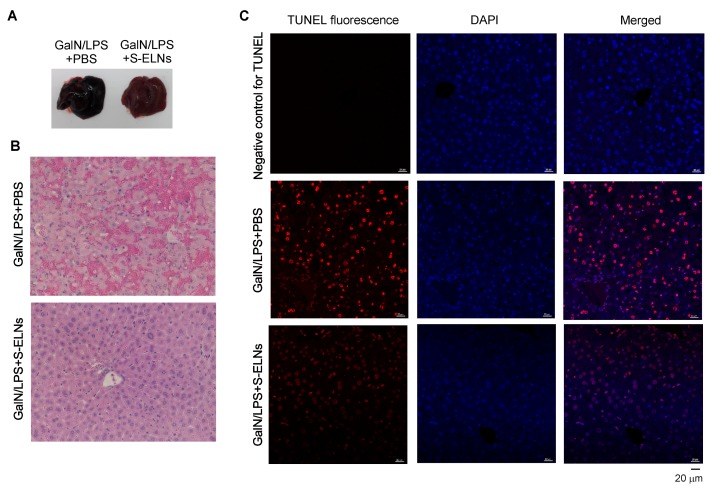
Figure 4.
Shiitake mushroom-derived exosome-like nanoparticles (S-ELNs) protected animals from D-galactosamine (GalN)/lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-triggered liver damage. C57BL/6J mice were administered with solvent phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or S-ELNs in PBS using intraperitoneal injection. 48 h later, the mice received a GalN/LPS mixture through intraperitoneal injection. The mice were sacrificed after 6 h, and their serum and liver were collected for analysis. (A) Representative pictures of whole livers of mice. (B) Representative images of Haemotoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining of liver tissues. Magnification: 40×. (C) Representative images of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining of liver tissues. Magnification: 40×. In the negative control for TUNEL staining, the sections were incubated with TUNEL mixture lacking the enzyme terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), which adds fluorescence-labeled dUTP at the single-and double-stranded DNA breaks. DAPI: 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole. N = 6−8/group.