Abstract
Bacterial coinfections occur in respiratory viral infections, but the attack rates and the clinical profile are not clear. The aim of this study was to determine bacterial coinfections in children hospitalized for acute expiratory wheezing with defined viral etiology. A total of 220 children aged 3 months to 16 years were investigated. The viral etiology of wheezing was confirmed by viral culture, antigen detection, serologic investigation, and/or PCR. Specific antibodies to common respiratory bacteria were measured from acute and convalescent serum samples. All children were examined clinically for acute otitis media, and subgroups of children were examined radiologically for sinusitis and pneumonia. Rhinovirus (32%), respiratory syncytial virus (31%), and enteroviruses (31%) were the most common causative viruses. Serologic evidence of bacterial coinfection was found in 18% of the children. Streptococcus pneumoniae (8%) and Mycoplasma pneumoniae (5%) were the most common causative bacteria. Acute otitis media was diagnosed in 44% of the children. Chest radiographs showed alveolar infiltrates in 10%, and paranasal radiographs and clinical signs showed sinusitis in 17% of the older children studied. Leukocyte counts and serum C-reactive protein levels were low in a great majority of patients. Viral lower respiratory tract infection in children is often associated with bacterial-type upper respiratory tract infections. However, coexisting bacterial lower respiratory tract infections that induce systemic inflammatory response are seldom detected.
Keywords: Respiratory Syncytial Virus, Sinusitis, Acute Otitis Medium, Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection, Serologic Evidence
Introduction
Acute expiratory wheezing is a common problem in children. Studies using many different viral techniques have shown that up to 88% of cases of children with wheezing are associated with respiratory virus infections [1]. The detection of a respiratory virus does not mean that the child has only a viral infection. Acute otitis media (AOM) is a common bacterial coinfection that occurs in 20–60% of cases of different respiratory virus infections [2, 3]. The occurrences of other bacterial coinfections, sinusitis, and pneumonia are not well known. The dilemma in young children is that sensitive and specific laboratory methods for the detection of bacterial infections are not available or are used only in research.
In a prospective study on acute expiratory wheezing, we found evidence of respiratory virus infection in 88% of the children [4]. Here we report the occurrence of bacterial-type coinfections in hospitalized children with defined viral infection. Children were examined for bacterial infections during hospitalization by means of daily clinical examinations, serologic tests for bacteria, hematologic investigations, and chest and paranasal sinus radiographs.
Patients and methods
Study subjects
We investigated bacterial coinfections in wheezing children with defined viral infection as part of a randomized double-blind trial evaluating the efficacy of systemic corticosteroids in the treatment of viral wheezing. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Turku University Hospital and complies with the current laws of Finland.
From 1 September 2000 through 31 May 2002, a total of 293 children were enrolled in the study in the Department of Pediatrics, Turku University Hospital. Children were included if they were 3 months to 16 years of age, had been admitted for acute wheezing or exacerbation of asthma, and if their parents had provided written informed consent. Excluded were children with chronic diseases (other than asthma or allergy), systemic glucocorticoid treatment within 4 weeks prior to the study, severe wheezing necessitating intensive care unit treatment, and previous participation in this study. Of the 293 children randomized for the efficacy study, 35 children were excluded because no evidence of viral infection was obtained, a further 17 children because their parents refused to continue the study at the hospital or during the 2–3 weeks of follow-up after hospitalization, 18 because no convalescent serum sample was obtained, 2 because they were admitted to the intensive care unit, and 1 because of a lack of hematologic analysis. Thus, a total of 220 children, all of whom had laboratory evidence of viral infection, were included in this study.
The patients were randomized to receive oral prednisolone or placebo for 3 days. The study physician examined the patients twice a day during hospitalization, at 8–10 a.m. and 8–10 p.m. At the follow-up visit 2–3 weeks after discharge, a convalescent blood sample was taken and all children were examined by the study physician. During the 2-week follow-up period, the guardian recorded the administration of the study drug and the child's symptoms in a diary.
Definitions of wheezing
The first acute expiratory wheezing episode in children <12 months of age was called bronchiolitis. Recurrent wheezing was called “asthma” according to the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program’s (NAEPP) recommendations [5]. If the illness did not fulfill the criteria of bronchiolitis or asthma, it was called “wheezy bronchitis”.
Virologic methods
The details of the virologic methods and results have been published separately [4]. The etiologic role of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), rhinovirus, enteroviruses, human metapneumovirus, influenza A and B viruses, adenoviruses, coronavirus, and parainfluenza virus types 1, 2, and 3 was investigated by virus culture, antigen detection, serologic investigation, and/or PCR assay.
Bacteriologic methods
Bacterial antibody assays were performed on acute and convalescent serum samples (n=220). IgG antibodies to Streptococcus pneumoniae pneumolysin and C-polysaccharide were measured by EIA, and a twofold or higher rise in antibody titers between paired serum samples was considered diagnostic [6]. Antibodies to nontypable Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis were detected by EIA using whole bacterial cell antigen, and a threefold or higher antibody rise between paired serum samples was considered diagnostic of acute infection [7]. IgM antibodies to Mycoplasma pneumoniae were measured from acute and convalescent serum samples by two commercial EIA kits (Serion Immunodiagnostica, Wurzburg, Germany, from September 2000 to February 2001, and Ani Labsystems, Helsinki, Finland, from March 2001 to June 2002). The presence of IgM antibodies in both serum samples or in only the second sample was considered indicative of an acute infection [8]. IgG, IgA, and IgM antibodies to chlamydial species were studied using a microimmunofluorescence method. The presence of IgM antibodies and/or a fourfold or greater change in IgG levels between paired serum samples was considered to indicate acute Chlamydia pneumoniae infection [9]. Antibodies were also measured using the EIA method (Ani Labsystems), and the presence of IgM antibodies and/or a 1.5-fold or greater change in IgG or IgA levels between paired serum samples was considered a diagnostic finding.
Hematologic methods
On admission, venous blood (n=220) was taken for determining total leukocyte count and the concentration of serum C-reactive protein (CRP, nephelometric method).
Assessment of clinical coinfections
The diagnostic criteria for AOM included the presence of middle ear effusion verified by pneumatic otoscopy, combined with at least one acute pathologic sign of a tympanic membrane: erythema, opacification, bulging, or fullness. The diagnosis of pneumonia was based on infiltrates on the chest radiograph. Findings were classified according to alveolar (dense fluffy opacity/consolidation) and/or interstitial (ill-defined diffuse opacity of interstitium) changes. During the second study year, posteroanterior and lateral chest radiographs were obtained from 102 of 108 (September 2001–June 2002) consecutive children. The findings were classified as alveolar and/or interstitial changes [10]. A plain radiograph of paranasal sinuses (occipitomental view) was taken at the follow-up visit 2–3 weeks after discharge from the hospital in 48 of 51 consecutive (October 2000–June 2002) children aged ≥3 years. Children with respiratory symptoms that persisted for >10 days and whose maxillary sinus radiograph showed a minimum mucosal thickening of ≥4 mm, total opacity, or an air-fluid level were classified as having sinusitis [11, 12]. All radiographs were reviewed by a pediatric radiologist.
Statistical analyses
Comparisons of the proportions were analyzed by the chi-squared test. The Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare differences between continuous variables. Statistical significance was established at a p level of <0.05; all p values were two-sided. The analyses were performed using SPSS/PC+ software (version 11.5; SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA).
Results
Table 1 shows the characteristics of the study children.
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of 220 study children with acute viral wheezing
| Age group | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 3–11 months (n=52) | 12–35 months (n=117) | ≥36 months (n=51) | |
| Clinical diagnosis | |||
| Bronchiolitis, no. (%) | 41 (79) | ||
| Wheezy bronchitis, no. (%) | 10 (19) | 96 (82) | 41 (80) |
| Acute asthma, no. (%) | 1 (2) | 21 (18) | 10 (20) |
| Acute otitis media | 34 (65) | 57 (49) | 5 (6) |
| Acute sinusitisa | 8 (17) | ||
| Alveolar pneumoniab | 3/30 (10) | 5/46 (11) | 2/26 (8) |
| Atopy, no. (%) | 3 (6) | 44 (38) | 36 (71) |
| Temperature >38.0°C on admission, no. (%) | 10 (19) | 27 (23) | 8 (16) |
| Duration of respiratory signs and symptoms on admission, median days (range) | 4 (1–28) | 3 (0–28) | 3 (1–11) |
| Duration of hospitalization, median days (range) | 1.9 (0.5–6.1) | 1.5 (0.5–8.7) | 1.3 (0.4–2.7) |
| Duration of symptoms after hospitalization, median days (range) | 4 (0–14) | 6 (0–20) | 6 (0–20) |
| Total duration of respiratory signs and symptoms, median days (range) | 12 (4–37) | 11 (1.8–117) | 11 (2.9–23) |
| Prednisolone treatment during hospitalization, no. (%) | 28 (54) | 61 (52) | 25 (49) |
| Antibiotic treatment, no. (%) | 37 (71) | 67 (57) | 13 (25) |
a48 patients ≥3 years were studied
b102 patients were studied
Virologic findings
Rhinovirus (32%), RSV (31%), enteroviruses (31%), and nontypable rhino/enterovirus (13%) were the most common causative agents detected. Originally, there were 43 cases of infection with nontypable picornavirus. A subsequent sequence analysis showed that 15 of them were rhinoviruses. As a sole etiologic agent, rhinovirus was detected in 25%, enteroviruses in 20%, and RSV in 18% of the subjects (Table 2) [4].
Table 2.
Serologic findings in 220 children with acute viral wheezing
| Organism | No. with viral wheezing | No. (%) with bacterial infection | Total no. (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. pneumoniae | H. influenzae | M. catarrhalis | C. pneumoniae | M. pneumoniae | |||
| Respiratory syncytial virus | 40 | 4a (10) | 1a (3) | 1 (3) | 1 (3) | 1 (3) | 8 (20) |
| Picornaviruses | 117 | 11 (9) | 2 (2) | 1 (1) | 4 (3) | 8 (7) | 26 (22) |
| Rhinovirus | 54 | 6 (11) | 1 (2) | 0 (0) | 1 (2) | 4 (7) | 12 (22) |
| Enteroviruses | 44 | 4 (9) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (7) | 2 (5) | 9 (21) |
| Nontypable picornaviruses | 19 | 1b (5) | 1c (5) | 1b (5) | 0 (0) | 2c (11) | 5 (26) |
| Other virusesd | 10 | 1 (10) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (0) | 2 (20) |
| Mixed viral infection | 53 | 1 (2) | 2 (4) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | 1 (2) | 6 (11) |
| Total | 220 | 17 (8) | 5 (2) | 3 (1) | 6 (3) | 11 (5) | 39 (18) |
aDual bacterial infection, H. influenzae and S. pneumoniae
bDual bacterial infection, M. catarrhalis and S. pneumoniae
cDual bacterial infection, H. influenzae and M. pneumoniae
dIncludes 4 human metapneumoviruses, 2 parainfluenza virus types 1–3, 3 adenoviruses, and 1 influenza A virus
Bacterial infections
Serologic evidence of bacterial coinfection was found in 39 of the 220 (18%) children with viral acute expiratory wheezing (Table 2). S. pneumoniae (8%), M. pneumoniae (5%), C. pneumoniae (3%), nontypable H. influenzae (2%), and M. catarrhalis (1%) were the causative agents. Three children had dual bacterial infections.
Hematologic findings
On admission, the median leukocyte count of the 220 children was 10.7×109/l (range 3.8–25.2×109/l) and the median CRP value 11 mg/l (range <1.0–191 mg/l). A leukocyte count ≥20.0×109/l was recorded in four (2%) children (Fig. 1); one of them had an M. pneumoniae infection. Six (2%) children had a CRP level ≥80 mg/l. One of these children had serologic evidence of bacterial infection (C. pneumoniae). No other bacterial infections were detected in children with high leukocyte counts or CRP levels. The leukocyte counts and CRP levels of children with serologically verified bacterial infections did not differ from those of children with nonbacterial infections (medians 11.0×109/l vs. 10.7×109/l; 9 vs. 12 mg/l, respectively).
Fig. 1.
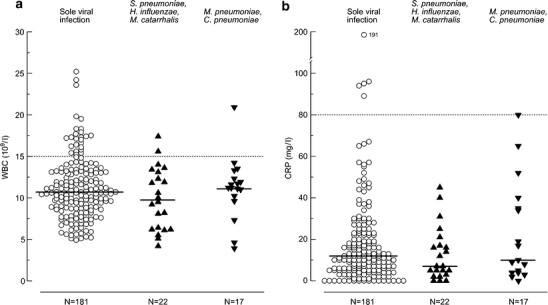
a Leukocyte counts and b CRP levels of 220 study children with acute viral wheezing (solid lines are medians; dashed lines are commonly used cutoff points for viral and bacterial infections)
Clinical profile of coinfections
AOM was diagnosed in 96 of 220 (44%) children (Table 3). On admission, 62 of 96 (65%) children had AOM; a further 25 (26%) developed AOM during hospitalization, and another 9 (9%) developed it during the 2–3 weeks of follow-up. Serologic investigation for the bacteria S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, or M. catarrhalis was positive in 11 of 96 (11%) children with AOM compared to 12 of 124 (10%) children without AOM.
Table 3.
Clinical profile of coinfections in 220 children with acute viral wheezing
| Type of virus | No. of children studied | No. (%) of virus-positive children with bacterial infection | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute otitis mediaa | Interstitial pneumonia (n=102 studied) | Alveolar pneumoniab (n=102 studied) | Sinusitis (n=48 studied) | ||
| Respiratory syncytial virus | 40 | 28 (70) | 29 (94) | 5 (16) | 1 (33) |
| Picornaviruses | 117 | 37 (32) | 42 (93) | 4 (9) | 5 (14) |
| Rhinovirus | 54 | 18 (33) | 15 (94) | 1 (6) | 3 (25) |
| Enteroviruses | 44 | 14 (32) | 16 (94) | 3 (18) | 2 (13) |
| Nontypable picornaviruses | 19 | 5 (26) | 11 (92) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Other virusesc | 10 | 4 (40) | 2 (100) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) |
| Mixed viruses | 53 | 27 (51) | 21 (88) | 0 (0) | 2 (25) |
| Total | 220 | 96 (44) | 94 (92) | 10 (10) | 8 (17) |
aNine children developed acute otitis media during the 2–3 weeks of follow-up
bAll these children also had interstitial infiltrates
cIncludes 4 human metapneumoviruses, 2 parainfluenza virus types 1–3, 3 adenoviruses, and 1 influenza A virus
Chest radiographs showed interstitial infiltrates in 94 of 102 (92%) children (Table 3). Ten of these 94 (10%) children also had alveolar infiltrates. In addition, atelectasis was found in 51%, enlarged lymph nodes in 42%, hyperaeration in 35%, and pleural fluid in 1% of the children. No cases of alveolar pneumonia alone or of lobar alveolar consolidation alone were seen. Of the ten children with alveolar pneumonia, three had serologic evidence of bacterial infection (C. pneumoniae in 2 and S. pneumoniae in 1). Paranasal radiographs at the follow-up visit showed total opacity in 9 and mucosal thickening of ≥4 mm in 4 of the 48 children ≥3 years of age studied. Eight of these children (17% of the 48 studied) had respiratory signs and symptoms at the follow-up visit that fulfilled criteria for clinical sinusitis. None of the children with sinusitis had positive serologic findings for bacteria.
Antibiotic treatment was given in the hospital to 102 of 220 (46%) children: 87 for AOM and 20 for pneumonia (five children had both AOM and pneumonia). During the 2-week follow-up period, another 17 (8%) children were treated with antibiotics: 8 for AOM, 3 for sinusitis, 3 for M. pneumoniae infection, and 3 for C. pneumoniae infection.
Effects of prednisolone treatment
Prednisolone treatment had no effect on the results of serologic tests for S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, or M. catarrhalis and no effect on the development of AOM or sinusitis (data not shown).
Discussion
We found that half of the children with acute viral wheezing had AOM, and one-fifth of the older children developed sinusitis during recovery from viral wheezing. However, although all children had a viral lower respiratory tract infection, only 3% of them developed bacterial-type pneumonia. One-fifth of the children had serologic evidence of a concomitant bacterial infection. High leukocyte counts and high serum CRP levels were recorded in only a few cases. Clinically, antibiotic treatment was considered indicated in half of the children, mainly due to AOM.
AOM was the most common bacterial-type complication in children with viral wheezing. Although development of AOM is closely associated with viral respiratory infections, it is generally considered a bacterial infection, since bacteria can be cultured from middle ear fluid in up to 90% of the children [13]. Clinically, it was important to note that, on admission, when the median duration of illness was 3 days, only 65% of the cases of AOM were detected and the rest were found during the follow-up period. In a previous study of the temporal development of AOM, we showed that 54% of AOM cases develop during the first 4 days after the onset of respiratory infection and 75% during the first week of illness [14]. Our findings of viral dependence agree with previous studies. RSV infection is the major risk factor for AOM; in this study, 70% of the children with RSV infection developed AOM [2, 3]. A novel observation was that enterovirus infection can be associated with AOM in one-third of the cases [15].
Most patients with viral respiratory tract infection develop radiologic sinusitis during the acute phase of the illness, and it has been suggested that this be called “viral sinusitis” [16]. In children, bacterial sinusitis should be suspected clinically if the symptoms of respiratory infection last for ≥10 days [12]. In young children, a great problem is that paranasal radiographs do not detect the opacity or mucosal thickness of the maxillary sinuses due to the similar density of the adjacent bone structures. For these two reasons, we only studied children ≥3 years of age, and we examined them 2 weeks after the acute illness. Even then, one-sixth of the children studied showed radiologic and clinical evidence of sinusitis. These findings raise questions about whether all these children with symptomatic sinusitis have a bacterial infection and whether they should be systematically identified and treated with antibiotics.
In earlier studies, 6–9% of children with a first episode of wheezing had had a pathologic chest radiograph [17]. We found no cases of lobar alveolar consolidation on chest radiographs, suggesting that typical bacterial pneumonia is a rare complication of viral wheezing. Three children had serologic evidence of bacterial infection and alveolar infiltrates. Nearly all children studied had minor interstitial infiltrates, suggesting that acute wheezing may present a prototype of viral pneumonia in children. This is further supported by the finding that pneumonic crackles can be often heard on auscultation in children with wheezing [17, 18]. The chest radiograph may not be sensitive enough to show the whole profile of lung infiltrates as seen in adults with pneumonia [19]. In clinical practice, chest radiographs should not be routinely performed in wheezy children, since they do not improve treatment results and may lead to inappropriate antibiotic use.
S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, and M. catarrhalis are the most common causes of bacterial respiratory tract infections in children. They can seldom be cultured from the blood, and invasive procedures such as tympanocentesis, maxillary sinus puncture, or lung tap are not beneficial and are not used in clinical practice. Measurement of antibody responses to these bacteria offers a noninvasive approach. Several studies have shown that 30–70% of children with pneumonia develop IgG antibodies against these bacteria, and measurements of specific antibody responses have been used in research [10, 20–23]. Very few patients with viral upper respiratory tract infection develop serologic responses to bacteria. For example, none of 26 children with parainfluenza virus-induced laryngitis [24] and 2 of 200 young adults with the common cold, usually caused by rhinovirus [25], showed a serologic response. This suggests that respiratory viral infections do not provide a nonspecific immune stimulation. Furthermore, only 2.7% of the 148 asymptomatic children had a significant increase in antibodies to S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, or M. catarrhalis in paired serum samples obtained 1 month apart [26].
The main problem, however, is still the lack of a gold standard with which the serologic results could be compared. In this study, 10% of the children with viral lower respiratory tract infection developed IgG antibodies to one of these three bacteria, suggesting that bacterial lower respiratory tract coinfections are rare. This finding is in agreement with radiologic findings of a low occurrence of alveolar infiltrates and a lack of lobar consolidations. In this study, AOM and sinusitis seldom induced bacterial antibody responses [27]. Rapola et al. [28] have reported development of antipneumolysin antibodies after pneumococcal carriage and pneumococcal AOM. M. pneumoniae and C. pneumoniae infections were detected in 8% of the children. Using PCR, Freymuth et al. [29] detected M. pneumoniae and C. pneumoniae in 8% of 132 children with acute exacerbation of asthma. In contrast, Esposito et al. [30], using serologic investigation and PCR, demonstrated M. pneumoniae in 22.5% and C. pneumoniae in 15.5% of children with acute wheezing [30]. Recently, Biscardi et al. [31] found M. pneumoniae infection in 20% and C. pneumoniae infection in 3.4% of 119 children hospitalized for severe asthma, and the benefits of antibiotic treatment were questioned.
Total leukocyte counts and serum CRP levels are generally used for differentiating a bacterial infection from a viral one. In the great majority of viral infections, the leukocyte count is <15×109/l and serum CRP level <80 mg/l, as also seen in this study [16, 32, 33]. Only a few patients had markedly increased leukocyte counts and CRP levels, supporting the concept of the rarity of invasive bacterial coinfections. No patient had both increased leukocyte counts and CRP levels.
Although we used the best possible efforts to detect bacterial infection, it is important to emphasize the limitations of this study. PCR methods to detect C. pneumoniae and M. pneumoniae were not used. The etiology of AOM and sinusitis were not studied microbiologically, and some of these infections may have been solely viral infections. In addition, some of our bacterial serologic tests are used only for research purposes, and their clinical value is not fully understood.
In conclusion, viral lower respiratory tract infection in children is seldom complicated by invasive bacterial infection. Coexisting bacterial-type upper respiratory tract infections, however, are common.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Pediatric Research Foundation, Finland, and the Academy of Finland.
References
- 1.Rawlinson WD, Waliuzzaman Z, Carter IW, Belessis YC, Gilbert KM, Morton JR. Asthma exacerbations in children associated with rhinovirus but not human metapneumovirus infection. J Infect Dis. 2003;187:1314–1318. doi: 10.1086/368411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ruuskanen O, Arola M, Putto-Laurila A, Mertsola J, Meurman O, Viljanen MK, Halonen P. Acute otitis media and respiratory virus infections. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989;8:94–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vesa S, Kleemola M, Blomqvist S, Takala A, Kilpi T, Hovi T. Epidemiology of documented viral respiratory infections and acute otitis media in a cohort of children followed from two to twenty-four months of age. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20:574–581. doi: 10.1097/00006454-200106000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jartti T, Lehtinen P, Vuorinen T, Österback R, van den Hoogen B, Osterhaus AD, Ruuskanen O. Respiratory picornaviruses and respiratory syncytial virus as causative agents of acute expiratory wheezing in children. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:1095–1101. doi: 10.3201/eid1006.030629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Expert panel report: guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma: update on selected topics 2002. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110:S141–S219. doi: 10.1016/S0091-6749(02)80002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jalonen E, Paton JC, Koskela M, Kerttula Y, Leinonen M. Measurement of antibody responses to pneumolysin—a promising method for the presumptive aetiological diagnosis of pneumococcal pneumonia. J Infect. 1989;19:127–134. doi: 10.1016/S0163-4453(89)91864-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Burman LA, Leinonen M, Trollfors B. Use of serology to diagnose pneumonia caused by nonencapsulated Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis. J Infect Dis. 1994;170:220–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.1.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Waris ME, Toikka P, Saarinen T, Nikkari S, Meurman O, Vainionpää R, Mertsola J, Ruuskanen O. Diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:3155–3159. doi: 10.1128/jcm.36.11.3155-3159.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dowell SF, Peeling RW, Boman J, Carlone GM, Fields BS, Guarner J, Hammerschlag MR, Jackson LA, Kuo C, Maass M, Messmer TO, Talkington DF, Tondella ML, Zaki SR, C. pneumoniae Workshop Participants Standardizing Chlamydia pneumoniae assays: recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (USA) and the Laboratory Centre for Disease Control (Canada) Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33:492–503. doi: 10.1086/322632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Virkki R, Juven T, Rikalainen H, Svedström E, Mertsola J, Ruuskanen O. Differentiation of bacterial and viral pneumonia in children. Thorax. 2002;57:438–441. doi: 10.1136/thorax.57.5.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wald ER, Milmoe GJ, Bowen A, Ledesma-Medina J, Salamon N, Bluestone CD. Acute maxillary sinusitis in children. N Engl J Med. 1981;304:749–754. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103263041302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ueda D, Yoto Y. The ten-day mark as a practical diagnostic approach for acute paranasal sinusitis in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1996;15:576–579. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199607000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Del Beccaro MA, Mendelman PM, Inglis AF, Richardson MA, Duncan NO, Clausen CR, Stull TL. Bacteriology of acute otitis media: a new perspective. J Pediatr. 1992;120:81–84. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(05)80605-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Heikkinen T, Ruuskanen O. Temporal development of acute otitis media during upper respiratory tract infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1994;13:659–661. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199407000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ruohola A, Heikkinen T, Waris ME, Puhakka T, Ruuskanen O. Intranasal fluticasone propionate does not prevent acute otitis media during viral upper respiratory infection in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;106:467–471. doi: 10.1067/mai.2000.108912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Puhakka T, Mäkelä MJ, Alanen A, Kallio T, Korsoff L, Arstila P, Leinonen M, Pulkkinen M, Suonpää J, Mertsola J, Ruuskanen O. Sinusitis in the common cold. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998;102:403–408. doi: 10.1016/S0091-6749(98)70127-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Walsh-Kelly CM, Hennes HM. Do clinical variables predict pathologic radiographs in the first episode of wheezing? Pediatr Emerg Care. 2002;18:8–11. doi: 10.1097/00006565-200202000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wainwright C, Altamirano L, Cheney M, Cheney J, Barber S, Price D, Moloney S, Kimberley A, Woolfield N, Cadzow S, Fiumara F, Wilson P, Mego S, VandeVelde D, Sanders S, O’Rourke P, Francis P. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial of nebulized epinephrine in infants with acute bronchiolitis. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:27–35. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Syrjälä H, Broas M, Suramo I, Ojala A, Lähde S. High-resolution computed tomography for the diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;27:358–363. doi: 10.1086/514675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Heiskanen-Kosma T, Korppi M, Jokinen C, Kurki S, Heiskanen L, Juvonen H, Kallinen S, Sten M, Tarkiainen A, Rönnberg PR, Kleemola M, Mäkelä PH, Leinonen M. Etiology of childhood pneumonia: serologic results of a prospective, population-based study. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998;17:986–991. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199811000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wubbel L, Muniz L, Ahmed A, Trujillo M, Carubelli C, McCoig C, Abramo T, Leinonen M, McCracken GH., Jr Etiology and treatment of community-acquired pneumonia in ambulatory children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1999;18:98–104. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199902000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Juven T, Mertsola J, Waris M, Leinonen M, Meurman O, Roibainen M, Eskola J, Saikku P, Ruuskanen O. Etiology of community-acquired pneumonia in 254 hospitalized children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000;19:293–298. doi: 10.1097/00006454-200004000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Michelow IC, Lozano J, Olsen K, Goto C, Rollins NK, Ghaffar F, Rodriguez-Cerrato V, Leinonen M, McCracken GH Jr (2002) Diagnosis of Streptococcus pneumoniae lower respiratory infection in hospitalized children by culture, polymerase chain reaction, serological testing, and urinary antigen detection. Clin Infect Dis 34:e1-e11, (http://www.journals.uchicago.edu/CID/journal/issues/v34n1/010294/010294.html) [DOI] [PubMed]
- 24.Korppi M, Launiala K, Leinonen M, Häkelä PH. Bacterial involvement in laryngeal infections in children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1990;79:564–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1990.tb11513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mäkelä MJ, Puhakka T, Ruuskanen O, Leinonen M, Saikku P, Kimpimäki M, Blomqvist S, Hyypiä T, Arstila P. Viruses and bacteria in the etiology of the common cold. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:539–542. doi: 10.1128/jcm.36.2.539-542.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nohynek H, Eskola J, Kleemola M, Jalonen E, Saikku P, Leinonen M. Bacterial antibody assays in the diagnosis of acute lower respiratory tract infection in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1995;14:478–484. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199506000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Virolainen A, Jero J, Chattopadhyay P, Karma P, Eskola J, Leinonen M. Comparison of serum antibodies to pneumolysin with those to pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides in children with acute otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1996;15:128–133. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199602000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rapola S, Jäntti V, Haikala R, Syrjänen R, Carlone GM, Sampson JS, Briles DE, Paton JC, Takala AK, Kilpi TM, Käyhty H. Natural development of antibodies to pneumococcal surface protein A, pneumococcal surface adhesin A, and pneumolysin in relation to pneumococcal carriage and acute otitis media. J Infect Dis. 2000;182:1146–1152. doi: 10.1086/315822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Freymuth F, Vabret A, Brouard J, Toutain F, Verdon R, Petitjean J, Gouarin S, Duhamel J, Guillois B. Detection of viral, Chlamydia pneumoniae and Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in exacerbations of asthma in children. J Clin Virol. 1999;13:131–139. doi: 10.1016/S1386-6532(99)00030-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Esposito S, Blasi F, Arosio C, Fioravanti L, Fagetti L, Droghetti R, Tarsia P, Allegra L, Principi N. Importance of acute Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae infections in children with wheezing. Eur Respir J. 2000;16:1142–1146. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3003.2000.16f21.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Biscardi S, Lorrot M, Marc E, Moulin F, Boutonnat-Faucher B, Heilbronner C, Iniquez JL, Chaussain M, Nicand E, Raymond J, Gendrel D. Mycoplasma pneumoniae and asthma in children. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:1341–1346. doi: 10.1086/392498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ruuskanen O, Putto A, Sarkkinen H, Meurman O, Irjala K. C-reactive protein in respiratory virus infections. J Pediatr. 1985;107:97–100. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(85)80624-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Putto A, Ruuskanen O, Meurman O, Ekblad H, Korvenranta H, Mertsola J, Peltola H, Sarkkinen H, Viljanen MK, Halonen P. C-reactive protein in the evaluation of febrile illness. Arch Dis Child. 1986;61:24–29. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


