Abstract
Background
Male partner involvement is an important and crucial determinant of prevention of mother to child transmission (PMTCT) of HIV. It creates an opportunity to reverse the transmission of HIV during pregnancy, labor, and breastfeeding. Thus, involving male partners during HIV screening of pregnant mothers at ANC is the key to fight against MTCT of HIV.
Objective
This study was designed to assess the magnitude and factors associated with male partner’s involvement on PMTCT service utilization among pregnant women who attended focused antenatal care (FANC) in Southern Ethiopia.
Methods
An institutional-based cross-sectional study was conducted among 420 randomly selected pregnant women who enrolled in PMTCT service at ANC clinics. Pre-tested and structured self-administered questionnaires were used to collect the data. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to determine the presence of statistically significant associations between the outcome variable and the independent variables with a p-value less than 0.05.
Results
A total of 409 pregnant women who had ANC follow-up have participated in this study. The majority 160 (39.1%) of the participants were in the age group of 25–29 years. The magnitude of male involvement in PMTCT service was 129 (29.8%). Number of ANC visits (3rd visit (AOR=2.36, CI=1.09, 5.10), 4th visit (AOR=3.49, CI=1.65, 7.38), birthplace interest (AOR=3.01, CI=1.16, 7.84), awareness about partner monthly income (AOR=2.17, CI=1.15, 4.11), source of family saving scheme (partner (AOR=2.99, CI=1.39, 6.43), self (AOR=8.59, CI=3.92, 18.82), both (AOR=5.13, CI=2.21, 11.92), maternal perception about the importance of consulting partner before HIV testing (AOR=9.30, CI=2.65, 32.64), and kinds of partner support (psychological (AOR=0.08, CI=0.02, 0.29), financial (AOR=0.33, CI=0.17, 0.68) were found to be significantly associated with male involvement in PMTCT.
Conclusion
This study found out that male partner involvement in PMTCT is low. Therefore, improving male partner involvement in PMTCT is recommended for improving maternal FANC service utilization and adherence with notification of their partner and provision of psychological and financial support.
Keywords: male partner, PMTCT, ANC service utilization, Ethiopia
Introduction
HIV/AIDS still remains the major challenge globally despite decades of advocacy, awareness raising and investing in programs to control its spread.1 It highly infects women and children and has serious impacts on women’s life.2 According to the UNAIDS report by 2019, it is projected that more than 33.3 million people globally are living with HIV and of whom 2.5 million will be infants and children.3 About 92% of HIV infected pregnant women are living in the region of Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA).4
The majority of children living with HIV are infected via mother to child transmission (MTCT).5 About 90% of new HIV infections among infants occur through MTCT. Without any intervention, the risk of MTCT ranges from 20% to 45%. However, with an evidence-based set of comprehensive intervention, this transmission rate can be reduced to less than 2%.6
Prevention of mother to child transmission (PMTCT) is an essential step and intervention strategy to ensure no child is born with HIV and safeguard HIV/AIDS-free generation.6 Therefore, ART should be maintained after the delivery and completion of breastfeeding for life. All infants born to HIV-positive mothers should receive a course of treatment as soon as possible after birth.7,8
World Health Organization (WHO) launches a comprehensive approach to the PMTCT program, i.e. primary prevention of HIV infection among childbearing age women, prevention of unintended pregnancies among women living with HIV, prevention of HIV transmission from HIV infected woman living to her infant, and providing comprehensive treatment, care and psychosocial and rehabilitative support to women living with HIV, their children, and families.9 In resource-limited settings with high rates of MTCT, due to their key decision-making role on the health of women and their children, including use of PMTCT interventions, family planning, and access to medical care, male partners must be considered as part of PMTCT program.10 Studies showed that low male participation in PMTCT services is strongly associated with high MTCT risk in exposed infants.11
Male partner involvement in PMTCT intervention has been associated with an increase in uptake of intervention by pregnant women, facilitates ART initiation and adherence, increases health facility delivery, and enables a good choice of breastfeeding plan.12 Various studies have demonstrated that male partner involvement can have a positive impact on the utilization of services such as antenatal care (ANC), facility-based delivery, HIV testing, and PMTCT.13 It may reduce the risk of (MTCT) by more than 40%.14
Even though Ethiopia started to implement PMTCT/ANC services since 2001, programs face different challenges such as little involvement by men.15 As studies done in Ethiopia found out that male partners’ involvement in PMTCT ranges from 10% to 53%.16–18 The studies show male involvement may be underutilized public health intervention to address both infant HIV infection and mortality in resource-poor setting.16 Therefore, the lack of male involvement in ANC/PMTCT of HIV programs, in particular, have been identified as major bottlenecks to effective program implementation.16–18 Several factors such as fear of disclosure of HIV results, lack of male partner support, fear of violence, abandonment, and stigmatization affect PMTCT service utilization.12
As most low- and middle-income countries, male involvement in PMTCT service utilization is said to be very low in many health facilities in Ethiopia. Therefore, this is one of the impending program gap negatively affecting PMTCT services uptake.19 A study conducted in Hadiya zone southern Ethiopia showed that only 29.2% of male partners were accompanying the partner to ANC clinics and 28.0% male partners were counselled and tested for HIV during their partners’ pregnancy.20 Hereafter, previously in a country, it was underlined as involving male partners in PMTCT can be considered as an opportunity for the delivery of further PMTCT services particularly partner testing, condom use, and infant feeding recommendations.21
Furthermore, male involvement in PMTCT has been inadequate and many pregnant women attend maternal health services unaccompanied and unsupported by their partners.13 Despite this, male involvement in PMTCT in Ethiopia is not well known. Hence, information on male involvement and associated factors of the pregnant women are urgently needed for prioritizing, designing, and initiating intervention programs aimed at reducing MTCT rate of HIV and producing a healthy and productive child. In addition, male involvement is an important determinant factor of PMTCT service uptake. Therefore, this study was aimed to assess the magnitude and factors associated with male partner’s involvement in PMTCT service utilization among pregnant women who attend FANC in selected institutions found in Hawassa town.
Study Area, Design, and Period
An institutional-based cross-sectional study design was conducted among pregnant women who enrolled in PMTCT service in randomly selected health facilities of Hawassa city, Southern, Ethiopia from April to May 2018. The city has two governmental hospitals and 9 health centers. In these health institutions, the PMTCT program offered with an integration of ANC services at MCH (mother and child health) department. We conducted this study in two hospitals (Hawassa university comprehensive-specialized hospital and Adare general hospital), and two health centers (Millennium and Tilite).
Population
Source Population
All pregnant women who enrolled in PMTCT service at ANC clinic in randomly selected government health facilities of Hawassa town during the study period were the source population.
Study Population
All sampled pregnant women who enrolled in PMTCT service at ANC clinic in randomly selected government health facilities of Hawassa town during the study period were the source population.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Pregnant women with age 18 and above were included in the study. However, those who were seriously ill to give personal information during the interview were excluded from the study.
Sample Size Determination and Sampling
The sample size was calculated using a single population proportion formula;
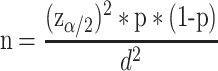 |
where the estimated prevalence of 53.0% was taken from the study conducted in Arbaminch, Ethiopia17 with 5% marginal error (d) and 95% CI (Zα/2=1.96) and adding a 10% non-response rate, the total sample size for this research was 420. Four health facilities were selected through random sampling technique. Secondly, the overall sample was proportionally allocated to the selected health facilities. Then, sampling frame was prepared for each selected health facility based on registration book appointment. Finally, a simple random sampling technique was used to select the required number of participants.
Data Collection Tools
Structured and pre-tested questionnaires were used to collect the data which was adapted from similar studies. The questionnaire was translated from English to Amharic by language experts in and back translated to English by another language expert to ensure consistency. The questionnaire had five parts, i.e. sociodemographic characteristics, women’s financial power and decision-making, risk perception, and health-seeking behavior, HIV counseling and testing practice and male partner involvement-related questions were incorporated. The level of male partner involvement in PMTCT was assessed using a six-item “ad hoc male involvement index” questionnaire. This index was designed with yes=1 and no=0 answer which was adapted from previous studies, i.e. from Uganda22 and Arbaminch, Ethiopia.17
Did your male partner know your appointment for ANC the last time you were pregnant?
Did you discuss with your male partner about counseling and testing for HIV the last time, you were pregnant?
Have you ever gone together with your male partner to an ANC/PMTCT clinic?
Have you ever counseled and tested for HIV together with your male partner at an ANC/PMTCT clinic?
Did your male partner support your antenatal visits financially?
Do your male partner accept if health professionals inform you to use a condom during the time of your pregnancy?
The total score of the items ranges from 0 to 6. A score of 4–6 was considered as “high involvement in PMTCT” and 0–3 as “low involvement in PMTCT” service utilization.23
Data Quality Control
Data were collected by trained clinical nurses and supervised by BSc Nurses. Two-day training for data collectors and supervisors were given about data collection methods and how to handle ethical issues. Pre-test was conducted on 5% of the study sample size before the main study was conducted to identify impending problems on data collection instruments and to check consistency of the questionnaires, and the performance of the data collectors. Regular supervision by the supervisor and the principal investigator were made to ensure that all necessary data are properly collected. Each day during data collection, filled questionnaires were checked for completeness and consistency by supervisors and principal investigator. Incomplete questionnaires were discarded.
Data Analysis
Collected data were entered to Epi-data version 3.1 and exported to SPSS for windows version 20 for analysis. Frequencies and percentages were computed for categorical variables. Binary and multivariate logistic regressions were used at 95% confidence interval (CI) were used to see the association between dependent and independent variables. After controlling confounding, variables that had a P-value of <0.05 were treated as predictor variables.
Results
Socio-Demographic Characteristics and Health-Seeking Behavior of Pregnant Women and Male Partner
A total of 409 pregnant women who had ANC follow-up have participated in this study. Majority 160 (39.1%) of the participants were in the age group of 25–29 years. More than half of male partners 284 (69.4%) were in the age group of 25–34 years as described in Table 1.
Table 1.
Socio-Demographic Characteristics of Pregnant Women and Their Male Partner Who Came to ANC Clinic for ANC/PMTCT Service in Hawassa Town, Southern Ethiopia, 2018 (N= 409)
| Variable | Description | Frequency (n) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 18–24 years | 185 | 45.2 |
| 25–29 years | 160 | 39.1 | |
| 30–34 years | 49 | 12.0 | |
| 35–39 years | 15 | 3.7 | |
| Marital status | Single | 3 | 7 |
| Married | 402 | 98.3 | |
| Divorced | 4 | 1 | |
| Level of school | No formal education | 32 | 7.8 |
| Primary education | 82 | 20.0 | |
| Secondary education | 114 | 27.9 | |
| Higher education | 181 | 44.3 | |
| Occupation | House wife | 182 | 44.5 |
| Government employee | 137 | 33.5 | |
| Unemployed | 76 | 18.6 | |
| Merchant | 14 | 3.4 | |
| Availability of own monthly income | Yes | 191 | 46.7 |
| No | 218 | 53.3 | |
| Monthly income (N=191) | <1400 ETB | 49 | 25.7 |
| 1401–2000 ETB | 62 | 32.5 | |
| 2001–2500 ETB | 35 | 18.3 | |
| >2500 ETB | 45 | 23.6 | |
| Availability of family saving system/scheme | Yes | 297 | 72.6 |
| No | 112 | 27.4 | |
| Responsibility of family saving scheme (n=297) | Partner saving | 134 | 45.1 |
| Self-saving | 100 | 33.7 | |
| Both partners saving | 63 | 21.2 | |
| Age of male partner | 15–24 years | 28 | 6.8 |
| 25–34 years | 284 | 69.4 | |
| 35+ years | 97 | 23.7 | |
| Educational status of male partner | No formal education | 16 | 3.9 |
| Primary education | 91 | 22.3 | |
| Secondary education | 84 | 20.5 | |
| Higher education | 218 | 53.3 | |
| Occupation of male partner | Governmental employee | 194 | 47.4 |
| Daily wage workers | 125 | 30.6 | |
| Merchant | 58 | 14.2 | |
| NGO employee | 16 | 3.9 | |
| Student | 12 | 2.9 | |
| Current marriage type of male partner | Monogamy | 397 | 97.1 |
| Polygamy | 12 | 2.9 |
Pregnancy and Decision Making Related Characteristics of Pregnant Women
Nearly one-fourth 106 (24.9%) of the women had unwanted current pregnancy. From the total participants, 329 (80.4%) of the pregnant women were interested to give birth at the health facility and nearly three-fourths 298(72.9%) had a birth preparedness plan (Table 2).
Table 2.
Pregnancy and Decision Making Related Characteristics of Pregnant Women Who Came to ANC Clinics in the Selected Health Centers for ANC/PMTCT Service in Hawassa Town, Southern Ethiopia, 2018 (N= 409)
| Variable | Description | Frequency (n) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pregnancy condition | Wanted | 303 | 74.1 |
| Unwanted | 106 | 24.9 | |
| Gravidity | Gravida I | 201 | 49.1 |
| Gravida II | 130 | 31.5 | |
| Gravida III | 42 | 10.3 | |
| Gravida IV and above | 36 | 8.8 | |
| Parity (N=208) | Para 0 | 201 | 49.1 |
| Para I | 130 | 31.5 | |
| Para II | 42 | 10.3 | |
| Para III and above | 36 | 8.8 | |
| Number of FANC visit | First visit | 90 | 22.0 |
| Second visit | 109 | 26.7 | |
| Third visit | 144 | 35.2 | |
| Fourth visit | 66 | 16.1 | |
| Birth place interest | Health facility | 329 | 80.4 |
| Home by TBA | 80 | 19.6 | |
| Birth preparedness plan | Yes | 298 | 72.9 |
| No | 111 | 27.1 | |
| Responses on importance of HIV test | For health workers only | 52 | 12.7 |
| For baby alone | 47 | 11.5 | |
| For partner alone | 15 | 3.7 | |
| For mother alone | 24 | 5.9 | |
| For mother and baby only | 114 | 27.9 | |
| For everyone | 157 | 38.3 | |
| Decisionmaker to use condom when desire | Partner | 116 | 28.4 |
| Self | 31 | 7.6 | |
| Both partner | 262 | 64.1 | |
| Decisionmaker to make HIV test | Partner | 45 | 11.0 |
| Self | 84 | 20.5 | |
| Both partner | 280 | 68.5 | |
| Decisionmaker for institutional delivery | Partner | 40 | 9.8 |
| Self | 82 | 20.2 | |
| Both partner | 287 | 70.2 | |
| Decisionmaker on baby-feeding option | Partner | 34 | 8.3 |
| Self | 144 | 35.2 | |
| Both partner | 231 | 56.5 |
PMTCT Care and Support Related Characteristics of Pregnant Women
More than two-thirds 278(68%) of participants had a discussion on HIV with their male partner. Almost two-thirds 260(64.4%) of pregnant women had got both psychological and financial support from their male partner as shown in Table 3.
Table 3.
PMTCT and HIV Care and Support Related Characteristics of Pregnant Women Who Came to ANC Clinics in the Selected Health Centers for ANC/PMTCT Service in Hawassa Town, Southern Ethiopia, 2018 (N= 409)
| Variable | Description | Frequency (n) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Life time HIV risk of pregnant women | Yes | 14 | 3.4 |
| No | 389 | 95.1 | |
| I do not know | 6 | 1.5 | |
| Kinds of life time HIV risk behaviour of women (N=14) | Multiple Sexual partner | 6 | 42.8 |
| Sexual contact without condom | 6 | 42.8 | |
| Sexual contact with HIV positive | 2 | 14.2 | |
| Discussion on HIV with partner | Yes | 278 | 68.0 |
| No | 131 | 32.0 | |
| Women’s history of HIV screening | Yes | 397 | 97.1 |
| No | 12 | 2.9 | |
| Women’s willingness and testing HIV test in current pregnancy | Yes | 398 | 97.3 |
| No | 11 | 2.7 | |
| Women’s reason for current HIV test refusal (N=11) | Inability to cope stress of being positive | 5 | 45.5 |
| Fear of rejection/stigma by community | 6 | 54.5 | |
| Women’s Current HIV testing result (N=398) | Positive | 7 | 1.8 |
| Negative | 391 | 98.2 | |
| Women’s disclosure of current test result to male partners (N=398) | Yes | 370 | 93.0 |
| No | 28 | 7.0 | |
| Women’s who consult partner before testing current HIV test (N=398) | Yes | 349 | 87.7 |
| No | 49 | 12.3 | |
| Partner Life time HIV risk | Yes | 26 | 6.4 |
| No | 364 | 89.0 | |
| I do not know | 19 | 4.6 | |
| Partner HIV ever tested history | Yes | 349 | 85.3 |
| No | 60 | 14.7 | |
| Partner disclosure history of HIV test result (N=349) | Yes | 304 | 87.1 |
| No | 45 | 12.9 | |
| Partner willingness to HIV test currently | Yes | 374 | 91.4 |
| No | 35 | 8.6 | |
| Partner reason for current HIV test refusal (N= 35) | Inability to cope stress of being positive | 18 | 51.4 |
| Fear of community rejection or stigma | 14 | 40.0 | |
| I do not know | 3 | 8.6 | |
| Kinds of partner support (N= 357) | Financial support | 87 | 24.4 |
| Psychological support | 40 | 11.2 | |
| Both financial and psychological support | 230 | 64.4 |
Level of Male Partner Involvement in PMTCT
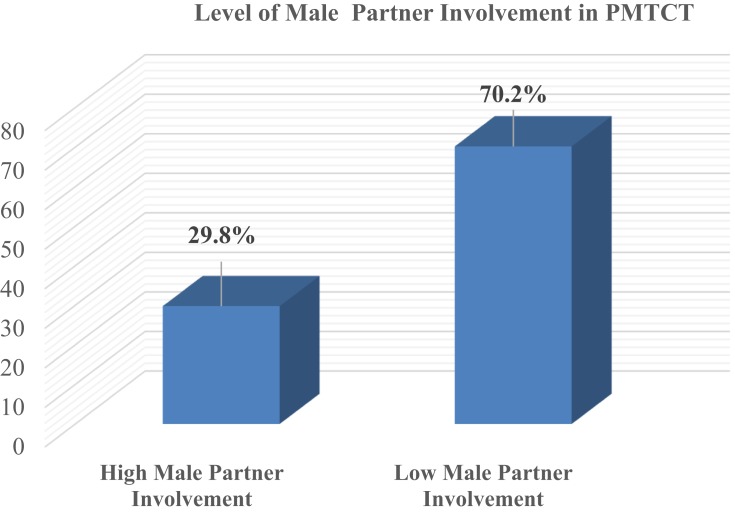
Around one-third 122 (29.8%) of the pregnant women had a high level of male partner involvement towards PMTCT service intake (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Level of male partner involvement in PMTCT among pregnant mothers who have ANC follow-up.
Factors Associated with Male Partner Involvement on PMTCT
In this study among many variables included in multiple linear regression; ANC visit (3rd visit (AOR=2.36, CI=1.09, 5.10) and 4th visit (AOR=3.49, CI=1.65, 7.38)), birthplace interest (AOR=3.01, CI=1.16, 7.84), awareness about partner monthly income (AOR=2.17, CI=1.15, 4.11), source of family saving scheme (partner (AOR=2.99, CI=1.39, 6.43), self (AOR=8.59, CI=3.92, 18.82), both (AOR=5.13, CI=2.21, 11.92)), maternal perception about the importance of consulting partner before HIV testing (AOR=9.30, CI=2.65, 32.64), and kinds of partner support (psychological (AOR=0.08, CI=0.02, 0.29), financial (AOR=0.33, CI=0.17, 0.68)) were found to be significantly associated with male involvement in PMTCT (Table 4).
Table 4.
Association Between Male Partner Involvement in ANC/PMTCT and Each Explanatory Variable (Crude & Adjusted OR) of Pregnant Women Who Came to ANC Clinics in the Selected Health Centers for ANC/PMTCT Service in Hawassa Town, Southern Ethiopia, 2018 (N= 409)
| Variable | Male Partner Involvement | COR (95% CI) | AOR (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | High | ||||
| Having birth preparedness plan | Yes | 204 (49.9%) | 94 (23.0%) | 1.37 (0.83, 2.24) | |
| No | 83 (20.3%) | 28 (6.8%) | 1 | ||
| FANC visit | First visit | 78 (19.1%) | 12 (2.9%) | 1 | 1 |
| Second visit | 72 (17.6%) | 37 (9.0%) | 0.44 (0.19, 1.00) | 0.66 (0.27, 1.59) | |
| Third visit | 88 (21.5%) | 56 (13.7%) | 1.48 (0.75, 2.92) | 2.36 (1.09, 5.10)* | |
| Fourth visit | 49 (12.0%) | 17 (4.2%) | 0.06 (0.96, 3.49) | 3.49 (1.65, 7.38)* | |
| Birth Place Interest | Home by TBA | 67 (16.4%) | 13 (3.2%) | 1 | 1 |
| Health facility | 220 (53.8%) | 109 (26.7%) | 2.55 (1.35, 4.83)* | 3.01(1.16, 7.84)* | |
| Awareness about partner monthly income | Yes | 168 (41.1%) | 100 (24.4%) | 3.22 (1.92, 5.40)* | 2.17(1.15, 4.11)* |
| No | 119 (29.1%) | 22 (5.4%) | 1 | 1 | |
| Maternal own monthly income | Yes | 115 (28.1%) | 115 (28.1%) | 2.47 (1.59, 3.82)* | |
| No | 172 (42.1%) | 46 (11.2%) | 1 | ||
| Source of family saving scheme | Partner saving | 99 (24.2%) | 35 (8.6%) | 2.69 (1.34, 5.39)* | 2.99 (1.39, 6.43)* |
| Self saving | 52 (12.7%) | 48 (11.7%) | 7.03 (3.49, 14.14)* | 8.59 (3.92, 18.82)* | |
| Both partner saving | 37 (9.0%) | 26 (6.4%) | 5.35 (2.49, 11.50)* | 5.13 (2.21, 11.92)* | |
| No saving | 99 (24.2%) | 13 (3.2%) | 1 | 1 | |
| Decision-maker for institutional delivery | Partner | 23 (5.6%) | 17 (4.2%) | 1 | |
| Pregnant women | 64 (15.6%) | 18 (4.4%) | 1.69 (0.87, 3.34) | ||
| Both partner and women | 200(48.9%) | 87(21.3%) | 0.65 (0.36, 1.15) | ||
| Pregnancy condition | Wanted | 198 (48.4%) | 105(25.7%) | 2.77 (1.57, 4.91)* | |
| Unwanted | 89 (21.8%) | 17 (4.2%) | 1 | ||
| Consulting partner before HIV testing | Yes | 230 (57.8%) | 119 (29.9%) | 7.93 (2.42, 26.04)* | 9.30 (2.65, 32.64)* |
| No | 46 (11.6%) | 3 (0.8%) | 1 | 1 | |
| Kinds of partner support | Psychological | 37 (10.4%) | 3 (0.8%) | 0.11 (0.03, 0.38)* | 0.08 (0.02, 0.29)* |
| Financial | 64 (17.9%) | 23 (6.4%) | 0.50 (0.29, 0.86)* | 0.33 (0.17, 0.68)* | |
| Both psychological and financial | 134(37.5%) | 96 (26.9%) | 1 | 1 | |
| Partner previous HIV testing history | Yes | 229 (64.0%) | 120 (33.5%) | 15.2 (3.65, 63.29)* | |
| No | 58 (14.2%) | 2 (0.5%) | 1 | ||
| Disclosure of partner previous HIV test result (N=349) | Yes | 193 (55.5%) | 111 (31.9%) | 2.30 (1.07, 4.95)* | |
| No | 36 (10.3%) | 9 (2.6%) | 1 | ||
Abbreviation: NB: *Statistically significant at P < 0.05.
Discussion
In this study, nearly one-third (29.8%) of pregnant women had got high male partner involvement in their PMTCT service. This finding was higher than the previous studies done in Gondar, Mekelle and Addis Ababa which accounts 20.9%, 20.1%, and 10%, respectively.16,18,24 Similarly, a study conducted in Kenya (15%) and Tanzania (24.7%) revealed that male partner participation in PMTCT was also lower than this study.25,26 The discrepancy might be due to the difference in socio-economic, health-care service accessibility and availability, level of health information provision and utilization.
In our study, those women who have third and fourth ANC visit have more likely to have male partner involvement. Women with multiple ANC visits may receive feedback and invitations to deliver for their male partner. Giving feedback to a partner might imply good couple communication and acceptance by the male partner to be involved in PMTCT.27 Exposing the male partner in PMTCT service increases an opportunity to test and counselling for HIV, and spousal communication on prevention and sexual negotiation.28
In this study couples who decided to give birth at the health facility is more likely to have male partner involvement. A pregnant woman with a supportive male partner would be more likely to deliver in a health facility by a skilled health professional.29
We found out that male partners who had monthly income and saving habit are more likely to be involved in ANC/PMTCT service utilization. Male partners did not have time to attend ANC with their partners since they utilize the time to source money to take care of their families when they have socio-economic difficulties.27 Distance, poor infrastructure, undeveloped transport system and cost of getting to the hospital restrain men from being engaged in PMTCT service.30 In addition, men with low-income levels opted to stay at home because they lacked enough money to travel with their partners to ANC clinics.22 In most Sub-Saharan African countries, the principal breadwinners in the family are men. Therefore, men mostly choose to spend their time at work fending for their families, instead of waiting for long hours at the clinics where for most of the time they are not involved. This may contribute to their lack of commitment at the clinics for PMTCT service.31
In this study, having consult of male partner by pregnant women also involves males nine times as those who do not in PMTCT service. If the couples discuss the need for HIV testing, that means they are ready to accept the test result and they are more likely to adhere to the PMTCT treatment.27 Those women who disclosed their HIV status to their male partners were more likely to engage in PMTCT services such as post-test counseling, accept antiretroviral prophylaxis, modify infant feeding practices and increase condom use.32
Male partners who provide support for their pregnant women both financially and psychologically are more likely considered to be involved in PMTCT. This decreases stigma on pregnant women and charging user fee also promote pregnant women participating in PMTCT services.30 This is because of the fact that men are decision-makers in many societies and families. Therefore, supporting pregnant mothers psychologically and financially promotes the involvement of male partners in ANC/PMTCT.
Limitation of the Study
This study does not completely guarantee the effect of confounding factors and there is a risk of biased responses such as social desirability bias by which pregnant women either exaggerate or minimize the role of the male partner for some reason. The situation may provide different results if male partners had been chosen for the interview.
Conclusions
In this study, the magnitude of male partner involvement in PMTCT service of pregnant women was 29.8%. The number of FANC visit, birthplace interest, awareness about partner monthly income, source of the family-saving scheme, maternal perception about the importance of consulting partner before HIV testing, and kinds of partner support were significant predictors of male involvement in PMTCT. Therefore, improving male partner involvement in PMTCT is recommended by improving maternal FANC service utilization and adherence with notification of their partner.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all participants and data collectors for devoting their time to contribute their ideas during data collection.
Funding Statement
No funding was received for this research work.
Abbreviations
FANC, Focused Antenatal Care; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; PMTCT, Prevention Mother to Child Transmission; WHO, World Health Organization.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Ethical clearance was obtained from Hawassa University College of Medicine and Health sciences, Institutional Review Board. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants gave written informed consent to participate in the study.
Data Sharing Statement
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to the obligation to secrecy towards the participants.
Author Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.UNAIDS. Report on the global AIDS epidemic. 2010.
- 2.Risley CL, Drake LJBD Economic Impact of HIV and Antiretroviral Therapy on Education Supply in High Prevalence Regions. 2014; [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 3.UNAIDS. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. Global AIDS Epidemic. UNAIDS Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic. UNAIDS, Geneva; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 4.UNAIDS. UNAIDS. Fact Sheet Sub Saharan Africa 2012. UNAIDS; 2012. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-11-11-0999-PDN [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.UNAIDS. Global AIDS epidemics. [Internet]. UNAIDS; 2014. Available from: www.unaids.org/en. Accessed February17, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 6.UNICEF. Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission (PMTCT) of HIV. UNICEF; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 7.World Health Organization (WHO). Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission of HIV Guideline. World Health Organization (WHO); 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 8.World Health Organization (WHO). Consolidated Guidelines on HIV Prevention, Diagnosis, Treatment and Care for Key Populations. World Health Organization (WHO); 2014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.World Health Organization (WHO). Strategic Approaches to the Prevention of HIV Infection in Infants: Reporting on a WHO Meeting: Morges, Switzerland, March 20 –22, 2002. WHO; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Akarro RRJ, Deonisia MSF. An evaluation of male involvement on the programme for PMTCT of HIV/AIDS: a case study of Ilala Municipal in Dares Salam, Tanzania. Arts Soc Sci Journal. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Aluisio A, Richardson BA, Bosire R, John-Stewart GM-ND, C. F. Male antenatal attendance and HIV testing are associated with decreased infant HIV infection and increased HIV-free survival. J Acquir Immune DeficSyndr. 2011;56(1):76–82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Elias M, Mmbaga EJ, Ahmed Abade Mohamed RSK. Male partner involvement in the prevention of mother to child transmission of HIV infection in Mwanza Region, Tanzania. Pan Afr Med J. 2017;8688:1–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.UNICEF. Improving Male Involvement to Support Elimination of Mother- To-Child Transmission of HIV in Uganda: A Case Study. UNICEF; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Africa I. The Downside of Male Involvement in PMTCT. Kenya: IRIN Africa; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Federal Ministry of Health [FMoH]. Complementary Continuous Quality Improvement Guidance Note. Addis Ababa: National Accelerated Scale Up Plan for PMTCT Service 2012; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Haile F, Brhan Y. Male partner involvements in PMTCT: a cross sectional study, Mekelle, Northern Ethiopia. BMC Pregnancy Child Birth. 2014;14:65. doi: 10.1186/1471-2393-14-65 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tilahun M, Mohammed S. male partner involvement in the prevention of mother to child transmission of HIV & associated factors in Arbaminch town & Arbaminch zuriya woreda. Hindawi Publ Corp Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:1–6. doi: 10.1155/2015/763876 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Takele A Assessment of male partner influence on pregnant women towards voluntary HIV testing and support on PMTCT in hospitals of Addis Abeba. 2015. Available from: etd.aau.edu.et. Accessed February17, 2020.
- 19.Chimwaza AF, Muula AS, Nyondo AF. Stakeholders’ perceptions on factors influencing male involvement in prevention of mother to child transmission of HIV services in Blantyre, Malawi. BMC Public Heal. 2014;14:1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Belato DT, Mekiso AB, Begashaw B. Male partners involvement in prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV services in Southern Central Ethiopia: in case of Lemo District, Hadiya Zone. AIDS Res Treat Conduct. 2017;2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mohammed F, Assefa N. Determinants of desire for children among HIV-positive women in the afar region, Ethiopia: case control study. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):1–9. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150566 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Byamugisha R, Tumwine JK, Semiyaga NTT. Attitudes to routine HIV counseling and testing, and knowledge about prevention of mother to child transmission of HIV in eastern Uganda: a cross-sectional survey among antenatal attendees. J Reprod Heal. 2010;10(12):7–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Byamugisha R, Tumwine JK, Semiyaga N, Tylleskär T. Determinants of male involvement in the prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV programme in Eastern Uganda: a cross-sectional survey. Reprod Health. 2010;7(12):1–9. doi: 10.1186/1742-4755-7-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Amano A. Male involvement in PMTCT and associated factors among men whom their wives had ANC visit 12 months prior to the study in Gondar town, North west Ethiopia. Pan Afr Med J. 2016;24:239. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2016.24.239.8460 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Elias M, Mmbaga EJ, Mohamed AA, Kishimba RS. Male partner involvement in the prevention of mother to child transmission of HIV infection in Mwanza Region, Tanzania. Pan Afr Med J. 2017;27:90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Katz DA, Kiarie JN, John-Stewart GC, et al. HIV testing men in the antenatal setting: understanding male nondisclosure. Int J STD AIDS. 2009;20(11):765–767. doi: 10.1258/ijsa.2009.009139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Alemayehu M, Etana B, Fisseha G, Haileslassie K, Henock Yebyo YB. The role of male partner involvement on mother’s adherence to PMTCT care and support, Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Fam Med Med Sci Res. 2014;3(4):4–10. doi: 10.4172/2327-4972.1000137 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.USAID. PMTCT: Addressing the Needs of Women and Their Partners to Improve Services. USAID; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sarko KA, Blevins M, Ahonkhai AA, Audet CM, Moon TD. HIV status disclosure, facility-based delivery and postpartum retention of mothers in a prevention clinical trial in rural Nigeria. Int Health. 2017;9(4):243–251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Skinner D, Mfecane S, Gumende T. Barriers to accessing PMTCT services in rural area, South Africa. African J AIDS Res. 2005;2:5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ongolly FK, Bukachi SA. Barriers to men ’ s involvement in antenatal and postnatal care in Butula, western Kenya. African J Prim Heal Care Fam Med. 2019;11(1):1–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.World Health Organization (WHO). Male Involvement in the Prevention of Mother-To-Child Transmission of HIV. WHO(World Health Organization); 2012. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Citations
- Takele A Assessment of male partner influence on pregnant women towards voluntary HIV testing and support on PMTCT in hospitals of Addis Abeba. 2015. Available from: etd.aau.edu.et. Accessed February17, 2020.