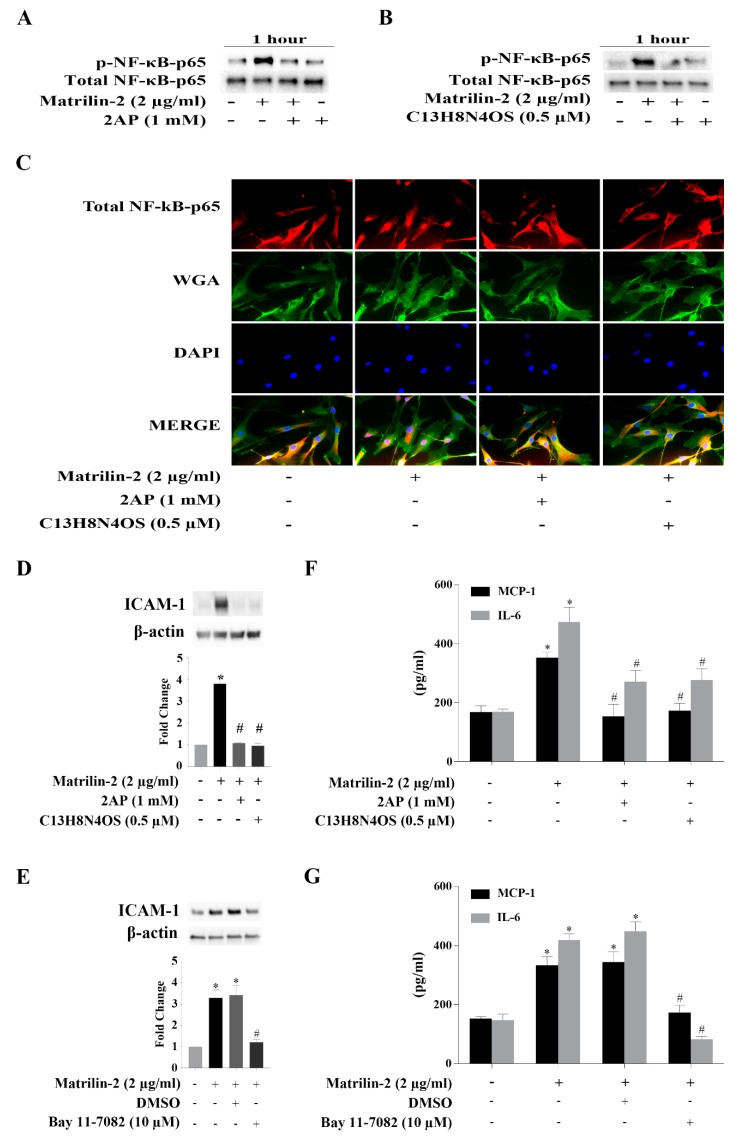
Figure 3.
Both PKR and NF-κB are critical for AVIC inflammatory responses induced by matrilin-2, and PKR is responsible for NF-κB activation. Human AVICs were treated with PKR inhibitors (C13H8N4OS and 2-AP) or NF-κB inhibitor (Bay 11-7082) for 1 h or left untreated, followed by stimulation with recombinant matrilin-2 for 1 h or 48 h. (A,B) Inhibition of PKR suppressed NF-κB phosphorylation. (C) Nuclear translocation of NF-κB was inhibited by PKR inhibitors. Representative images of immunofluorescence staining show NF-κB (red) in human AVICs. Alexa 488–tagged wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) was applied to outline plasma membrane (green). DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) was applied for nuclei counterstaining (blue). Original magnification, ×40 objective. (D,E) Inhibition of PKR or NF-κB markedly reduced ICAM-1 production following matrilin-2 stimulation. (F,G) PKR and NF-κB inhibitors markedly reduced MCP-1 and IL-6 release following stimulation with matrilin-2. Values are means ± SE. n = 5 experiments using distinct cell isolates; * P < 0.05 vs. control; # P < 0.05 vs. matrilin-2 alone.