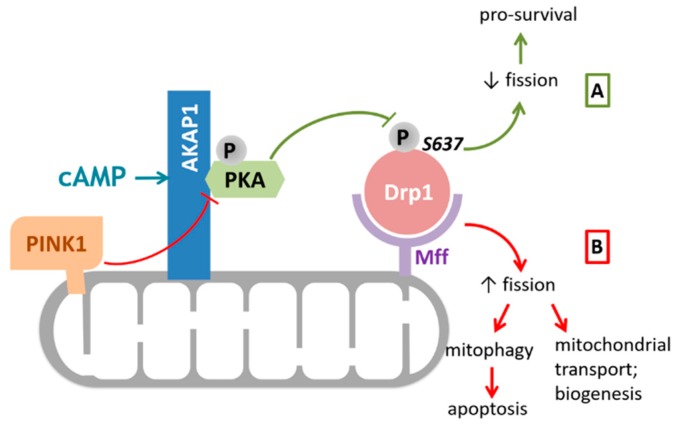
Figure 2.
AKAP1 modulates mitochondrial fission by regulating Drp1 activity via PKA. PKA can be recruited to the OMM by binding to AKAP1. (A) Drp1 is recruited to the mitochondria via Mff where, upon activation by cAMP, PKA deactivates Drp1 through phosphorylation at Ser637. The resulting opposed mitochondrial fission promotes cell survival under pathological conditions such as ischemia and reperfusion injury. (B) PINK1 can dissociate the AKAP1–PKA complex in a kinase activity dependent manner and therefore blocks the anti-fission role of AKAP1–PKA. Increased mitochondrial fission through unopposed Drp1 activation is important for the initiation of mitophagy and apoptosis, as well as for mitochondrial biogenesis and transport. Abbreviations: AKAP1, A kinase anchoring protein 1; Drp1, dynamin related protein 1; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; Mff, mitochondrial fission factor; PKA, protein kinase A; PINK1, PTEN-induced kinase 1.