Abstract
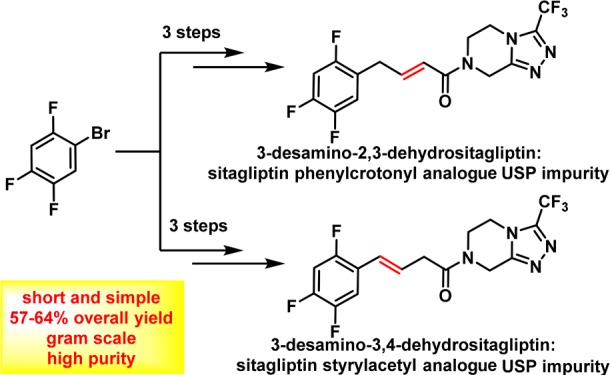
Various organic impurities (starting materials, reagents, intermediates, degradation products, by-products, and side products) could be present in active pharmaceutical ingredients affecting their qualities, safeties, and efficacies. Herein, we present the efficient syntheses of two United States Pharmacopeia impurities of an antidiabetic drug sitagliptin, a potent and orally active dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor: 3-desamino-2,3-dehydrositagliptin and 3-desamino-3,4-dehydrositagliptin. Our three-step synthetic approach is based on the efficient cobalt-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction of 1-bromo-2,4,5-trifluorobenzene and methyl 4-bromocrotonate in the first step, followed by hydrolysis of corresponding ester with 3 M HCl to (E)-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-2-enoic acid in high overall yield, whereas the reaction with 3 M NaOH resulted in the carbon–carbon double bond regio-isomerization and hydrolysis to give the (E)-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-3-enoic acid in 92% yield. Both acid derivatives were converted to title compounds via the amide bond formation with 3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazine. Extensive screening of coupling/activation reagents, bases, and solvents reviled that the amide bond is formed the most efficiently using the (COCl)2/Et3N in THF or alternatively EDC/NMM/(DMAP or HOBt) in DMF obtaining the title compounds in 68–76% yields and providing the overall yields for the three-step process in the range of 57–64% on a gram scale. The presented study also demonstrates the importance of a proper selection of solvent, base, and coupling/activating reagent for amide bond formation using Michael acceptor-type allylbenzene derivatives as coupling partners to minimize the carbon–carbon double bond regio-isomerization.
Introduction
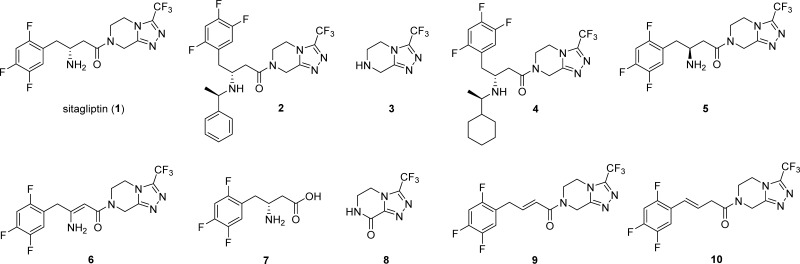
Sitagliptin ((3R)-3-amino-1-(3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl)-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-1-one (1), Figure 1) is a potent and orally active dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-4) inhibitor discovered by Merck.1 After the approval by FDA in 2006, it has been used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2 under the brand name Januvia.2 Sitagliptin is the most important drug in the class of DPP-4 inhibitors or even among antidiabetes drugs overall with a market value of more than US$ 11.4 billion in 2018 (US$ 7.5 billion for monoproduct and US$ 3.9 billion for fixed-dose combination with metformin; IQVIA Analytics Link data).
Figure 1.
Sitagliptin (1) and its main impurities 2–10.
The majority of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are produced by organic syntheses; therefore, various organic impurities such as starting materials, reagents, intermediates, by-products, and side products could be present in the API. Furthermore, some impurities are also formed during the degradation process under storage conditions.3 Impurity profile studies are thus essential to ensure purity, quality, safety, and efficacy during API development.3−5 In the case of sitagliptin, small quantities of degradation impurities or related substances may have an impact on its antidiabetic activity and may be potentially toxic. Therefore, based on the value of sitagliptin in diabetes treatment, it is of huge importance that the quality of the drug is properly controlled using high quality analytical standards of impurities.5m Up to date, several structurally diverse impurities of sitagliptin were reported in the literature and pharmacopeia (Figure 1)4,6−8 such as the 1-phenylethyl derivative of sitagliptin 2 and 3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazine (3) as intermediates in the manufacturing process, a recently reported 1-cyclohexylethyl derivative of sitagliptin 4 and enantiomer impurity 5, which are side reaction products generated during the catalytic hydrogenation in the final step of sitagliptin synthesis.4 Other impurities reported as sitagliptin intermediates and/or degradation products are enamine impurity 6, acid impurity 7, triazole derivative 8, and two alkene derivatives 9 (3-desamino-2,3-dehydrositagliptin; also known as United States Pharmacopeia (USP) sitagliptin phenylcrotonyl analogue impurity) and 10 (3-desamino-3,4-dehydrositagliptin; also known as UPS sitagliptin styrylacetyl analogue impurity). Compounds 9 and 10 are specified impurities with limits of NMT 0.2% in the United States Pharmacopeia monograph for sitagliptin tablets.8 Acid impurity 7 was reported as a product of hydrolysis4 as well as a degradation product,6,7a whereas impurities 8–10 are degradation related impurities (DRIs) that occur as a result of the degradation processes.6,7a Furthermore, alkene impurity 9 is also a process-related impurity formed by acid-catalyzed elimination of amine during the hydrogenolysis reaction.4
Some synthetic routes for impurities 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 9, and 10 were reported in the scientific4,9 and patent10−15 literatures, whereas recently identified cyclohexyl impurity 4 was synthesized by Bandichhor and co-authors.4 Interestingly, synthesis of impurity 9 was reported mainly starting from sitagliptin or late stage intermediates,4,10 while only one four-step synthetic procedure from 2,4,5-trifluorophenylacetic acid was reported in a Chinese patent application.12 Furthermore, two additional steps are needed if 2,4,5-trifluorophenylacetic acid is prepared from readily available 1,2,4,5-tetrafluorobenzene.16 Similarly, the synthesis of alkene impurity 10 was mentioned only in the patent literature;11,14,15 however, the starting materials were only late stage sitagliptin intermediates or sitagliptin. The aim of our study was thus to develop an efficient and straightforward synthetic route to alkene impurity 10 from a simple, readily available, and cheap starting material. Furthermore, we also considered the preparation of alkene impurity 9 by developing a novel, concise, and high-yielding procedure.
Results and Discussion
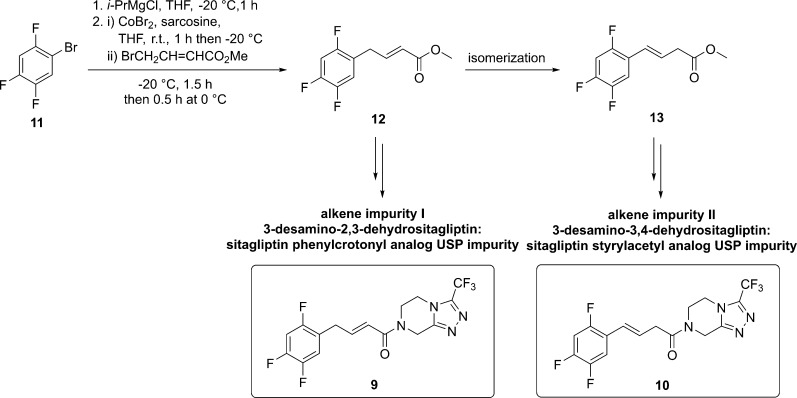
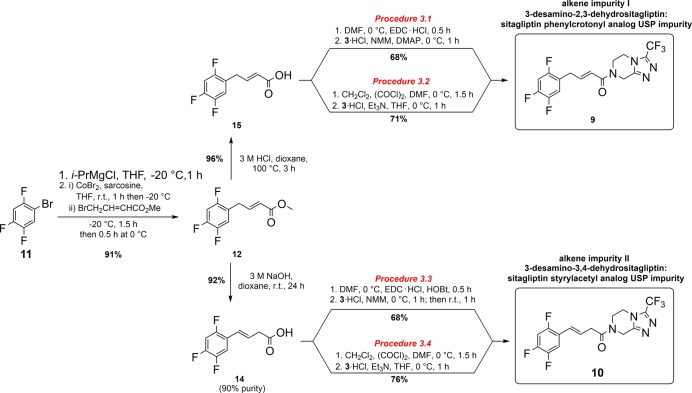
According to the context described above, our goal was to develop the most convenient synthetic routes to alkene impurities 9 and 10 from readily available starting materials such as fluorinated benzene derivatives. In light of our previous studies17,18 where we presented two synthetic approaches using cobalt- or iron-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction, we decided to use the cobalt-catalyzed reaction for the preparation of methyl (E)-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-2-enoate (12) as our key intermediate.18 It was synthesized in a one-step reaction from 1-bromo-2,4,5-trifluorobenzene (11), which was converted to the corresponding arylmagnesium bromide using isopropylmagnesium chloride as a Grignard exchange reagent. After, aryl Grignard reagent reacted further with methyl 4-bromocrotonate under cobalt-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction to obtain methyl (E)-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-2-enoate (12) in a 91% yield on a 17 g scale (Scheme 1).
Scheme 1. Our Synthetic Approach for Preparation of Alkene Impurities I (9) and II (10) via the Intermediate 12.
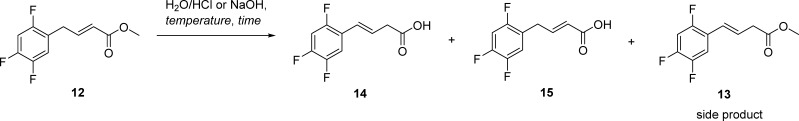
Our first attempt to develop a synthetic route to alkene impurity 10 from methyl (E)-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-2-enoate (12) was to perform regio-isomerization of allylbenzene intermediate 12 to the regio-isomerized product 13 (Scheme 1). Previous studies have indicated that bases, such as NH3,19 LiOtBu,20 LiHMDS,21 K2CO3,22,23 KF,24−26 KOH,25 and KOtBu,25,27 can promote the regio-isomerization of the allylbenzene derivative. Accordingly, the conversion of 12 to 13 in the presence of different bases (NaH, Et3N, NMM, and DBU) was monitored by NMR (see the Supporting Information, Table S1). The results revealed that the best ratio of 12/13 was 0.23:1, which was obtained with NMM (10 equiv.) after a 72-h reaction time (Table S1, entry 9). Additionally, the use of NaOH as a base was also examined; however, regio-isomerization along with the hydrolysis of methyl ester occurred. Nevertheless, acid 14 was obtained in high yield (Table 1), which prompted us to synthesize the alkene impurity 10 by using the coupling reaction between the acid 14 and amine 3. On the other hand, the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis led only to unisomerized acid 15 (Table 1). Therefore, we decided to incorporate hydrolysis of methyl ester 12 to corresponding acids 15 and 14 for the syntheses of both alkene impurities 9 and 10, respectively.
Table 1. Optimization of Reaction Conditions for Hydrolysis of 12 to 14.
| entry | solventa | time (h) | temperature | molar ratio 14/15/13b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.2 M NaOH | 0.5 | r.t. | 1:0.46:0.16 |
| 2 | 0.2 M NaOH | 24 | r.t. | 1:0.30:0.02 |
| 3 | 0.2 M NaOH | 168 | r.t. | 1:0.27:0 |
| 4 | 1 M NaOH | 0.5 | r.t. | 1:0.20:0.12 |
| 5 | 1 M NaOH | 24 | r.t. | 1:0.12:0.04 |
| 6 | 3 M NaOH | 0.5 | r.t. | 1:0.16:0.10 |
| 7 | 3 M NaOH | 24 | r.t. | 1:0.13:0.04 |
| 8 | 3 M NaOH | 72 | r.t. | 1:0.10:0.04 |
| 9 | 3 M NaOH | 168 | r.t. | 1:0.20:0 |
| 10 | 3 M NaOH | 0.5 | 100 °C | 1:0.16:0.06 |
| 11 | 3 M HCl | 0.5 | r.t. | NRc |
| 12 | 3 M HCl | 24 | r.t. | NRc |
| 13 | 3 M HCl | 3 | 100 °C | 0.07:1:0 |
Reaction conditions: 12 (1.0 mmol), 1,4-dioxane (5 mL), solvent (5 mL), time (0.5–168 h), temperature (room temperature (r.t.) or reflux (100 °C)).
Calculated by NMR analysis.
NR: no reaction occurred, only 12 detected.
In a continuation of our study, we optimized the hydrolysis of methyl ester 12 to acids 14 and 15 with regard to the reaction time, temperature, and amount of base used (Table 1). In the case of NaOH, the main challenge was to obtain fully regio-isomerized acid 14 without the presence of unisomerized acid 15 or unhydrolyzed regio-isomerized methyl ester 13. A prolonged reaction time and low molarity of NaOH did not circumvent this problem (Table 1, entries 1–3). Increasing the molarities of used NaOH to 1 and 3 M provided better selectivity and lowered the formation of 15 and 13 (Table 1, entries 4–8). Furthermore, heating and a shorter reaction time also did not improve the ratio (Table 1, entry 10). In the end, the optimal reaction conditions were obtained when methyl ester 12 was hydrolyzed up to 90% with 3 M NaOH in 24 or 72 h (Table 1, entries 7 and 8). On the other hand, almost complete hydrolysis to 15 occurred by refluxing with 3 M HCl (Table 1, entry 13), whereas no product 15 was detected at room temperature (Table 1, entries 11 and 12). To sum up, acid-catalyzed hydrolysis led to almost quantitative conversion of ester 12 to acid 15, whereas in basic condition hydrolysis of an ester 12 concomitant with regio-isomerization reaction to acid 14 occurred. However, regio-isomerization did not occur quantitatively (the most optimal ratio was 1:0.10 as shown in Table 1, entry 8) despite the use of concentrated basic solutions and a prolonged reaction time.
With the appropriate reaction conditions for the preparation of acid derivatives 14 and 15 in hand, the next focus was on the screening of different activating reagents for their use in the construction of title compounds 9 and 10 via coupling with 3. Two main objectives of optimization had to be monitored carefully, reaction yield and selectivity. It was found that compound 9 is prone to regio-isomerization to 10 under the reaction conditions and/or workup. Because both compounds have similar physico-chemical properties, they were difficult to separate completely by column chromatography. Selectivity of reaction conditions was thus highly important. Therefore, we decided to test two different approaches to find the optimal selectivity: a coupling reagent approach and acid activation via an oxalyl chloride (acid chloride) approach. The most common coupling reagents such as DCC (N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide), EDC (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide), TBTU (2-(1H-benzotriazole-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethylaminium tetrafluoroborate), DPPA (diphenylphosphoryl azide), and CDI (1,1′-carbonyldiimidazole) were examined in the presence of NMM (N-methylmorpholine) in this study (Table S2), and the overall yield and selectivity ratio were determined by HPLC analysis. The conducted screening of above mentioned coupling methods and coupling reagents demonstrated that the best results are obtained when 15 was activated with oxalyl chloride in CH2Cl2 in the presence of a catalytic amount of DMF at 0 °C for 1.5 h followed by the addition of 3 × HCl and NMM in MeCN at 0 °C and stirring for 1 h. This procedure afforded an 88% overall yield of 9 + 10 with a 9/10 ratio of 7.8 (Table S2, entry 19). Among all coupling reagents, the best performance in terms of selectivity was noted for EDC, which afforded a 61% overall yield of 9 + 10 with a 9/10 ratio of 16 (Table S2, entry 5).
Our next goal was to select the most appropriate solvent for coupling reaction between 15 and 3 using EDC as a coupling reagent in the presence of NMM. Our previous experiments demonstrated that the longer reaction time did not improve the overall yield of product 9; therefore, only two different reaction times were examined (1 h at 0 °C or the first hour at 0 °C and the second hour at room temperature, see Table S3). When coupling reactions of 15 and 3 with EDC were conducted, DMF was selected as the most optimal solvent with a 77% yield and selectivity ratio of 30.4 (Table S3, entry 10). In the case of the acid activation approach, THF was the most optimal solvent leading to promising an 84% yield and 30.8 selectivity ratio (Table S3, entry 13).
The most important part of the optimization process was the selection of the appropriate base since it could lead to the regio-isomerization of 9 to 10. In fact, NMR study in deuterated DMF (Figure S15) and THF (Figure S16) revealed that compound 9 undergoes regio-isomerization to 10 when treated with an organic base, such as NMM or Et3N. The regio-isomerization was observed at 0 °C as well as at room temperature where the equilibrium ratio of 9/10 is 1:4 or 1:6.14 after 24 h in deuterated DMF or THF, respectively (Figures S15 and S16). Our further NMR study by 2D NMR techniques (see the Supporting Information, Figures S4 and S11) in CDCl3 showed that the identification of 9 versus 10 or vice versa can be proved by heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC).
The addition of a base was necessary to form the free base of 3 that would be capable of coupling reactions with 14 and 15. In addition, the HCl salt of 3 was not soluble in most organic solvents. Different bases such as NMM, Et3N, pyridine, and DMAP were screened, which resulted in large differences in terms of yields and selectivities in both reactions, with EDC and oxalyl chloride (Table 2). Et3N (Table 2, entries 3 and 4) was slightly less appropriate compared to NMM (Table 2, entries 1 and 2) when EDC was used, whereas pyridine and DMAP (Table 2, entries 5 and 6) led to lower yields and worse selectivities. The combinations of bases NMM and DMAP (Table 2, entries 7–10) improved the yield and retained good selectivity only when a 9:1 mixture was used (Table 2, entry 7). On the other hand, NMM and Py combination gave less optimal outcomes (Table 2, entries 11 and 12). According to this study, it could be seen that the selection of a base is the most critical step for the selective preparation of amide 9. The use of NMM with 10% of DMAP as a base and also a catalyst improved the yield to 85%, preserving the good selectivity ratio about 20:1. In the case of activation of carboxylic acid with oxalyl chloride (Table 2, entries 13–15), Et3N was selected as the most optimal base giving a 91% yield and 23.6 selectivity ratio (Table 2, entry 14).
Table 2. Base Screening for Amidation to Alkene Impurity I (9).
| entry | basea | activating reagent | time(h) | temperature | overall yielda,b9 + 10 (%) | selectivity ratio 9:10c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NMM | EDC | 1 | 0 °C | 53 | 31.9 |
| 2 | NMM | EDC | 2 | r.t. | 77 | 30.4 |
| 3 | Et3N | EDC | 1 | 0 °C | 67 | 17.5 |
| 4 | Et3N | EDC | 2 | r.t. | 61 | 15.5 |
| 5 | Py | EDC | 2 | r.t. | 43 | 26.2 |
| 6 | DMAP | EDC | 2 | r.t. | 39 | 11.1 |
| 7 | NMM/DMAP = 9/1 | EDC | 1 | 0 °C | 85 | 20.5 |
| 8 | NMM/DMAP = 9/1 | EDC | 2 | r.t. | 75 | 17.0 |
| 9 | NMM/DMAP = 1/1 | EDC | 1 | 0 °C | 57 | 15.8 |
| 10 | NMM/DMAP = 1/1 | EDC | 2 | r.t. | 54 | 14.8 |
| 11 | NMM/Py = 1/1 | EDC | 1 | 0 °C | 44 | 18.9 |
| 12 | NMM/Py = 1/1 | EDC | 2 | r.t. | 42 | 18.7 |
| 13 | NMMb | (COCl)2 | 1 | 0 °C | 84 | 30.8 |
| 14 | Et3Nb | (COCl)2 | 1 | 0 °C | 91 | 23.6 |
| 15 | Pyb | (COCl)2 | 2 | 0 °C | 70 | 13.4 |
Reaction conditions by coupling reagent method: (i) 15 (0.50 mmol, 0.108 g), DMF (5 mL), 0 °C, EDC × HCl (0.50 mmol, 0.096 g), 0.5 h; (ii) 3 × HCl (0.5 mmol, 0.114 g), base (0.5 mmol), 0 °C for 1 h, then r.t. for 1 h. By acid chloride method: (i) 15 (0.46 mmol, 0.10 g), CH2Cl2, oxalyl chloride (0.92 mmol, 0.079 mL), DMF (cat.), 0 °C, 1.5 h; (ii) 3 × HCl (0.46 mmol, 0.105 g), base (0.92 mmol), THF (5 mL), 0 °C, 1 h.
Determined by HPLC.
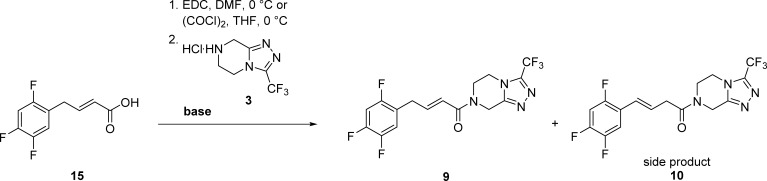
Our study indicated that the addition of a base favors regio-isomerization of the allylbenzene derivative leading to the more stable isomerized alkene derivative, such as compound 13, 14, or 10. Therefore, the reaction of isomerized acid 14 to alkene impurity 10 is much less problematic in terms of selectivity. Moreover, the addition of a base will favor the formation of isomerized alkene impurity 10. With the appropriate reaction conditions for amidation of 15 to alkene impurity I (9) in hand, we decided to use the optimized oxalyl chloride/Et3N procedure for conversion of 14 to alkene impurity II (10), which was then isolated in a high 76% yield. Furthermore, we also decided to examine the amidation of 14 using EDC as a coupling reagent. Since EDC/HOBt combination gave a higher yield and favorized the formation of 10 over 9 compared to EDC (Table S2, entries 4–9), we used the EDC/HOBt/NMM procedure for the final step of the synthesis of 10, which was obtained in a satisfactory 68% yield. Thus, we proved that the acid chloride method is more suitable for the last step of the syntheses of both alkene impurities 9 and 10 (Scheme 2).
Scheme 2. Our final Optimized 3-Step Synthetic Approach for Preparation of Alkene Impurities I (9) and II (10) from Readily Available 1-Bromo-2,4,5-trifluorobenzene (11).
Conclusions
In this study, we established two new straightforward and efficient synthetic approaches to two important USP impurities of sitagliptin: 3-desamino-2,3-dehydrositagliptin 9 and 3-desamino-3,4-dehydrositagliptin 10. These impurities can be generated during the manufacturing process of sitagliptin or the shelf-life of sitagliptin-based drug products. Even though the syntheses of impurities 9 and 10 were already described in the literature and patents4,9−15 prior our work, our novel synthetic approach starts from the commercially available and most importantly cheap starting material 1-bromo-2,4,5-trifluorobenzene (11), which is converted to 9 or 10 in only three steps with satisfactory overall yields ranging from 57 to 64% and purity above 95%. The key reaction was the amide bond formation where the challenging regio-isomerization as a side reaction occurred. Our study indicated that the selection of a base has a high impact on the levels of formation of a side product 10, thus presenting the most critical feature for selective synthesis of compound 9. The highest yield (71%) with a satisfactory selectivity ratio of isolated product 9 was obtained using 15, oxalyl chloride, and Et3N as a base at 0 °C. On the other hand, the reaction of regio-isomerized acid 14 to alkene impurity 10 is less problematic in terms of selectivity, resulting in a 68 or 76% yield for the EDC/HOBt or acid chloride method, respectively.
To sum up, our work provides facile and reliable access to two key USP impurities that could be used as analytical standards and thereby enables reliable quality control of important antidiabetic drug sitagliptin. Finally, we believe that our work clearly demonstrates the importance of proper selection of solvent, base, and coupling/activating reagents to minimize the carbon–carbon double bond regio-isomerization when Michael acceptor-type allylbenzene derivatives are subjected to amide bond formation.
Experimental Section
General Information
All reagents and solvents purchased commercially (from Sigma-Aldrich, Acros Organics, Apollo Scientific, TCI, ABCR GmbH & Co) were used without further purification unless noted otherwise. Tetrahydrofuran was distilled over sodium and dichloromethane was distilled over calcium hydride. Other anhydrous solvents (acetonitrile, DMF) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and used without further purification. The reactions with anhydrous solvents were performed in oven-dried glasswares under an argon atmosphere. Melting points were determined on a Reichert micro-hot-stage apparatus and are uncorrected. Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) analysis was performed on silica-gel plates (Merck DC Silica plates 60 GF254). Visualization of compounds was done by illumination with a UV lamp (254 nm). Flash column chromatography was performed on Merck silica gel 60 (mesh size, 70–230), using the indicated solvents. 1H and 13C spectra were recorded with a Bruker Avance III 400 MHz NMR (400 and 100 MHz) instrument at 295 K. Proton spectra were referenced to the signal of CDCl3 (7.26 ppm) or DMSO-d6 (2.50 ppm). Carbon chemical shifts were determined relative to the 13C signal of CDCl3 (77.16 ppm) or DMSO-d6 (39.52 ppm). Assignments of some proton and carbon resonances were performed by 2D NMR techniques (1H–1H gs-COSY, 1H–13C gs-HSQC, and 1H–13C gs-HMBC). Coupling constants (J) are given in hertz (Hz). Multiplicities are indicated as follows: s, singlet; d, doublet; dd, double doublet; td, triple doublet; t, triplet; dt, double triplet; ddd, double of doublet of doublet; m, multiplet; and br, broadened. HPLC chromatograms of pure compounds 9 and 10 were recorded on a Thermo Scientific Dionex UltiMate 3000 with a UV detector (254 nm) equipped with an Agilent Extend C18 column (3.5 μm, 4.6 × 150 mm), a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min, an inj. volume of 20 μL, at 25 °C, and an eluent system of H2O (A) and CH3CN (B). The following gradient was applied: 0–20 min, 10 → 100% B. Isocratic mixture of CH3CN 35% and H2O 65% was used for the analyses of the reaction mixtures via HPLC, with a flow rate of 1 mL/min, and a column temperature of 25 °C. Peak areas of liquid chromatogram were monitored and determined at 254 nm. The reaction yield was calculated in the reference to the known concentration of acetanilide as a standard. Sample preparation: 50 μL of reaction mixture was diluted with 950 μL of acetanilide solution in acetonitrile. The sample was further diluted (1/10) with acetonitrile and filtered to obtain the final sample for HPLC analysis.
Optimized Synthetic Procedures for Alkene Impurities 9 and 10
Synthesis of methyl (E)-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-2-enoate (12): a dry and nitrogen-flushed flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer and a rubber septum was charged with anhydrous THF (36 mL) and cooled to −20 °C. 1-Bromo-2,4,5-trifluorobenzene (11) (25.0 g, 118.5 mmol; 13.9 mL) was introduced through a septum, followed by the dropwise addition (addition rate: 0.666 mL/min) of i-PrMgCl (118.5 mmol, 59.25 mL; 2.0 M solution in THF). The reaction mixture was stirred at −20 °C for an additional 1 h. The solution of (2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)magnesium chloride obtained was immediately used further.
A flame-dried and nitrogen-flushed flask equipped with a stirring bar and a rubber septum was charged with CoBr2 (anhydrous, beads, 1.0 g, 4.57 mmol), sarcosine (dried 16 h under vacuum at 50 °C, 8.46 mmol, 0.754 g) and dissolved in anhydrous THF (564 mL) under an argon atmosphere. After 1 h, the reaction mixture was cooled to −20 °C, and methyl 4-bromocrotonate (15.15 g, 84.63 mmol, 10.0 mL) was added. After 15 min, the prepared solution of (2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)magnesium chloride (118.5 mmol, 109 mL) was added dropwise (addition rate: 1.387 mL/min), and the solution obtained was stirred for 1.5 h at −20 °C and an additional 0.5 h at 0 °C. Afterward, the saturated ammonium chloride solution (300 mL) was added to the reaction mixture, which was further washed with ethyl acetate (2 × 500 mL). The combined organic phases were washed with brine (250 mL), dried with anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered, and evaporated. The oil residue was purified by flash column chromatography using diethyl ether/petroleum ether (1:10) as a mobile phase to obtain methyl (E)-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-2-enoate (12) (17.68 g, 91%) as a colorless oil.17,181H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 3.45 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 2H), 3.69 (s, 3H), 5.78 (dtd, J = 15.6, 1.7, 0.5 Hz, 1H), 6.86–7.00 (m, 3H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 30.85 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 51.59, 105.65 (ddd, J = 28.1, 20.7, 0.7 Hz), 118.31 (ddd, J = 19.2, 5.8, 1.3 Hz), 121.09 (ddd, J = 18.5, 5.5, 4.3 Hz), 122.91, 144.65, 146.82 (ddd, J = 244.9, 12.5, 3.7 Hz), 149.04 (ddd, J = 250.3, 14.4, 12.3 Hz), 155.83 (ddd, J = 245.2, 9.4, 2.8 Hz), 166.52.
Synthesis of (E)-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-3-enoic acid (14): methyl (E)-4-(2,4,5 trifluorophenyl)but-2-enoate (3) (21.7 mmol, 5.0 g) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (100 mL), 3 M NaOH (100 mL) was added, and then the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 24 h. The solution was washed with diethyl ether (2 × 50 mL), and the water phase was acidified to pH 1 and extracted with diethyl ether (4 × 50 mL). Combined organic phases were washed with brine (100 mL), dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and evaporated to obtain 4.30 g (92%) of a crude oil product, which contained about 90% of 14 and 10% of 15. The crude product was used in the next reaction without further purification. For 14: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 3.33 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 6.25–6.32 (m, 1H), 6.57 (d, J = 16.1 Hz, 1H), 6.87–6.93 (m, 1H), 7.23–7.30 (m, 1H), 10.24 (br s, exchanged, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 37.89, 105.54 (dd, J = 28.4, 20.9 Hz), 114.37 (dd, J = 19.8, 5.0 Hz), 121.11 (ddd, J = 14.5, 5.8, 4.3 Hz), 123.99 (m), 125.09 (dd, J = 4.0, 2.4 Hz), 146.87 (ddd, J = 244.0, 13.0, 3.5 Hz), 149.12 (ddd, J = 251.7, 14.6, 12.6 Hz), 154.84 (ddd, J = 248.3, 9.1, 2.3 Hz), 174.53. ESI-HRMS ([M + H]+, m/z): Calcd for C10H8O2F3, 217.04709; found, 217.04695; ([M-H]−, m/z): Calcd for C10H6O2F3, 215.03254; found, 215.03207.
Synthesis of (E)-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-2-enoic acid (15): methyl (E)-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-2-enoate (12) (21.7 mmol, 5.0 g) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (50 mL), 3 M HCl (50 mL) was added, and then the reaction mixture was slowly heated to reflux (around 100 °C). The reaction was monitored by TLC (if needed, an additional amount of concentrated HCl was added). Usually, after 3 h heating at 100 °C, the ester hydrolyzed. During the evaporation of 1,4-dioxane, a white solid was formed. Approximately 50 mL of azeotropic mixture was evaporated, the remaining suspension was cooled to 0 °C, and the solid was filtered off and dried to obtain 4.50 g (96%) of 15. Mp 95–98 °C (water/dioxane). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 3.52 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H), 5.80 (dt, J = 15.6, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 6.91–7.02 (m, 2H), 7.11 (dt, J = 15.6, 6.6 Hz, 1H), 11.02 (br s, exchanged, 1H); the spectrum is in accordance with literature data.2813C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 30.15, 105.96 (dd, J = 28.8, 21.2 Hz), 118.82 (dd, J = 19.4, 6.0 Hz), 122.08 (ddd, J = 18.5, 5.7, 4.5 Hz), 123.38, 144.71, 146.06 (ddd, J = 242.3, 12.5, 3.6 Hz), 148.14 (ddd, J = 247.1, 14.0, 13.1 Hz), 155.55 (ddd, J = 243.6, 9.9, 2.3 Hz), 166.82.
Final Optimized Procedures for Amidation to (E)-1-(3-(Trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl)-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-2-en-1-one (Alkene Impurity I, 9)
Procedure 3.1 (EDC, NMM/DMAP): (E)-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-2-enoic acid 15 (5.0 mmol, 1.08 g) was dissolved in anhydrous DMF (50 mL) and cooled to 0 °C. EDC × HCl (5.25 mmol, 1.006 g) was added, and the reaction was stirred at 0 °C for 0.5 h. Afterward, 3 × HCl (5.0 mmol, 1.14 g), NMM (4.5 mmol, 0.495 mL), and DMAP (0.5 mmol, 0.061 g) were added. The resulting reaction mixture was stirred for 1 h at 0 °C. To the reaction mixture, ethyl acetate (200 mL) was added and washed with 10% citric acid (2 × 100 mL), water (100 mL), and brine (100 mL). The organic phase was evaporated, and the oily residue was purified by gradient flash column chromatography (mobile phases: 1 to 8% of MeOH in diethylether) to obtain 1.32 g (68%) of 9 as a colorless oil.
Procedure 3.2 (oxalyl chloride, Et3N): (E)-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-2-enoic acid 15 (5.6 mmol, 1.21 g) was charged with anhydrous CH2Cl2 (10 mL) and cooled to 0 °C. Oxalyl chloride (9.5 mmol, 0.81 mL) and three drops of anhydrous DMF were added, and the reaction was stirred at 0 °C for 1.5 h. The solvent was then evaporated and dissolved in anhydrous THF (10 mL). Afterward, the obtained solution was cooled down to 0 °C and quickly added to a precooled (0 °C) solution of 3 × HCl (5.6 mmol, 1.28 g) and Et3N (11.2 mmol, 1.56 mL) in anhydrous THF (15 mL), which was stirred for 1 h at room temperature prior to the addition. The resulting reaction mixture was stirred for 1 h at 0 °C. To the reaction mixture, ethyl acetate (200 mL) was added and washed with 10% citric acid (2 × 100 mL), water (100 mL), and brine (100 mL). The organic phase was evaporated, and the oil residue was purified by gradient flash column chromatography (mobile phases: 1 to 8% of MeOH in diethyl ether) to obtain 1.55 g (71%) of 9 as a colorless oil.
(E)-1-(3-(Trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl)-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-2-en-1-one (9): a colorless oil/gel; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 3.52 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H), 4.07 (br s, 2H), 4.16–4.18 (m, 2H), 4.98 (s, 2H), 6.24 (dt, J = 15.1, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 6.88–6.94 (m, 1H), 6.95–7.04 (m, 2H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 31.35 (d, J = 1.9 Hz), 38.56, 42.61, 43.39, 105.80 (dd, J = 28.1, 20.8 Hz), 118.30 (q, J = 270.5 Hz), 118.36 (dd, J = 19.3, 5.8 Hz), 120.55, 120.99 (ddd, J = 18.3, 5.2, 4.5 Hz), 143.75 (q, J = 40.1 Hz), 144.96, 146.86 (dd, J = 245.1, 12.6, 3.7 Hz), 149.11 (ddd, J = 250.6, 14.3, 12.3 Hz), 149.90, 155.88 (ddd, J = 245.2, 9.3, 2.7 Hz), 165.40. ESI-HRMS ([M + H]+, m/z): Calcd for C16H13N4OF6, 391.09881; found, 391.09853; ([M – H]−, m/z): Calcd for C16H11N4OF6, 389.08425; found, 391.08476; HPLC: tR = 9.20 min (98.3 area % at 254 nm). Spectroscopic data are in accordance with literature.6
Final Optimized Procedures for Amidation to (E)-1-(3-(Trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl)-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-3-en-1-one (Alkene Impurity II, 10)
Procedure 3.3 (EDC/HOBt, 1.2 equiv of NMM): crude (E)-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-3-enoic acid 14 (3.25 mmol, 0.702 g) was dissolved in anhydrous DMF (50 mL) and cooled to 0 °C. EDC × HCl (3.58 mmol, 0.686 g) and HOBt (3.58 mmol, 0.484 g) were added, and the reaction was stirred at 0 °C for 0.5 h. Afterward, 3 × HCl (3.25 mmol, 0.52 g) and NMM (3.9 mmol, 0.43 mL) were added. The resulting reaction mixture was stirred for 1 h at 0 °C and 1 h at room temperature. To the reaction mixture, ethyl acetate (200 mL) was added and washed with 10% citric acid (2 × 100 mL), water (100 mL), and brine (100 mL). The organic phase was evaporated, and the oily residue was purified by gradient flash column chromatography (mobile phases: 1 to 8% of MeOH in diethyl ether) to obtain 0.868 g (68%) of 10 as a white solid.
Procedure 3.4 (oxalyl chloride, Et3N): crude (E)-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-3-enoic acid 14 (6.2 mmol, 1.35 g) was charged with anhydrous CH2Cl2 (10 mL) and cooled to 0 °C. Oxalyl chloride (10.5 mmol, 0.90 mL) and three drops of anhydrous DMF were added, and the reaction was stirred at 0 °C for 1.5 h. The solvent was then evaporated, and the residue dissolved in anhydrous THF (10 mL). Afterward, the obtained solution was cooled down to 0 °C and quickly added to a precooled solution (0 °C) of 3 × HCl (6.2 mmol, 1.42 g) and Et3N (12.4 mmol, 1.73 mL) in anhydrous THF (20 mL), which was stirred for 1 h at room temperature prior to the addition. The resulting reaction mixture was stirred for 1 h at 0 °C. To the reaction mixture, ethyl acetate (200 mL) was added and washed with 10% citric acid (2 × 100 mL), water (100 mL), and brine (100 mL). The organic phase was evaporated, and the oily residue was purified by gradient flash column chromatography (mobile phases: 1 to 8% of MeOH in diethyl ether) to obtain 1.83 g (76%) of 10 as a white solid.
(E)-1-(3-(Trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl)-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)but-3-en-1-one (10): white solid; Mp 105–107 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 3.43 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H), 3.99–4.12 (m, 2H), 4.15–4.26 (m, 2H), 4.96 (5.02)* (s + s, 2H), 6.31 (dt, J = 15.9, 6.6 Hz, 1H), 6.52 (d, J = 16.2 Hz, 1H), 6.83–6.90 (m, 1H), 7.20–7.28 (m, 1H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 37.69 (37.78)*, 38.28 (41.93)*, 42.71 (39.44)*, 43.32 (43.72)*, 105.80 (dd, J = 28.3, 20.9 Hz), 114.62 (dd, J = 19.7, 4.8 Hz), 118.27 (q, J = 270.7 Hz), 120.95 (m), 124.44 (125.09)*, 125.40, 143.91 (q, J = 39.8 Hz), 144.96, 147.06 (ddd, J = 243.7, 12.7, 3.1 Hz), 149.24 (ddd, J = 244.0, 25.8, 12.9 Hz), 149.60, 155.02 (ddd, J = 248.3, 9.1, 2.4 Hz), 169.39 (169.77)*; *mixture of rotamers. ESI-HRMS ([M + H]+, m/z): Calcd for C16H13N4OF6, 391.09881; found, 391.09845; ([M-H]−, m/z): Calcd for C16H11N4OF6, 389.08425; found, 391.08481; HPLC: tR = 9.47 min (98.7 area% at 254 nm). Spectroscopic data are in accordance with literature.6
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Slovenian Research Agency (research core funding no. P1-0208). This manuscript is dedicated in memoriam to Prof. Dr. Janez Levec (1943-2020); University of Ljubljana, Slovenia and National Institute of Chemistry, Slovenia.
Supporting Information Available
The Supporting Information is available free of charge at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsomega.9b04393.
1H, 13C, HSQC, and HMBC NMR spectra of compounds 9 and 10; HPLC chromatograms and MS spectra of compounds 9 and 10; reaction screening details for regio-isomerization of 12 to 13; reaction screening details for hydrolysis and regio-isomerization of 12 to 14 and 15; and reaction screening details for the formation of an amide bond (PDF)
Author Contributions
§ M.S. and R.F. contributed equally to this work. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Supplementary Material
References
- Kim D.; Wang L.; Beconi M.; Eiermann G. J.; Fisher M. H.; He H.; Hickey G. J.; Kowalchick J. E.; Leiting B.; Lyons K.; Marsilio F.; McCann M. E.; Patel R. A.; Petrov A.; Scapin G.; Patel S. B.; Roy R. S.; Wu J. K.; Wyvratt M. J.; Zhang B. B.; Zhu L.; Thornberry N. A.; Weber A. E. (2R)-4-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl]-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-amine: a potent, orally active dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 141–151. 10.1021/jm0493156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak R.; Bridgeman M. B. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors in the management of diabetes. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 35, 509–513. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou L.; Mao B.; Reamer R.; Novak T.; Ge Z. Impurity profile tracking for active pharmaceutical ingredients: case reports. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 44, 421–429. 10.1016/j.jpba.2006.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metil D. S.; Sampath A.; Reddy J. R.; Chandrashekar E. R. R.; Dahanukar V. H.; Reddy C. V. R.; Bandichhor R. Efficient and convenient synthetic routes for sitagliptin impurities. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 2723–2729. 10.1002/slct.201702552. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- a Ahuja S.; Alsante K. M.. Handbook of isolation and characterization of impurities in pharmaceuticals; 1st ed.; Ahuja S., Ed.; Alsante K. M., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, 2003, Volume 5, pp 119–143. [Google Scholar]; b Ahuja S.; Scypinski S.. Handbook of modern pharmaceutical analysis; Volume 10, 2nd ed.; Ahuja S., Ed.; Scypinski S., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, 2011; pp 59–169. [Google Scholar]; c Schniepp S.Overview of USP-NF requirements for stability purposes. In Handbook of stability testing in pharmaceutical development; Kim H.-B., Ed.; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, 2009; pp 189–199. [Google Scholar]; d Hostyn S.; Persich P.; Jhajra S; Vanhoutte K.. Protocols for characterization of degradation products with special emphasis on mutagenic degradation impurities. In Methods for stability testing of pharmaceuticals; Bajaj S., Ed.; Singh S., Ed.; Springer Nature: New York, 2018; pp 123–142. [Google Scholar]; e Jain D.; Basniwal P. K. Forced degradation and impurity profiling: recent trends in analytical perspectives. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 86, 11–35. 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; f Holm R.; Elder D. P. Analytical advances in pharmaceutical impurity profiling. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 87, 118–135. 10.1016/j.ejps.2015.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; g Görög S. Critical review of reports on impurity and degradation product profiling in the last decade. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 101, 2–16. 10.1016/j.trac.2017.09.012. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; h Olsen B. A.; Sreedhara A.; Baertschi S. W. Impurity investigations by phases of drug and product development. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 101, 17–23. 10.1016/j.trac.2017.10.025. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; i Singh D. K.; Sahu A.; Kumar S.; Singh S. Critical review on establishment and availability of impurity and degradation product reference standards, challenges faced by the users, recent developments, and trends. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 101, 85–107. 10.1016/j.trac.2017.10.021. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; j Maggio R. M.; Calvo N. L.; Vignaduzzo S. E.; Kaufman T. S. Pharmaceutical impurities and degradation products: Uses and applications of NMR techniques. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 101, 102–122. 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; k Foti C.; Alsante K.; Cheng G.; Zelesky T.; Zell M. Tools and workflow for structure elucidation of drug degradation products. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 49, 89–99. 10.1016/j.trac.2013.06.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; l Popkin M. E.; Borman P. J.; Omer B. A.; Looker A.; Kallemeyn J. M. Enhanced approaches to the identification, evaluation, and control of impurities. J. Pharm. Innov. 2019, 14, 176–184. 10.1007/s12247-018-9363-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; m Roy J. Pharmaceutical impurities—A mini-review. AAPS PharmSciTech 2002, 3, 1–8. 10.1208/pt030206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonune D. P.; Mone M. K. Isolation, characterization of degradation products of sitagliptin and development of validated stability-indicating HPLC assay method for sitagliptin api and tablets. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res 2013, 4, 3494–3503. 10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.4(9).3494-03. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- a Farooqui I.; Kakde R. B. Reversed-phase liquid chromatography with mass detection and NMR characterization of sitagliptin degradation related impurities. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2016, 38, 4240–4230. [Google Scholar]; b Prasad P. B. N.; Satyanarayana K.; Krishna M. G. Impurity profiling and regulatory aspects of sitagliptin active pharmaceutical ingredient. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2018, 7, 6–11. 10.36106/IJSR. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Pharmacopoeia , 2016, U.S. Pharmacopoeia and National Formulary [USP39–NF34], Volume 3, Rockville, Md: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc; 2016. [Google Scholar]; USP monographs, (a) Sitagliptin Phosphate, 5854–5855; (b) Sitagliptin Tablets, 5852–5854.
- Bao H.; Bayeh L.; Tambar U. Catalytic enantioselective allylic amination of olefins for the synthesis of ent-sitagliptin. Synlett 2013, 24, 2459–2463. 10.1055/s-0033-1340079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janagani S.; Thaduri V. K.; Vamaraju R.. Expedient synthesis of sitagliptin and its phosphate hydrate salt. WO2015/120111 A2, 2015.
- Peng F.; Gao Y.; He Y.; Wu Z.. Sitagliptin impurity synthesis method. CN105085531 B, 2017.
- Gao Y.; He Y.; Peng F.; Wu Z.; Feng B.. Synthesis method of sitagliptin impurities. CN105130999 A, 2015.
- Lai J.; Kou J.. Preparation method of sitagliptin impurity. CN 104387393 A, 2015.
- Zhang S.; Yang H.; Ge J.; Shen L.; Yang L.; Wang L.; Wang J.. Preparation method of sitagliptin phosphate analog I. CN106397444 A, 2015.
- Gao Y.; He Y.; Peng F.; Feng B.; Wu Z.. Method for synthesizing sitagliptin impurity. CN105330664 A, 2016.
- Feng Q.; Xia X.; Zheng Y.; Kong X.. Preparation method of 2,4,5-trifluoro phenylacetic acid. CN104418727 A, 2015.
- Sova M.; Frlan R.; Gobec S.; Stavber G.; Časar Z. D-Glucosamine in iron-catalysed cross-coupling reactions of Grignards with allylic and vinylic bromides: application to the synthesis of a key sitagliptin precursor. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2015, 29, 528–535. 10.1002/aoc.3327. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Frlan R.; Sova M.; Gobec S.; Stavber G.; Časar Z. Cobalt-catalyzed cross-coupling of Grignards with allylic and vinylic bromides: use of sarcosine as a natural ligand. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 7803–7809. 10.1021/acs.joc.5b01156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin L.; Zard S. Z. Radical-based route to 2-(trifluoromethyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazoles and trifluoromethyl-substituted polycyclic 1,2,4-triazoles and dihydrofurans. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 1577–1580. 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b00457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X.-Y.; Li J.-S.; Wang J.-Y.; Wang S.-Q.; Li Y.-M.; Zhu Y.-J.; Zhou R.; Ma W.-J. Cu-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of vinyl epoxide with organoboron compounds: access to homoallylic alcohols. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 41561–41565. 10.1039/C8RA09048C. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guha S. K.; Shibayama A.; Abe D.; Sakaguchi M.; Ukaji Y.; Inomata K. “Syn-effect” in the conversion of (E)-α,β-unsaturated esters into the corresponding β,γ-unsaturated esters and aldehydes into silyl enol ethers. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn 2004, 77, 2147–2157. 10.1246/bcsj.77.2147. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann R.; Sasson Y. An evaluation of polyethylene-glycol as a catalyst in liquid-gas phase transfer catalysis: the base-catalyzed isomerization of allylbenzene. J. Mol. Catal. 1985, 33, 201–208. 10.1016/0304-5102(85)85102-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- al-Maskery I.; Girling K.; Jackson S. D.; Pugh L.; Spence R. R. High activity solid base catalysts for alkenyl aromatic isomerisation. Top. Catal. 2010, 53, 1163–1165. 10.1007/s11244-010-9554-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishna A. S.; Suri S. K.; Prasad Rao K. R. K.; Sivaprakash K.; Singh B. B. Potassium fluoride on alumina-A versatile reagent for isomerization of olefins. Synth. Commun. 1990, 20, 345–348. 10.1080/00397919008052774. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ngoc Thach L.; Lieu Hanh D.; Ba Hiep N.; Radhakrishna A. S.; Singh B. B.; Loupy A. Further Improvements in isomerization of olefins in solvent-free conditions. Synth. Commun. 1993, 23, 1379–1384. 10.1080/00397919308011226. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Luu T. X.; Lam T.; le T.; Duus F. Fast and green microwave-assisted conversion of essential oil allylbenzenes into the corresponding aldehydes via alkene isomerization and subsequent potassium permanganate promoted oxidative alkene group cleavage. Molecules 2009, 14, 3411–3424. 10.3390/molecules14093411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cram D. J.; Uyeda R. T. Intramolecular proton transfer in a base-catalyzed allylic rearrangement. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1962, 84, 4358–4359. 10.1021/ja00881a041. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hayama N.; Kuramoto R.; Földes T.; Nishibayashi K.; Kobayashi Y.; Pápai I.; Takemoto Y. Mechanistic insight into asymmetric hetero-Michael addition of α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids catalyzed by multifunctional thioureas. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12216–12225. 10.1021/jacs.8b07511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.