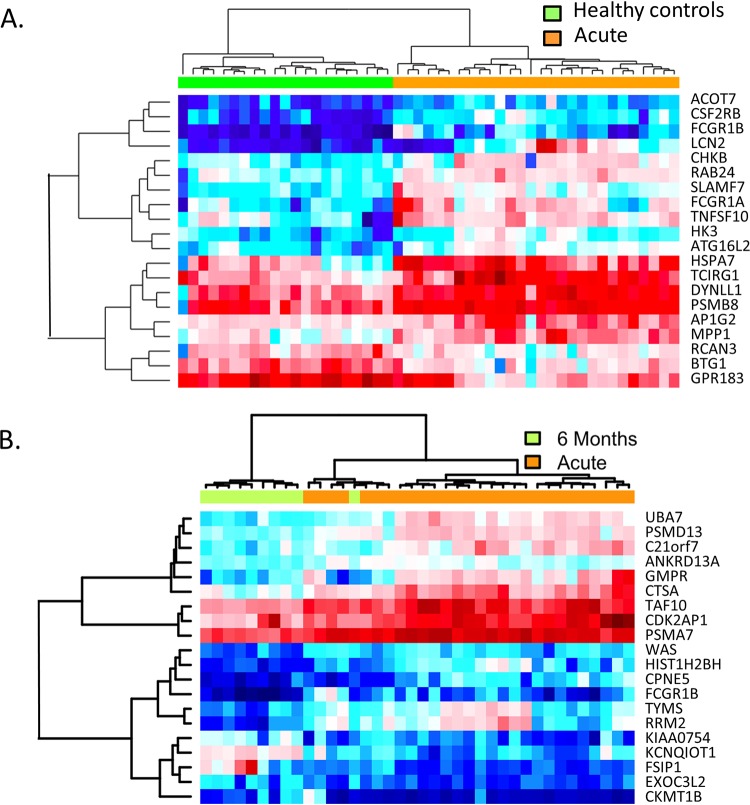
FIG 5.
Twenty-gene classifier sets identified by random forest analysis accurately distinguish between disease states. (A) Hierarchical clustering was performed with samples from acute LD subjects (orange) and healthy donors (green) based on normalized expression intensities of 20 genes having the highest random forest importance levels for these groups (shown on right and in Table 4). (B) A second unique set of 20 genes (shown on the right and in Table 5) having the highest random forest importance levels when comparing acute LD subjects (orange) and 6-month convalescent LD subjects (green) was used for hierarchical clustering of samples from these groups.