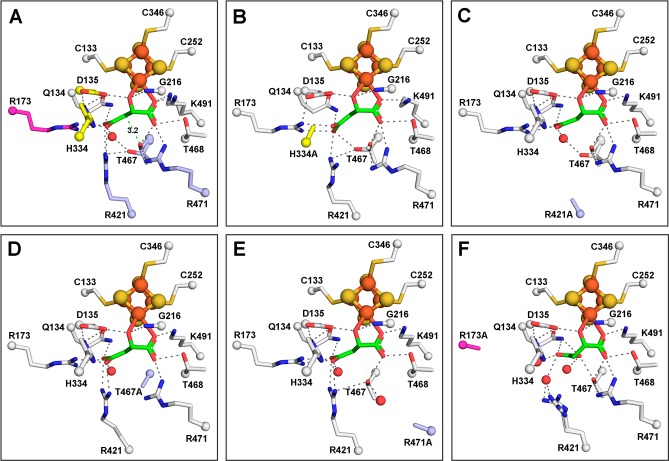
Figure 2.
Active sites of LmFH-2 variants reveal similar S-malate-binding modes with LmFH-2-R173A displaying the largest variation. (A) LmFH-2 in a complex with S-malate. The proposed catalytic residues are colored yellow (D135 and H334 from chain B) and light blue (T467, R421, and R471). Residue R173 that is proposed to play a role in the correct positioning of the substrate in the active site is colored magenta. The distance from the T467 OH group to the S-malate C3 is shown as a green dashed line. (B) LmFH-2-H334A in a complex with S-malate. The H334A substitution is colored yellow. (C) LmFH-2-R421A in a complex with S-malate. The R421A substitution is colored light blue. (D) LmFH-2-T467A in a complex with S-malate. The T467A substitution is colored light blue. (E) LmFH-2-R471A in a complex with S-malate. The R471A substitution is colored light blue. (F) LmFH-2-R173A in a complex with S-malate. The R173A substitution is colored magenta. The substrate S-malate is colored green. The [4Fe-4S] cluster is shown as orange (Fe) and yellow (S) spheres. The water molecules are shown as red spheres. The hydrogen bonds are shown as gray dashed lines.