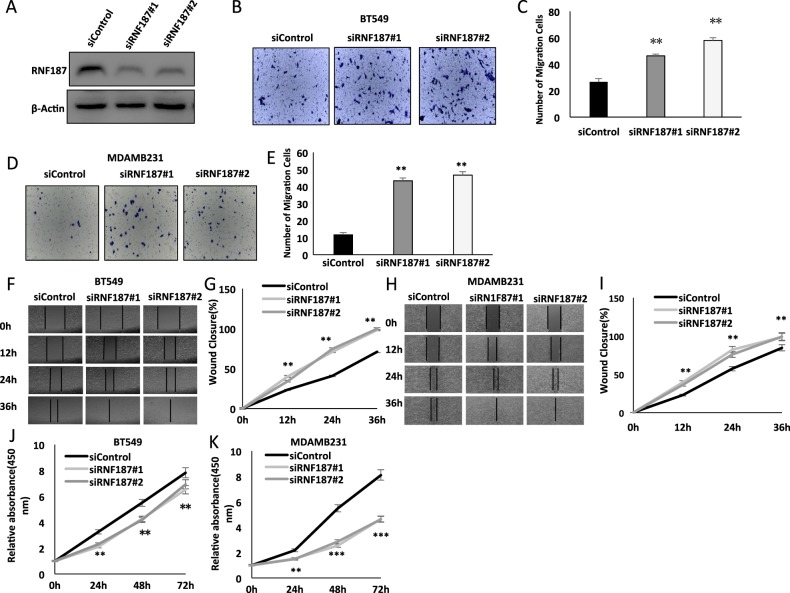
Fig. 1. RNF187 inhibits migration and invasion in triple negative breast cancer cells.
a RNF187 knocking down efficiency in TNBC cell lines. BT549 cells were transfected with RNF187 siRNA. The knockdown efficiency was measured via western blot. b, c RNF187 depletion promotes TNBC cell migration in BT549 cells. Two independent siRNA were used in the study. Transwell was used to check the migration capacity. The cell number was counted and Data are presented as ±SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (student’s t-test). d, e RNF187 depletion promotes TNBC cell migration in MDAMB231 cells. Two independent siRNA were used in the study. Transwell was used to check the migration capacity. The cell number was counted and Data are presented as ±SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (student’s t-test). f, g Wound-healing assay of BT549 cells were transfected with indicated 50 nM RNF187 siRNA (mix of #1 and #2) or 50 nM control siRNA. Quantification of wound closure at the indicated time points. Data are presented as ± SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (student’s t-test). h, i Wound-healing assay of MDAMB231 cells were transfected with indicated 50 nM RNF187 siRNA (mix of #1 and #2) or 50 nM control siRNA. Quantification of wound closure at the indicated time points. Data are presented as ± SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (student’s t-test). j, k RNF187 depletion inhibits TNBC cancer cell proliferation. BT549 and MDAMB231 cells were transfected with siControl or siRNF187. After 24 h, the WST assay was used to determine the cellar metabolic activity at indicated time points after infection. Experiments were done in triplicates. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 for cell growth comparison.