Abstract
Angiosarcoma is a highly aggressive cancer of blood vessel-forming cells with few effective treatment options and high patient mortality. It is both rare and heterogenous, making large, well powered genomic studies nearly impossible. Dogs commonly suffer from a similar cancer, called hemangiosarcoma, with breeds like the golden retriever carrying heritable genetic factors that put them at high risk. If the clinical similarity of canine hemangiosarcoma and human angiosarcoma reflects shared genomic etiology, dogs could be a critically needed model for advancing angiosarcoma research. We assessed the genomic landscape of canine hemangiosarcoma via whole exome sequencing (47 golden retriever hemangiosarcomas) and RNA sequencing (74 hemangiosarcomas from multiple breeds). Somatic coding mutations occurred most frequently in the tumor suppressor TP53 (59.6% of cases) as well as two genes in the PI3K pathway: the oncogene PIK3CA (29.8%) and its regulatory subunit PIK3R1 (8.5%). The predominant mutational signature was the age-associated deamination of cytosine to thymine. As reported in human angiosarcoma, CDKN2A/B was recurrently deleted and VEGFA, KDR, and KIT recurrently gained. We compared the canine data to human data recently released by The Angiosarcoma Project, and found many of the same genes and pathways significantly enriched for somatic mutations, particularly in breast and visceral angiosarcomas. Canine hemangiosarcoma closely models the genomic landscape of human angiosarcoma of the breast and viscera, and is a powerful tool for investigating the pathogenesis of this devastating disease.
Introduction
Angiosarcoma is an aggressive cancer of blood-vessel forming cells, associated with poor survival times (1–3). There is an unmet need for new diagnostics and therapies for these patients. However, the rarity of this cancer (approximately 0.01% of all cancers) (4,5) has limited large-scale genomic studies so far. Canine hemangiosarcoma is a relevant clinical model for understanding the pathophysiology of human angiosarcoma. The human and canine diseases share many clinical similarities, and hemangiosarcoma is common in dogs, occurring in some breeds (notably the golden retriever) with a frequency up to 20% (6). This means that using canine hemangiosarcoma as a model for human disease would yield sample cohorts of a magnitude inaccessible using human data alone. However, for dogs to be an effective model of this disease in the era of precision medicine, detailed genomic characterization of canine hemangiosarcoma must be undertaken, and the results directly compared to existing and emerging genomic data from human angiosarcoma.
Angiosarcoma can form anywhere in the vasculature. In human patients, it most commonly occurs in the skin of the head, neck, and scalp, the breast, the extremities, and less frequently in the liver, right auricle of the heart, bone, and spleen (7). Prognosis is poor, with metastatic disease occurring in approximately 50% of cases (8), and a median overall survival time of approximately 50 months for local disease and 10 months in metastatic cases (9). Treatment involves surgical resection with wide margins, plus or minus radiation therapy, as well as adjuvant chemotherapy in the metastatic disease setting (3). Many angiosarcomas are initially sensitive to doxorubicin, paclitaxel, or targeted agents, but resistance to these therapies is virtually inevitable (3).
While most cases of angiosarcoma in humans occur without known cause, there are several known risk factors. These tumors can arise secondary to radiation therapy for other cancers or chronic lymphedema (3). Other known risk factors include UV irradiation, given the typical locations of cutaneous angiosarcomas on the head and neck (10–12), as well as occupational exposure to vinyl chloride (13), arsenic exposure (14), and use of anabolic steroids (15). Genetically, angiosarcoma is associated with familial syndromes including Li-Fraumeni syndrome (TP53 mutations) (16) and Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome (PIK3CA mutations) (17). However, these syndromes do not solely cause angiosarcoma (7), and angiosarcomas are not present in the majority of cases.
Canine hemangiosarcoma is the histopathological equivalent of human angiosarcoma (18), and follows a similar, aggressive clinical course. In dogs, the most common tumor locations are the spleen, right auricle of the heart, liver, and skin or subcutaneous tissue (19,20). The different anatomical distribution seen in the human and canine diseases is likely due, at least in part, to the lack of secondary cases in dogs. Treatment protocols for dogs with hemangiosarcoma similarly involve wide surgical resection, followed by adjuvant chemotherapy. Survival times are short - a median of 4–6 months after surgical resection with adjuvant chemotherapy, with a 1 year survival rate of approximately 10% (21–23). Biological risk factors have not yet been identified in dogs. Genetically, dog breeds display differential predisposition to specific cancers, indicating that there are heritable risk factors that have become common as a result of inbreeding based on selection or drift. In a previous genome-wide association study, we identified several loci significantly associated with the risk of hemangiosarcoma in the golden retriever (24).
Recent targeted next-generation sequencing of human angiosarcomas has begun to reveal the somatic mutational spectrum of this disease. It has so far proven to be fairly heterogeneous - no pathognomonic mutations or copy number aberrations occur in all cases, and tumors from different primary locations or with different underlying etiologies have genomic differences. TP53 and genes in the MAPK pathway are frequently mutated (25), and mutations in PLCG1 and PTPRB are common, particularly in secondary angiosarcomas (25,26). Although the PI3K pathway is activated in some human angiosarcomas (27,28), PIK3CA mutations have so far not been commonly reported in human angiosarcoma studies (26,29). Genes in the VEGF pathway are frequently gained or amplified, including VEGFA, and KDR (25,28). The tumor suppressor CDKN2A is frequently deleted, while the MYC oncogene is frequently amplified, most commonly in radiation-associated tumors (25,28).
In dogs, a recent whole-exome sequencing study of a small cohort of 20 hemangiosarcomas showed that the top recurrently mutated genes were PIK3CA and TP53 (30). Earlier candidate gene studies of canine hemangiosarcomas reported mutations in TP53 (31), PTEN (32), and PDGFRA and PDGFRB (33). An analysis of somatic copy number aberrations in visceral hemangiosarcomas from five breeds found that VEGFA was recurrently gained, while CDKN2A was frequently deleted (34). MYC copy number gain was infrequent, likely reflective of the fact that secondary hemangiosarcomas are not seen in canine patients (34). While these earlier studies provide clues as to the genetic features of canine hemangiosarcoma, there is very little of the genome-wide data needed for comprehensive comparison to human angiosarcoma.
In order to assess the potential utility of hemangiosarcoma as a model for angiosarcoma at the molecular level, we performed the largest exome sequencing study of hemangiosarcoma to date, and complemented our exome data with oligonucleotide array comparative genomic hybridization (oaCGH) copy number data and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) data in partially overlapping cohorts of hemangiosarcoma cases. We then performed comparative analyses of our results with those released by The Angiosarcoma Project direct-to-patient initiative. In this way, we have created a detailed genomic profile of this cancer in the golden retriever breed, and begun vetting this canine cancer as a comparative model for human angiosarcoma, and potentially other tumors.
Materials and Methods
Additional Materials and Methods can be found in the Supplementary Materials and Methods, and a workflow in Figure S1.
Canine hemangiosarcoma sample collection for exome sequencing
Samples were obtained as part of necessary diagnostic procedures with owner consent. DNA from tumor tissue and whole blood was collected from 47 golden retrievers with visceral hemangiosarcoma. Samples were collected from dogs referred for treatment at the University of Minnesota (UMN) Veterinary Medical Center and samples submitted to the Modiano laboratory for diagnostic assessment and/or use in research (n = 34), from cases seen at the North Carolina State University (NCSU) Veterinary Hospital (n = 8), or from diagnostic samples sent to Antech Diagnostics (n = 5). Cases where date of diagnosis was known (n = 36), were diagnosed between 2000 and 2014. Tumor samples were either frozen (n = 17), or formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE, n = 30, Table S1). Procedures involving animal use were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees at the Broad Institute, UMN, or NCSU.
Sample preparation
DNA was extracted and sequencing libraries prepared using the Kapa Hyper Prep Kit (Table S2). For 66 samples, additional cycles of PCR were required to obtain sufficient DNA for exome capture, while libraries from 28 samples were re-constructed from source DNA using the standard protocol (See SI).
Exome capture
The Roche Nimblegen SeqCap-EZ capture canine exome (120705_CF3_Uppsala_Broad_EZ_HX1) was used for hybrid exome capture, following the manufacturer’s protocol.
Sequencing and read alignments
The barcoded exome-captured libraries were multiplexed in pools of 8, and sequenced on the Illumina HiSeq 2500 to a target depth of 60x in the tumor and 30x in the normal, reaching a mean depth of 78x in the tumor and 63x in the normal. Reads were aligned to the CanFam3.1 reference genome using BWA. PCR duplicate reads were flagged using the Picard tool MarkDuplicates. Following the Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK) Best Practices, we then performed Base Quality Score Recalibration (BQSR) using a set of approximately 19 million known canine germline variant locations.
Somatic variant calling
Somatic mutations were called using MuTect2, using the default settings with the addition of the --dontUseSoftClippedBases option, which was added to avoid calling a large number of artifactual indels in our FFPE-preserved samples (See SI). In order to further refine our set of somatic variant calls, and to avoid artifacts, we also called variants using the GATK4 version of Mutect2, and kept only the consensus of calls which passed in both the GATK3 and GATK4 versions. Both sets of calls were filtered using a “panel of normals” created using all 47 normal (germline) samples, as well as germline samples from previous studies of canine lymphoma, osteosarcoma, and melanoma. Calls were further filtered to exclude oxidation artifacts, and were removed if they overlapped locations with known germline variants. Variants were further filtered if the position had low coverage (defined as a read depth less than 20 in the normal, less than 40 in the tumor, or less than 4 alternate allele reads in the tumor), or had excessive read depth (greater or equal to mean read depth + 5 x standard deviation), to filter out potential alignment errors. Finally, variants with a median read position < 10 were filtered to remove potential artifacts.
Variant annotation
Variants were annotated using the variant effect prediction program SnpEff v4.2. Where multiple effects were predicted for a single variant, the most damaging predicted effect was selected. Coding variants were analyzed using the smg function in Genome MuSiC 0.4 to determine which genes were significantly mutated above the background rate. The merge-concurrent-muts option was applied to count multiple mutations in the same gene within a sample as a single mutation, and a false discovery rate (FDR) threshold of 0.1 using the convolution test (CT) was applied.
Canine mutational signature discovery
Mutational signatures, considering point mutations and their genomic context, were extracted using a Bayesian non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) algorithm. The discovered signatures were compared to known signatures in COSMIC (35), as well as those reported in the literature for human angiosarcoma (36). The overall landscape of mutations was plotted for different groupings of samples using the SomaticSignatures package.
RNA-sequencing of canine hemangiosarcomas
Seventy-four snap-frozen samples were obtained from seventy-three dogs with hemangiosarcoma (41 golden retrievers and 32 dogs from 13 other breeds or from mixed breeding)(Kim, et al., manuscript in preparation). RNA-seq data from 51 of the hemangiosarcoma tissues had been published previously (37,38). RNA-seq libraries were generated as described previously (37).
Somatic copy number detection in canine hemangiosarcomas
Analysis of somatic copy number aberrations (SCNAs) in our canine whole exome sequencing data was limited by the inclusion of both frozen and formalin-fixed (FFPE) samples. The FFPE samples appeared to have an increased number of amplifications and deletions when compared with the frozen samples, possibly as a result of DNA fragmentation during the fixation process (39). While we were able to partially account for this using GC correction (40), we were not able to completely remove the bias between the two groups (Figure S6). Hence, we instead used oaCGH data to interrogate copy number changes in a cohort of 69 golden retrievers with hemangiosarcoma tumors, of which 28 were also included in the exome sequencing cohort. SCNAs were called from oligonucleotide array comparative genomic hybridization (oaCGH), as described previously (34), using a ~180,000-feature microarray (Agilent Technologies) with approximately 26 kb resolution throughout the dog genome.
Accessing human data from The Angiosarcoma Project for comparative analysis
We compared the somatic mutations and SCNAs present in our cohort of canine hemangiosarcomas to the results reported by The Angiosarcoma Project, a direct-to-patient sequencing project run by the Count Me In initiative (JoinCountMeIn.org). Somatic mutations and SCNAs derived from whole exome sequencing data from 48 samples from 36 patients were downloaded from CBioPortal, and somatic mutations classified as nonsense, missense, splice site, or splice region were kept for analysis. For our analysis, we selected only the annotated primary tumor site from each patient, including 30 tumors - 17 breast, five visceral (one each of right atrium, spleen, lung, abdomen, and bladder wall), and eight head, face, neck, and scalp (HFNS) tumors.
Pathway analysis in canine and human data
Pathway analysis was performed on the canine and human mutational data using the DAVID Functional Annotation Tool. For the overall enrichment analyses, all genes with coding nonsynonymous, splice site, or splice region somatic mutations were used. Functional annotation charts were created for KEGG pathways using the default options, using the Benjamini-Hochberg method to control the false discovery rate. Analysis was performed independently for the canine data and the human data, mapping genes from both species to Homo sapiens reference to avoid confounding due to differences in gene annotation between the species. Canine Ensembl gene IDs were mapped to their human 1:1 orthologs using Ensembl’s BioMart (41).
Results
Simple somatic mutations
TP53 and PIK3CA are commonly mutated in canine hemangiosarcomas
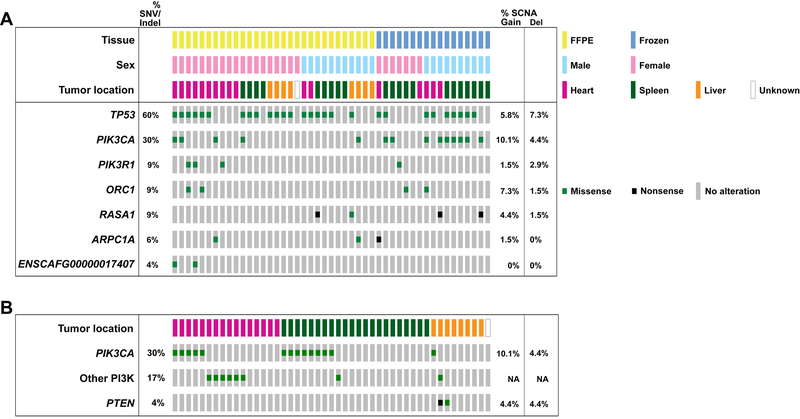
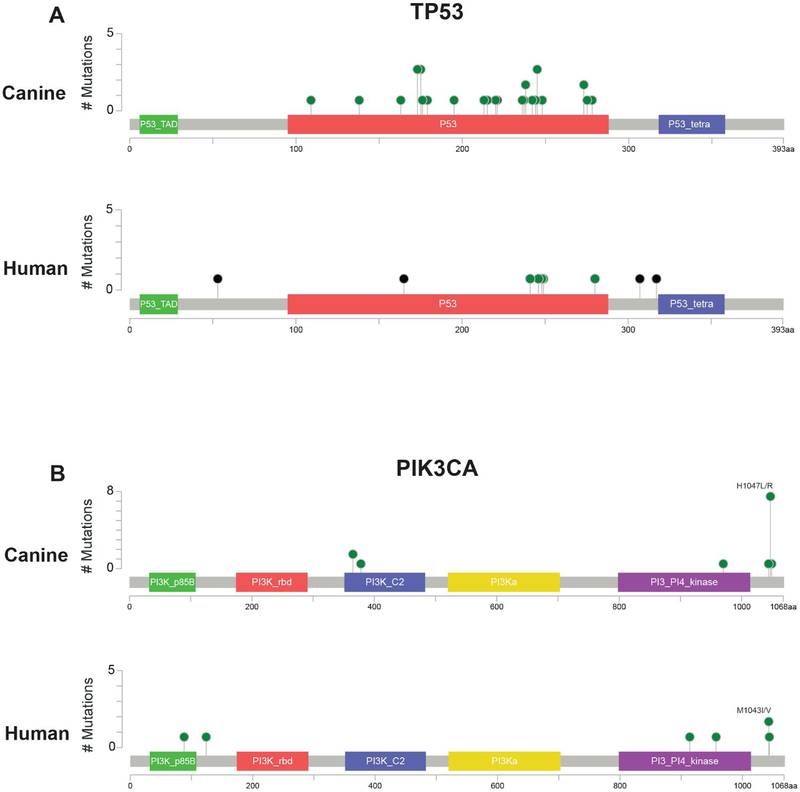
The seven significantly mutated genes (SMGs) in the canine hemangiosarcomas contained well-known cancer genes, including TP53, as well as two genes in the PI3K pathway (Table 1, Figure 1). Tumor suppressor TP53 was most frequently mutated (28/47 cases, 59.6%), with all 28 cases carrying at least one mutation affecting the DNA binding domain (Figure 2). Oncogene PIK3CA (14/47, 29.8%) and its regulatory subunit PIK3R1 (4/47, 8.5%) were both mutated. Ten of the fourteen cases with PIK3CA mutations had a mutation at amino acid position 1047, a hotspot frequently mutated in many types of human cancers (42) (Figure 2). The remaining four SMGs were ORC1 (4/47, 8.5%), RASA1 (4/47, 8.5%), ARPC1A (3/47, 6.4%), and ENSCAFG00000017407 (2/47, 4.3%), a “one-to-many” ortholog of human ATP5PD with 27 paralogs in the canine genome. Overall, 59 genes that were mutated at least once in the canine dataset are annotated as likely causal in the COSMIC Cancer Gene Census (43), including TP53, PIK3CA, and PIK3R1 (Table S3).
Table 1.
Significantly mutated genes in golden retriever hemangiosarcoma tumors. Significantly mutated genes with an FDR < 0.1, calculated using Genome MuSiC. SNVs: single nucleotide variants, Covd Bps: number of basepairs with adequate coverage in gene, Muts pMbp: mutations per megabase.
| Gene ID | Gene name | Indels | SNVs | Total Mutations | Covd Bps | Muts pMbp | p-value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP53 | Tumor protein p53 | 3 | 25 | 28 | 72,582 | 386 | 0 | 0 |
| PIK3CA | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha | 0 | 14 | 14 | 156,415 | 90 | 0 | 0 |
| PIK3R1 | phosphoinositide-3-kinase regulatory subunit 1 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 124,857 | 32 | 7.3×10−8 | 5.9×10−4 |
| ORC1 | origin recognition complex subunit 1 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 133,219 | 30 | 1.3×10−7 | 8.2×10−4 |
| RASA1 | RAS p21 protein activator 1 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 136,539 | 29 | 3.2×10−6 | 1.6×10−2 |
| ARPC1A | actin related protein 2/3 complex subunit 1A | 0 | 3 | 3 | 72,351 | 41 | 1.3×10−5 | 5.1×10−2 |
| ENSCAFG00000017407 | 1-to-many ortholog of human ATP synthase peripheral stalk subunit d (ATP5PD) | 0 | 2 | 2 | 22,074 | 91 | 1.7×10−5 | 5.9×10−2 |
Figure 1. Per-sample annotation of metadata.
A) somatic mutations in the seven significantly mutated genes B) somatic mutations in the PI3K gene family by tumor location. ‘Other PI3K’ category includes mutations in PIK3CB, PIK3C2G, PIK3C3, PIK3R1, and PIK3R5). SNV, single nucleotide variant; Indel, insertion/deletion; SCNA, somatic copy number aberrations. SCNA frequencies are calculated based on oaCGH data from 69 canine hemangiosarcoma samples.
Figure 2.
Lollipop plots showing the positions of the (A) Tumor protein p53 (TP53) and (B) Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA) mutations in the canine and human data. Canine mutational locations were lifted over to the human hg19 reference genome using the LiftOver tool. Green: missense mutation, Black: truncating mutation.
Variant allele fraction and effect predictions
For further insight into whether the four SMGs not annotated in COSMIC are likely to be driver mutations, we investigated the variant allele fraction (VAF) of each and whether missense mutations were predicted to be deleterious or tolerated using the SIFT (44) score via Ensembl’s Variant Effect Predictor (45). The median VAF for the four RASA1 mutations was 0.12 (range 0.08 – 0.23). Three mutations were nonsense mutations, with the fourth a missense mutation predicted to to be deleterious (SIFT score 0), supporting a causal role for these mutations. Similarly, the median VAF of the three ARPC1A mutations was 0.16 (range 0.12 – 0.17), with one nonsense mutation, and two missense mutations at the same position, predicted to be deleterious (SIFT score 0). The median VAF for the four ORC1 mutations (all at the same position) was lower, at 0.08, and the change was predicted to be tolerated (SIFT score 0.06). The two mutations in ENSCAFG00000017407 also had a low median VAF (0.05), and were predicted to be tolerated (SIFT score 1).
Comparison with top mutated genes in human angiosarcoma
The most commonly mutated genes in the human data were TP53 (8/30 tumors, 29%), followed by KDR, LRP2, RYR2, and ABCA13 with mutations in 7/30 tumors each, and PIK3CA, FLG, ASXL3, MYH14, and UNC13C, mutated in 6/30 tumors each. However, the distribution of these mutations varied by tumor location. In the human data, breast tumors were the only location to carry PIK3CA mutations (n = 6 patients), and were the most common location for KDR mutations. TP53 mutations occurred in all locations, but were more common in HFNS and visceral tumors. KDR was much less frequently mutated in the canine cohort, with only one case having a nonsynonymous mutation, predicted to be tolerated. Of the canine SMGs, two human tumors also had RASA1 mutations; one was a nonsense mutation and the other was predicted to be deleterious.
Differential patterns of mutations found in some tumor locations
The pattern of mutations in the PI3K gene family varied by tumor location in the canine data, as well. In the canine cases, a slightly higher proportion of heart tumors (11/16, 68.8%) compared to splenic tumors (9/22, 40.9%) had PI3K alterations, although this difference was not significant (pchi-sq=0.09). Liver tumors had slightly fewer overall alterations in the PI3K gene family (3/8, 37.5%), and were less likely to have PIK3CA mutations (1/8, 12.5%), although this was not statistically significant.
Comparison of mutational burden by tumor location in canine and human data
We found fewer nonsynonymous mutations in the canine tumors than reported in the human tumors overall, while the number of nonsynonymous, splice site, or splice region mutations per sample varied significantly by tumor location in human cases. In the canine cohort, there were a median of 23 nonsynonymous coding mutations per sample (range 1–152; Supplementary Table S1), which was closest to the human breast (median = 32, n = 17), and visceral (median = 40, n = 5) tumors. In the dogs, there was a small difference in the total number of nonsynonymous and splice site/region mutations between heart (median = 31, n = 15, outlier with 152 mutations removed) and splenic (n = 22, median = 17.5) tumors (pTukeyHSD = 0.04). In the human data, there was a significant difference in the median number of mutations by tumor location, with head, face, neck, and scalp (HFNS, n = 8) tumors having a higher mutational burden (median = 596.5) than breast or visceral tumors (pANOVA = 3.6 × 10−5)(46).
Comparative pathway analysis highlights similarity between canine and human tumors
We compared the gene functional annotations enriched in hemangiosarcoma to those enriched in breast and visceral angiosarcoma and those enriched in HFNS angiosarcoma (Table 2). KEGG pathways enriched in canine hemangiosarcoma overlapped with KEGG pathways enriched in both subtypes of angiosarcoma. Pathways enriched in hemangiosarcoma included a larger fraction of those enriched in visceral and breast angiosarcoma (75%, vs. 48% of pathways enriched in HFNS angiosarcoma), however, the total number of pathways shared was greater between hemangiosarcoma and HFNS angiosarcoma (10 pathways). Pathways shared between hemangiosarcoma and visceral and breast angiosarcoma included pathways in cancer (pcanine = 3.6 × 10−4, pvisceral/breast = 4.8 × 10−2), Rap1 signaling pathway (pcanine = 5.8 × 10−3, pvisceral/breast = 9.0 × 10−3) and central carbon metabolism in cancer (pcanine = 3.0 × 10−3, pvisceral/breast = 2.3 × 10−2). Pathways shared between hemangiosarcoma, visceral and breast angiosarcoma, and HFNS angiosarcoma included focal adhesion pathway (pcanine = 1.4 × 10−3, pvisceral/breast = 2.2 × 10−2, pHFNS = 8.1 × 10−4), calcium signaling pathway (pcanine = 2.8 × 10−2, pvisceral/breast = 5.4 × 10−3, pHFNS = 1.9 × 10−2), and long-term depression (pcanine = 1.5 × 10−2, pvisceral/breast = 7.1 × 10−3, pHFNS = 8.6 × 10−3).
Table 2.
KEGG pathways enriched in hemangiosarcoma, breast and visceral angiosarcoma, and HFNS angiosarcoma. Blue: pathways enriched in both visceral and breast angiosarcoma and hemangiosarcoma; Yellow: pathways enriched in both HFNS angiosarcoma and hemangiosarcoma; Green: pathways enriched in all three groups.
| Angiosarcoma - visceral and breast | Hemangiosarcoma | Angiosarcoma - HFNS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Term | p-value | Term | p-value | Term | p-value |
| hsa04020:Calcium signaling pathway | 5.4E-03 | hsa05200:Pathways in cancer | 3.6E-04 | hsa02010:ABC transporters | 2.5E-08 |
| hsa04730:Long-term depression | 7.1E-03 | hsa04360:Axon guidance | 3.8E-04 | hsa04510:Focal adhesion | 8.1E-04 |
| hsa04015:Rap1 signaling pathway | 9.0E-03 | hsa04919:Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | 5.9E-04 | hsa04512:ECM-receptor interaction | 9.6E-04 |
| hsa04510:Focal adhesion | 2.2E-02 | hsa04664:Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | 6.7E-04 | hsa04740:Olfactory transduction | 1.1E-03 |
| hsa04720:Long-term potentiation | 2.2E-02 | hsa04510:Focal adhesion | 1.4E-03 | hsa04724:Glutamatergic synapse | 1.3E-03 |
| hsa04010:MAPK signaling pathway | 2.3E-02 | hsa05146:Amoebiasis | 1.4E-03 | hsa04974:Protein digestion and absorption | 2.9E-03 |
| hsa05230:Central carbon metabolism in cancer | 2.3E-02 | hsa05214:Glioma | 1.5E-03 | hsa04611:Platelet activation | 3.8E-03 |
| hsa05200:Pathways in cancer | 4.8E-02 | hsa05215:Prostate cancer | 1.5E-03 | hsa04610:Complement and coagulation cascades | 8.1E-03 |
| hsa04070:Phosphatidylinositol signaling system | 1.7E-03 | hsa04976:Bile secretion | 8.1E-03 | ||
| hsa05230:Central carbon metabolism in cancer | 3.0E-03 | hsa04730:Long-term depression | 8.6E-03 | ||
| hsa05223:Non-small cell lung cancer | 3.4E-03 | hsa04713:Circadian entrainment | 8.7E-03 | ||
| hsa05221:Acute myeloid leukemia | 3.4E-03 | hsa04723:Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | 9.5E-03 | ||
| hsa04750:Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | 3.8E-03 | hsa04022:cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | 1.8E-02 | ||
| hsa04012:ErbB signaling pathway | 3.9E-03 | hsa05033:Nicotine addiction | 1.9E-02 | ||
| hsa04015:Rap1 signaling pathway | 5.8E-03 | hsa04020:Calcium signaling pathway | 1.9E-02 | ||
| hsa05213:Endometrial cancer | 5.9E-03 | hsa04024:cAMP signaling pathway | 2.9E-02 | ||
| hsa04151:PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 1.2E-02 | hsa05146:Amoebiasis | 3.4E-02 | ||
| hsa05231:Choline metabolism in cancer | 1.3E-02 | hsa04151:PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 4.1E-02 | ||
| hsa04014:Ras signaling pathway | 1.3E-02 | hsa04080:Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | 4.4E-02 | ||
| hsa04730:Long-term depression | 1.5E-02 | hsa05205:Proteoglycans in cancer | 4.6E-02 | ||
| hsa00562:Inositol phosphate metabolism | 1.5E-02 | hsa04925:Aldosterone synthesis and secretion | 4.8E-02 | ||
| hsa04370:VEGF signaling pathway | 1.6E-02 | ||||
| hsa04713:Circadian entrainment | 1.7E-02 | ||||
| hsa05222:Small cell lung cancer | 1.9E-02 | ||||
| hsa04725:Cholinergic synapse | 2.2E-02 | ||||
| hsa04915:Estrogen signaling pathway | 2.3E-02 | ||||
| hsa04723:Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | 2.5E-02 | ||||
| hsa04724:Glutamatergic synapse | 2.6E-02 | ||||
| hsa04020:Calcium signaling pathway | 2.8E-02 | ||||
| hsa04662:B cell receptor signaling pathway | 2.9E-02 | ||||
| hsa04611:Platelet activation | 3.1E-02 | ||||
| hsa05218:Melanoma | 3.3E-02 | ||||
| hsa04917:Prolactin signaling pathway | 3.3E-02 | ||||
| hsa05220:Chronic myeloid leukemia | 3.6E-02 | ||||
| hsa05205:Proteoglycans in cancer | 3.7E-02 | ||||
| hsa04921:Oxytocin signaling pathway | 4.5E-02 | ||||
In addition, functional annotation enrichment analysis of the genes mutated in hemangiosarcoma, visceral and breast angiosarcoma, and HFNS angiosarcoma found that they were enriched in many of the same protein domains. Shared domains include Fibronectin Type III (pcanine = 9.5 × 10−9, pvisceral/breast = 6.3 × 10−5, pHFNS = 3.0 × 10−15), Epidermal growth factor-like domain (pcanine = 1.5 × 10−3, pvisceral/breast = 5.6 × 10−5, pHFNS = 4.0 × 10−16), and Tyrosine protein kinase active site (pcanine = 6.9 × 10−4, pvisceral/breast = 3.8 × 10−3, pHFNS = 2.3 × 10−6). Both visceral and breast and HFNS angiosarcomas were enriched in cadherins (pvisceral/breast = 4.9 × 10−4, pHFNS = 4.7 × 10−16), HFNS highly so, while hemangiosarcoma was not (pcanine = 0.14). In addition, HFNS angiosarcoma was enriched in ABC-transporters (p = 2.8 × 10−7), while visceral and breast angiosarcoma and canine hemangiosarcoma were not (Table S7).
Pathways and gene families previously reported in the angiosarcoma literature
Several pathways and gene families have been previously reported to be affected in the human angiosarcoma literature. Mutations in both PLCG1 and PTPRB have been reported to be recurrent (26), particularly in secondary angiosarcoma. In the human data, 12 patients had mutations in eight phospholipase C genes, including PLCG1 (n = 5, Table 3). Seven canine cases (15%) had mutations in PLC genes, including one in PLCG1. Twenty protein tyrosine phosphatases were mutated in twelve samples in human, including two patients with PTPRB mutations. While none of the canine tumors had somatic mutations in PTPRB, eight cases (17%) harbored a mutation in one of nine other protein tyrosine phosphatase genes (Table 3).
Table 3.
Overlap of mutated genes between canine hemangiosarcoma and human angiosarcoma tumors in several gene families and pathways. Significantly mutated genes bolded.
| Gene family | Human only | Shared | Canine only |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Phosphatidyl- inositol signaling
KEGG Pathway |
DGKB, DGKD, DGKQ, IMPA2, INPP4B, ITPR1, ITPR2, ITPR3, PI4KA, PIK3CG, PIK3R2, PIP5K1B, PLCB1, PRKCB |
DGKI,
PIK3C2G,PIK3CA,
PLCB2, PLCB3, PLCG1, PLCG2, PTEN |
DGKG, PIK3C3, PIK3CB, PIK3R1, PIK3R5, PLCB4, PLCE1 |
| Phospholipase C | PLCB1, PLCH1, PLCXD1, PLCXD3 | PLCB2, PLCB3, PLCG1, PLCG2 | PLCB4, PLCE1 |
| Protein tyrosine phosphatase | PTP4A2, PTPN7, PTPN9, PTPN13, PTPN23, PTPRA, PTPRB, PTPRC, PTPRH, PTPRO, PTPRQ, PTPRR, PTPRS, PTPRT | PTPN5, PTPN22, PTPRD, PTPRJ, PTPRK, PTPRZ1 | PTP4A1, PTPDC1, PTPN4 |
| LDL receptor related proteins | LRP3 | LRP1, LRP1B, LRP2, LRP4 | |
|
Histone methyltransferase/demethylase
activity GO terms |
EHMT2, KDM4A, KDM4B, KDM4D, KDM5C, KDM6B, KMT2B, KMT2C, NSD1, PHF2, PRDM16, PRDM7, PRDM9, SETD2, SETDB1, SETDB2 | KDM5A, KMT2D, MECOM | JMJD1C, KDM3A, KMT2A, PRMT2 |
|
MAPK signaling pathway
KEGG Pathway |
AKT3, ARRB1, CACNA1A, CACNA1B, CACNA1G, CACNA1I, CACNA1S, CACNA2D1, CACNA2D2, CACNA2D3, CACNB1, CACNB3, CACNG3, CHP2, CHUK, DUSP4, EGF, FGF7, FGF12, FGFR2, FLNC, GRB2, HRAS, HSPA1L, MAP2K3, MAP3K4, MAP3K5, MAP3K11, MAP4K1, MAP4K3, MAP4K4, MAPK10, MAPK8IP3, MOS, MYC, NF1, NTRK1, NTRK2, PAK2, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, PPP3CA, PRKCB, PTPN7, PTPRR, RAF1, RAPGEF2, RASGRF2, RASGRP3, RPS6KA1, RPS6KA5, RPS6KA6, TAOK1, TGFB2 | BRAF, CACNA1D, CACNA1E, CACNA1H, CACNB2, FGFR3, MECOM, NRAS, PLA2G4A, PTPN5, RASA1, SOS2, TP53 | CACNA1C, IL1B, MAP3K6, MAP3K13, NFATC4, PLA2G4E, PPM1B, RASGRF1, RASGRP1, RPS6KA3, SOS1, STK4 |
|
Protein tyrosine kinase
activity GO terms |
ALK, BLK, CLK2, CLK3, DDR1, DDR2, DSTYK, EGF, EPHA2, EPHA3, EPHA4, EPHA6, EPHB4, EPHB6, ERBB2, ERBB3, FGF7, FGFR2, FLT4, FRK, HSP90AA1, KIT, MAP2K3, MATK, MERTK, NTRK1, NTRK2, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, PKDCC, PTK2B, RET, ROR2, ROS1, SGK223, SRMS, STYK1, SYK, TEC, TTK, TYRO3, ZAP70 | EPHA5, EPHA7, ERBB4, FGFR3, FLT3, IGF1R, JAK1, KDR, NTRK3, PTK2, TIE1, TTN | CDC37, EFNB3, EPHB2, FYN, IL3RA, NRG1, NRP1, STAT5A, TEK, TYK2 |
The MAPK pathway has been reported to be frequently affected by mutations in angiosarcoma (25), and we found the visceral and breast angiosarcomas to be enriched in mutations in MAPK pathway genes (p = 0.02, Table 2). We noted mutations in 25 genes in the MAPK pathway in the canine cohort, including the SMGs TP53 and RASA1. In the human data, 67 genes in the MAPK pathway were mutated. Thirteen of these genes were mutated in both the canine and human data (Table 3). Although we found mutations in genes involved in histone methyltransferase/demethylase activity in both species, consistent with earlier human studies (47), we saw no significant enrichment on a pathway level in either the canine or human cohorts (Table 3). Tyrosine protein kinases were enriched in both hemangiosarcoma and angiosarcoma. In the human data, 55 genes in the GO Protein Tyrosine Kinase Activity pathway were mutated, while 22 genes in this pathway were mutated in the canine data, with 12 genes mutated in both human and canine samples (Table 3). Low-density lipoprotein receptors were enriched for mutations in the canine data (p = 0.03), and human HFNS tumors (p = 0.05), and LRP2 was one of the most frequently mutated genes in the human dataset (mutated in 7/30 tumors). While mutations in the LDL receptor-related protein family have not been widely reported in human angiosarcoma, they have recently been shown to play a role in a variety of cancers (48). We found that four LDL receptor-related protein genes were mutated in both hemangiosarcoma and angiosarcoma, with an additional gene mutated in angiosarcoma only (Table 3).
Mutational signature of aging is present across all canine tumors
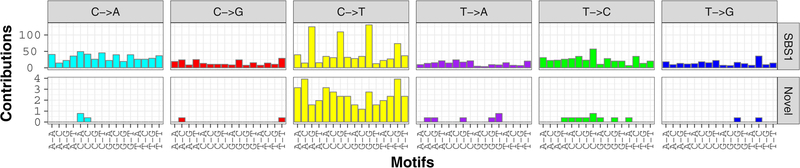
Analysis of mutational signatures, which capture the mutational landscape of tumors and are shaped by both genetic factors and environmental exposure, revealed similarities between canine hemangiosarcoma and human angiosarcoma, as reported by Thibodeau, et al. (36). We analyzed the signatures of trinucleotide mutational frequencies present in golden retriever hemangiosarcomas, and found a strong signature of mutations arising through spontaneous deamination of methylated cytosines in CpG islands, corresponding to COSMIC signature SBS1 and generally associated with aging (35) (Figure 3, Figures S3–S5). In addition, we see a faint signature not described in COSMIC (Figure 3). The overall mutational landscape was consistent across all canine hemangiosarcoma tumors, regardless of tumor location or tissue preservation method (Figures S2 – S4).
Figure 3.
Mutational signatures called using Bayesian NMF in the entire canine hemangiosarcoma cohort, showing the count of mutations (y-axis) in each trinucleotide context (x-axis). This analysis reveals the COSMIC SBS1 aging signature (top), and a faint novel signature (bottom).
Canine RNA-seq analysis validates exome mutations and extends findings to additional breeds
We validated our exome sequencing somatic mutation calls using RNA-seq data from a partially overlapping set of dogs (n = 74 tumor samples from 73 dogs from 14 breeds, as well as mixed-breed dogs, Table S4). Thirteen golden retrievers from the exome cohort with mutations in SMGs had the same tumor location included in the RNA-seq data, with a total of 25 SMG mutations among them. We excluded 2 frameshift deletion variants from the validation, as they showed evidence of deletion in the pileup data, but also unexpected alternate alleles. Of the remaining 23 variants, we validated 15 (65%) mutations. Of the eight sites which were not validated, one was a nonsense mutation, which may have been subject to nonsense-mediated decay, five had a variant allele fraction (VAF) less than 0.1, and three variants came from samples with tumor purity estimate (≤ 35%) on histological examination, suggesting that tumor heterogeneity and stromal contamination may be a contributing factor to variants not being replicated (Table S5). In the RNA-seq data, four tumor samples from three dogs with variants in the SMGs were from a different tumor site than was included in the exome discovery cohort. In this subset, we were able to detect the mutation discovered in the same individual, but a different tumor location in 4/8 (50%) cases. Overall, the group of variants which we were unable to validate came from tumor samples with a significantly lower estimated tumor purity on histology (pt-test = 0.04), but this difference was not significant based on tumor purity estimates from the program ESTIMATE (pt-test = 0.4, Table S5).
The RNA-seq cohort also confirmed that the TP53 and PI3K mutations were not breed-specific, but were present across different breeds. Excluding the 19 golden retrievers who were also included in the exome cohort, we looked to see whether somatic mutations corresponding to those observed in the exome cohort could be found in other cases, which included golden retrievers (n = 22), Portuguese water dogs (PWD, n = 6), German Shepherd Dogs (GSD, n = 6), mixes (n = 6), boxers (n = 2), Labrador retrievers (Labs, n = 2), Keeshonds (n = 2), and other breeds (n = 8, one each of American Staffordshire Terrier, Bernese Mountain Dog, Bichon Frise, Briard, Bullmastiff, Gordon setter, Parson’s Russell Terrier, and Saluki). We found mutations at the same sites as discovered in the exome cohort in TP53 (n = 14, 26%, 5 breeds), PIK3CA (n = 11, 20%, 6 breeds), and PIK3R1 (n = 4, 7%, 4 breeds, Table S6).
Somatic copy number aberrations
SCNAs in canine hemangiosarcoma recurrently affect known cancer genes
We surveyed SCNAs in genes known to be involved in hemangiosarcoma and angiosarcoma. The genes most recurrently affected by DNA copy number aberrations in the oaCGH data were VEGFA, with copy number gain in 19% of cases, KDR, gained in 22%, KIT, gained in 17%, and the tumor suppressor CDKN2A/B, deleted in 22% (Table S8). The MYC oncogene had copy number gain in 9% of cases. Copy number aberrations in the top significantly mutated genes were relatively rare (Figure 1A, Table S8).
Copy number gains in KDR and losses in AXIN1 are common in both dogs and humans
Comparison of SCNAs in the human data and canine oaCGH data revealed recurrent copy number aberrations in known cancer genes KDR and AXIN1 in both species. Copy number gains in KDR occurred in approximately 27% of human samples, and 22% of canine samples. AXIN1 was lost in 20% of human and 22% of canine samples. In addition, the genes PTK6, ARFRP1, and RTEL1 showed copy number loss in 17% of human and canine samples, however, these genes are close together, and also showed copy number gains in a number of canine samples (Table S9).
SCNA profiles differ among cases with and without PIK3CA mutations
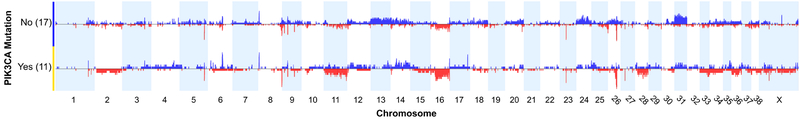
We examined the SCNA profiles of hemangiosarcoma cases with and without TP53 and PIK3CA mutations in the 28 cases with both exome sequencing and oaCGH data. There were no significant differences in the relative frequency of any given CNA between the CNA profiles of cases with and without TP53 mutations. However, significant differences were detected between cases with PIK3CA mutations and those without (Figure 4), using a two-tailed Fisher’s Exact test and a minimum differential threshold of 25% between the two groups. A region on chromosome 11 at approximately 22.6 Mb, near the UBE2B (ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2B) gene, was deleted in 4/11 cases with PIK3CA mutations, and 0/17 without (p < 0.016). Similarly, the CDKN2B gene, located distally on chromosome 11 at 41.2Mb, was deleted in 4/11 cases with PIK3CA mutations, and 0/17 cases without (p < 0.016). A region on chromosome 24 at 21.2 Mb was gained in 7/17 cases without PIK3CA mutation and 0/11 with PIK3CA mutation (p < 0.023). This region overlaps the anti-apoptotic BCL2L1 gene. Broad copy number gains along the length of chromosome 31 were more frequent in cases without PIK3CA mutations compared to those with PIK3CA mutations.
Figure 4.
Comparison of DNA copy number aberration profiles between cases with PIK3CA mutation and those without. Blue = copy number gain, red = copy number loss. (Thomas, et al., manuscript in preparation)(34)
Discussion
Detailed molecular profiling of canine hemangiosarcoma has revealed both similarities and differences in the genetic landscape between dogs and humans. In particular, visceral canine hemangiosarcoma showed strong similarities to human angiosarcoma of the viscera and breast. Our findings have important implications for comparative oncology, as the study of canine hemangiosarcoma has the potential to improve our understanding of the pathophysiology of both canine hemangiosarcoma and human angiosarcoma, and to improve treatment and outcomes in both species.
Tumor suppressor TP53 was the top significantly mutated gene in the canine data. The majority of mutations occurred in the DNA binding domain, likely causing loss of function (Figure 2). TP53 was also the only significantly mutated gene in the human Angiosarcoma Project data, and it has been frequently reported as mutated in targeted sequencing studies of angiosarcoma (25).
We found that the PI3K pathway was commonly mutated in canine hemangiosarcoma. A total of 23 canine tumors (48.9%) had at least one somatic mutation affecting this gene family (Figure 1A). Tumors with a mutation in the PI3K family tended to have only one mutation in this family. The PI3K pathway is one of the most commonly altered pathways in cancer, playing an important role in signal transduction leading to cell proliferation, survival, differentiation, and regulation of metabolism and immunity (49,50). PIK3CA is an oncogene (51) that has been shown to be mutated in human glioblastoma, breast, gastric, colorectal, lung, and endometrial cancers (52). Ten of the 14 PIK3CA mutations in our canine cohort occurred at amino acid position 1047, a mutational hotspot in many human cancers (42). Mutations within this domain have been shown to increase catalytic activity (53).
Of the less frequently mutated SMGs, PIK3R1 is annotated as a likely driver mutation by COSMIC. In addition, variant allele fraction and SIFT scores support a potential role for RASA1 and ARPC1A as driver mutations. RASA1 is a negative regulator of the RAS and MAPK pathways, and plays an important role in vascular formation (54,55). Germline RASA1 mutations can cause capillary malformation - arteriovenous malformation syndrome (56). Somatic mutations in this gene have been found in a subset of human basal cell carcinomas, and expression has been correlated with survival in invasive ductal breast carcinomas and hepatocellular carcinomas (57,58). ARPC1A plays an important role in regulating the actin cytoskeleton, which functions in the migration and invasiveness of pancreatic carcinoma cells (59). There is less support for a causal role for ORC1 and ENSCAFG00000017407, however, it is important to note that the SIFT score does not annotate activating mutations - for example, the hotspot mutations in PIK3CA (known to be drivers in many human cancers) are also predicted to be tolerated.
There were also potentially important differences in somatic mutations between the two species. In the human data, mutations in TP53 and PIK3CA tended to be mutually exclusive, while we did not see this pattern in the canine tumors. In addition, PIK3CA mutations were exclusively found in breast tumors in the small human data set, while we found them to be common in cardiac and splenic tumors in dogs. Within the canine visceral tumors, we found fewer mutations in PIK3CA in liver tumors. These differences in distribution of PIK3CA mutations by tumor location may be due to genetic heterogeneity of the cancer, with tumors in different locations activating the PI3K pathway at different points, or relying on alterations in different pathways to affect an essential protein downstream. It is also possible that this difference is due to the small number of human visceral angiosarcomas currently sequenced, and the small number of liver tumors in the canine cohort.
Another potentially important difference between the two species is that, while copy number gains in KDR are common in both species, somatic mutations in this gene were seen in over 20% of human tumors, but in only one canine tumor. As the KDR receptor is upstream of the PI3K pathway, it is possible that mutations in either may lead to a similar phenotype. We also saw more copy number gains of VEGFA in our canine cohort (19% vs. 0 in the human data), and as VEGFA is upstream of KDR, this copy number gain may serve a similar role to KDR mutations in the canine tumors. In addition, whole genome sequencing will be necessary to determine whether there are common regulatory mutations affecting this gene in canine hemangiosarcoma.
In the human data, mutation rates were significantly different between different tumor locations, with head and neck angiosarcomas having a much higher mutational burden, as reported by Painter, et al. (46). It is possible that the higher mutational burden in these tumors is due to UV exposure. It would be interesting to compare these findings to canine cutaneous and subcutaneous hemangiosarcomas, which were not included in the current study. In the canine visceral hemangiosarcoma, a slight difference was found between mutational burden in heart and splenic tumors. It is possible that the golden retrievers have a lower overall somatic mutation burden than humans, as they likely have a higher germline risk burden, given the high incidence of hemangiosarcoma in the breed. Further studies in dogs will be necessary to determine whether the lower mutation rate is correlated with breed risk, or if in this case it is an artifact of how mutations were called.
Tumors in both dogs and humans were enriched for mutations in protein tyrosine kinases, which are important regulators of cellular growth and division signals and are commonly mutated in cancers. There were also recurrent mutations in the protein tyrosine phosphatase gene family in both species. This may suggest an alternate mechanism of tyrosine kinase overactivation, as protein tyrosine phosphatases deactivate tyrosine kinase signaling by dephosphorylating proteins in opposition to kinase phosphorylation (60). In addition, phospholipase C proteins play a crucial role in cellular signalling pathways by hydrolyzing phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into the second messengers DAG and IP3, passing on signals from receptor tyrosine kinases (61). The canine hemangiosarcomas were enriched for phospholipase C genes, including PLCG1, and PLCG1 mutations were recurrent in the human tumors.
The shared enriched pathways between canine hemangiosarcomas and human angiosarcomas provide insight into disease pathogenesis for both species. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been effective against angiosarcoma in the clinic, but tumor heterogeneity and the development of resistance have limited their long-term utility. They have also shown promise against hemangiosarcoma in vitro (62), but so far have been less promising in the veterinary clinic (63). Future investigation of the interaction between the many affected pathways will help to determine the potential for combination therapy targeting multiple of these pathways or a common downstream effector to combat resistance.
A recent study in 13 radiation-induced and 3 spontaneous breast angiosarcomas detected the irradiation signature, as well as the aging signature, and a unique C>T signature (36). The median age of patients in this human cohort was 74.5 years (36). Canine hemangiosarcomas looked very similar, in that we primarily saw the aging signature and low levels of a novel C>T signature. This novel signature bore some resemblance to the signature reported in the human angiosarcomas, including higher levels of C>T mutations at C nucleotides flanked by A-A or A-T, however, there were also differences, such as a high number of mutations flanked by T-G in the dogs, and a low number of these in the human cohort. A larger study will be needed to decipher whether this is a novel angiosarcoma-related signature or whether it represents noise. The lack of the irradiation signature was anticipated as our canine data did not include any tumors secondary to radiation therapy.
We examined copy number changes in canine hemangiosarcoma in genes previously reported to be affected in hemangiosarcoma and angiosarcoma. Most common were copy number gain of VEGFA and KDR, and loss of CDKN2A/B. The MYC oncogene, which has been reported amplified in human angiosarcoma and canine hemangiosarcoma, was only rarely gained in our dataset and showed no evidence of high-level amplification. This makes sense, given that it is more common in radiation-induced tumors, which were not present in the canine cohort.
Our data suggest that visceral canine hemangiosarcoma could be developed as a model for primary human angiosarcoma. Detailed molecular characterization of canine hemangiosarcoma revealed many similarities, but also some important differences, between canine hemangiosarcoma and human angiosarcoma. Future work should include analysis of larger sample sizes, including recalling all currently available human angiosarcoma data using the same methods, in order to decipher potential molecular subtypes and to facilitate a more complete comparison between tumors in different locations. An integrated understanding of the interaction between mutations in the many enriched signaling pathways may be useful for determining treatment strategy, for example, the feasibility of combinations of targeted inhibitors or the prevention of convergent resistance. Our data suggest that clinical trials evaluating therapeutic approaches in dogs with this disease might also inform human medicine.
Supplementary Material
Implications.
We characterize the genomic landscape of canine hemangiosarcoma and demonstrate its similarity to human angiosarcoma.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all of the dogs and owners who participated in our research, as well as the veterinarians who collected samples. The results included here include the use of data from The Angiosarcoma Project (https://ascproject.org/), a project of Count Me In (https://joincountmein.org/), downloaded March 2019. We would also like to thank Dr. Scott Moroff, Vice-President and Chief Scientific Officer of Antech Diagnostics, for contributing tumor and paired blood samples to our research. This work was funded by American Kennel Club (AKC) Canine Health Foundation (CHF) grants #422 (JFM), 1131 (JFM), and 1889-G (JFM, MB, KLT, EKK), NIH grants R03CA191713 (JFM), P30CA077598 (NIH Comprehensive Cancer Center Support Grant to the Masonic Cancer Center, University of Minnesota), R37CA218570 (EKK, CP), and R24OD018250 (EKK), National Canine Cancer Foundation (NCCF) grants DM06CO-003 (JFM) and JHK15MN-004 (JHK), and Morris Animal Foundation grant D10CA-501 (JFM, MB, KLT). KLT is the recipient of a Distinguished Professor award from the Swedish Research Council. IE is supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from the Swedish Medical Research Council, SSMF. JFM is supported by the Alvin and June Perlman Chair in Animal Oncology at the University of Minnesota. MB is supported in part by the Oscar J. Fletcher Distinguished Professorship in Comparative Oncology Genetics at NC State University. ALS is supported by NCI R50 CA211249.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest statement: J.F. Modiano is a partner (paid consultant) for Veterinary Research Associates, reports receiving a commercial research grant from Boston Scientific, and has ownership interest (including patents) in Half Moon Bay Biotechnology, LLC. No potential conflict of interests were disclosed by the other authors.
Data availability
The whole-exome sequencing data, as well as the RNA-seq data that has not been previously published, has been submitted to the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA). WES data: BioProject PRJNA552034, BioSamples SAMN12173468 - SAMN12173561. RNA-seq data: BioProject PRJNA562916, BioSamples SAMN12659339 - SAMN12659361.
References
- 1.Penel N, Marréaud S, Robin Y-M, Hohenberger P. Angiosarcoma: state of the art and perspectives. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2011;80:257–63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Abraham JA, Hornicek FJ, Kaufman AM, Harmon DC, Springfield DS, Raskin KA, et al. Treatment and outcome of 82 patients with angiosarcoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:1953–67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Florou V, Wilky BA. Current and Future Directions for Angiosarcoma Therapy. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2018;19:14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Antonescu C. Malignant vascular tumors—an update. Mod Pathol. United States & Canadian Academy of Pathology; 2014;27:S30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Glickman L, Glickman N, Thorpe - Retriever Club of America National … R, 1999. The Golden Retriever Club of America National Health Survey 1998–1999. grca.org [Internet]. 1999; Available from: https://www.grca.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/healthsurvey1-1.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 7.Young RJ, Brown NJ, Reed MW, Hughes D, Woll PJ. Angiosarcoma. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:983–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mark RJ, Poen JC, Tran LM, Fu YS, Juillard GF. Angiosarcoma: a report of 67 patients and a review of the literature. Cancer: Interdisciplinary International Journal of the American Cancer Society. Wiley Online Library; 1996;77:2400–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lahat G, Dhuka AR, Hallevi H, Xiao L, Zou C, Smith KD, et al. Angiosarcoma: clinical and molecular insights. Ann Surg. 2010;251:1098–106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stenbäck F. Cellular injury and cell proliferation in skin carcinogenesis by UV light. Oncology. 1975;31:61–75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cioffi A, Reichert S, Antonescu CR, Maki RG. Angiosarcomas and other sarcomas of endothelial origin. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2013;27:975–88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Maddox JC, Evans HL. Angiosarcoma of skin and soft tissue: a study of forty-four cases. Cancer. 1981;48:1907–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Makk L, Creech JL, Whelan JG Jr, Johnson MN. Liver damage and angiosarcoma in vinyl chloride workers. A systematic detection program. JAMA. 1974;230:64–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Centeno JA, Mullick FG, Martinez L, Page NP, Gibb H, Longfellow D, et al. Pathology related to chronic arsenic exposure. Environ Health Perspect. 2002;110 Suppl 5:883–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Falk H, Thomas LB, Popper H, Ishak KG. Hepatic angiosarcoma associated with androgenic-anabolic steroids. Lancet. 1979;2:1120–3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Calvete O, Martinez P, Garcia-Pavia P, Benitez-Buelga C, Paumard-Hernández B, Fernandez V, et al. A mutation in the POT1 gene is responsible for cardiac angiosarcoma in TP53-negative Li-Fraumeni-like families. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ploegmakers MJM, Pruszczynski M, De Rooy J, Kusters B, Veth RPH. Angiosarcoma with malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour developing in a patient with Klippel--Trénaunay--Weber syndrome. Sarcoma. Hindawi Publishing Corporation; 2005;9:137–40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kim J-H, Graef AJ, Dickerson EB, Modiano JF. Pathobiology of Hemangiosarcoma in Dogs: Research Advances and Future Perspectives. Vet Sci China. 2015;2:388–405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Oksanen A. Haemangiosarcoma in dogs. J Comp Pathol. 1978;88:585–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Brown NO, Patnaik AK, MacEwen EG. Canine hemangiosarcoma: retrospective analysis of 104 cases. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1985;186:56–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Withrow SJ, Page RL. Withrow and MacEwen’s Small Animal Clinical Oncology. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wendelburg KM, Price LL, Burgess KE, Lyons JA, Lew FH, Berg J. Survival time of dogs with splenic hemangiosarcoma treated by splenectomy with or without adjuvant chemotherapy: 208 cases (2001–2012). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2015;247:393–403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sorenmo KU, Jeglum KA, Helfand SC. Chemotherapy of Canine Hemangiosarcoma With Doxorubicin and Cyclophosphamide. J Vet Intern Med. 1993;7:370–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tonomura N, Elvers I, Thomas R, Megquier K, Turner-Maier J, Howald C, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies shared risk loci common to two malignancies in golden retrievers. PLoS Genet. 2015;11:e1004922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Murali R, Chandramohan R, Möller I, Scholz SL, Berger M, Huberman K, et al. Targeted massively parallel sequencing of angiosarcomas reveals frequent activation of the mitogen activated protein kinase pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6:36041–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Behjati S, Tarpey PS, Sheldon H, Martincorena I, Van Loo P, Gundem G, et al. Recurrent PTPRB and PLCG1 mutations in angiosarcoma. Nat Genet. 2014;46:376–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Italiano A, Chen C-L, Thomas R, Breen M, Bonnet F, Sevenet N, et al. Alterations of the p53 and PIK3CA/AKT/mTOR pathways in angiosarcomas: a pattern distinct from other sarcomas with complex genomics. Cancer. 2012;118:5878–87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wagner MJ, Ravi V, Menter DG, Sood AK. Endothelial cell malignancies: new insights from the laboratory and clinic. npj Precision Oncology. Nature Publishing Group; 2017;1:11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Je EM, An CH, Yoo NJ, Lee SH. Mutational analysis of PIK3CA, JAK2, BRAF, FOXL2, IDH1, AKT1 and EZH2 oncogenes in sarcomas. APMIS. 2012;120:635–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang G, Wu M, Maloneyhuss MA, Wojcik J, Durham AC, Mason NJ, et al. Actionable mutations in canine hemangiosarcoma. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0188667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mayr B, Zwetkoff S, Schaffner G, Reifinger M. Tumour suppressor gene p53 mutation in a case of haemangiosarcoma of a dog. Acta Vet Hung. 2002;50:157–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dickerson EB, Thomas R, Fosmire SP, Lamerato-Kozicki AR, Bianco SR, Wojcieszyn JW, et al. Mutations of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted from chromosome 10 in canine hemangiosarcoma. Vet Pathol. 2005;42:618–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Abou Asa S, Mori T, Maruo K, Khater A, El-Sawak A, Abd el-Aziz E, et al. Analysis of genomic mutation and immunohistochemistry of platelet-derived growth factor receptors in canine vascular tumours. Vet Comp Oncol. 2015;13:237–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Thomas R, Borst L, Rotroff D, Motsinger-Reif A, Lindblad-Toh K, Modiano JF, et al. Genomic profiling reveals extensive heterogeneity in somatic DNA copy number aberrations of canine hemangiosarcoma. Chromosome Res. 2014;22:305–19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Forbes SA, Beare D, Gunasekaran P, Leung K, Bindal N, Boutselakis H, et al. COSMIC: exploring the world’s knowledge of somatic mutations in human cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:D805–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Thibodeau BJ, Lavergne V, Dekhne N, Benitez P, Amin M, Ahmed S, et al. Mutational landscape of radiation-associated angiosarcoma of the breast. Oncotarget. 2018;9:10042–53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gorden BH, Kim J-H, Sarver AL, Frantz AM, Breen M, Lindblad-Toh K, et al. Identification of three molecular and functional subtypes in canine hemangiosarcoma through gene expression profiling and progenitor cell characterization. Am J Pathol. 2014;184:985–95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Borgatti A, Koopmeiners JS, Sarver AL, Winter AL, Stuebner K, Todhunter D, et al. Safe and Effective Sarcoma Therapy through Bispecific Targeting of EGFR and uPAR. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017;16:956–65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Do H, Dobrovic A. Sequence artifacts in DNA from formalin-fixed tissues: causes and strategies for minimization. Clin Chem. 2015;61:64–71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Benjamini Y, Speed TP. Summarizing and correcting the GC content bias in high-throughput sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:e72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kinsella RJ, Kähäri A, Haider S, Zamora J, Proctor G, Spudich G, et al. Ensembl BioMarts: a hub for data retrieval across taxonomic space. Database. 2011;2011:bar030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lawrence MS, Stojanov P, Mermel CH, Robinson JT, Garraway LA, Golub TR, et al. Discovery and saturation analysis of cancer genes across 21 tumour types. Nature. 2014;505:495–501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sondka Z, Bamford S, Cole CG, Ward SA, Dunham I, Forbes SA. The COSMIC Cancer Gene Census: describing genetic dysfunction across all human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18:696–705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ng PC, Henikoff S. SIFT: Predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3812–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.McLaren W, Gil L, Hunt SE, Riat HS, Ritchie GRS, Thormann A, et al. The Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor. Genome Biol. 2016;17:122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Painter C, Jain E, Dunphy M, Anastasio E, McGillicuddy M, Stoddard R, et al. Abstract B085: High mutation burden and response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in angiosarcomas of the scalp and face. Proceedings of the Fourth CRI-CIMT-EATI-AACR International Cancer Immunotherapy Conference: Translating Science into Survival. American Association for Cancer Research; 2019. page B085–B085. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kunze K, Spieker T, Gamerdinger U, Nau K, Berger J, Dreyer T, et al. A recurrent activating PLCG1 mutation in cardiac angiosarcomas increases apoptosis resistance and invasiveness of endothelial cells. Cancer Res. 2014;74:6173–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gonias SL, Karimi-Mostowfi N, Murray SS, Mantuano E, Gilder AS. Expression of LDL receptor-related proteins (LRPs) in common solid malignancies correlates with patient survival. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0186649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Fruman DA, Chiu H, Hopkins BD, Bagrodia S, Cantley LC, Abraham RT. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell. 2017;170:605–35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cully M, You H, Levine AJ, Mak TW. Beyond PTEN mutations: the PI3K pathway as an integrator of multiple inputs during tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:184–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Chang HW, Aoki M, Fruman D, Auger KR, Bellacosa A, Tsichlis PN, et al. Transformation of Chicken Cells by the Gene Encoding the Catalytic Subunit of PI 3-Kinase. Science. American Association for the Advancement of Science; 1997;276:1848–50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, et al. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science. 2004;304:554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hon W-C, Berndt A, Williams RL. Regulation of lipid binding underlies the activation mechanism of class IA PI3-kinases. Oncogene. 2012;31:3655–66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Pamonsinlapatham P, Hadj-Slimane R, Lepelletier Y, Allain B, Toccafondi M, Garbay C, et al. p120-Ras GTPase activating protein (RasGAP): a multi-interacting protein in downstream signaling. Biochimie. 2009;91:320–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Henkemeyer M, Rossi DJ, Holmyard DP, Puri MC, Mbamalu G, Harpal K, et al. Vascular system defects and neuronal apoptosis in mice lacking ras GTPase-activating protein. Nature. 1995;377:695–701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Eerola I, Boon LM, Mulliken JB, Burrows PE, Dompmartin A, Watanabe S, et al. Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation, a new clinical and genetic disorder caused by RASA1 mutations. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;73:1240–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Liu Y, Liu T, Sun Q, Niu M, Jiang Y, Pang D. Downregulation of Ras GTPase‑activating protein 1 is associated with poor survival of breast invasive ductal carcinoma patients. Oncol Rep. 2015;33:119–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Chen Y-L, Huang W-C, Yao H-L, Chen P-M, Lin P-Y, Feng F-Y, et al. Down-regulation of RASA1 Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2017;37:781–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Laurila E, Savinainen K, Kuuselo R, Karhu R, Kallioniemi A. Characterization of the 7q21-q22 amplicon identifies ARPC1A, a subunit of the Arp2/3 complex, as a regulator of cell migration and invasion in pancreatic cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2009;48:330–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Elson A. Stepping out of the shadows: Oncogenic and tumor-promoting protein tyrosine phosphatases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018;96:135–47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kim MJ, Kim E, Ryu SH, Suh P-G. The mechanism of phospholipase C-γ1 regulation. Exp Mol Med. Nature Publishing Group; 2000;32:101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Lyles SE, Milner RJ, Kow K, Salute ME. In vitro effects of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor, masitinib mesylate, on canine hemangiosarcoma cell lines. Vet Comp Oncol. 2012;10:223–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Gardner HL, London CA, Portela RA, Nguyen S, Rosenberg MP, Klein MK, et al. Maintenance therapy with toceranib following doxorubicin-based chemotherapy for canine splenic hemangiosarcoma. BMC Vet Res. 2015;11:131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.