Significance
Many insects change their development and/or physiology to overcome adverse times of the year. Although photoperiod and temperature are known to regulate this change, the underlying mechanism largely remains to be elucidated. The crickets Modicogryllus siamensis overwinter as nymphs with a reduced growth rate and increased molts. This study showed that their nymphal development is regulated by photoperiod and temperature by two separate pathways: the JH signaling pathway is involved in photoperiodic regulation of molts, and the insulin/target of rapamycin signaling pathway regulates growth rate in a temperature-dependent manner. Our findings not only deepen our understanding of the molecular mechanisms for seasonal adaptation but also shed light on the insects’ evolutionary strategy to invade temperate zones where photoperiod and temperature change seasonally.
Keywords: nymphal development, photoperiod, temperature, myo, insulin/TOR signaling pathway
Abstract
Insects living in the temperate zone enter a physiological state of arrested or slowed development to overcome an adverse season, such as winter. Developmental arrest, called diapause, occurs at a species-specific developmental stage, and embryonic and pupal diapauses have been extensively studied in mostly holometabolous insects. Some other insects overwinter in the nymphal stage with slow growth for which the mechanism is poorly understood. Here, we show that this nymphal period of slow growth is regulated by temperature and photoperiod through separate pathways in the cricket Modicogryllus siamensis. The former regulates the growth rate, at least in part, through the insulin / target of rapamycin (TOR) signaling pathway. Lower temperature down-regulates the expression of insulin-like peptide (Ms’Ilp) and Target of rapamycin (Ms’Tor) genes to slow down the growth rate without affecting the number of molts. The latter regulates the number of molts independent of temperature. Short days increase the number of molts through activation of the juvenile hormone (JH) pathway and down-regulation of myoglianin (Ms’myo), a member of the TGFβ family, which induces adult metamorphosis. In contrast, long days regulate Ms’myo expression to increase during the fifth to sixth instar to initiate adult metamorphosis. When Ms’myo expression is suppressed, juvenile hormone O-methyl transferase (Ms’jhamt) was up-regulated and increased molts to prolong the nymphal period even under long-day conditions. The present findings suggested that the photoperiod regulated Ms’myo, and the JH signaling pathway and the temperature-controlled insulin/TOR pathway cooperated to regulate nymphal development for overwintering to achieve seasonal adaptation of the life cycle in M. siamensis.
Fitting life cycles to a seasonally changing environment is a prerequisite for insects living in the temperate zone (1, 2). Their common strategy is to enter a state of developmental arrest (diapause) or reduced growth rate, during which insects overcome the adverse period of the year, which is unsuited for growth and reproduction. The most widely used and important cue for entering this state is day length or night length in a 24 h day (photoperiod). The photoperiodic information is perceived by specific photoreceptors and transmitted to a photoperiodic clock, which measures the lengths of the photophase or scotophase to determine the given photoperiod to be a long day (LD) or short day (SD) (3). The LD or SD information is then conveyed to the regulatory system that induces diapause/reduced growth rate or nondiapause/faster growth rate responses. There are lines of evidence suggesting that a circadian clock is involved in the photoperiodic clock (4–6). Temperature also plays an important role in regulating development. It often modifies the degree of the photoperiodic response (7, 8) and sometimes alters the critical day length for switching between LD and SD responses (2). In addition, temperature changes the developmental time course, by slowing down or accelerating the developmental rate and changing the number of instars (9, 10).
The mechanism of nymphal development underlying the seasonal adaptation includes regulation of cellular and tissue growth and/or molting (11, 12). The cellular and tissue growth rates are mainly controlled by the insulin signaling pathway, in which the insulin-like peptide (ILP) binds to the insulin receptor (InR) to stimulate a series of signal transduction cascades and eventually promotes protein synthesis, cell growth, and cell division (13). The target of rapamycin (TOR) pathway shares a number of key regulators and associates with the insulin signaling pathway, sensing nutritional states and also promoting cellular and tissue growth (14–16). Therefore, these two pathways are normally referred to as the insulin/TOR signaling pathway. However, the growth of insects is restricted by the sclerotized cuticle. To allow growth and development, the old cuticle must be shed and replaced with a new and larger one as the insect grows. This process is called molting and is controlled by hormonal factors. When body size reaches a certain level, the molting process starts, including secretion of a cerebral neuropeptide, prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) (17), which stimulates the prothoracic gland to produce a steroid hormone, ecdysone (18). Ecdysone is then converted to 20 hydroxyecdysone (20E) that promotes molting through the expression of various molting-related genes (19, 20). However, the nature of molting is determined by juvenile hormone (JH) (21, 22). When humoral JH levels are maintained higher, 20E induces nymphal molting. When humoral JH is eliminated or reduced below a certain level, the metamorphosis from nymph to adult is initiated. The action of JH is mediated by a JH-inducible gene, Krüppel homolog 1 (Kr-h1) (23, 24). JH is produced in the corpora allata (CA) from Acetyl–CoA through various enzymatic reactions (25) (SI Appendix, Fig. S1). The final reaction of JH production is the conversion from the inactive JH precursor to active JH, and this reaction is controlled by JH acid O-methyltransferase (JHAMT), a rate-limiting enzyme encoded by the gene jhamt (26). Recently, it was reported that a member of the TGF-β family, myoglianin (myo), down-regulates the expression of jhamt, and, consequently, reduces the level of JH and leads to metamorphosis (27).
Insects enter diapause at a species-specific stage with developmental arrest through modulating a certain step of the above-mentioned developmental process. For example, the tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta enters diapause at the pupal stage by inactivation of cerebral PTTH secretion (28), the silk moth Bombyx mori as an embryo by a diapause hormone (29), and the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster and the mosquito Culex pipiens as an adult by a mechanism involving the insulin signaling pathway (12). However, for those overwintering as nymphs with a reduced developmental rate, the underlying molecular mechanism is still largely unknown. Hence, this study aimed to explore the mechanism controlling the nymphal developmental rate in a bivoltine insect, the cricket Modicogryllus siamensis, which occurs twice a year and overwinters as nymphs and shows clear photoperiodic responses in its nymphal development (30, 31). At 25 °C, most nymphs become adult at ∼60 d after hatching from eggs, undergoing 7 or 8 molts under LD, whereas under SD, the nymphal period elongates with an increased number of molts for overwintering. These nymphal developmental time courses are determined by photoperiod only during the first and second instar nymphs (30). In the present study, we first examined the effects of temperature on nymphal development under LD and SD conditions and then tested the possible involvement of the JH signaling and the insulin/TOR signaling pathways with RNA interference (RNAi)-mediated gene-silencing experiments. Our results suggested that nymphal development was controlled by two distinct mechanisms: one was the photoperiodic control of the number of nymphal molts, including the JH signaling pathway, in which Ms’myo plays a key role, and the other was temperature control of the growth rate through the insulin/TOR signaling pathway.
Results
Photoperiod and Temperature Regulate Nymphal Development.
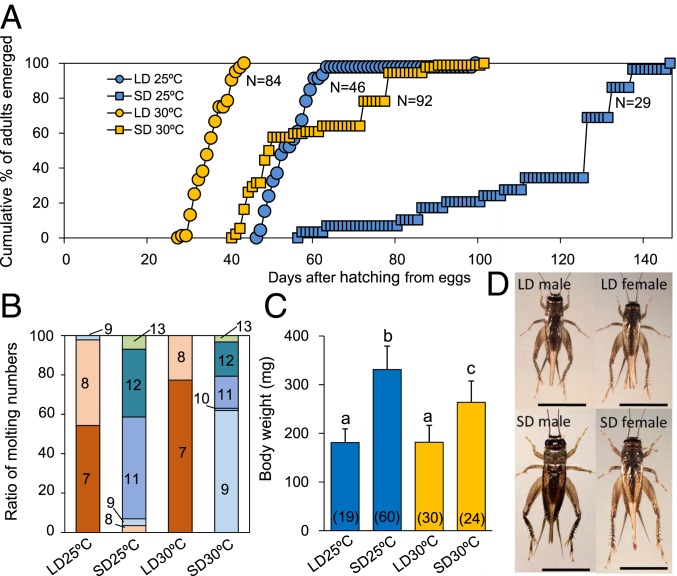
As mentioned above, the nymphal developmental time course is determined by the photoperiod during the first two instar nymphal stages in the cricket M. siamensis (30). We first examined whether temperature (25 °C or 30 °C) affects nymphal development under LD (16L:8D) or SD (12L:12D) conditions. Molting was examined every day, and the results are shown in Fig. 1. Under LD at 25 °C, 98% of the crickets synchronously became adults between 47 and 63 d after hatching from eggs and undergoing 7 or 8 molts, whereas the remaining 2% became adults after 9 molts (Fig. 1 A and B). Under SD at 25 °C, 2% became adults after 8 molts, whereas the remaining 98% became adults after 9 or more molts (Fig. 1B). Adults emerged between 57 and 146 d after hatching with the median of ∼130 d (Fig. 1A), which was significantly later than that for the LD (Kruskal–Wallis test, P < 0.01). At 30 °C, the nymphal growth rate was accelerated both under LD and SD (Fig. 1A). Under LD, adults emerged synchronously between 28 and 43 d after hatching from eggs and experiencing 7 or 8 molts, whereas under SD, adults occurred between 41 and 101 d with a median of 49 d, after 9–13 molts (Fig. 1 A and B). The adult emergence under SD occurred significantly later than under LD at 30 °C (Steel–Dwass test, P < 0.01) but at nearly the same timing as that under LD at 25 °C (Steel–Dwass test, P > 0.7).
Fig. 1.
Effects of photoperiod and temperature on nymphal development in the cricket Modicogryllus siamensis under long-day (LD, 16L:8D) or short-day conditions (SD, 12L:12D) at 25 °C and 30 °C. (A and B) Adult emergence patterns after hatching from eggs (A) and proportions of molt numbers before adult emergence (B). The number of animals used was 84, 46, 92, and 29 for LD 30 °C, LD 25 °C, SD 30 °C, and SD 25 °C, respectively. Numbers in different color fractions in B indicate the number of molts. (C) Adult body weight (mean ± SEM) measured at 1 d after adult emergence. Values with different letters significantly differ from each other (Tukey test, P < 0.05). Numbers in parenthesis indicate the number of animals used. (D) Photographs of LD and SD adult crickets raised at 30 °C. (Scale bar, 1 cm.)
Body size was greater in SD crickets at both 25 °C and 30 °C (Fig. 1D). Average adult body weight was 181.1 ± 27.9 mg and 181.8 ± 34.7 mg for LD at 25 °C and 30 °C, respectively (Fig. 1C). Under SD, size was significantly greater at 25 °C (330.9 ± 48.1 mg) than that at 30 °C (263.7 ± 43.7 mg) (Tukey test, P < 0.05), but both were much greater than those under LD (Tukey test, P < 0.05) (Fig. 1C).
Expression Profiles of Ms’myo and Ms’jhamt during Nymphal Development.
Our results showed that photoperiodic regulation of nymphal development was associated with changes in the number of nymphal molts. Because metamorphosis from nymph to adult is known to be induced by reduced levels of JH that is caused by the inhibition of JHAMT through myoglianin (27), we next investigated the possible involvement of Ms’myo in the photoperiodic regulation of nymphal development. We first examined the Ms’myo messenger RNA (mRNA) expression in the head, including the corpora cardiaca (CC)–CA complex, thorax, abdomen, and legs in the second instar nymphs at ZT6 (ZT = zeitgeber time, ZT0 corresponds to lights on). The expression levels were highest in the head followed by the thorax but were only negligible in the abdomen and legs (Tukey test, P < 0.05, SI Appendix, Fig. S2). No significant sexual differences in expression levels were found.
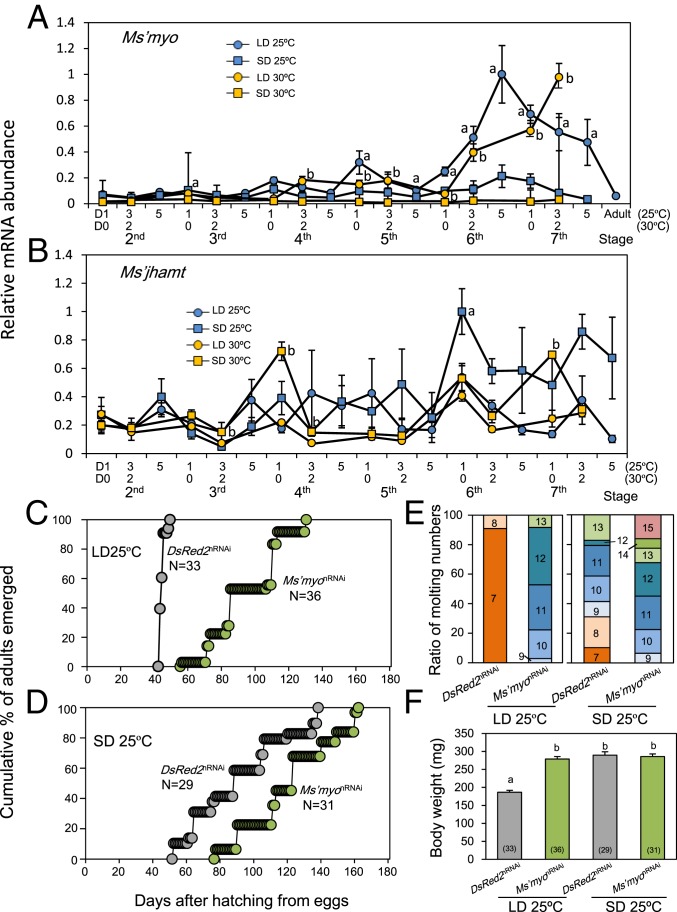
To examine whether expressions of Ms’myo and Ms’jhamt changed with nymphal development, mRNA levels of Ms’myo and Ms’jhamt were measured by quantitative real-time RT-PCR (qPCR) in nymphal heads at ZT6 during the second to seventh instar period under LD and SD at 25 °C and 30 °C. Under LD, Ms’myo expression was maintained at a low level until the fourth instar, exhibited a slight increase during the fourth or fifth instar, and had a steep increase during the sixth instar, peaking at seventh instar (30 °C) or the late sixth instar, to maintain a high level during the seventh instar period (25 °C) (Fig. 2A). At the adult stage, it returned to a basal level (Fig. 2A). Under SD, Ms’myo mRNA levels were maintained at a very low level until the end of the seventh instar, irrespective of temperature (Fig. 2A).
Fig. 2.
Involvement of Ms’myo in photoperiodic regulation of nymphal development in the cricket Modicogryllus siamensis. (A and B) Expression patterns of Ms’myo (A) and Ms’jhamt (B) mRNAs during nymphal development under long-day (LD, 16L:8D, circles) and short-day (SD, 12L:12D, squares) conditions at 25 °C (blue) or 30 °C (orange). Ms’myo mRNA levels were significantly higher under LD than SD for the last three instar nymphs. Ms’jhamt levels tended to be higher under SD throughout the tested period. Values were an average of four samples, including three heads each, and error bars indicate SEM. a and b indicate a significant difference between LD and SD at 25 °C and 30 °C, respectively. (C–F) Effects of Ms’myo nymphal RNAi (Ms’myonRNAi) on adult emergence under LD (C) and SD (D), molt numbers (E), and body weights (F) at 25 °C. Gray and green symbols in C, D, and F indicate DsRed2nRNAi control and Ms’myonRNAi crickets, respectively. N and numbers in parenthesis indicate the number of animals used. Numbers in E indicate the number of molts. Ms’myonRNAi significantly delayed adult emergence (U test, P < 0.001) and increased molt numbers compared with that of DsRed2nRNAi crickets (U test, P < 0.001). Body weights were significantly increased in Ms’myonRNAi-treated crickets under LD (Tukey test, P < 0.05). Values with different letters significantly differ from each other.
The mRNA level of Ms’jhamt significantly fluctuated both under LD and SD (Fig. 2B), but no significant differences were found between the two temperatures. Under SD, it was consistently higher than in LD animals, except for day 5 of the third, day 3 of the fourth, and day 1 of the fifth instar at 25 °C and day 0 of the second instar at 30 °C, although a significant difference was found at day 1 of the sixth instar at 25 °C and day 3 of the third, day 0 and 2 of the fourth, and day 0 of the seventh instar at 30 °C.
Ms’myo Is Involved in Photoperiodic Responses of Nymphal Development.
To investigate whether Ms’myo is involved in the regulation of developmental rate by photoperiod, nymphal development of crickets treated with Ms’myo double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) on day 1 of the fourth instar was observed. The effectiveness of dsMs’myo was confirmed by measuring Ms’myo mRNA levels under LD (30 °C) at ZT6 on day 1 of the sixth instar. The Ms’myo levels were significantly reduced compared to that of control (t test, P < 0.01) (Fig. 3A). At 25 °C the LD control crickets treated with dsDsRed2 became adults between days 43 and 49 after hatching from eggs with a median of 44 d (Fig. 2C), undergoing seven or eight molts similar to that of intact crickets (Fig. 2E). The nymphal RNAi (nRNAi) of Ms’myo (Ms’myonRNAi) not only prolonged the nymphal period but also increased the number of instars (Fig. 2 C and E). In the treated crickets, adults emerged between 56 and 130 d after hatching with a median of 85 d (Fig. 2C), which was significantly later than that of the control crickets (U test, P < 0.01). The number of molts was at least 9 and 13 at the most (Fig. 2E), and the number of molts was significantly greater than that of the DsRed2nRNAi control crickets (U test, P < 0.001). The body weights of the treated crickets significantly increased nearly to that of the SD control animals (Fig. 2F) (Tukey test, P < 0.001). The Ms’myonRNAi treatment also exhibited significant effects under SD. It prolonged the nymphal period and increased the number of molts (Fig. 2 D and E) (U test, P < 0.001). Control crickets treated with DsRed2nRNAi emerged between 52 and 138 d, whereas Ms’myonRNAi-treated crickets became adults between 77 and 162 d (Fig. 2D). The number of molts significantly increased from 7–13 to 9–15 (Fig. 2E). Body weight was not affected (Fig. 2F) (Tukey test, P = 1.0). At 30 °C, quite similar effects of Ms’myonRNAi were obtained (SI Appendix, Fig. S3). Both under LD and SD, Ms’myonRNAi animals showed significant elongation of the nymphal period with an increased number of molts compared with those of the DsRed2nRNAi controls. A significant increase in adult body weight was also observed in Ms’myonRNAi crickets under LD (SI Appendix, Fig. S3B).
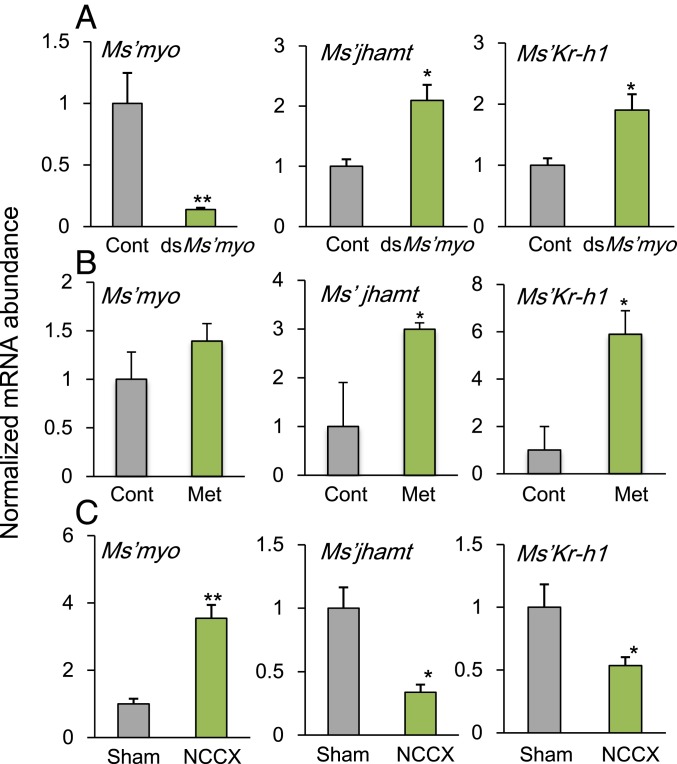
Fig. 3.
Effects of dsMs’myo (A), methoprene treatments (B), or NCC I+II severance (C) on the relative abundance of Ms’myo, Ms’jhamt, and Ms’Kr-h1 mRNAs in the head of Modicogryllus siamensis. Values are an average of four samples containing three heads each, shown relative to those of the DsRed2RNAi controls (A and B) or those of sham operated crickets (C). Males and females were pooled. The abundance of Ms’rp49 mRNA was used as an internal reference. Error bars indicate SEM. Asterisks represent significant differences between control and treated crickets: **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, t test. (A) mRNA levels were measured on day 1 in the sixth instar nymphs treated with dsDsRed2 (black) or dsMs’myo (light green) on day 1 in the fourth instar under LD (16L:8D) at 30 °C. The samples were collected at 6 h after light-on (ZT6). Ms’myonRNAi significantly suppressed Ms’myo mRNA levels, whereas Ms’jhamt and Ms’Kr-h1 levels were significantly up-regulated. (B) mRNA levels were measured on day 3 in the sixth instar nymphs, which were treated with methoprene on day 3 of the fifth instar. Methoprene up-regulates Ms’jhamt and Ms’Kr-h1 expression but had no clear effect on Ms’myo levels. (C) mRNA levels were measured 24 h after the NCC I+II severance (NCCX) on day 1 of the seventh instar nymphs. The operation resulted in the up-regulation of Ms’myo and down-regulation of Ms’jhamt and Ms’Kr-h1. For further explanations, see text.
Ms’myo Suppresses Ms’jhamt and Ms’Kr-h1 Expression.
We then examined whether Ms’myonRNAi affected expression levels of Ms’jhamt and Ms’Kr-h1, which leads to nymphal molting. mRNA levels were measured by qPCR in the head, including the CC–CA complex, on day 1 at ZT6 of the sixth instar nymphs treated with dsDsRed2 or dsMs’myo on day 1 of the fourth instar under LD at 30 °C. The mRNA levels of Ms’jhamt and Ms’Kr-h1 were significantly increased compared to those of control crickets (t test, P < 0.05; Fig. 3A), suggesting that Ms’myo suppresses Ms’jhamt and Ms’Kr-h1.
JH Does Not Affect Ms’myo Expression.
To determine whether JH affected Ms’myo expression, 1 μL of 150 mM methoprene, a JH analog, was topically applied on the dorsal surface on day 3 of fifth instar nymphs. When measured on day 3 of the sixth instar, no significant changes were observed in Ms’myo expression levels, whereas a significant increment was observed in Ms’jhamt and Ms’Kr-h1 mRNA levels (Fig. 3B). Thus, JH did not seem to affect Ms’myo expression levels.
Brain Suppresses Ms’myo Expression.
To examine whether Ms’myo mRNA expression levels were controlled by the brain, the nerves corporis cardiaci (NCC) I+II connecting the brain and the CC–CA complex was cut near CC in the seventh (final) instar for LD crickets kept at 30 °C. The mRNA levels of Ms’myo, Ms’jhamt, and Ms’Kr-h1 were measured 24 h after the operation. The Ms’myo mRNA levels were significantly increased compared to those of control crickets (Fig. 3C), whereas the Ms’jhamt and Ms’Kr-h1 mRNA levels were significantly reduced compared to sham operated controls (Fig. 3C), suggesting that the cerebral control was neural and inhibited Ms’myo expression in CA.
Involvement of the Insulin/TOR Signaling Pathway.
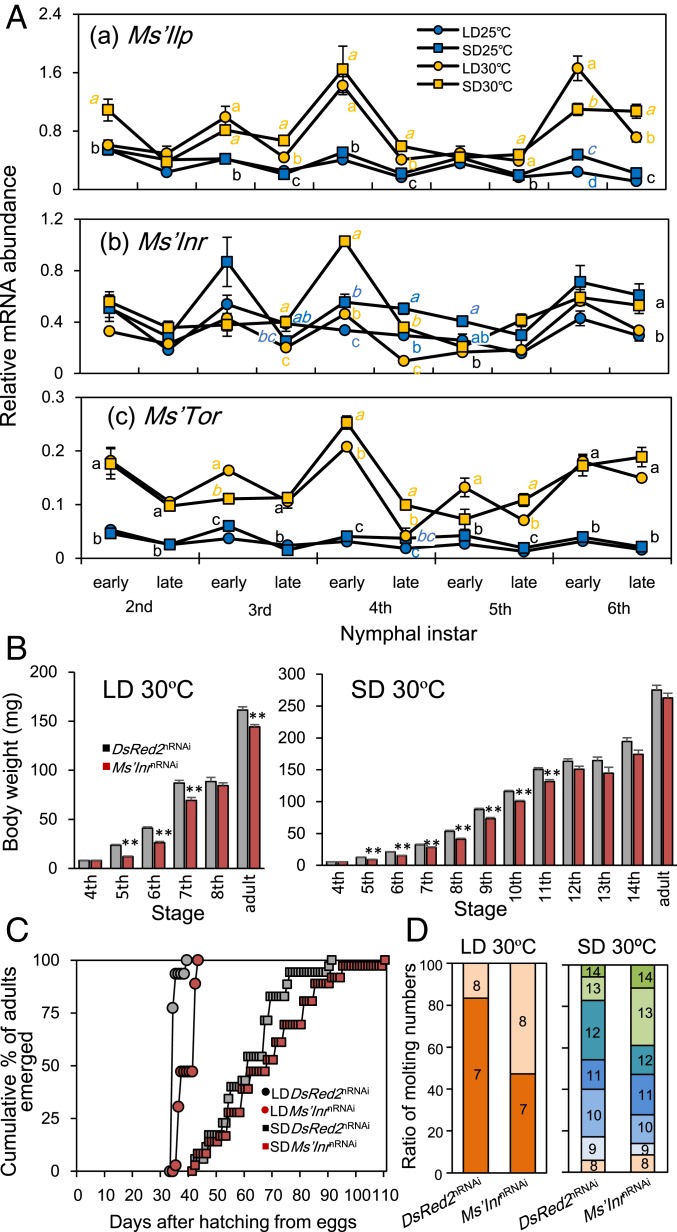
In insects, the growth rate is regulated by the insulin/TOR signaling pathway, which is activated by ILP binding to InR and promotes growth through various molecular components, including TOR (13). Thus, we examined the possible involvement of the pathway in the higher developmental rate at 30 °C by measuring the mRNA levels of Ms’Ilp, a Drosophila Ilp5 ortholog, Ms’Insulin receptor (Ms’Inr), and Ms’Tor in the head of nymphs (Fig. 4A). Measurements were performed on the day of molting (30 °C) or 1 d after molting (25 °C) (early) and the third (30 °C) or fifth day (25 °C) of each instar (late). Transcript levels of these genes tended to fluctuate with molting cycles with a peak just after molting (Fig. 4A). Ms’Ilp and Ms’Tor were indeed significantly up-regulated at 30 °C. The Ms’Inr transcript levels fluctuated around similar levels at 25 °C and 30 °C but were significantly higher at most points under SD. The higher levels of Ms’Ilp and Ms’Tor at 30 °C are likely responsible for the higher nymphal growth rates at 30 °C, which were evident when the nymphal developmental time courses were compared between 25 °C and 30 °C in DsRed2nRNAi-treated control crickets with respect to body weight (SI Appendix, Fig. S5).
Fig. 4.
Involvement of the insulin/TOR signaling pathway in growth rate regulation by temperature in Modicogryllus siamensis. (A) Expression patterns of Ms’Ilp (a), Ms’Inr (b), and Ms’Tor (c) mRNA levels during nymphal development under long-day (LD, 16L:8D, circles) and short-day (SD, 12L:12D, squares) conditions at 25 °C (blue) and 30 °C (orange). Different letters indicate that values are significantly different from each other at the same stage (Tukey test, P < 0.05). Colored letters indicate the category of the value labeled with the same color symbol. Black letters indicate that values closely located are in the same category. (B) Suppression of the growth rate by Ms’InrnRNAi under LD and SD at 30 °C. Under both LD and SD, Ms’InrnRNAi-treated crickets (brown column) showed less of an increase in body weight compared with that of DsRed2nRNAi-treated controls (gray column). **P < 0.01, t test. Error bars in A and B indicate SEM. (C) Adult emergence was delayed by Ms’InrnRNAi treatment. Brown and gray symbols indicate Ms’InrnRNAi-treated and DsRed2nRNAi-treated crickets, respectively. Circles and squares indicate results under LD and SD, respectively. (D) Molt numbers of Ms’InrnRNAi-treated and DsRed2nRNAi-treated crickets. Under LD, Ms’InrnRNAi significantly increased the ratio of crickets with 8 molts (U test, P < 0.01) but never induced a ninth or later molt. No significant changes were induced under SD (U test, P > 0.18).
We then examined the role of the insulin/TOR signaling pathway by RNAi-mediated knockdown of Ms’Inr expression at 30 °C. Treatment with dsMs’Inr at day 0 of the fourth instar significantly reduced the growth rate in the following instars as measured by the body weight under both LD and SD (Fig. 4B). Under SD, the reduction was not significant after the 12th instar, probably because the effect of applied dsMs’Inr was diminished. The nymphal periods were prolonged, but the effect was significant only under LD (U test, P < 0.01) (Fig. 4C). The number of nymphal molts in Ms’InrnRNAi crickets was almost the same as the DsRed2nRNAi-treated controls, with 8 being the greatest under LD and 8–14 under SD (Fig. 4D). The ratio of adults with 8 molts was significantly increased in Ms’InrnRNAi-treated crickets (U test, P < 0.005). At 25 °C, Ms’InrnRNAi treatment yielded similar results but was less effective than at 30 °C (SI Appendix, Fig. S4). The growth rate was slowed down in a few instars following the treatment, whereas significant changes were observed in neither nymphal periods nor molting numbers (SI Appendix, Figs. S4 and S5). Thus, the insulin/TOR signaling pathway likely participated in the regulation of the growth rate in a temperature-dependent manner, but does not determine the number of molts. A comparison of adult body weight between 25 °C and 30 °C shows that the body weight tended to be greater at 25 °C than at 30 °C: the body weights of DsRed2nRNAi crickets were 289.5 ± 9.4 mg (average ± SEM), 275.4 ± 7.2 mg, 186.4 ± 5.4 mg, and 161.5 ± 3.2 mg, and those of Ms’InrnRNAi crickets were 279.9 ± 7.7 mg, 262.8 ± 7.4 mg, 173.2 ± 3.0 mg, and 143.3 ± 2.3 mg, for 25 °C under SD, 30 °C under SD, 25 °C under LD, and 30 °C under LD, respectively (SI Appendix, Fig. S6). However, the difference was only significant under LD conditions. The higher body weight at 25 °C might be attributable to the longer developmental period, but this hypothesis needs to be tested in future studies. The Ms’InrnRNAi treatment tended to reduce the adult body weight, although the effects were statistically significant only under LD conditions (SI Appendix, Fig. S6). The low effectiveness of Ms’InrnRNAi under SD is most likely attributable to a low level of Ms’Ilp expression (Fig. 4A).
Discussion
The Nymphal Development in M. siamensis.
The present study revealed that nymphal development was regulated by two distinct factors, photoperiod and temperature, in the cricket M. siamensis. Photoperiod determined the number of instars and the ultimate body weight, whereas temperature regulated growth rate. The developmental rate at 30 °C was much faster than that at 25 °C under both LD and SD, whereas no significant difference was found in the number of instars between at 25 °C and 30 °C in respective photoperiodic conditions (Fig. 1). The increase in growth rate at the higher temperature was most likely mediated, at least in part, by the insulin/TOR signaling pathway, because Ms’Ilp and Ms’Tor were higher at 30 °C, and the knockdown of Ms’Inr reduced the growth rate (Fig. 4 and SI Appendix, Figs. S4 and S5). In many insects, temperature affects not only the developmental rate but also the number of instars, including orthopteran species, such as the cricket Pteronemobius nitidus (9) and the grasshopper Chorthippus brunneus (32). These two orthopterans are univoltine with adults occurring only once a year, using temperature to change instar numbers to fit their life cycle to the year. However, M. siamensis is a bivoltine species with adults occurring twice a year and may adopt a different strategy to fit into seasonal changes using temperature to control growth rate only. This hypothesis should be tested by examining other bivoltine species.
The photoperiod dependency of the instar number has been reported for several species (33–35). The metamorphosis from nymph to adult is thought to begin when body size reaches a fixed threshold (17). Thus, it is hypothesized that when growth occurs at a slow rate during an adverse environmental time, nymphs need extra molting to reach the threshold body size (36). In this study, although the cricket M. siamensis grew quickly at 30 °C both under LD and SD, the SD nymphs molted as many times as at 25 °C. This fact is apparently inconsistent with the above-mentioned compensation scenario. The body sizes under SD for M. siamensis at 25 °C and 30 °C were nearly the same, suggesting that there is a fixed body size for SD crickets, which is almost independent of growth rate and temperature. The larger SD crickets were more fecund than the smaller LD crickets. This may compensate for the decrease in the population size during the longer developmental time to become an adult when confronted with an adverse time of cold and fasting during winter.
In Yamaguchi City (34°N), Japan, it takes ∼240 d from autumn to early summer, whereas SD nymphs under experimental conditions become adults in ∼120 d at 25 °C. Under natural field conditions, the average temperature during this period is ∼12 °C. This low temperature most likely slows down the growth rate and lengthens the nymphal period. As a result, crickets can successfully overwinter and adapt to the local seasonal environmental changes.
Role of Ms’myo in Photoperiodic Regulation of Nymphal Development.
The present study revealed that Ms’myo is a key component of the photoperiodic system that regulates the time course of nymphal development. myo is predominantly expressed in the CA in Gryllus bimaculatus (27). The same may be true in M. siamensis because the transcripts of Ms’myo were most abundantly detected in the head, including the CC–CA complex by qPCR (SI Appendix, Fig. S2).
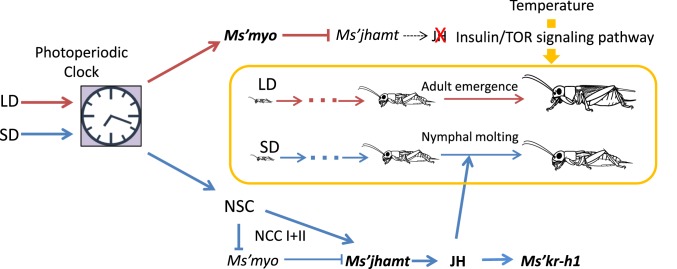
A large difference in Ms’myo and Ms’jhamt mRNA levels between LD and SD nymphs was found during the fifth to seventh instar stage (Fig. 2 A and B). This finding suggests that the timing of the increase in Ms’myo expression is important for the determination of metamorphosis. This hypothesis was confirmed by Ms’myonRNAi treatments at the fourth instar that resulted in a dramatic delay in adult emergence (Fig. 2 C and D and SI Appendix, Fig. S3). This fact suggests that Ms’myo is involved in the regulatory system downstream of the photoperiodic time-measurement system because the sensitive stage for photoperiod is limited to within the first and second instar stages (30). When mRNA levels of Ms’myo were reduced by nRNAi, the mRNA levels of Ms’jhamt and Ms’Kr-h1 were up-regulated (Fig. 3A), leading to extra nymphal molts and, eventually, a delay in adult emergence even under LD conditions (Fig. 2 C–E and SI Appendix, Fig. S3). These results suggest that Ms’myo and the JH signaling pathway are involved in the photoperiodic determination of instar numbers in M. siamensis (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
A scheme of the photoperiodic control of nymphal development in the cricket Modicogryllus siamensis. NSC; neurosecretory cells. Dark red and blue lines indicate long-day (LD) and short-day (SD) pathways, respectively. LDs stimulate Ms’myo expression during the fifth to seventh instar stage, which suppresses Ms’jhamt expression and reduces JH synthesis, leading to adult emergence. SDs suppress Ms’myo expression and stimulate Ms’jhamt expression during the same stage, which increases JH production, resulting in nymphal molts, hence leading to slow nymphal development. Temperature regulates the growth rate through the insulin/TOR signaling pathway to accelerate or slow down at higher or lower temperatures, respectively. Slow development for overwintering is most likely maintained by short photoperiods and cold temperatures during autumn to winter. For further explanations, see text.
Photoperiodic Regulation of Ms’myo Expression.
Our results showed that the Ms’myo mRNA levels were increased when the NCC I+II was cut in the last instar nymphs, whereas at this time Ms’jhamt was down-regulated (Fig. 3C). Considering that the application of the JH analog had no significant effect on the Ms’myo mRNA levels (Fig. 3B), it is suggested that Ms’myo expression is suppressed by the brain through the NCC I+II and that the increased Ms’myo expression suppresses Ms’jhamt expression. Thus, it is most likely that in SD animals, a photoperiodic control from the brain stimulates Ms’jhamt expression and suppresses Ms’myo expression, whereas under LD, Ms’myo expression is up-regulated by a photoperiodically programmed mechanism, and Ms’jhamt expression is suppressed during the fifth and later nymphal stages (Fig. 5). Although this hypothesis awaits to be tested experimentally in future studies, it is consistent with the earlier findings that the cricket CA has an innervation from the pars lateralis neurosecretory cells (37), which may include allatotropins that stimulate JH synthesis (38).
An important remaining issue is how photoperiods regulate Ms’jhamt and Ms’myo expression. Because the photoperiodic-sensitive stage is limited during the first and second instar periods in M. siamensis (30), the time course of nymphal development should be committed by the end of the second instar. One possible mechanism is through epigenetic control, such as chromatin or DNA modification. In fact, trimethylation of histone H3K27 is involved in photoperiodic modulation of the circadian rhythms in the cricket, Gryllus bimaculatus (39). In G. bimaculatus, photoperiods modulate the circadian waveform of the locomotor rhythm and the optic lobe electrical activity in an experience-dependent manner, and the modulated waveform continues for a long period (40, 41). Because the circadian clock most likely plays an important role in photoperiodic-time measurement (5), the modification of the clock caused by trimethylation of H3K27 may be involved in the photoperiodic control of Ms’jhamt and Ms’myo expression in M. siamensis. This possibility should be tested in future studies.
Materials and Methods
Experimental Animals.
The crickets, Modicogryllus siamensis, were obtained from a laboratory colony, which was established from those collected in Yamaguchi City (34°N), Japan, in July 1999. They were fed laboratory chow and water and maintained under standard environmental conditions with a 16 h light:8 h dark cycle (16L:8D 16:8; L, 06:00–20:00, Japan Standard Time, JST) and a constant temperature of 25 ± 0.5 °C. The light intensity was ∼700 lx. Eggs laid in moist cotton were transferred to a plastic box (6.5 × 6.5 × 10 cm) and maintained in an incubator (MFD-153; Sanyo Medical Co.), in which experimental conditions were set until hatching.
cDNA Cloning.
We first searched for Ms’myo, Ms’jhamt, Ms’Kr-h1, Ms’Ilp, Ms’Inr, and Ms’Tor genes in the RNA-seq data for day 1 of the sixth instar and day 3 of the second instar nymphs. The sequence data used for searching the genes were those reported for Gryllus bimaculatus (27, 42). cDNA fragments of these genes were obtained by an RT-PCR strategy as described in SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods.
Measurement of mRNA Levels.
qPCR was used to measure mRNA levels of Ms’myo (GenBank accession no. LC457977), Ms’jhamt (LC458777), Ms’Kr-h1 (LC460294), Ms’Iip (LC460295), Ms’Inr (LC458778), and Ms’Tor (LC460296) genes. The qPCR primers used are listed in SI Appendix, Table S1. RNA extraction, cDNA synthesis, and qPCR conditions are described in SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods.
RNA Interference.
The synthesis of double-stranded RNA was performed as described in SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods. For nRNAi, on day 1 of the fourth instar, nymphs were anesthetized by CO2 and injected with dsRNA solution (69 nL) at the base of a hind leg with an injector. They were kept under respective photoperiodic conditions before and after dsRNA injection.
Methoprene Treatment.
Methoprene, a JH analog, was dissolved in acetone at a concentration of 150 mM. A 1-μL sample of methoprene solution was applied topically on day 3 of the fifth instar nymphs under LD conditions at 30 °C with a Hamilton syringe. Nymphs were immobilized with CO2 anesthesia, and the application was made on the dorsal surface of the thorax. The crickets were used for measurement of Ms’myo, Ms’jhamt, and Ms’Kr-h1 mRNA levels at ZT6 on day 3 of the sixth instar.
Surgical Operation.
For surgical sectioning of NCC I+II, crickets were placed on a specially designed plastic platform with the head fixed with a colophonium–beeswax mixture. A square part of the head cuticle just above the brain was cut using a razor knife and removed to expose the NCC I+II, which was then cut with a small pair of scissors. The cuticle was replaced, and the wounds were sealed with a small amount of melted wax.
Analysis of Nymphal Development.
To analyze nymphal development, newly hatched nymphs were transferred to a rearing box (6.5 × 6.5 × 10 cm), supplied with food and water ad libitum. They were kept in an incubator (MFD-153, Sanyo Medical Co.) under either long-day (16L:8D) or short-day (12L:12D) conditions at a constant temperature of 25 ± 0.5 °C or 30 ± 0.5 °C. To record the molt number, nymphs were observed every day, and newly molted nymphs and adults were transferred to different boxes.
Statistics.
The Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare the adult emergence patterns and the number of molts between the two groups. When multiple comparisons of adult emergence patterns were necessary the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by a post hoc Steel–Dwass test was used. To compare the means of two groups, a t test was used. When the means of multiple groups were compared, an ANOVA followed by the Tukey test was used.
Availability of Data and Materials.
All sequences of the genes used in this study can be accessed in DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank with accession numbers indicated in the text. All relevant material is contained within the article or SI Appendix.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by the grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (23370033) (to K.T.).
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
Data deposition: The complementary DNA sequences of Ms’myo, Ms’jhamt, Ms’Kr-h1, Ms’Ilp, Ms’Inr, and Ms’Tor have been deposited in DNA Data Bank of Japan (DDBJ), http://getentry.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/top-j.html. Their accession numbers are LC457977, LC458777, LC460294, LC460295, LC458778, and LC460296, respectively.
This article contains supporting information online at https://www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1922747117/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Saunders D. S., Steel C. G. H., Vafopoulou X., Lewis R. D., Insect Clocks (Elsevier, Amsterdam, ed. 3, 2002), p. 560. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Beck S. D., Insect Photoperiodism (Academic Press, New York, ed. 2, 1980), p. 387. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Saunders D. S., Insect photoperiodism: Seeing the light. Physiol. Entomol. 37, 207–218 (2012). [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stehlík J., Závodská R., Shimada K., Sauman I., Kostál V., Photoperiodic induction of diapause requires regulated transcription of timeless in the larval brain of Chymomyza costata. J. Biol. Rhythms 23, 129–139 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sakamoto T., Uryu O., Tomioka K., The clock gene period plays an essential role in photoperiodic control of nymphal development in the cricket Modicogryllus siamensis. J. Biol. Rhythms 24, 379–390 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ikeno T., Numata H., Goto S. G., Circadian clock genes period and cycle regulate photoperiodic diapause in the bean bug Riptortus pedestris males. J. Insect Physiol. 57, 935–938 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kogure M., The influence of light and temperature on certain characters of the silk-worm, Bombyx mori. J. Dept. Agr. Kyushu Univ. 4, 1–93 (1933). [Google Scholar]
- 8.Saunders D. S., The temperature-compensated photoperiodic clock ‘programming’ development and pupal diapause in the flesh-fly, Sarcophaga argyrostoma. J. Insect Physiol. 17, 801–812 (1971). [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tanaka S., Multiple photoperiodic control of the seasonal life cycle in Pteronemobius nitidus Bolivar (Orthoptera: Gryllidae). Kontyu 47, 465–475 (1979). [Google Scholar]
- 10.Behrens W., Hoffmann K.-H., Kempa S., Gäßler S., Merkel-Wallner G., Effects of diurnal thermoperiods and quickly oscillating temperatures on the development and reproduction of crickets, Gryllus bimaculatus. Oecologia 59, 279–287 (1983). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lin X., Smagghe G., Roles of the insulin signaling pathway in insect development and organ growth. Peptides 122, S0196-9781(18)30032-9 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sim C., Denlinger D. L., Insulin signaling and the regulation of insect diapause. Front. Physiol. 4, 189 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen C., Jack J., Garofalo R. S., The Drosophila insulin receptor is required for normal growth. Endocrinology 137, 846–856 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Antonova Y., Arik A. J., Moore W., Riehle M. A., Brown M. R., “2–Insulin-like peptides: Structure, signaling, and function” in Insect Endocrinology, Gilbert L. I., Ed. (Academic Press, San Diego, 2012), pp. 63–92. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Britton J. S., Lockwood W. K., Li L., Cohen S. M., Edgar B. A., Drosophila’s insulin/PI3-kinase pathway coordinates cellular metabolism with nutritional conditions. Dev. Cell 2, 239–249 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Oldham S., Hafen E., Insulin/IGF and target of rapamycin signaling: A TOR de force in growth control. Trends Cell Biol. 13, 79–85 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nijhout H. F., A threshold size for metamorphosis in the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta (L.). Biol. Bull. 149, 214–225 (1975). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bollenbacher W. E., Granger N. A., Katahira E. J., O’Brien M. A., Developmental endocrinology of larval moulting in the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. J. Exp. Biol. 128, 175–192 (1987). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Granger N. A., Bollenbacher W. E., “Hormonal control of insect metamorphosis” in Metamorphosis, Gilbert L. I., Freiden E., Eds. (Plenum Press, New York, ed. 2, 1981), pp. 105–137. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Davis M. B., Li T., Genomic analysis of the ecdysone steroid signal at metamorphosis onset using ecdysoneless and EcRnullDrosophila melanogaster mutants. Genes Genomics 35, 21–46 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gilbert L. I., Granger N. A., Roe R. M., The juvenile hormones: Historical facts and speculations on future research directions. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 30, 617–644 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Riddiford L. M., Hiruma K., Zhou X., Nelson C. A., Insights into the molecular basis of the hormonal control of molting and metamorphosis from Manduca sexta and Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 33, 1327–1338 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Minakuchi C., Zhou X., Riddiford L. M., Krüppel homolog 1 (Kr-h1) mediates juvenile hormone action during metamorphosis of Drosophila melanogaster. Mech. Dev. 125, 91–105 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Minakuchi C., Namiki T., Shinoda T., Krüppel homolog 1, an early juvenile hormone-response gene downstream of methoprene-tolerant, mediates its anti-metamorphic action in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. Dev. Biol. 325, 341–350 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Noriega F. G., Juvenile hormone biosynthesis in insects: What is new, what do we know, and what questions remain? Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 967361 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shinoda T., Itoyama K., Juvenile hormone acid methyltransferase: A key regulatory enzyme for insect metamorphosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 11986–11991 (2003). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ishimaru Y., et al. , TGF-β signaling in insects regulates metamorphosis via juvenile hormone biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, 5634–5639 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tomioka K., Agui N., Bollenbacher W. E., Electrical properties of the cerebral prothoracicotropic hormone cells in diapausing and non-diapausing pupae of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Zool. Sci. 12, 165–173 (1995). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yamashita O., Diapause hormone of the silkworm, Bombyx mori: Structure, gene expression and function. J. Insect Physiol. 42, 669–679 (1996). [Google Scholar]
- 30.Taniguchi N., Tomioka K., Duration of development and number of nymphal instars are differentially regulated by photoperiod in the cricket Modicogryllus siamensis (Orthoptera: Gryllidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 100, 275–281 (2003). [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ueda H., et al. , Cryptochrome genes mediate photoperiodic responses in the cricket Modicogryllus siamensis. Physiol. Entomol. 43, 285–294 (2018). [Google Scholar]
- 32.Willott S. J., Hassall M., Life-history responses of British grasshoppers (Orthoptera: Acrididae) to temperature change. Funct. Ecol. 12, 232–241 (1998). [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chippendale G. M., Yin C.-M., Endocrine activity retained in diapause insect larvae. Nature 246, 511–513 (1973). [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rock G. C., Shaffer P. L., Tufted apple budmoth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae): Effects of constant day-lengths and temperatures on larval diapause development. Environ. Entomol. 12, 71–75 (1983). [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ballmer G. R., Pratt G. F., Instar number and larval development in Lycaena phlaeas hypophlaeas (Boisduval) (Lycaenidae). J. Lepid. Soc. 43, 59–65 (1989). [Google Scholar]
- 36.Esperk T., Tammaru T., Nylin S., Intraspecific variability in number of larval instars in insects. J. Econ. Entomol. 100, 627–645 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Virant-Doberlet M., Horseman G., Loher W., Huber F., Neurons projecting from the brain to the corpora allata in orthopteroid insects: Anatomy and physiology. Cell Tissue Res. 277, 39–50 (1994). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kataoka H., et al. , Identification of an allatotropin from adult manduca sexta. Science 243, 1481–1483 (1989). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hamada Y., Tokuoka A., Bando T., Ohuchi H., Tomioka K., Enhancer of zeste plays an important role in photoperiodic modulation of locomotor rhythm in the cricket, Gryllus bimaculatus. Zoological Lett. 2, 5 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Koga M., Ushirogawa H., Tomioka K., Photoperiodic modulation of circadian rhythms in the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. J. Insect Physiol. 51, 681–690 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tomioka K., Chiba Y., Light cycle during post-embryonic development affects adult circadian parameters of the cricket (Gryllus bimaculatus) optic lobe pacemaker. J. Insect Physiol. 35, 273–276 (1989). [Google Scholar]
- 42.Dabour N., et al. , Cricket body size is altered by systemic RNAi against insulin signaling components and epidermal growth factor receptor. Dev. Growth Differ. 53, 857–869 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All sequences of the genes used in this study can be accessed in DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank with accession numbers indicated in the text. All relevant material is contained within the article or SI Appendix.