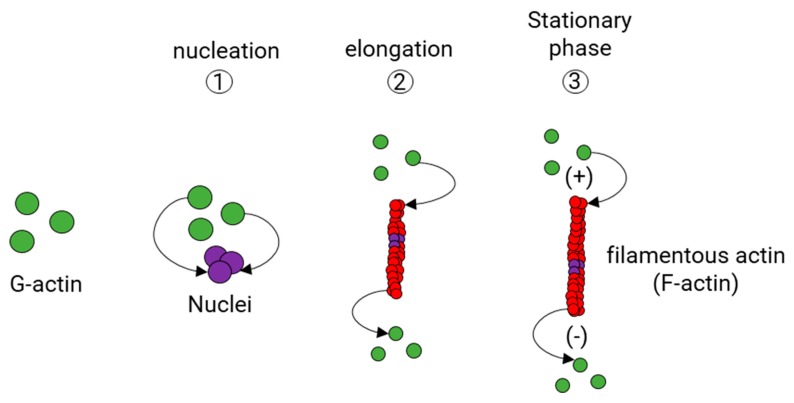
Figure 4.
Polymerization of actin filaments. First, actin monomers linked to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) (G-actin, green) form an aggregate (violet) that grows exponentially by the addition of monomers to both ends of the filament (elongation phase). In the end, actin filaments reach a stationary state with G-actin, and actin filaments have a double-helical conformation.