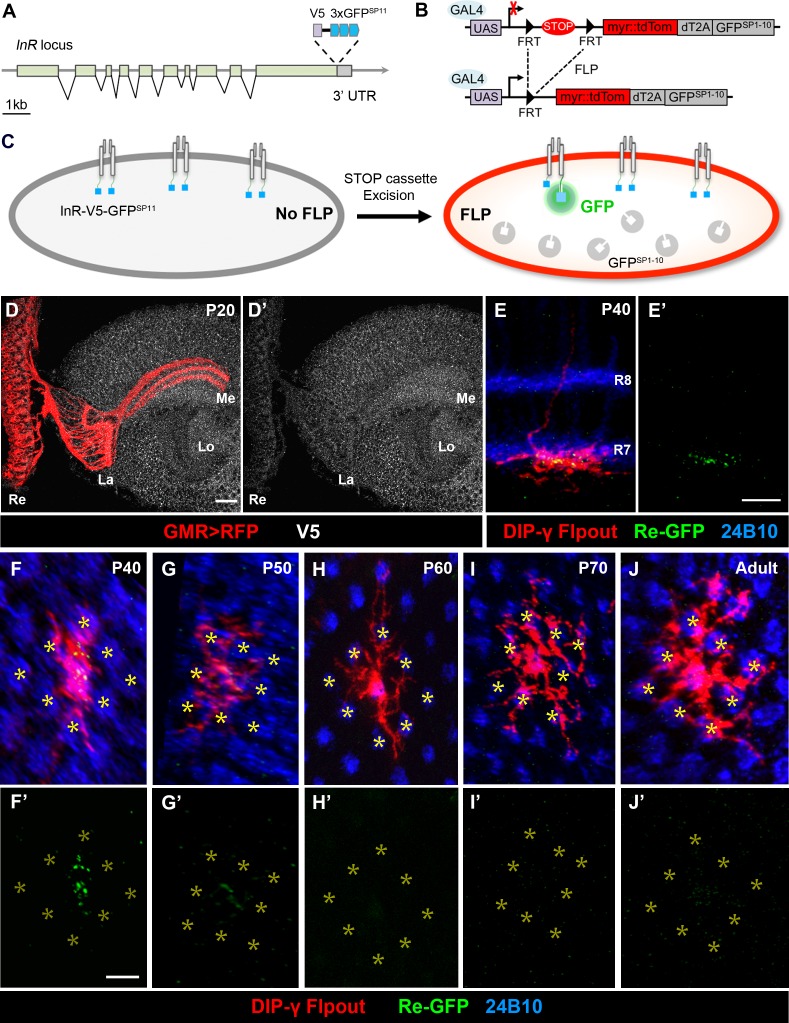
Figure 4. Split-GFP tagging of insulin receptor reveals its endogenous expression pattern in the optic lobe and Dm8 dendrites.
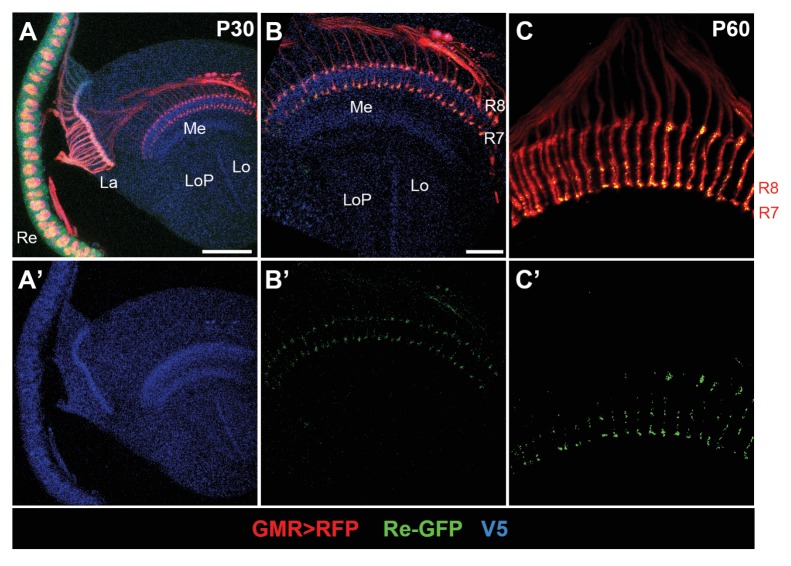
(A–C) Schematics depict the split-GFP tagging strategy to visualize endogenous insulin receptor (InR) expression at single cell resolution. (A) Three copies of split-GFP11 (3x GFPSP11, blue) and a V5 epitope (grey) were inserted into the end of the coding region of the InR locus, immediately before the stop codon. (B) Heat-shock-induced expression of flippase recombinase (FLP) excised the STOP cassette flanked by two FRTs, allowing the targeted neurons to express membrane-tethered tdTomato (myr::tdTom) and split-GFP1-10 (GFPSP1-10) in the cytosol. (C) After excision of the STOP cassette, the targeted neurons express tdTom and GFPSP1-10. The cytosolic GFPSP1-10 binds to GFPSP11 on the intracellular C-terminus of InR, constituting a functional GFP to indicate the location of the endogenous InR. (D–D’) Endogenous InR in the optic lobe was visualized by anti-V5 staining (white) in developing pupae at 20 hr APF (after puparium formation). The photoreceptors were labeled by GMR-Gal4-driven RFP (red). InR was highly expressed in the cell bodies of visual cortex neurons and the neuropils of neurons in the visual system. Re, retina; La, lamina; Me, medulla; Lo, lobula. Scale bar, 10 μm. (E–E’) Endogenous InR is highly expressed in the central area of Dm8 dendrites at 40 hr APF. tdTom (red) labels a single Dm8 flipout clone, which simultaneously expresses GFPsp1-10 after STOP cassette excision. The photoreceptors R7/8 layers and growth cones of R7 were labeled by anti-24B10 (blue). InR, indicated by the prominent GRASP signals (green), was located in the central region of Dm8 dendrites, shown in dorsoventral views. Scale bar, 5 μm. (F–J’) The temporal patterns of endogenous InR expression in Dm8 dendrites surrounded by eight adjacent R7 growth cones (yellow asterisks), shown in proximodistal views. Single Dm8 neurons were labeled by DIP-γ-Gal4 with Flp-FRT flipout system (red). The R7 photoreceptors were labeled with anti-24B10 (blue) and GRASP signals (green). InR is strongly expressed in the central area of Dm8 dendrites at 40 hr APF (F, F'), subsides at 50 hr APF (G, G') and is absence at 60 hr (H, H’), 70 hr (I, I’) APF and adult (J, J').