Abstract
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak, first reported in Wuhan, China, has rapidly swept around the world just within a month, causing global public health emergency. In diagnosis, chest computed tomography (CT) manifestations can supplement parts of limitations of real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay. Based on a comprehensive literature review and the experience in the frontline, we aim to review the typical and relatively atypical CT manifestations with representative COVID-19 cases at our hospital, and hope to strengthen the recognition of these features with radiologists and help them make a quick and accurate diagnosis.
Key Points
• Ground glass opacities, consolidation, reticular pattern, and crazy paving pattern are typical CT manifestations of COVID-19.
• Emerging atypical CT manifestations, including airway changes, pleural changes, fibrosis, nodules, etc., were demonstrated in COVID-19 patients.
• CT manifestations may associate with the progression and prognosis of COVID-19.
Keywords: Coronavirus infections; Pneumonia; Tomography, X-ray computed
Introduction
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a highly infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), was firstly reported in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China, and rapidly spreads to other domestic cities and countries beyond China [1]. On January 30, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared this ongoing outbreak as a global public health emergency and raised the risk of COVID-19 to very high at the global level on February 28, 2020 [2]. A total of 88,948 COVID-19 cases with 3043 deaths were confirmed as of March 2, 2020, of which 80,174 were from China and 8774 were from other 64 countries [3]. In COVID-19 diagnosis, real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) of viral nucleic acid is regarded as the reference standard; however, recent studies addressed the importance of chest computed tomography (CT) examination in COVID-19 patients with false negative RT-PCR results [4, 5], and reported the CT sensitivity as 98% [6]. Additionally, according to the official diagnosis and treatment protocol (6th edition) declared by the National Health Commission of China [7], CT examination is of great significance not only in diagnosing COVID-19 but also in monitoring disease progression and evaluating therapeutic efficacy.
Bilateral distribution of ground glass opacities (GGO) with or without consolidation in posterior and peripheral lungs was the cardinal hallmark of COVID-19 [8, 9]. However, with further analysis of increasing cases, a diversity of interesting CT imaging features were found, including crazy paving pattern, airway changes, reversed halo sign etc. [10–12], which may shed light on the possible mechanism of lung injury in COVID-19. A recent editorial by Kay et al [13] also encouraged researchers to focus the many faces of COVID-19 for its better recognition and accurate diagnosis.
Therefore, with a comprehensive review of published studies and the experience of COVID-19 imaging interpretation in frontline, we aim to review the typical and relatively atypical CT manifestations of COVID-19 in a pictorial fashion and help radiologists to familiarize these possible imaging features of COVID-19.
CT manifestations of COVID-19
SARS-CoV-2 was reported to utilize angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) as the cell receptor into humans [14], and firstly causing pulmonary interstitial damages and subsequent with parenchymal changes. Table 1 shows the CT manifestations of COVID-19 in published articles. Reportedly, chest CT images could manifest different imaging features or patterns in COVID-19 patients with a different time course and disease severity [18, 20]. Hereinafter, we will respectively describe each imaging feature of COVID-19 with RT-PCR confirmed cases at our hospital.
Table 1.
The occurrence rate of different CT manifestations of COVID-19 in published articles
| Author | No. of patients | CT scan | GGO | Consolidation | GGO + consolidation | Interlobular septal thickening | Reticular pattern | Crazy paving | Air bronchogram | Bronchial wall thickening | Bronchiolectasis | Pleural thickening | Pleural effusion | Subpleural line | Nodule | Reversed halo sign | Lymphadenopathy | Pericardial effusion | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wu et al [15] | 80 | S | 91% (73/80) | 63% (50/80) | - | 59% (47/80) | - | 29% (23/80) | - | 11% (9/80) | - | - | 6% (5/80) | 20% (16/80) | - | - | 4% (3/80) | 5% (4/80) | - |
| Pan et al [16] | 63 | S | 86% (54/63) | 19% (12/63) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 13% (8/63) | - | - | - | Fibrous stripes 17% (11/63) |
| Yoon et al [17] | 9* | M | 45% (35/77) | 5% (2/40) | 50% (20/40) | - | - | 10% (4/40) | 21% (16/77) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3% (1/37) | - | - | - |
| Shi et al [18] | 81 | S | 65% (53/81) | 17% (14/81) | - | 35% (28/81) | 4% (3/81) | 10% (8/81) | 47% (38/81) | - | 11% (9/81) | 32% (26/81) | 5% (4/81) | - | 6% (5/81) | - | 6% (5/81) | - | Cystic change 10% (8/81) |
| Chung et al [9] | 21 | S | 57% (12/21) | 29% (6/21) | 29% (6/21) | - | 14% (3/21) | 19% (4/21) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Song et al [19] | 51 | S | 76% (39/51) | 55% (28/51) | 59% (30/51) | 75% (38/51) | 22% (11/51) | - | 80% (41/51) | - | - | - | 8% (4/51) | - | - | - | 6% (3/51) | 6% (3/51) | - |
| Pan et al [20] | 21 | M | 73% (60/82) | 63% (52/82) | - | - | - | 23% (19/82) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Fang et al [6] | 51 | S | 72% (36/50) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bernheim et al [12] | 121 | S | 34% (41/121) | 2% (2/121) | 41% (50/121) | - | - | 5% (6/121) | - | 12% (14/121) | - | - | 1% (1/121) | - | - | 2% (2/121) | - | - | Bronchiectasis 1% (1/121) |
| Ai et al [21] | 1014 | S | 46% (409/888) | 50% (447/888) | - | 1% (8/888) | 1% (8/888) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3% (24/888) | - | - | - | - |
| NG et al [22] | 21 | S | 86% (18/21) | 62% (13/21) | 19% (4/21) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Li et al [23] | 83 | S | 98% (81/83) | 64% (53/83) | - | 63% (52/83) | 5% (4/83) | 36% (30/83) | 23% (19/83) | - | - | 8% (7/83) | 20% (17/83) | 7% (6/83) | - | 8% (7/83) | 5% (4/83) | - | |
| Chen et al [24] | 99 | S | 14% (14/99) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Guan et al [25] | 1099 | S | 56% (550/975) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
*77 lesions in 9 patients were assessed (40 patchy to confluent lesions and 37 nodular lesions)
COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; No. of patients, number of patients; M, multiple, indicating multiple CT scans were assessed; S, single, indicating single CT scan was assessed; GGO, ground glass opacities
Ground glass opacity
GGO were defined as hazy areas with slightly increased density in lungs without obscuration of bronchial and vascular margins, which may be caused by partial displacement of air due to partial filling of airspaces or interstitial thickening [26]. In patients with COVID-19, unilaterally or bilaterally GGO with a peripheral lung and subpleural distribution are commonly encountered [16, 19, 22] (Fig. 1a). In the very first radiologic investigation of 21 patients by Chung et al [9], GGO was found in 57% patients and was believed to be the earliest radiographically visible CT manifestation in some patients. These results are consistent with those of other subsequent studies, presenting GGO as the most common imaging finding with occurrence rate of up to 98% [23]. Recently, the first post-mortem biopsy in a COVID-19 patient was reported [27], showing pulmonary edema and hyaline membrane formation in both lungs, which we speculate may be the underlying pathological driver of GGO sign. Moreover, GGO are often accompanied by other features or patterns, including reticular and/or interlobular septal thickening and consolidation [19]. GGO together with small areas of consolidation may suggest an organizing pneumonia pattern of lung injury [28].
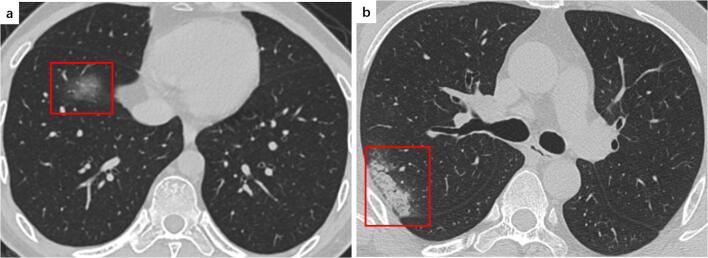
Fig. 1.
a A 35-year-old male COVID-19 patient presenting fever and headache for 1 day. CT scan shows a pure ground glass opacity in the right lower lobe (red frame). b A 47-year-old male COVID-19 patient presenting fever for 7 days. CT scan shows consolidation in the right lobe subpleural area (red frame)
Consolidation
Consolidation refers to alveolar air being replaced by pathological fluids, cells, or tissues, manifested by an increase in pulmonary parenchymal density that obscures the margins of underlying vessels and airway walls [26]. Multifocal, patchy, or segmental consolidation, distributed in subpleural areas or along bronchovascular bundles, is usually presented in COVID-19 patients (Fig. 1b) with occurrence rate of 2~64% [12, 15, 23]. In COVID-19 patients, consolidation may relate to cellular fibromyxoid exudates in alveoli [27]. In addition, consolidation was considered as an indication of disease progression. A recent study showed lung involvement gradually increased to consolidation up to 2 weeks after disease onset [20], which concurs with another conclusion that GGO could progress to or co-existed with consolidations within 1–3 weeks [18]. Likewise, Song et al found more consolidative lesions in patients with longer time interval between symptom onset and CT scan or older than 50 years old [19], suggesting that this manifestation could serve as an alert in the management of patients.
Reticular pattern
Reticular pattern was defined as thickened pulmonary interstitial structures such as interlobular septa and intralobular lines [26, 29], manifested as a collection of innumerable small linear opacities on CT images (Fig. 2a). The formation of this pattern might associate with interstitial lymphocyte infiltration causing interlobular septal thickening [27]. Several studies have listed reticular pattern with interlobular septal thickening as the common chest CT manifestation of COVID-19, only second to GGO and consolidation [15, 18, 19]. As the disease course gets longer, the prevalence of reticular pattern could increase in COVID-19 patients [18].
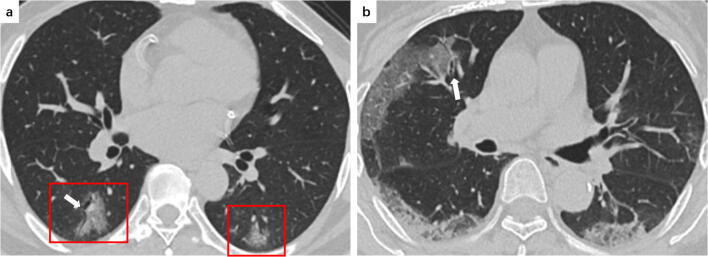
Fig. 2.
a A 34-year-old female COVID-19 patient presenting fever with dry cough for 2 days. CT scan shows slight reticular pattern in the left lower lobe and subpleural area (red frame). b An 81-year-old female COVID-19 patient presenting fever with cough for 7 days. CT scan shows reticular pattern superimposed on the background of GGO, resembling the sign of crazy paving stones in the right middle lobe (red frame)
Crazy paving pattern
Crazy paving pattern demonstrates as thickened interlobular septa and intralobular lines with superimposition on a GGO background, resembling irregular paving stones (Fig. 2b), which was not frequently observed as GGO and consolidation [20, 26]. Based on the previous pathological knowledge of SARS, this sign may result from the alveolar edema and interstitial inflammatory of acute lung injury [15, 30]. Recent investigations reported 5~36% COVID-19 patients with crazy paving pattern in their studies [12, 23]. Additionally, in combination with diffuse GGO and consolidation, crazy paving pattern can be the signal of COVID-19 entering progressive or peak stage [20].
Air bronchogram
Air bronchogram was defined as a pattern of air-filled (low-attenuation) bronchi on a background of opaque (high-attenuation) airless lung [26] and was reported to be another CT manifestation of COVID-19 [17, 19] (Fig. 3a). However, according to a recent general observation report of the COVID-19 autopsy [31], gelatinous mucus attachment was present in the lung bronchus; therefore, we infer the low-attenuation bronchi in CT imaging may be filled with gelatinous mucus instead of air. Moreover, this sign was often accompanied by slightly bronchiolar dilatation, and thus we think it may be more appropriate to term it as bronchiolectasis. As for the dry cough in COVID-19 patients, we surmise it may be explained by the high viscosity of mucus and the damage of dilated bronchioles, resulting in insufficient sputum motility.
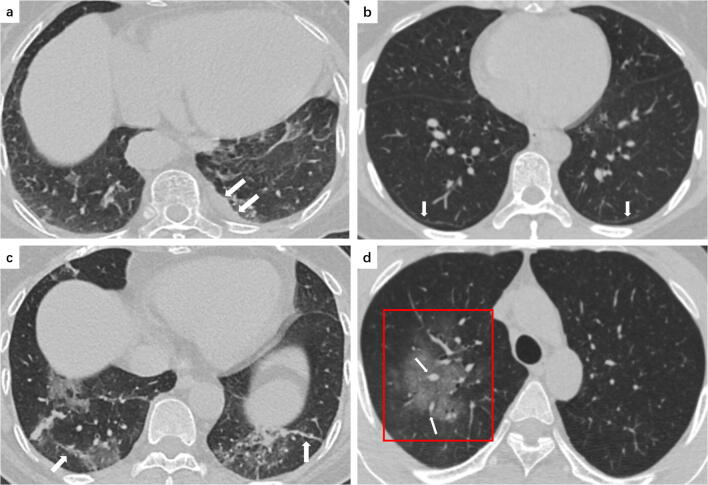
Fig. 3.
a A 48-year-old male COVID-19 patient presenting fever for 5 days. CT scan shows bilateral GGO in the lower lobe (red frames) and air bronchogram (white arrow) in the left subpleural area. b A 66-year-old male COVID-19 patient presenting fever with cough for 7 days. CT scan shows reticular pattern in the subpleural areas of the bilateral lower lobe, GGO, and bronchial wall thickening (white arrow) in the right middle lobe
Airway changes
Airway changes include bronchiectasis and bronchial wall thickening (Fig. 3b). Bronchiectasis was reported in some COVID-19 cases [4, 10], while bronchial wall thickening has been reported in around 10% to 20% COVID-19 patients [15, 23]. Pathogenesis can be the inflammatory damage of the bronchial wall and the bronchial obstruction, resulting in the destruction of bronchial wall structure, proliferation of fibrous tissue, fibrosis, and tractive bronchiectasis [26]. Li et al investigated 83 COVID-19 patients and found the incidence of bronchial wall thickening in severe/critical patients was significantly higher than that in ordinary patients [23].
Pleural changes
Pleural changes including pleural thickening (Fig. 4a) and pleural effusion were reported in COVID-19, among which, the former sign is more prevalent [18]. According to a recent study comprising 81 patients with COVID-19, 32% of them demonstrated pleural thickening while 5% showed pleural effusion [12, 18]. Based on the experience of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection and recent findings [18, 23], the presence of pleural effusion may suggest a poor prognosis in COVID-19. Moreover, the recent autopsy report also revealed a photo of pleural thickening with extensive adhesion in a COVID-19 patient [31], suggesting consistency between CT imaging presentations and autopsy findings.
Fig. 4.
a An 80-year-old female COVID-19 patient presenting fever for 7 days. CT scan shows left pleural thickening (white arrows). b A 43-year-old female COVID-19 patient presenting fever and chills for 5 days. CT scan shows subpleural lines (white arrows) in bilateral lower lobes. c A 66-year-old female COVID-19 patient presenting cough and myalgia for 7 days. CT scan shows bilateral GGO and fibrous stripes (white arrows) in the left lower lobe. d A 35-year-old male COVID-19 patient presenting fever and headache for 1 day. CT scan shows a large area of GGO (red frame) in the right upper lobe with multiple small vascular enlargement (white arrows)
Subpleural curvilinear line
This manifestation was defined as a thin curvilinear opacity with 1–3 mm thickness, lying less than 1 cm from and parallel to the pleural surface [26] (Fig. 4b). Wu et al [15] and Li et al [23] both reported around 20% of patients with COVID-19 demonstrated this sign, which might relate to pulmonary edema or fibrosis of COVID-19.
Fibrosis
CT manifestations of fibrosis or fibrous stripes were also observed in COVID-19 (Fig. 4c). Pan et al [16] reported 17% COVID-19 patients with fibrous stripes in their study. Fibrous lesions may form during the healing of pulmonary chronic inflammation or proliferative diseases, with gradual replacement of cellular components by scar tissues. Currently, the relation between fibrosis and patients’ prognosis is debatable. Some researchers suggested the presence of fibrosis indicates good prognosis of a COVID-19 patient with stabilizing disease status [16]. However, others argued that fibrosis might indicate a poor outcome of COVID-19, reporting it may subsequently progress to peak stage or result in pulmonary interstitial fibrosis disease [20, 32].
Vascular enlargement
Vascular enlargement is often described as the dilatation of pulmonary vessels around and within the lesions on CT images (Fig. 4d). One previous study reported this particular CT manifestation on a RT-PCR-negative COVID-19 patient who was admitted to a hospital 6 days after symptom onset [4]. Although rarely reported, we found this manifestation in most of our cases, which might be attributed to the damage and swelling of the capillary wall caused by pro-inflammatory factors.
Air bubble sign
Air bubble sign refers to a small air-containing space in the lung (Fig. 5a), which might be the pathological dilation of a physiological space or a cross section of the bronchiolectasis, or associated with the process of consolidation resorption. Shi et al termed this sign as round cystic change in their study [18], while Kong et al reported it as cavity sign [32]. However, given the displayed pictures in their studies and the definition of cyst and cavity [26], we believe it may be more appropriate to term this small bubble-like air-containing space as air bubble sign.
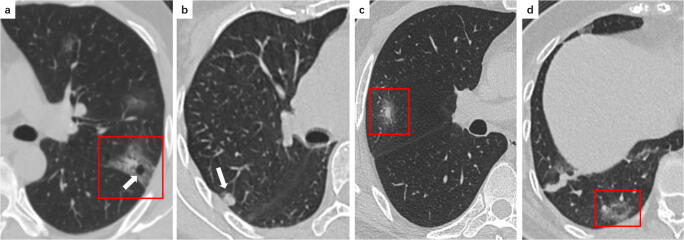
Fig. 5.
a A 49-year-old male COVID-19 patient presenting fever with diarrhea for 3 days. CT scan shows a patchy GGO (red frame) with an air bubble sign (white arrow) in the apicoposterior segment of the upper left lobe. b A 76-year-old female COVID-19 patient presenting fever with cough for 4 days. CT scan shows an irregular nodule (white arrow) in the posterior segment of the right upper lobe. c A 46-year-old male COVID-19 patient presenting fever with dry cough for 5 days. CT scan shows a solid nodule surrounded by a ground glass halo in the lateral segment of the right middle lobe (red frame). d A 66-year-old woman confirmed with COVID-19 presenting fever and myalgia for 7 days. CT scan shows a reversed halo sign (red frame) in the posterior basal segment of the right lower lobe
Nodules
A nodule refers to a rounded or irregular opacity with well- or poorly defined edges, measuring less than 3 cm in diameter [26] (Fig. 5b). This sign has been frequently associated with viral pneumonia [33]. As reported, 3~13% of COVID-19 patients can appear with multifocal solid irregular nodules [16, 21] or nodules with visible halo sign [34].
Halo sign
Halo sign was defined as nodules or masses surrounded by ground glass [26] (Fig. 5c). In current limited research, only Li et al [34] reported a case of halo sign in a 27-year-old female COVID-19 patient. In the past, halo sign is thought to be associated with perilesional hemorrhage in angioinvasive fungal infections or hypervascular metastases [35], as well as viral infections and organizing pneumonia [36]. However, the main pathological driver of this manifestation remains unknown at present.
Reversed halo sign or atoll sign
Reversed halo sign, also known as atoll sign, was under a definition of a focal rounded GGO surrounded by a more or less complete ring-like consolidation [26] (see Fig. 5d). It was initially reported to be specific for cryptogenic organizing pneumonia [37, 38] but was subsequently described in other patients [39]. Recently, this sign was reported in several COVID-19 cases, which may be attributed to disease progression making consolidation developed around GGO or lesion absorption leaving a decreased intensity in the center [5, 12, 17, 40].
Lymphadenopathy
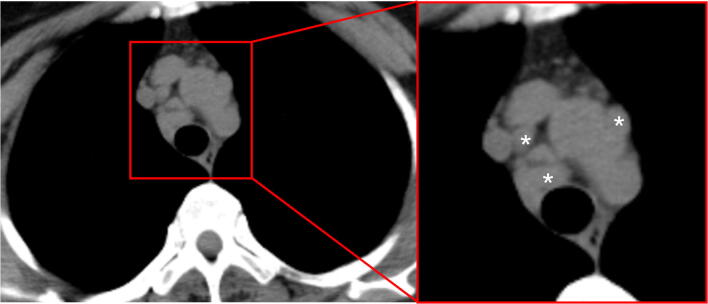
Thresholds for lymphadenopathy were somewhat arbitrary, typically 1 cm in short taxis diameter for mediastinal nodes [26] (Fig. 6). Lymphadenopathy was reported in 4~8% of patients with COVID-19 [15, 18]. Moreover, lymphadenopathy was considered one of the significant risk factors of severe/critical COVID-19 pneumonia [23]. Occurring with pleural effusion and extensive tiny lung nodules may suggest bacterial superinfection [41].
Fig. 6.
A 49-year-old female COVID-19 patient presenting chest pain for 14 days. CT scan shows enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes (asterisks)
Pericardial effusion
Pericardial effusion is rare to identify in COVID-19 patients, with incidence of approximately 5%, which may indicate the occurrence of severe inflammation [15, 23]. A recent study found severe/critical COVID-19 patients showed higher incidences of pericardial effusion than ordinary patients [23].
Summary
Early recognition and isolation of COVID-19 patients is of crucial importance in controlling this outbreak, especially in those with false negative RT-PCR or without symptoms. Although bilateral GGO and consolidation were reported as the predominant imaging characteristics in COVID-19, chest CT manifestations can vary in different patients and stages. In this paper, we review the typical and atypical CT manifestations with representative pictures and, hopefully, help familiarize radiologists with these features and make right diagnosis when encountering. Moreover, as the COVID-19 autopsies were in progress, we believe that the radiologic-pathologic correlation will be further explored, which is expected to be helpful in determining prognostic imaging features and guiding clinical treatment.
Abbreviations
- ACE2
Angiotensin-converting enzyme-2
- COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019
- CT
Computed tomography
- GGO
Ground glass opacities
- MERS-CoV
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus
- RT-PCR
Real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
- WHO
World Health Organization
Funding information
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Compliance with ethical standards
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Bin Song.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Methodology
• retrospective
• observational
• performed at one institution
Footnotes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Zheng Ye and Yun Zhang contributed equally to this work.
References
- 1.Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W et al (2020) A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
- 2.World Health Organization (2020) Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report–39. World Health Organization, Geneva. Available via https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200228-sitrep-39-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=5bbf3e7d_2. Accessed 3 Mar 2020
- 3.World Health Organization (2020) Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report–42. World Health Organization, Geneva. Available via https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/20200302-sitrep-42-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=d863e045_2. Accessed 3 Mar 2020
- 4.Xie X, Zhong Z, Zhao W, Zheng C, Wang F, Liu J (2020) Chest CT for typical 2019-nCoV pneumonia: relationship to negative RT-PCR testing. Radiology. 10.1148/radiol.2020200343 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.Huang P, Liu T, Huang L et al (2020) Use of chest CT in combination with negative RT-PCR assay for the 2019 novel coronavirus but high clinical suspicion. Radiology. 10.1148/radiol.2020200330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Fang Y, Zhang H, Xie J et al (2020) Sensitivity of chest CT for COVID-19: comparison to RT-PCR. Radiology. 10.1148/radiol.2020200432 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China (2020) The diagnostic and treatment protocol of COVID-19. China. Available via http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-02/19/content_5480948.htm Accessed 3 Mar 2020
- 8.Wang D, Hu B, Hu C et al (2020) Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 10.1001/jama.2020.1585 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 9.Chung M, Bernheim A, Mei X et al (2020) CT imaging features of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Radiology. 10.1148/radiol.2020200230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Fang Y, Zhang H, Xu Y, Xie J, Pang P, Ji W (2020) CT manifestations of two cases of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) pneumonia. Radiology. 10.1148/radiol.2020200280 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 11.Qian L, Yu J, Shi H (2020) Severe acute respiratory disease in a Huanan seafood market worker: images of an early casualty. Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging. 10.1148/ryct.2020200033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 12.Bernheim A, Mei X, Huang M et al (2020) Chest CT findings in coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): relationship to duration of infection. Radiology. 10.1148/radiol.2020200463 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 13.Kay F, Abbara S (2020) The many faces of COVID-19: spectrum of imaging manifestations. Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging. 10.1148/ryct.2020200037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 14.Xu X, Chen P, Wang J, et al. Evolution of the novel coronavirus from the ongoing Wuhan outbreak and modeling of its spike protein for risk of human transmission. Sci China Life Sci. 2020;2020:1–4. doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1637-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wu J, Wu X, Zeng W et al (2020) Chest CT findings in patients with corona virus disease 2019 and its relationship with clinical features. Invest Radiol. 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000670 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Pan Y, Guan H, Zhou S et al (2020) Initial CT findings and temporal changes in patients with the novel coronavirus pneumonia (2019-nCoV): a study of 63 patients in Wuhan, China. Eur Radiol. 10.1007/s00330-020-06731-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 17.Yoon S, Lee K, Kim J et al (2020) Chest radiographic and CT findings of the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): analysis of nine patients treated in Korea. Korean J Radiol. 10.3348/kjr.2020.0132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 18.Shi H, Han X, Jiang N et al (2020) Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet Infect Dis. 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30086-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 19.Song F, Shi N, Shan F et al (2020) Emerging coronavirus 2019-nCoV pneumonia. Radiology. 10.1148/radiol.2020200274
- 20.Pan F, Ye T, Sun P et al (2020) Time course of lung changes on chest CT during recovery from 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pneumonia. Radiology. 10.1148/radiol.2020200370
- 21.Ai T, Yang Z, Hou H et al (2020) Correlation of chest CT and RT-PCR testing in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: a report of 1014 cases. Radiology. 10.1148/radiol.2020200642 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 22.Ng M-Y, Lee EY, Yang J et al (2020) Imaging profile of the COVID-19 infection: radiologic findings and literature review. Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging. 10.1148/ryct.2020200034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23.Kunhua Li JW, Wu F, Guo D, Chen L, Zheng F, Li C (2020) The clinical and chest CT features associated with severe and critical COVID-19 pneumonia. Invest Radiol. 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000672 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X et al (2020) Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 25.Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y et al (2020) Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 26.Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon H, McLoud TC, Muller NL, Remy J. Fleischner Society: glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology. 2008;246:697–722. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2462070712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Xu Z, Shi L, Wang Y et al (2020) Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir Med. 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 28.Kanne JP (2020) Chest CT findings in 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections from Wuhan, China: key points for the radiologist. Radiology. 10.1148/radiol.2020200241 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 29.Ajlan AM, Ahyad RA, Jamjoom LG, Alharthy A, Madani TA. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection: chest CT findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;203:782–787. doi: 10.2214/AJR.14.13021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wong K, Antonio GE, Hui DS, et al. Thin-section CT of severe acute respiratory syndrome: evaluation of 73 patients exposed to or with the disease. Radiology. 2003;228:395–400. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2283030541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Xi Liu RW, Guoqiang Q, Wang Y et al (2020) A observational autopsy report of COVID-19 (Chinese). J Forensic Med 36:19–21
- 32.Kong W, Agarwal PP (2020) Chest imaging appearance of COVID-19 infection. Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging. 10.1148/ryct.2020200028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 33.Franquet T. Imaging of pulmonary viral pneumonia. Radiology. 2011;260:18–39. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11092149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Li X, Zeng X, Liu B, Yu Y (2020) COVID-19 infection presenting with CT halo sign. Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging. 10.1148/ryct.2020200026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 35.Kuhlman JE, Fishman EK, Siegelman S. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in acute leukemia: characteristic findings on CT, the CT halo sign, and the role of CT in early diagnosis. Radiology. 1985;157:611–614. doi: 10.1148/radiology.157.3.3864189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pinto PS. The CT halo sign. Radiology. 2004;230:109–110. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2301020649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zompatori M, Poletti V, Battista G, Diegoli M. Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia (BOOP), presenting as a ring-shaped opacity at HRCT (the atoll sign). A case report. Radiol Med. 1999;97:308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kim SJ, Lee KS, Ryu YH, et al. Reversed halo sign on high-resolution CT of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia: diagnostic implications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;180:1251–1254. doi: 10.2214/ajr.180.5.1801251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gasparetto EL, Escuissato DL, Davaus T, et al. Reversed halo sign in pulmonary paracoccidioidomycosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;184:1932–1934. doi: 10.2214/ajr.184.6.01841932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Xu RDM, Li L, Zhen Z, Wang H, Hu X (2020) CT imaging of one extended family cluster of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) including adolescent patients and “silent infection”. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 10.21037/qims.2020.02.13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 41.Kanne JP, Little BP, Chung JH, Elicker BM, Ketai LH (2020) Essentials for radiologists on COVID-19: an update—radiology scientific expert panel. Radiology. 10.1148/radiol.2020200527 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]