Abstract
Recent suggestions of nanoscale heat confinement on the surface of synthetic and biogenic magnetic nanoparticles during heating by radio frequency-alternating magnetic fields have generated intense interest because of the potential utility of this phenomenon for noninvasive control of biomolecular and cellular function. However, such confinement would represent a significant departure from the classical heat transfer theory. Here, we report an experimental investigation of nanoscale heat confinement on the surface of several types of iron oxide nanoparticles commonly used in biological research, using an all-optical method devoid of the potential artifacts present in previous studies. By simultaneously measuring the fluorescence of distinct thermochromic dyes attached to the particle surface or dissolved in the surrounding fluid during radio frequency magnetic stimulation, we found no measurable difference between the nanoparticle surface temperature and that of the surrounding fluid for three distinct nanoparticle types. Furthermore, the metalloprotein ferritin produced no temperature increase on the protein surface nor in the surrounding fluid. Experiments mimicking the designs of previous studies revealed potential sources of the artifacts. These findings inform the use of magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia in engineered cellular and molecular systems.
Significance
This manuscript investigates the possibility of nanoscale heat confinement on the surface of iron oxide nanoparticles and the metalloprotein ferritin in a radio frequency-alternating magnetic field. Previous results suggesting such confinement have generated intense interest because of their implications for noninvasive control over cellular function in deep tissue but have also drawn skepticism owing to their departure from the well-established theory of heat diffusion. In this study, we provide a definitive answer to whether any such confinement occurs.
Introduction
The radio frequency heating of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) is an established technique for the ablative treatment of diseases such as cancer and an emerging tool in basic biological research. In a typical application of this method, radio frequency-alternating magnetic fields (RF-AMFs) are used to remotely heat a bolus of injected SPIONs in a tissue, raising the local temperature to a critical level to kill diseased cells or increase their sensitivity to chemotherapy or radiotherapy (1). As single-domain magnets, SPIONs can generate heat in response to RF-AMF stimulation via dissipative losses associated with rigid body rotation (Brownian relaxation) or internal magnetic realignment (Néel relaxation) (2, 3, 4, 5). Significant theoretical (6,7) and computational (8,9) work has been done to model the interplay of these relaxation mechanisms and their contribution to the heat generated by the particle. In an effort to use magnetic fields to control rather than kill specific cells, recent work has combined nanoparticle-based radio frequency hyperthermia in the well-tolerated temperature range of 37–42°C with the targeted expression of temperature-sensitive biomolecules such as the temperature-gated ion channel TRPV1 (10). This “magnetogenetic” approach enables RF-AMF to turn on calcium currents in cells, leading to activation of insulin secretion or neural circuit activity (11,12).
A key requirement for effective magnetogenetic manipulation is for the heat generated by SPIONs to be localized to the target cells and not appreciably affect surrounding tissue. However, the extent of this thermal confinement is a matter of considerable debate. It is widely accepted that a small bolus of particles generates a millimeter-scale heat diffusion zone during RF-AMF, affecting cells within this region and not outside it. In addition, several studies have suggested that heat is preferentially confined to the nanoscale vicinity of individual magnetic nanoparticles during RF-AMF stimulation, resulting in a large steady-state temperature gradient at the surface of the nanoparticle (10,13, 14, 15). Such nanoscale confinement would enable the actuation of thermal bioswitches attached to a SPION without significantly heating the rest of the cell. Further extending this concept, it has been proposed that genetically encoded magnetic nanoparticles such as ferritin, which produce insignificant bulk heating in response to RF-AMF because of their small magnetic coercivity, could nevertheless activate temperature-sensitive ion channels, to which they are tethered because of the heat-concentrating effect of thermal confinement (11,16).
Although millimeter-scale heat diffusion profiles are uncontroversial, the concept of nanoscale heat confinement near the surface of nanoparticles in aqueous suspension represents a significant departure from established heat transport theory (17). In a classical analysis, the steady-state temperature profile emanating from a spherical source can be predicted by Fourier’s heat diffusion law (18):
Here, Q is the heating power of the source, c is the thermal conductivity of the medium (0.64 W m−1 K−1 for water), r is the distance from the center of the source, and ΔT is the temperature above an infinitely far location in the bath. This continuum analysis is consistent with experimental and computational studies of heat transport from laser-heated gold nanoparticles in fluid, whose ability to generate over 100 nW of heat per particle results in a measurable temperature difference between the nanoscale vicinity of the particle surface and the bulk fluid bath (18, 19, 20, 21). However, when applied to SPIONs, which typically generate less than 30 fW of heat per particle under RF-AMF (22), Fourier’s law predicts a negligible temperature difference between the vicinity of a single particle and the bulk fluid (e.g., ΔT = 373 nK for Q = 30 fW and r = 10 nm in water). Thus, although the concerted action of many SPIONs in a ferrofluid effectively heats the bulk fluid, Fourier theory does not predict a measurable temperature gradient emanating from the surface of individual particles. When this analysis is extended to account for a finite thermal interface resistance at the particle surface, it also predicts a temperature discontinuity between the solid particle and the fluid, which is measurable for laser-heater gold nanoparticles (23). However, this effect would, again, have an exceedingly small magnitude for a 30-fW source, assuming an interface resistance in the range of previously characterized nanoparticle values (20,23).
Contradicting these predictions of Fourier’s law, several studies using optical thermometry at the surface of magnetic nanoparticles in RF-AMF have reported local heating of several K relative to the bulk (10,13,14). This literature is cited in magnetogenetics studies as a way to motivate and explain the biological results observed (11,16). However, given the direct conflict between these results and classical theory and the controversial reception of several recent works on magnetogenetics (17), a careful re-examination of the possibility of nonclassical heat confinement at the surface of SPIONs and ferritin and the potential artifacts confounding previous studies is greatly needed.
To address this need, we introduce an experimental approach allowing us to measure the temperature at the surface of magnetic nanomaterials and in surrounding fluid during RF-AMF application using a simultaneous all-optical readout with 0.1°C sensitivity (Fig. 1 a). Using this approach, we measure three different types of SPIONs representing a range of sizes, core compositions, and surface chemistries, revealing no measurable difference in temperature between the particle surface and the bulk solution during RF-AMF heating. Meanwhile, ferritin fails to show any heat generation. These results suggest that nanomagnetic hyperthermia follows the classical heat transfer theory. Additional experiments recapitulating previous measurement approaches reveal potential sources of artifacts that could be misinterpreted as nonclassical thermal confinement.
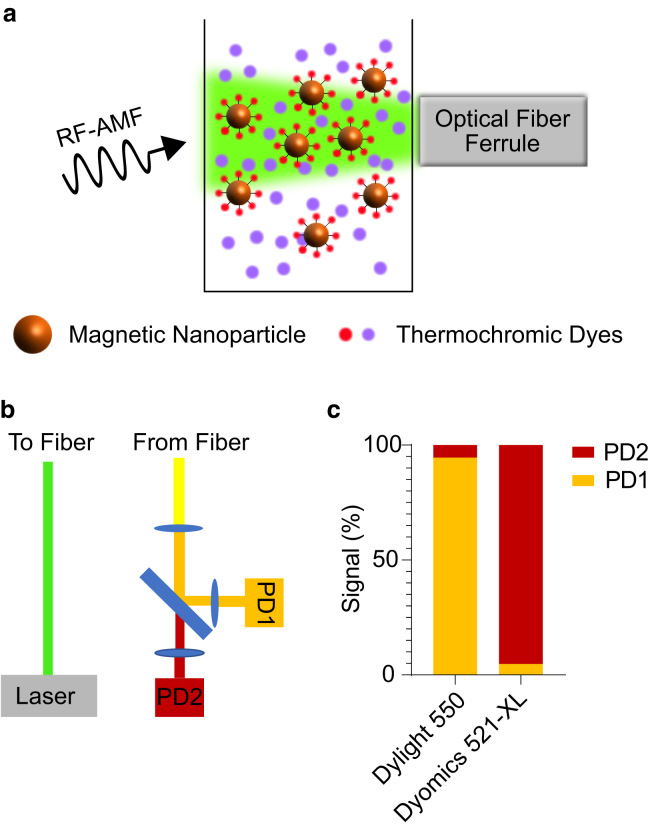
Figure 1.
Nanoscale thermometry during magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia. (a) A diagram of the experimental setup involving the simultaneous optical measurement of the temperature of the nanoparticle surface and surrounding fluid during radio frequency-alternating magnetic field (RF-AMF) application using thermochromic dyes as nanoscale temperature probes is shown. (b) A diagram of the optical path is shown in which both dyes are excited using a modulated 532-nm laser, and the emitted fluorescent signal is spectrally separated to independently evaluate the fluorescence of each dye on a silicon photodiode. The photodiode voltage is demodulated and amplified using an analog lock-in amplifier. (c) Independently measuring the fluorescence of unmixed Dylight 550-labeled nanoparticles and DY-521XL shows that our system can discriminate between these dyes with less than 6% cross talk. (See Fig. S1 for the spectra of Dylight 550-labeled nanoparticles and DY-521XL.) To see this figure in color, go online.
Materials and Methods
Probe conjugation and sample preparation for commercial magnetic nanoparticles
To precisely measure the temperature of the surface of our magnetite nanoparticle samples (SHA-10 and SHA-20; Ocean Nanotech, San Diego, CA), we conjugated Dylight 550 N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) ester (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) to the amine groups on the magnetite nanoparticle surface in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) buffer (21–040, comprising 0.144 g/L KH2PO4, 9 g/L NaCl, 0.795 g/L anhydrous Na2HPO4 (pH 7.4), and 300 mOsm/kg H2O; Corning, Tewksbury, MA) with a particle concentration of 1 mg/mL and a 10-fold excess of Dylight 550 to amine groups on the particle surface. The reaction was allowed to proceed under mechanical agitation at room temperature for 10 h. Next, the sample was dialyzed overnight against a 4000-fold volume excess of 10 mM Tris HCl (pH 8) to hydrolyze any unreacted NHS groups and separate the unbound dye from the nanoparticle solution. The sample was then dialyzed overnight against a 4000-fold volume excess of PBS and concentrated to the desired final solution using 10 kDa centrifugal filters (Amicon, Millipore-Sigma, Burlington, MA). Our fluid temperature probe, DY-521XL (Dyomics, Jena, Germany), was mixed into the ferrofluid solution at a sufficient concentration to balance the fluorescent intensities of the two dyes. Horse spleen ferritin (F4503; Sigma-Aldrich, Raleigh, NC) went through the identical preparation, with the exception that the labeling reaction ratio was 100 dye molecules per ferritin. Magnetite nanoparticle and ferritin iron concentrations were quantified using a total iron quantification kit (I7505; Pointe Scientific, Canton, MI) after digesting samples at 75°C in nitric acid for 4 h. Ferritin protein concentration was quantified using a bicinchoninic acid protein assay (23225; Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Core-shell nanoparticle synthesis and characterization
We synthesized core cobalt ferrite nanoparticles by the thermal decomposition method. Cobalt(II) chloride (3.25 mmol), iron(III) acetylacetonate (5.00 mmol), oleylamine (91.2 mmol), oleic acid (31.6 mmol), and octyl ether (49.9 mmol) were mixed into a three-neck, round-bottom flask under an Ar atmosphere. The reaction mixture was heated up to 300°C. After 1 h, the resulting cobalt ferrite nanoparticles were isolated by centrifugation and washed with hexane and ethanol.
Core-shell nanoparticles composed of a cobalt ferrite core and a manganese ferrite shell were then synthesized by the seed-mediated growth method. Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles (0.34 mmol), manganese(II) chloride (3.25 mmol), iron(III) acetylacetonate (5.00 mmol), oleylamine (60.8 mmol), oleic acid (15.8 mmol), and trioctylamine (34.3 mmol) were added to a three-neck, round-bottom flask under an Ar atmosphere. The reaction mixture was heated to 350°C and maintained for 1 h. The core-shell nanoparticle was obtained by centrifugation and washing processes. (See Fig. S5 for particle characterization.)
As-synthesized core-shell nanoparticles were coated with a silica shell and conjugated with Dylight 550 using a previously reported method with minor modifications (24,25). Amine-functionalized core-shell nanoparticles were conjugated with Dylight 550 NHS ester in dimethylsulfoxide with a particle concentration of 1 mg/mL and dye concentration of 0.1 mg/mL. The reaction was allowed to proceed in microtube mixer (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) at 1500 rotations per minute for 8 h at room temperature. The products were purified on a magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS) MS column (Miltenyi Biotec, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany) and eluted with dimethylsulfoxide. The sample was then reacted with 1 mg of succinic anhydride per 1 mg/mL of particle solution for an additional 8 h at room temperature in vigorous shaking. The products were purified again on a MACS MS column and eluted with pure water. To make sure that there was no remaining free Dylight 550, the products were purified using dye removal columns (22858; Thermo Fisher Scientific) three times. In each step, metal concentration of the core-shell nanoparticle was measured using inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectroscopy.
Fluorometry
We used a custom-built fiberoptic fluorometer to probe the fluorescent intensity of our optical thermometers. Excitatory light was provided by an OBIS 532-LS laser (Coherent, Santa Clara, CA) modulated with an 80-kHz sinusoidal signal. The laser light traveled through the outer ring of an optical fiber bundle whose end was housed in a custom polyetheretherketone (PEEK) fiber ferrule (Ocean Optics, Largo, FL) that was mechanically coupled to our plastic sample holder. Magnetite particles and ferritin were suspended within this holder in PBS, whereas the core-shell nanoparticles were suspended in pure water. Fluorescence from both dyes was collected via the central core in the fiber bundle. The collected fluorescence was coupled to air via a 10-mm 0.22 NA fiber optic collimator (88–180; Edmund Optics, Barrington, NJ) and notch filtered to eliminate the signal from the 532-nm laser. The resulting light was split using a long-pass dichroic mirror. The reflected leg was short-pass filtered at 600 nm, and the transmitted leg was long-pass filtered at 650 nm. All filters and mirrors were from Thorlabs (Newton, NJ). The signal from each dye was focused onto a silicon photodiode (DET36A; Thorlabs). Photodiode signals were amplified by lock-in amplifiers locked to the laser modulation frequency with a 300-ms integration time. Resulting signals were digitized in a Molecular Devices Axon Digidata 1550 acquisition system (Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA) and processed using MATLAB (The MathWorks, Natick, MA).
Electromagnet construction and characterization
We designed three distinct electromagnets for our study, corresponding to three frequency ranges: 400–648 kHz, 1–5 MHz, and 30–40 MHz. Adapted from previously published designs, our 400- to 648-kHz electromagnet produced a strong magnetic field in a 10-mm gap in a water-cooled Ferroxcube 3F3 toroid wound with litz wire (26). The toroid was placed in series with a high-voltage mica capacitor (1–5 nF depending on the desired resonance) forming a series resistor-inductor-capacitor circuit. To impedance match this circuit with a 50-Ω standard, we constructed a toroidal transformer out of a Ferroxcube 3F3 toroid and placed a variable ballast resistor (40–47 Ω) on the 50-Ω side of the transformer. Alternating current (AC) signals were generated by a Stanford Research Systems SG380 signal generator (Sunnyvale, CA) and amplified by an Electronics and Innovation 1020L radio frequency amplifier (Rochester, NY). Our 1- to 5-MHz system used the same signal generator and amplifier to drive a toroidal electromagnet with better high-frequency performance but a lower saturation magnetization (Ferrite 52; Fair-Rite Wallkill, NY), which was balanced by a single vacuum-variable capacitor. Our 30- to 40-MHz electromagnet used three vacuum-variable capacitors to tune and impedance match an air-cored solenoid to a 50-Ω high-frequency amplifier (ZHL-3A-S+; Mini-Circuits, Brooklyn, NY). The air-cored solenoid had a gap in the windings to insert our sample holder. All field strengths were measured using a custom-built magnetic search loop attached to a 100-MHz digital oscilloscope. Stimulus timing was controlled with Labview.
Sample calibration chamber
Our custom-built temperature-controlled cuvette holder was composed of a copper block with a gap machined in the front to hold an optical glass cuvette (Fireflysci Type 507; Fireflysci, Staten Island, NY) and a fan-cooled thermoelectric plate on the back. The temperature of the fluid was monitored using an immersed fiberoptic phosphor temperature probe (PRB-G20; Osensa, Burnaby, BC, Canada). Using a proportional-integral-derivative control system, the copper block temperature was stepped three times between a randomly permuted list of five temperatures. A 5-min settling time was allowed in between temperature changes. The fluorescence of both dyes was evaluated for 30 s after the settling time using the system described in Fluorometry above.
Results
Our temperature measurements made use of two spectrally separable, strongly thermochromic organic dyes to independently measure the temperature on the nanoparticle surface and in the surrounding bath (Fig. 1 a). The surface probe Dylight 550 NHS ester was conjugated to the surface of nanoparticles via amine cross-linking, whereas the fluid probe DY-521XL was dissolved freely in the solution. The two dyes were excited at the same time by a modulated 532-nm laser via the outer ring of an optical fiber bundle, and the resulting fluorescent signal was collected via a separate core of the same fiber bundle. The emitted light was split using a series of dichroic filters and mirrors to isolate the signal from the two fluorescent dyes, which was transduced to voltage by silicon photodiodes connected to analog lock-in amplifiers (Fig. 1 b). The dyes were readily spectrally separated because of the large Stokes shift of DY-521XL, with channel cross talk below 6% (Figs. 1 c and S1). Special care was taken to minimize free Dylight 550 in the solution and ascertain that the vast majority of the fluorescence measured for this dye was coming from the nanoparticle surface (Table S1).
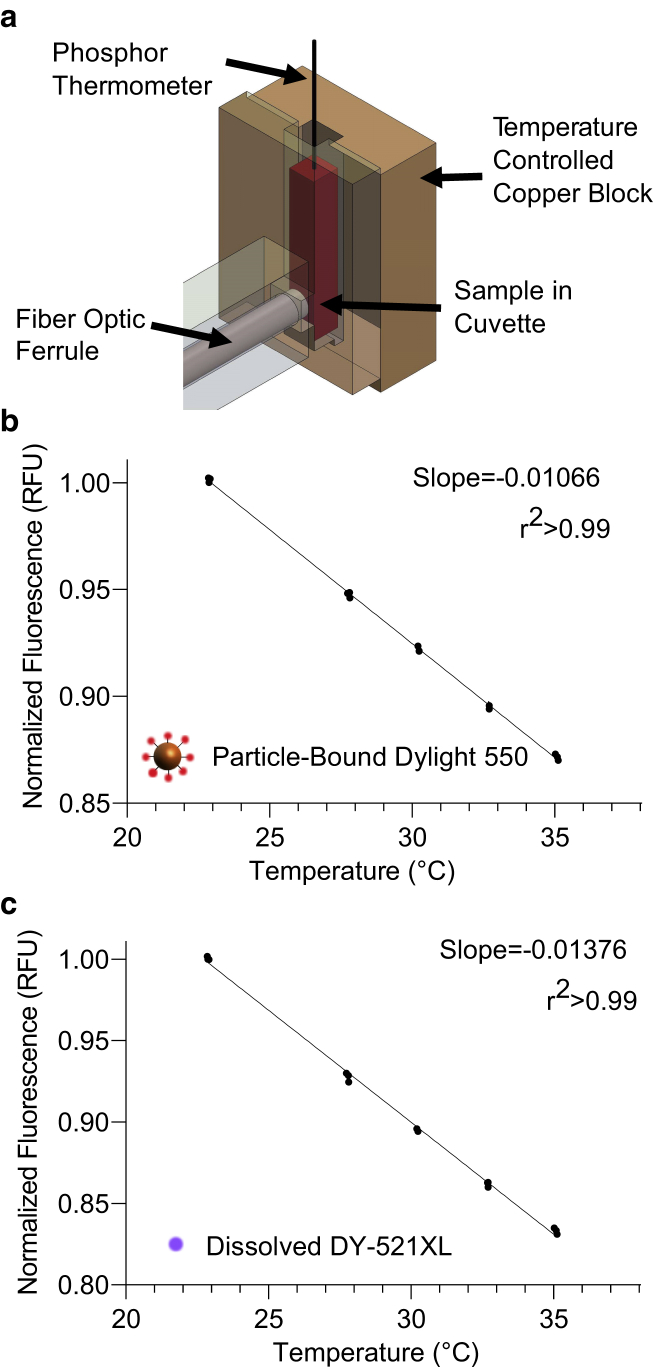
Before applying RF-AMF, we calibrated the thermochromic response of each individual dye-labeled ferrofluid sample by measuring the fluorescence intensity of both dyes while varying the temperature using a custom-built temperature-controlled cuvette holder (Fig. 2 a). The sample was cycled three times between a randomly permuted list of five temperatures. Bulk fluid temperature was monitored during this calibration procedure using a 450-μm diameter phosphor thermal probe. Both fluorophores showed a strong linear decrease in fluorescence over the experimental temperature range (Fig. 2, b and c).
Figure 2.
Thermochromic calibration of particle-bound and free dye. (a) A diagram of the calibration setup is shown. For each individual ferrofluid sample, a calibration was obtained by monitoring the change in fluorescence intensity of each dye in response to temperature cycling in a custom temperature-controlled cuvette holder. (b-c) A representative of calibration curves from a ferrofluid containing Dylight 550-labeled 12-nm iron oxide nanoparticles (b) and free DY-521XL solution (c) is shown. Fluorescence at five temperatures were measured three times in a randomly permuted sweep. The points represent the average of each measurement. The error bars represent mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) and are not shown if smaller than the plotted symbols. To see this figure in color, go online.
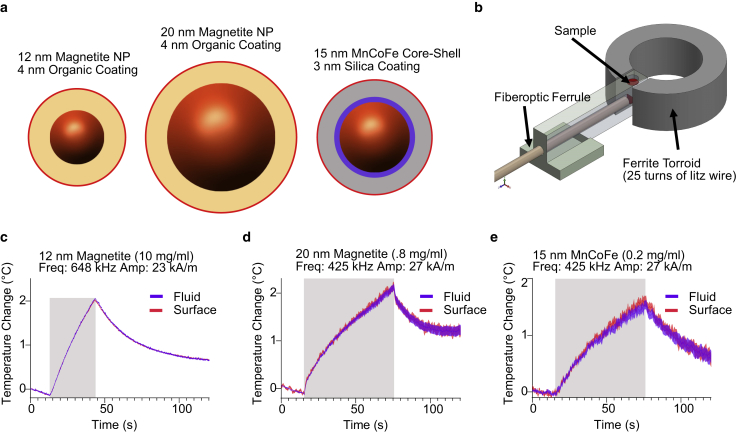
Our study of synthetic nanoparticle RF-AMF heating used three distinct magnetic nanoparticle compositions (Fig. 3 a). First, we examined commercially available 12-nm magnetite nanoparticles (core radius: μ = 5.98 nm, σ = 0.636 nm, Fig. S6), which are superparamagnetic and similar in core size to ferritin. Second, we measured the responses of commercial 20-nm iron oxide nanoparticles (core radius: μ = 10.14 nm, σ = 1.073 nm, Fig. S7). This core size is commonly used in radio frequency hyperthermia owing to its significant specific-loss power (22,27). According to the manufacturer, both of these particle types are coated with a 4-nm-thick organic shell comprising a monolayer of oleic acid and a monolayer of amphiphilic polymer. Third, we examined the heating behavior of a ferrofluid containing custom-synthesized 15-nm core-shell nanoparticles (Fig. S5), which have exceptionally high coercivity and heating ability (24). These nanoparticles were coated with a 3-nm-thick silica layer. All particles had surface amine groups enabling dye conjugation.
Figure 3.
Synthetic nanoparticle ferrofluids show no measurable difference between the temperature on the surface of the nanoparticle and in the solution. (a) A diagram of the structure of the three nanoparticle types tested with RF-AMF heating is shown. (b) A diagram is given of the hyperthermia apparatus, which generates a concentrated magnetic field in a gapped toroid wound with litz wire, acting as the inductor in a series-resonant resistor-inductor-capacitor circuit. The fluorescence is measured with a fiberoptic fluorometer with lock-in amplification. (c–e) Surface and fluid temperatures measured for 12-nm magnetite (c), 20-nm magnetite (d), and 15-nm MnCoFe (e) nanoparticle solutions during RF-AMF application are shown. The mean and mean ± SEM temperature for particle surface (red) and surrounding fluid (blue) are plotted for each sample, with the frequency and field parameters specified above the plot. RF-AMF application period is denoted by gray shading. Each trace denotes the mean ± SEM of 20 runs of RF-AMF stimulation. The cooling seen before the RF-AMF stimulus results from the cooling of the toroid between stimuli (see Fig. S3). To see this figure in color, go online.
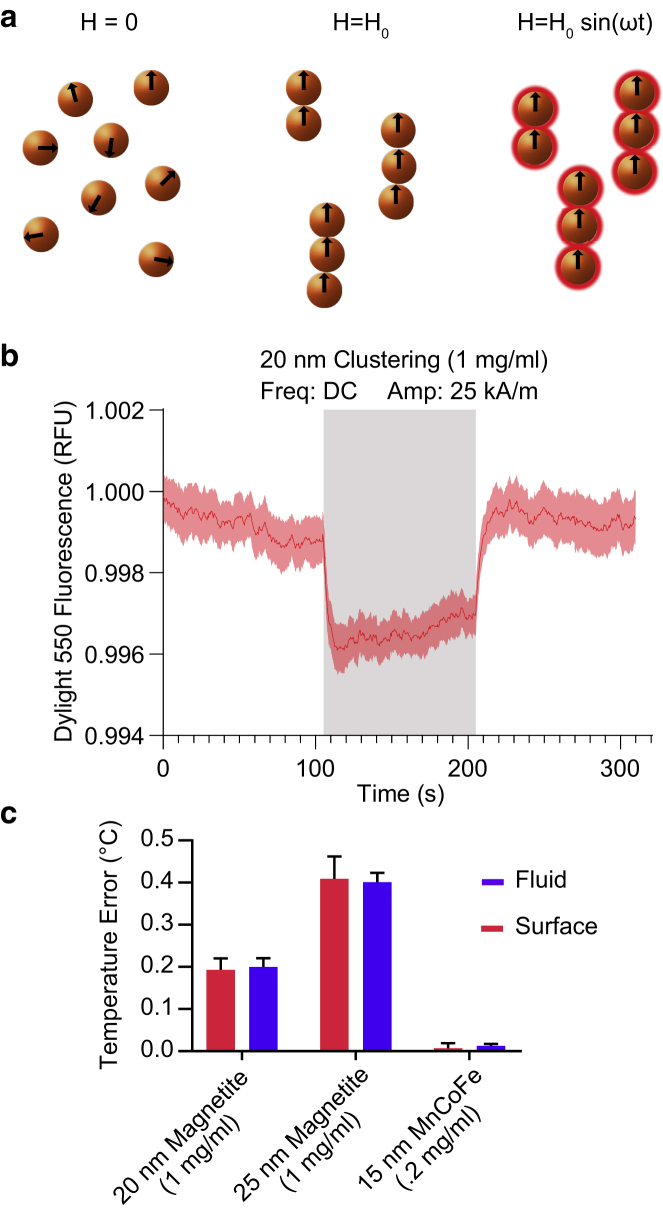
After calibration, we measured the fluorescence of particle-bound and free dye in response to strong RF-AMF produced by a water-cooled gapped ferrite toroid wound with litz wire (Fig. 3 b). This allowed us to apply fields of up to 27 kA/m at frequencies of 420–648 kHz, within the range of common parameters in literature. Samples in shortened 5-mm silica tubes were placed inside a sample housing jacketed by constant airflow to minimize heat transfer from the toroid. We applied RF-AMF stimulation for 20 cycles of 1-min or 30-s duration, with 9 min of rest between cycles to allow the toroid to cool. Samples were tested at different concentrations to ensure sufficient heating of the fluid with small magnetite particles while minimizing particle clustering for larger and more magnetic particles. We performed three trials for each sample with separate nanoparticle batches, and representative results for each particle type are shown in Fig. 3, c–e (additional trials shown in Fig. S2). All three nanoparticle compositions generated significant heat because of RF-AMF. However, in each case, we observed no measurable difference between the temperature of the bulk fluid and the temperature of the nanoparticle surface throughout the experimental time course. This was true for all three particle types despite their different core sizes, shell materials and thickness, and concentration in the fluid. These results suggest that heat transfer from SPIONs follows the classical theory.
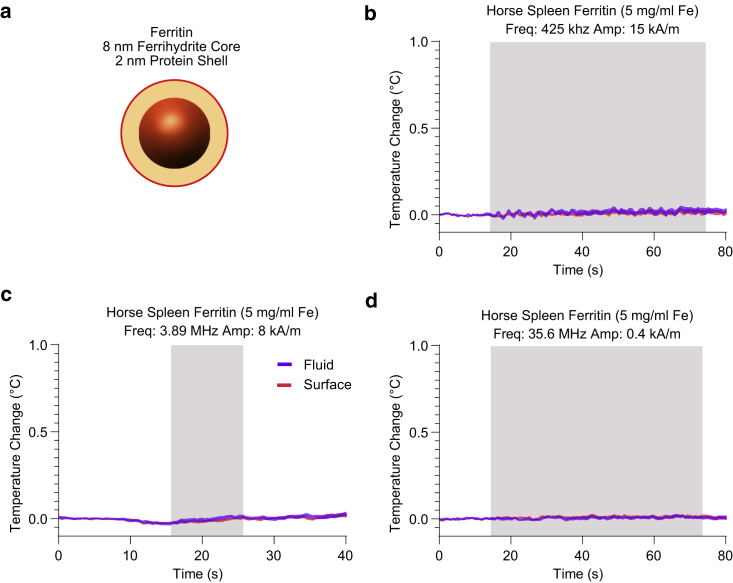
Having examined the possibility of nanoscale heat confinement at the surface of synthetic magnetic nanoparticles, we used the same nanoscale thermometry technique to investigate the heating ability of ferritin, which comprises a 2-nm-thick protein shell enclosing an 8-nm antiferromagnetic ferrihydrite core (Fig. 4 a; (28)). A disordered surface layer of the core gives rise to uncompensated magnetic spins, resulting in a small magnetic moment. Because these uncompensated spins are only weakly coupled, the Néel relaxation rate of the ferritin core is in the gigahertz range (29,30), suggesting that this protein is not expected to experience dynamic hysteresis under RF-AMF at kilohertz and megahertz frequencies. This has been confirmed by previous thermometry of bulk ferritin ferrofluids (31). Nevertheless, several studies have proposed ferritin heating under RF-AMF as a mechanism of thermal actuation in engineered cellular signaling pathways (11,16) by invoking the possibility of surface thermal confinement, unmeasurable by bulk techniques. To investigate the possibility of heat confinement on the ferritin surface under RF-AMF stimulation, we conjugated Dylight 550 NHS ester to the surface amines of horse spleen ferritin, a widely studied model ferritin containing an average of 2600 iron atoms per core. We mixed the resulting ferrofluid with DY-521XL and calibrated the thermochromic response of both dyes as we did for synthetic nanoparticles. We then applied RF-AMF at three different frequencies spanning 425 kHz to 35.6 MHz, covering the field parameters used in previous reports of magnetogenetic control (10,11,16). At no frequency were we able to measure heating of the ferritin-containing solution, nor did we observe heat buildup on the protein surface (Fig. 4, b–d). The small background heating from the 425-kHz toroid, measured using a blank sample containing only DY 521-XL in PBS, was subtracted from the low-frequency study to try to detect any small heating contribution from the ferritin (Fig. S4). These results confirm that ferritin does not produce significant heating, either at the bulk scale or at the nanoscale, under RF-AMF up to tens of megahertz in frequency.
Figure 4.
Ferritin shows no measurable heating in response to RF-AMF stimulation. (a) The diagram of the structure of ferritin, comprising a 2-nm-thick protein shell encapsulating a 6- to 8-nm ferrihydrite core, is shown. (b–d) The surface (red) and fluid (blue) temperature monitored for ferritin during RF-AMF application for three frequency regimes, as labeled in the figure, is shown. Each trace denotes the mean ± SEM of 20 runs of RF-AMF stimulation. The RF-AMF application period is denoted by gray shading. A small (<0.2°C) temperature variation from the 440-kHz toroid was measured using a PBS blank and subtracted from (b) (see Fig. S4). To see this figure in color, go online.
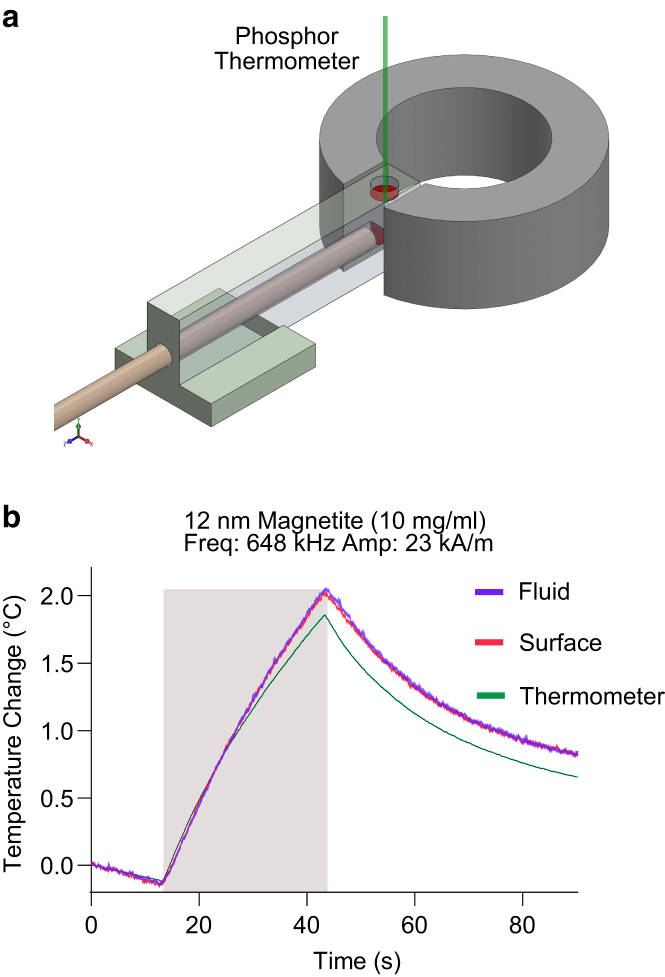
Although our data with synthetic magnetic nanoparticles and ferritin strongly suggest that heat transfer from magnetic nanoparticles under RF-AMF is consistent with classical heat transfer theory, several previous studies using optical thermometry have suggested otherwise (10,13,32). To uncover possible sources of this discrepancy, we examined two potential sources of artifacts. First, several previous studies measured particle surface temperature with a thermochromic dye while measuring the bulk temperature with a physical thermometer placed in the solution (13,32). We reasoned that the combined effects of the finite thermal mass of such a thermometer, even for a small phosphor or semiconductor-based thermal probe, and the thermal connection between the thermometer and the air outside the solution would cause its temperature response to underestimate the heating of the surrounding fluid during RF-AMF application, resulting in an apparent thermal gradient between the background fluid and the nanoparticle surface. To test this hypothesis, we immersed a 450-μm diameter thermal probe in a ferrofluid containing 10 mg/mL of the 12-nm Dylight 550-labeled magnetite nanoparticles and free DY521-XL dye (Fig. 5 a). Although the temperature response of the two dyes to RF-AMF matched within the measurement error, the solid thermal probe temperature appeared to be lower (Fig. 5 b). This artifact demonstrates the need for equivalency between the methods measuring the nanoparticle surface temperature and the surrounding fluid temperature.
Figure 5.
Artifactual measurement of enhanced surface heating due to the use of a solid thermal probe. (a) The diagram of the experimental setup for measuring ferrofluid heating under RF-AMF that includes a solid thermal probe measurement of fluid temperature in addition to measurements of the particle surface and fluid using thermochromic dyes is shown. (b) The temperature was measured by our solid thermal probe (green) and thermochromic measurements of temperature at the particle surface (red) and in the fluid (blue). Each trace denotes the mean ± SEM of 20 runs of RF-AMF stimulation. To see this figure in color, go online.
A second phenomenon reported in the literature involves a rapid, almost instantaneous, increase in the apparent particle surface temperature, followed by a more gradual heating of both the particle and the fluid (10,13,32). We hypothesized that this observation could be caused by particle clustering due to interparticle attraction under an applied field, which has been predicted by previous computational work (33). Particle clustering increases the scattering of both excitatory illumination and emitted light, which would manifest as a dip in the measured fluorescence of thermochromic probes in our apparatus (Fig. 6, a–c). Because the probes’ fluorescent output also decreases in response to increasing temperature, this dip in fluorescence could be misinterpreted as a jump in temperature experienced by the dyes. To examine this effect, we applied a direct current (DC) field that we predicted would cause clustering without heating the particles. We ran a DC current through our gapped toroid inductor to produce a DC field comparable to the peak field of our 440-kHz AC signal. In a suspension of 20-nm magnetite particles at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, the measured fluorescence dropped immediately after the DC field was applied and recovered after the field was turned off (Fig. 6 b). This effect would be even more pronounced at higher ferrofluid concentrations, at which field-induced clustering would be more evident. In our experiments, the fluorescence of both dyes is affected similarly because our optical measurement is orthogonal to the magnetic field direction, such that the expected linear chain assembly of the magnetic particles (34,35) does not preferentially shield the particle-bound dye from the light path (Fig. 6 c). Although both dyes in our system were affected similarly, previous studies comparing the response of a surface dye to an immersed thermometer would, again, arrive at the erroneous conclusion that there is a thermal gradient between the nanoparticle surface and the surrounding fluid.
Figure 6.
Artifact in optical thermometry due to nanoparticle clustering under applied field. (a) A diagram of superparamagnetic nanoparticle clustering without an applied magnetic field (left), with an applied DC field (middle), and with an applied AC field (right) is shown. Under both applied field conditions, the particles are expected to cluster into chains, with heating occurring under the AC field. Clustering is expected to increase with the particle concentration and with the strength of the applied field, H0. In our optical setup, particle clustering is expected to diminish the measured fluorescence of both particle-bound and dissolved dyes. (b) The fluorescence of Dylight 550 bound to the surface of 20-nm nanoparticles during the application of a 25 kA/m DC field (stimulus period indicated with gray shading) is shown. The trace denotes the mean ± SEM of 10 runs of RF-AMF stimulation. (c) The apparent temperature jump due to the decreased fluorescence of the thermochromic dyes at the particle surface (red) and in the fluid (blue) is shown. Bars denote mean ± SEM of 10 runs of RF-AMF stimulation. To see this figure in color, go online.
Taken together, our results show that for suspensions of several commonly used synthetic magnetic nanoparticles, there is no significant difference between the surface temperature of the nanoparticle and the temperature of the surrounding fluid during RF-AMF stimulation. These findings are consistent with classical heat transfer theory and experiments conducted with other nanomaterials (36,37) while contradicting several previous experimental results with SPIONs and demonstrating two potential sources of artifacts in optical temperature measurement. Several questions regarding the nanoscale phenomena involved in magnetic nanoparticles’ response to RF-AMF remain unanswered. For example, our results do not directly address the temperature of the interior of the solid nanoparticle, as in some previous studies (14). A much higher interfacial thermal resistance than measured for other nanoparticles (20,23,38) could produce a measurable difference in the interior temperature relative to the surrounding fluid. In addition, given that the temporal resolution of our technique is substantially below the RF frequency applied to the sample, we would be unable to detect oscillating or transient thermal gradients that might arise due to magnetocaloric effects (39,40). Additionally, our study does not directly contradict nor provide an explanation for the preferential cleavage of thermolabile covalent bonds seen at the surface of magnetic nanoparticles under RF-AMF stimulation, as documented in several well-controlled studies (22,41). It is possible that such cleavage is due to nonclassical, nonequilibrium, or nonthermal effects.
We believe our thermochromic dye readout corresponds closely to the scenario of nanoparticles or ferritin attached to temperature-sensitive ion channels. Although particles bound to a protein on the cell membrane experience a more crowded and heterogenous environment than tested in our aqueous suspensions, the physics of magnetic hyperthermia are not expected to change. This is especially true for the Néel-dominated relaxation of ferritin and other small magnetic nanoparticles, which is unaffected by viscosity and rotational restriction. Thus, our experiments’ inability to support the heat confinement mechanisms proposed to underlie the activation of several magnetogenetic constructs suggests that a re-examination of the mechanisms put forward in these reports may be warranted. Meanwhile, the millimeter-scale heating of tissues by concentrated synthetic SPIONs remains a viable approach to magnetogenetic actuation consistent with Fourier’s law (12,15). In addition, potential mechanical coupling between nanoparticle rotation or displacement and directly tethered mechanosensitive ion channels remains to be evaluated in future studies.
Author Contributions
H.C.D. and M.G.S. conceived the study. H.C.D. constructed the experimental apparatus, prepared the reagents, acquired the data, and analyzed the data. H.P. assisted in apparatus construction and data acquisition. S.K., J.-H.L., T.-H.S., and J.C. synthesized and functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. H.C.D. and M.G.S. wrote the manuscript with input from all other authors. M.G.S. supervised the research.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Polina Anikeeva, Arnd Pralle, Michael Christiansen, George Varnavides, Pradeep Ramesh, and Markus Meister for helpful discussions and Yuxing Yao for assistance with electron microscopy.
This research was supported by the Burroughs Wellcome Career Award at the Scientific Interface, the Packard Fellowship in Science and Engineering, the Rosen Center for Bioengineering, and the Center for Environmental Microbial Interactions at Caltech.
Editor: Brian Salzberg.
Footnotes
Supporting Material can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2020.01.028.
Supporting Material
References
- 1.Giustini A.J., Petryk A.A., Hoopes P.J. Magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia in cancer treatment. Nano Life. 2010;1:17–32. doi: 10.1142/S1793984410000067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brown W.F. Thermal fluctuations of a single-domain particle. Phys. Rev. 1963;130:1677–1686. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Landau L., Lifshitz E. 3 - On the theory of the dispersion of magnetic permeability in ferromagnetic bodies. Reprinted from Physikalische Zeitschrift der Sowjetunion8, Part 2, 153, 1935. In: Pitaevski L.P., editor. Perspectives in Theoretical Physics. Pergamon; 1992. pp. 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rosensweig R.E. Heating magnetic fluid with alternating magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002;252:370–374. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sukhov A., Berakdar J. Temperature-dependent magnetization dynamics of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2008;20:125226. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Stoner Edmund C., Wohlfarth E.P. A mechanism of magnetic hysteresis in heterogeneous alloys. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A. 1948;240:599–642. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Usadel K.D., Usadel C. Dynamics of magnetic single domain particles embedded in a viscous liquid. J. Appl. Phys. 2015;118:234303. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nowak U., Mryasov O., Chantrell R. Spin dynamics of magnetic nanoparticles: beyond Brown's theory. Phys. Rev. B. 2005;72:172410. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chalopin Y., Bacri J.-C., Devaud M. Nanoscale Brownian heating by interacting magnetic dipolar particles. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:1656. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01760-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Huang H., Delikanli S., Pralle A. Remote control of ion channels and neurons through magnetic-field heating of nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010;5:602–606. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2010.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Stanley S.A., Gagner J.E., Friedman J.M. Radio-wave heating of iron oxide nanoparticles can regulate plasma glucose in mice. Science. 2012;336:604–608. doi: 10.1126/science.1216753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chen R., Romero G., Anikeeva P. Wireless magnetothermal deep brain stimulation. Science. 2015;347:1477–1480. doi: 10.1126/science.1261821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Piñol R., Brites C.D.S., Millán A. Joining time-resolved thermometry and magnetic-induced heating in a single nanoparticle unveils intriguing thermal properties. ACS Nano. 2015;9:3134–3142. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b00059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dong J., Zink J.I. Taking the temperature of the interiors of magnetically heated nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2014;8:5199–5207. doi: 10.1021/nn501250e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Munshi R., Qadri S.M., Pralle A. Magnetothermal genetic deep brain stimulation of motor behaviors in awake, freely moving mice. eLife. 2017;6:e27069. doi: 10.7554/eLife.27069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stanley S.A., Sauer J., Friedman J.M. Remote regulation of glucose homeostasis in mice using genetically encoded nanoparticles. Nat. Med. 2015;21:92–98. doi: 10.1038/nm.3730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Meister M. Physical limits to magnetogenetics. eLife. 2016;5::e17210. doi: 10.7554/eLife.17210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Berciaud S., Lasne D., Lounis B. Photothermal heterodyne imaging of individual metallic nanoparticles: theory versus experiment. Phys. Rev. B. 2006;73:045424. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Honda M., Saito Y., Kawata S. Nanoscale heating of laser irradiated single gold nanoparticles in liquid. Opt. Express. 2011;19:12375–12383. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.012375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Merabia S., Shenogin S., Barrat J.-L. Heat transfer from nanoparticles: a corresponding state analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:15113–15118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901372106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Baral S., Rafiei Miandashti A., Richardson H.H. Near-field thermal imaging of optically excited gold nanostructures: scaling principles for collective heating with heat dissipation into the surrounding medium. Nanoscale. 2018;10:941–948. doi: 10.1039/c7nr08349a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Romero G., Christiansen M.G., Anikeeva P. Localized excitation of neural activity via rapid magnetothermal drug release. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016;26:6471–6478. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ge Z., Cahill D.G., Braun P.V. AuPd metal nanoparticles as probes of nanoscale thermal transport in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2004;108:18870–18875. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lee J.-H., Jang J.T., Cheon J. Exchange-coupled magnetic nanoparticles for efficient heat induction. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011;6:418–422. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Shin T.-H., Kang S., Cheon J. A magnetic resonance tuning sensor for the MRI detection of biological targets. Nat. Protoc. 2018;13:2664–2684. doi: 10.1038/s41596-018-0057-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Christiansen M.G., Howe C.M., Anikeeva P. Practical methods for generating alternating magnetic fields for biomedical research. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017;88:084301. doi: 10.1063/1.4999358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chen R., Christiansen M.G., Anikeeva P. Maximizing hysteretic losses in magnetic ferrite nanoparticles via model-driven synthesis and materials optimization. ACS Nano. 2013;7:8990–9000. doi: 10.1021/nn4035266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Harrison P.M., Arosio P. The ferritins: molecular properties, iron storage function and cellular regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1996;1275:161–203. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(96)00022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Koralewski M., Pochylski M., Gierszewski J. Magnetic properties of ferritin and akaganeite nanoparticles in aqueous suspension. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013;15:1902. doi: 10.1007/s11051-013-1902-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schäfer-Nolte E., Schlipf L., Wrachtrup J. Tracking temperature-dependent relaxation times of ferritin nanomagnets with a wideband quantum spectrometer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014;113:217204. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.217204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fantechi E., Innocenti C., Ceci P. A smart platform for hyperthermia application in cancer treatment: cobalt-doped ferrite nanoparticles mineralized in human ferritin cages. ACS Nano. 2014;8:4705–4719. doi: 10.1021/nn500454n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Polo-Corrales L., Rinaldi C. Monitoring iron oxide nanoparticle surface temperature in an alternating magnetic field using thermoresponsive fluorescent polymers. J. Appl. Phys. 2012;111:07B334. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhao Z., Rinaldi C. Magnetization dynamics and energy dissipation of interacting magnetic nanoparticles in alternating magnetic fields with and without a static bias field. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2018;122:21018–21030. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wilson R.J., Hu W., Wang S.X. Formation and properties of magnetic chains for 100 nm nanoparticles used in separations of molecules and cells. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009;321:1452–1458. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.02.066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Branquinho L.C., Carrião M.S., Bakuzis A.F. Effect of magnetic dipolar interactions on nanoparticle heating efficiency: implications for cancer hyperthermia. Sci. Rep. 2013;3:2887. doi: 10.1038/srep02887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Paulo P.M.R., Gaiduk A., Orrit M. Photothermal correlation spectroscopy of gold nanoparticles in solution. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2009;113:11451–11457. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gupta A., Kane R.S., Borca-Tasciuc D.-A. Local temperature measurement in the vicinity of electromagnetically heated magnetite and gold nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2010;108:064901. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ge Z., Kang Y., Cahill D.G. Thermal transport in au-core polymer-shell nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2005;5:531–535. doi: 10.1021/nl047944x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Duret G., Polali S., Robinson J.T. Magnetic entropy as a proposed gating mechanism for magnetogenetic ion channels. Biophys. J. 2019;116:454–468. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Barbic M. Possible magneto-mechanical and magneto-thermal mechanisms of ion channel activation in magnetogenetics. eLife. 2019;8:e45807. doi: 10.7554/eLife.45807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Riedinger A., Guardia P., Pellegrino T. Subnanometer local temperature probing and remotely controlled drug release based on azo-functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2013;13:2399–2406. doi: 10.1021/nl400188q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.