The recent outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by a new zoonotic coronary virus, SARS-CoV-2 [1], is being a great threat to public health. Up to February 11, 2020, it is reported that over 70,000 persons have been infected with SARS-CoV-2 in China [2]. The COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection represents a spectrum of clinical severity [3–5]. Some patients are asymptomatic or have merely mild upper respiratory tract symptoms. However, SARS-CoV-2 causes pneumonia that can be severe and characterized by fever, cough, dyspnea, bilateral pulmonary infiltrates, and acute respiratory injury. It is estimated that approximately 20% of patients are developing severe respiratory illness, with the overall mortality around 2.3% [2]. Thereby, it is critical to identify individuals who confer intrinsic susceptibility to become severe or even critically ill upon infection, for the purposes of prevention and treatment, especially when there is no drug directly targeting at SARS-CoV-2 that has been proven to be clinically effective. In the study, we explored potential host risk factors associated with severe cases at admission in a retrospective cohort of 487 patients in Zhejiang Province of China and attempt to establish a score system to identify high-risk individuals. We reviewed medical records, laboratory findings, and pulmonary CT scan of each patient with COVID-19, provided by the local health authority and inputted into a pre-specified electronic data collection form. Clinical outcomes were followed up to February 17, 2020. The primary endpoint was occurrence of death and severe cases.
A total of 487 COVID-19 patients were included for analysis, with 49 (10.1%) severe cases at admission. As shown in Table 1, severe cases are elderly (56 (17) vs. 45 (19), P < 0.001), with more male (73.5% vs. 50.9%, P = 0.003). They have a higher incidence of hypertension (53.1% vs. 16.7%, P < 0.001), diabetes (14.3% vs. 5.0%, P = 0.009), cardiovascular diseases (8.2% vs. 1.6%, P = 0.003), and malignancy (4.1% vs. 0.7%, P = 0.025), and less exposure to epidemic area (49.0% vs. 65.1%, P = 0.027), but more infected family members (P = 0.031). On multivariate analysis, elder age (OR 1.06 [95% CI 1.03–1.08], P < 0.001), male (OR 3.68 [95% CI 1.75–7.75], P = 0.001), and presence of hypertension (OR 2.71 [95% CI 1.32–5.59], P = 0.007) are independently associated with severe disease at admission, irrespective of adjustment of time to admission.
Table 1.
Demographic, epidermiological characteristics, and underlying comorbidities of patients with confirmed 2019-nCoV infection
| Variables | Total (N = 487) | Mild (N = 438) | Severe (N = 49) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 46 (19) | 45 (19) | 56 (17) | < 0.001 |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 259 (53.2%) | 223 (50.9%) | 36 (73.5%) | |
| Female | 228 (46.8%) | 215 (49.1%) | 13 (26.5%) | 0.003 |
| Occupation | ||||
| Agricultural worker | 140 (28.7%) | 122 (27.9%) | 18 (36.7%) | |
| Self-employed | 219 (45.0%) | 203 (46.3%) | 16 (32.7%) | |
| Employee | 82 (16.8%) | 79 (18.0%) | 3 (6.1%) | |
| Retired | 38 (7.8%) | 26 (5.9%) | 12 (24.5%) | |
| Student | 8 (1.6%) | 8 (1.8%) | 0 (0%) | < 0.001 |
| Smoking history | ||||
| Yes | 40 (8.2%) | 34 (7.8%) | 6 (12.2%) | |
| No | 434 (89.1%) | 391 (89.3%) | 43 (87.8%) | |
| Unknown | 13 (2.7%) | 13 (2.7%) | 0 (0%) | 0.331 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Hypertension | 99 (20.3%) | 73 (16.7%) | 26 (53.1%) | < 0.001 |
| Diabetes | 29 (6.0%) | 22 (5.0%) | 7 (14.3%) | 0.009 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 11 (2.3%) | 7 (1.6%) | 4 (8.2%) | 0.003 |
| Malignancy | 5 (1%) | 3 (0.7%) | 2 (4.1%) | 0.025 |
| Chronic liver diseases | 22 (4.5%) | 20 (4.6%) | 2 (4.1%) | 0.877 |
| Chronic renal diseases | 7 (1.4%) | 5 (1.1%) | 2 (4.1%) | 0.101 |
| Others | 32 (6.6%) | 27 (6.1%) | 5 (10.2%) | 0.279 |
| Exposure to confirmed cases | 186 (38.2%) | 173 (39.5%) | 13 (26.5%) | 0.077 |
| Family cluster | ||||
| 0 | 392 (80.5%) | 352 (80.4%) | 40 (81.6%) | |
| 1 | 67 (13.8%) | 63 (14.4%) | 4 (8.2%) | |
| 2 | 12 (2.5%) | 12 (2.7%) | 0 (0%) | |
| ≥ 3 | 16 (3.3%) | 11 (2.5%) | 5 (10.2%) | 0.031 |
| Recent travel or residence to/in epidemic area | 309 (63.4%) | 285 (65.1%) | 24 (49.0%) | 0.027 |
| Time from onset of symptom to admission | 2 (3) | 2 (3) | 3 (5) | 0.10 |
Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD), median (interquartile range), or number (percent). Comparisons between mild and severe cases were performed by the Mann-Whitney U test or a chi-square test
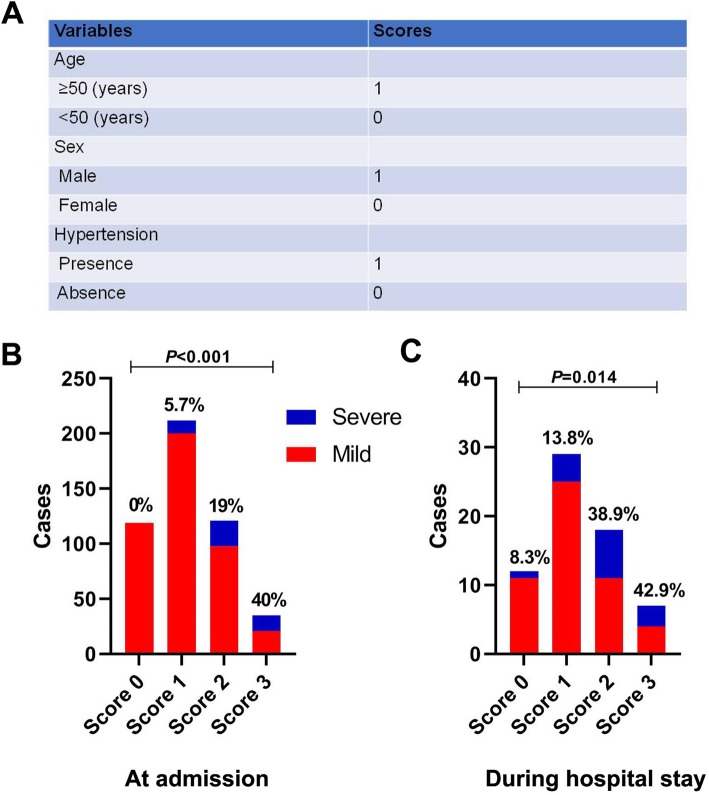
Then, we defined a host risk score on the basis of the three risk factors, to assess the intrinsic host susceptibility to develop severe cases of COVID-19 (Fig. 1a). As shown in Fig. 1b, a step-wise increase in the incidence of severe COVID-19 at admission was observed with the increment of the host risk score (P < 0.001). The performance of the score was also validated in 66 patients who presented mild at admission and were under follow-up during hospital stay. Fifteen patients progressed to severe COVID-19 within a median follow-up time of 15 days. No death was reported by the end of follow-up. A similar trend to the above was confirmed when analyzing the correlation between host risk score and occurrence of severe COVID-19 (P = 0.014) (see Fig. 1c).
Fig. 1.
Definition of host risk factor score and incidences of severe cases by host risk score. The host risk factor score was calculated by the sum of three variables (a). The incidences of severe cases at admission (b) or developing during hospitalization (c) were compared across the different score groups by a linear-by-linear association test
In summary, by identifying host risk factors associated with severe COVID-19, this study shed light on the underlying mechanisms of disease progression. In particular, the major finding that hypertension is a host risk factor for severe COVID-19 may underscore the involvement of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) in the pathogenesis of this disease. Additionally, the host risk score provides a useful tool to identify high-risk individuals, which is helpful for designing specific strategies for prevention and treatment of this disease. But further studies, particularly those enrolling Wuhan patients, are needed to validate the findings.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Authors’ contributions
JS and YS conceptualized the idea and designed the study. YS and XY drafted the manuscript, and JS revised it. XY, HZ, HW, and RZ participated in the data collection, analysis, and interpretation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (nos. 81670567 and 81870425) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets and materials used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The ethics committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University reviewed and approved this study. Written consent was obtained from each patient or his/her authorized representatives following a full explanation of the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Yu Shi and Xia Yu contributed equally to this work.
References
- 1.Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(8):727–733. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Emergency Response Epidemiology T The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020;41(2):145–151. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, Qiu Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Wei Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):507–513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Xu X-W, Wu X-X, Jiang X-G, Xu K-J, Ying L-J, Ma C-L, Li S-B, Wang H-Y, Zhang S, Gao H-N, et al. Clinical findings in a group of patients infected with the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-Cov-2) outside of Wuhan, China: retrospective case series. BMJ. 2020;368:m606. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets and materials used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.