Figure 2.
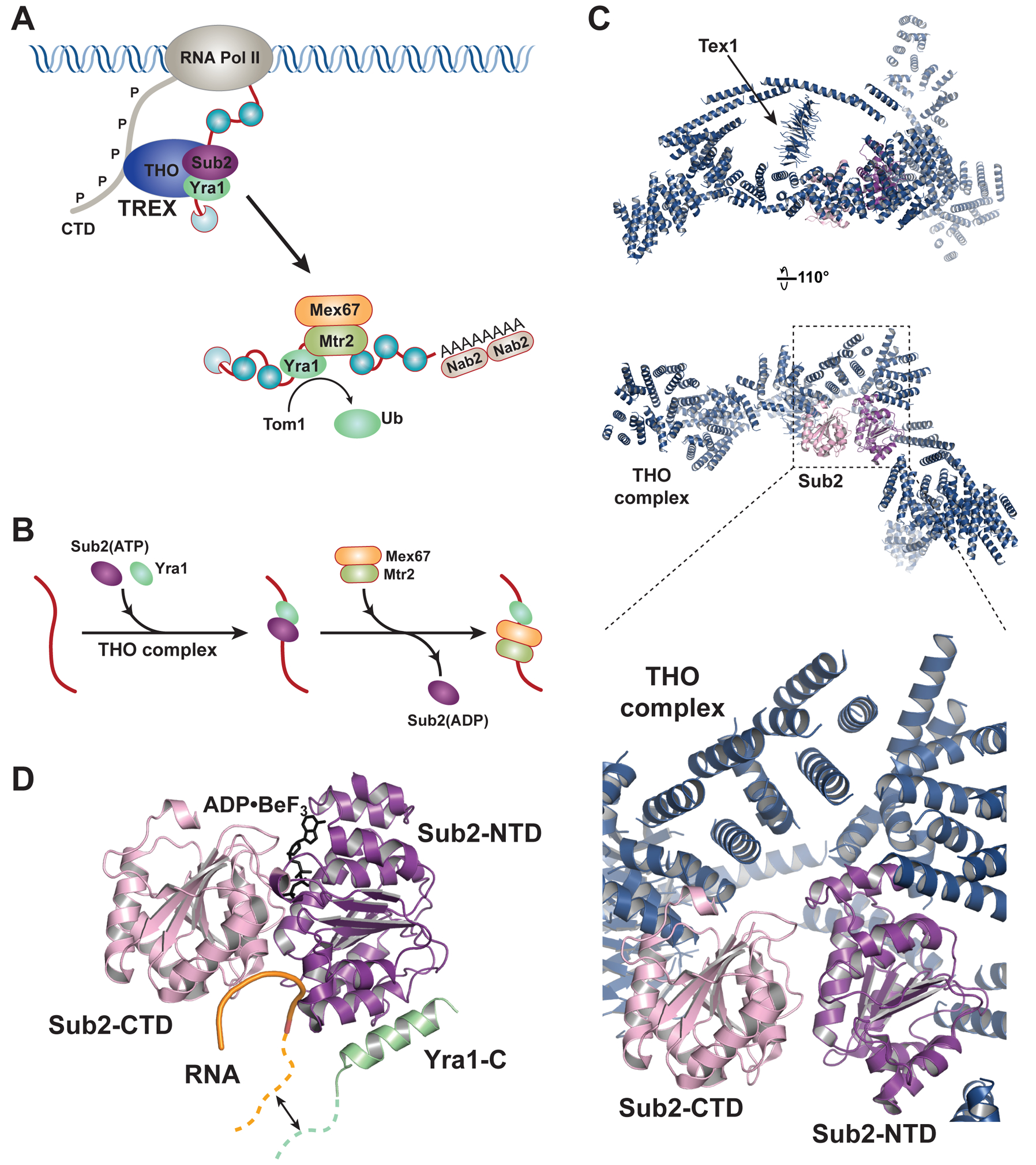
ATPase mediated nuclear mRNP assembly. (A) Yeast TREX complex THO•Sub2•Yra1 travels with RNA Pol II and facilitates loading of the export receptor onto mRNA. (B) A detailed view of the stepwise remodeling reactions driven by the Sub2 ATPase. THO is omitted from the RNA because the dynamics of THO association with mRNA is not known. (C) A 6.0 Å resolution structure of Sub2 bound to a THO core complex which contains S. cerevisiae Tho21–1207, Hpr11–603, Mft11–256, and Thp21–26, as well as S. bayanus Tex11–380 (PDB ID 5SUQ). Top two panels show the overall architecture of the complex. THO is represented by a polyalanine model and only the Tex1 subunit is assigned. The bottom panel highlights the THO-Sub2 binding interface. (D) Structure of Sub2 in association with a truncated Yra1 (Yra1-C, a.a. 208–226) and poly (U) RNA in the presence of ADP•BeF3 (PDB ID 5SUP). The bound RNA is sharply bent, which is characteristic of DEAD-box proteins. The Yra1 region preceding the crystallized fragment is capable of binding RNA (depicted by a green dashed line), and has been proposed to extend the RNA binding site in the Sub2•Yra1 complex.
