Abstract
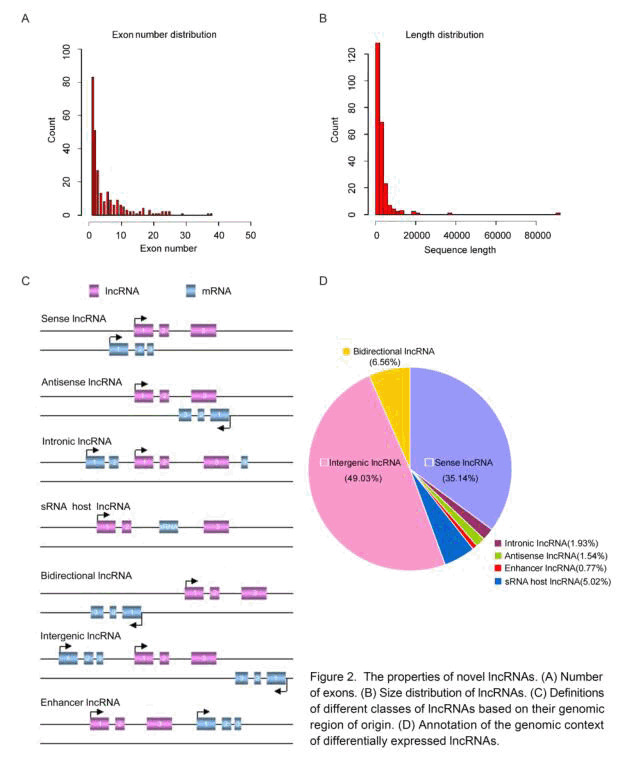
Coxsackievirus A16 (CVA16) is one of major pathogens of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) in children. Long non-coding RNAs (IncRNAs) have been implicated in various biological processes, but they have not been associated with CVA16 infection. In this study, we comprehensively characterized the landscape of IncRNAs of normal and CVA16 infected rhabdomyosarcoma (RD) cells using RNA-Seq to investigate the functional relevance of IncRNAs. We showed that a total of 760 IncRNAs were upregulated and 1210 IncRNAs were downregulated. Out of these dysregulated IncRNAs, 43.64% were intergenic, 22.31% were sense, 15.89% were intronic, 8.67% were bidirectional, 5.59% were antisense, 3.85% were sRNA host IncRNAs and 0.05% were enhancer. Six dysregulated IncRNAs were validated by quantitative PCR assays and the secondary structures of these IncRNAs were projected. Moreover, we conducted a bioinformatics analysis of an IncRNAs (ENST00000602478) to elucidate the diversity of modification and functions of IncRNAs. In summary, the current study compared the dysregulated IncRNAs profile upon CVA16 challenge and illustrated the intricate relationship between coding and IncRNAs transcripts. These results may not only provide a complete picture of transcription in CVA16 infected cells but also provide novel molecular targets for treatments of HFMD.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary material is available for this article at 10.1007/s12250-015-3693-1 and is accessible for authorized users.
Keywords: Coxsackievirus A16 (CVA16), RNA-Seq, Long non-coding RNA(IncRNA), gene expression
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary material, approximately 3505 KB.
Supplementary material, approximately 244 KB.
Supplementary material, approximately 1.89 MB.
Supplementary material, approximately 420 KB.
Supplementary material, approximately 236 KB.
Footnotes
ORCID: 0000-0003-3271-4342
References
- Alvarez-Dominguez J R, Hu W, Yuan B, Shi J, Park S S, Gromatzky A A, Van Oudenaarden A, Lodish H F. Global discovery of erythroid long noncoding RNAs reveals novel regulators of red cell maturation. Blood. 2014;123:570–581. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-10-530683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertone P, Stolc V, Royce T E, Rozowsky J S, Urban A E, Zhu X, Rinn J L, Tongprasit W, Samanta M, Weissman S, et al. Global identification of human transcribed sequences with genome tiling arrays. Science. 2004;306:2242–2246. doi: 10.1126/science.1103388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake JA, Harris MA. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2008. The Gene Ontology (GO) project: structured vocabularies for molecular biology and their application to genome and expression analysis. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borodina T, Adjaye J, Sultan M. A strand-specific library preparation protocol for RNA sequencing. Methods Enzymol. 2011;500:79–98. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385118-5.00005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bu Q, Hu Z, Chen F, Zhu R, Deng Y, Shao X, Li Y, Zhao J, Li H, Zhang B, et al. Transcriptome analysis of long non-coding RNAs of the nucleus accumbens in cocaine-conditioned mice. J Neurochem. 2012;123:790–799. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X, Tan X, Li J, Jin Y, Gong L, Hong M, Shi Y, Zhu S, Zhang B, Zhang S, et al. Molecular epidemiology of coxsackievirus A16: intratype and prevalent intertype recombination identified. PLoS One. 2013;8:e82861. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z, Luo Y, Yang W, Ding L, Wang J, Tu J, Geng B C, Yang J. Comparison Analysis of Dysregulated IncRNAs Profile in Mouse Plasma and Liver after Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0133462. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinger ME, Amaral PP, Mercer TR, Pang KC, Bruce SJ, Gardiner BB, Askarian-Amiri ME, Ru K, Solda G, Simons C, et al. Long noncoding RNAs in mouse embryonic stem cell pluripotency and differentiation. Genome Res. 2008;18:1433–1445. doi: 10.1101/gr.078378.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djebali S, Davis C A, Merkel A, Dobin A, Lassmann T, Mortazavi A, Tanzer A, Lagarde J, Lin W, Schlesinger F, et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature. 2012;489:101–108. doi: 10.1038/nature11233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du J, Yuan Z, Ma Z, Song J, Xie X, Chen Y. KEGG-PATH: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes-based pathway analysis using a path analysis model. Mol Biosyst. 2014;10:2441–2447. doi: 10.1039/c4mb00287c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteller M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:861–874. doi: 10.1038/nrg3074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fatica A, Bozzoni I. Long non-coding RNAs: new players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15:7–21. doi: 10.1038/nrg3606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez JA, Wapinski OL, Yang YW, Bureau JF, Gopinath S, Monack DM, Chang HY, Brahic M, Kirkegaard K. The NeST long ncRNA controls microbial susceptibility and epigenetic activation of the interferon-gamma locus. Cell. 2013;152:743–754. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong C, Maquat LE. IncRNAs transactivate STAU1-mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 3' UTRs via Alu elements. Nature. 2011;470:284–288. doi: 10.1038/nature09701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guil S, Esteller M. Cis-acting noncoding RNAs: friends and foes. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012;19:1068–1075. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y, Liu N, Wang JP, Wang YQ, Yu XL, Wang ZB, Cheng XC, Zou Q. Regulatory long non-coding RNA and its functions. J Physiol Biochem. 2012;68:611–618. doi: 10.1007/s13105-012-0166-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josset L, Tchitchek N, Gralinski L E, Ferris M T, Eisfeld A J, Green RR, Thomas MJ, Tisoncik-Go J, Schroth GP, Kawaoka Y, et al. Annotation of long non-coding RNAs expressed in collaborative cross founder mice in response to respiratory virus infection reveals a new class of interferon-stimulated transcripts. RNA Biol. 2014;11:875–890. doi: 10.4161/rna.29442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapranov P, Cheng J, Dike S, Nix DA, Duttagupta R, Willingham AT, Stadler PF, Hertel J, Hackermuller J, Hofacker IL, et al. RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science. 2007;316:1484–1488. doi: 10.1126/science.1138341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornienko AE, Guenzl PM, Barlow DP, Pauler FM. Gene regulation by the act of long non-coding RNA transcription. BMC Biol. 2013;11:59. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-11-59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee JT. Epigenetic regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Science. 2012;338:1435–1439. doi: 10.1126/science.1231776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao Q, Wang Y, Yao X, Bian L, Wu X, Xu M, Liang Z. Coxsackievirus A16: epidemiology, diagnosis, and vaccine. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10:360–367. doi: 10.4161/hv.27087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattick JS. The central role of RNA in human development and cognition. FEBS Lett. 2011;585:1600–1616. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattick JS, Makunin IV. Hum Mol Genet. 2006. Non-coding RNA; p. 15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Mattick JS. Long non-coding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10:155–159. doi: 10.1038/nrg2521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang J, Zhu X, Chen Y, Wei H, Chen Q, Chi X, Qi B, Zhang L, Zhao Y, Gao GF, et al. NRAV, a long noncoding RNA, modulates antiviral responses through suppression of interferonstimulated gene tran-scription. Cell Host Microbe. 2014;16:616–626. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.10.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng X, Gralinski L, Armour CD, Ferris MT, Thomas MJ, Proll S, Bradel-Tretheway BG, Korth MJ, Castle JC, Biery MC, et al. MBio. 2010. Unique signatures of long noncoding RNA expression in response to virus infection and altered innate immune signaling; p. 1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren J, Wang X, Zhu L, Hu Z, Gao Q, Yang P, Li X, Wang J, Shen X, Fry EE, et al. Structures of coxsackievirus A16 capsids with native antigenicity, implications for particle expansion, receptor binding and immunogenicity. J Virol. 2015;89:10500–10511. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01102-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybarczyk A, Szostak N, Antczak M, Zok T, Popenda M, Adamiak R, Blazewicz J, Szachniuk M. New in silico approach to assessing RNA secondary structures with non-canonical base pairs. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015;16:276. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0718-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y, He X, Zhu G, Tu H, Liu Z, Li W, Han S, Yin J, Peng B, Liu W. Coxsackievirus A16 elicits incomplete autophagy involving the mTOR and ERK pathways. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0122109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Zhou L. Molecular phylogeny of coxsackievirus A16. J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52:3829–3830. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01330-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tafer H, Hofacker IL. RNAplex: a fast tool for RNA-RNA interaction search. Bioinformatics. 2008;24:2657–2663. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg S L. TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1105–1111. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, Van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28:511–515. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang KC, Chang HY. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 2011;43:904–914. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L, Wang S, Li W. RSeQC: quality control of RNAseq experiments. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:2184–2185. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T, Tian C, Zhang W, Luo K, Sarkis PT, Yu L, Liu B, Yu Y, Yu XF. 7SL RNA mediates virion packaging of the antiviral cytidine deaminase APOBEC3G. J Virol. 2007;81:13112–13124. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00892-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei W, Guo H, Li J, Ren S, Wei Z, Bao W, Hu X, Zhao K, Zhang W, Zhou Y, et al. Circulating HFMD-associated coxsackievirus A16 is genetically and phenotypically distinct from the prototype CV-A16. PLoS One. 2014;9:e94746. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel A, Akbasli E, Gorodkin J. RIsearch: fast RNA-RNA interaction search using a simplified nearest-neighbor energy model. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:2738–2746. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterling C, Koch M, Koeppel M, Garcia-Alcalde F, Karlas A, Meyer TF. Evidence for a crucial role of a host non-coding RNA in influenza A virus replication. RNA Biol. 2014;11:66–75. doi: 10.4161/rna.27504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang KC, Yamada KA, Patel AY, Topkara VK, George I, Cheema FH, Ewald GA, Mann DL, Nerbonne JM. Deep RNA sequencing reveals dynamic regulation of myocardial noncoding RNAs in failing human heart and remodeling with mechanical circulatory support. Circulation. 2014;129:1009–1021. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.003863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu QS, Guo WS, Cheng LM, Lu YF, Shen JY, Li P. Glucocorticoids Significantly Influence the Transcriptome of Bone Microvascular Endothelial Cells of Human Femoral Head. Chin Med J (Engl) 2015;128:1956–1963. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.160564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Q, Chen CY, Yedavalli VS, Jeang KT. NEAT1 long noncoding RNA and paraspeckle bodies modulate HIV-1 posttranscriptional expression. MBio. 2013;4:e00596. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00596-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu G, Zheng Y, Zhang L, Shi Y, Li W, Liu Z, Peng B, Yin J, Liu W, He X. Coxsackievirus A16 infection triggers apoptosis in RD cells by inducing ER stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;441:856–861. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.10.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L, Zhu J, Liu Y, Chen Y, Li Y, Huang L, Chen S, Li T, Dang Y, Chen T. Methamphetamine induces alterations in the long non-coding RNAs expression profile in the nucleus accumbens of the mouse. BMC Neurosci. 2015;16:18. doi: 10.1186/s12868-015-0157-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material, approximately 3505 KB.
Supplementary material, approximately 244 KB.
Supplementary material, approximately 1.89 MB.
Supplementary material, approximately 420 KB.
Supplementary material, approximately 236 KB.


