Abstract
Study objectives
To characterize adult Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced bronchiolitis requiring hospitalization.
Design
We encountered an adult patient with severe bronchiolitis in the absence of pneumonia due to M pneumoniae. To determine the relative frequency of such a condition, we retrospectively reviewed the medical records of adults over a 4-year period with a hospital discharge diagnosis of “bronchiolitis” from a university hospital.
Setting
University Hospital of the University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, Denver, CO.
Study subjects
From 1994 to 1998, 10 adult inpatients were identified with a diagnosis of bronchiolitis. There were two with respiratory bronchiolitis, one with panbronchiolitis, one patient with bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP), and six with acute inflammatory bronchiolitis. Including the initial patient, three had a definitive clinical diagnosis of Mycoplasma-associated bronchiolitis.
Results
The three adult patients with bronchiolitis due to M pneumoniae are unusual because they occurred in the absence of radiographic features of a lobar or patchy alveolar pneumonia. Hospital admission was occasioned by the severity of symptoms and gas exchange abnormalities. One patient had bronchiolitis as well as organizing pneumonia (BOOP) that responded favorably to corticosteroid treatment. The other two had high-resolution CT findings diagnostic of an acute inflammatory bronchiolitis. One of the patients with inflammatory bronchiolitis had an unusual pattern of marked ventilation and perfusion defects localized predominantly to the left lung. All three had restrictive ventilatory impairment on physiologic testing.
Conclusions
In adults, Mycoplasma-associated bronchiolitis without pneumonia is rarely reported, but in hospitalized patients, it may be more common than expected and may be associated with severe physiologic disturbances.
Key words: bronchiolitis, bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia, constrictive bronchiolitis, infectious bronchiolitis, inflammatory bronchiolitis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Abbreviations: BOOP, bronchiolitis obliterans organizingpneumonia; HRCT, high-resolution CT; PCR, polymerase chainreaction
A number of pulmonary complications have been reported to occur with Mycoplasma pneumoniaeinfection. These include pneumonia, tracheobronchitis, obliterative bronchitis, bronchiectasis, pneumatocele formation, MacLeod-Swyer-James syndrome, pleural effusion, interstitial fibrosis, lung abscess, and exacerbation or possibly initiation of reactive airway disease.1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Small airways disease (bronchiolitis) in the form of an inflammatory bronchiolitis, constrictive bronchiolitis obliterans, or bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP) also occurs.12 13 14Bronchiolitis due to M pneumoniae usually accompanies a bronchopneumonia. Readily recognized in pediatric patients, documented infectious bronchiolitis in adults is unusual.15 16 Herein we describe three adult patients with bronchiolitis due to M pneumoniae and review the literature concerning small airways disease caused by infectious agents in adults, with particular emphasis on M pneumoniae.
Materials and Methods
Patients with a hospital discharge diagnosis of bronchiolitis, from April 1, 1994 to April 1, 1998, were identified from the University Hospital discharge database of the University of Colorado Health Sciences Center. A retrospective chart review was performed to identify those with a diagnosis of M pneumoniae- associated bronchiolitis.
Results
Ten adult patients were identified with a physician discharge diagnosis of bronchiolitis. Of these, three had a definitive diagnosis of M pneumoniae-associated bronchiolitis. All three were previously healthy adults who presented with acute small airways disease due to M pneumoniae but without the radiographic features of lobar or patchy alveolar infiltrates that are characteristic of M pneumoniae pneumonia. One patient had BOOP and two had an acute inflammatory bronchiolitis. All had significant restrictive lung disease and gas exchange abnormalities. Two were treated with corticosteroids and had a favorable response.
Case Report
Case 1
A previously healthy nonsmoking 39-year-old man complained of 10 days of progressive dyspnea and a productive cough. He also reported nausea, one episode of vomiting, and watery diarrhea for 3 days. On examination, his temperature was 37.7˚C, pulse rate was 87 beats/min, BP was 120/70 mm Hg, and respiratory rate was 22 breaths/min. Physical examination was notable for moderate respiratory distress and bilateral crackles. The chest radiograph demonstrated a fine nodular interstitial pattern (Fig 1 ). A room air arterial blood gas revealed a pH of 7.43, Pco 2 of 36 mm Hg, Po 2of 41 mm Hg, and an oxygen saturation of 78%. The peripheral WBC count was 9.4 × 109/L, with 61% neutrophils, 24% lymphocytes, and 12% monocytes. Treatment with IV erythromycin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole was initiated. Sputum culture revealed mixed flora. Blood cultures were negative. On hospital day 3, due to the lack of improvement, he underwent a video-assisted thoracoscopic biopsy of the left lower lobe and lingula. This revealed extensive proliferative (exudative) bronchiolitis with organizing pneumonia consistent with BOOP (Fig 2 ). Microbiological staining and cultures of the tissue were negative. The acute serum cold agglutinin titer was 1:512 and the M pneumoniae IgG (complement fixation) was 1:64. The IgM antibody for M pneumoniae was 1:2,560. Convalescence titers for cold agglutinin and IgM were negative. A regimen of IV methylprednisolone was started, 250 mg every 6 h, and the regimen of erythromycin was continued. The patient was discharged from the hospital on hospital day 11 to complete a 3-week course of erythromycin, 500 mg four times daily, and prednisone, 80 mg once daily. Pulmonary function at hospital discharge revealed an FEV1 of 2.03 L (54%), FVC of 2.74 L (59%), FEV1/FVC of 74%, thoracic gas volume of 2.26 L (66%), residual volume of 1.05 L (66%), and total lung capacity of 3.57 L (56%), consistent with severe restrictive lung disease. After 1 month, a chest radiograph revealed only minimal linear scarring at the left lung base. At 5 months, the FEV1 improved to 2.67 L (69%), FVC to 3.52 L (68%), and FEV1/FVC was 76%. Prednisone dosage was tapered over 9 months, guided by improvement in the patient's symptoms and reduction of oxygen requirements.
Figure 1.
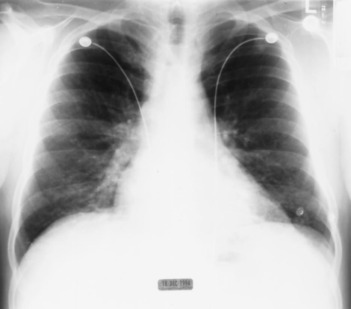
Chest radiograph of patient 1, demonstrating a fine nodular interstitial pattern, especially at the bases.
Figure 2.
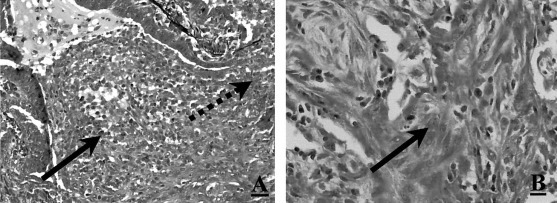
Left, A: lung micrograph of patient 1 showing granulation tissue (Masson's body, arrow), projecting into a respiratory bronchiole through the site indicated by the dashed arrow (pentachrome, original magnification ×200). Note the presence of mucus more proximally in the bronchiolar lumen. Right, B:granulation tissue cast filling an alveolar duct (arrow). Note the presence of branching cast of granulation tissue composed of elongated fibroblasts admixed with lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnification ×400).
Case 2
A 46-year-old previously healthy nonsmoking man complained of upper respiratory tract symptoms for 1 week. This was followed by a nonproductive cough, dyspnea, bilateral pleuritic chest pain, and fevers for 2 days prior to hospital admission. On examination, he was in mild-to-moderate respiratory distress. His temperature was 38.0˚C, pulse rate was 120 beats/min, BP was 122/74 mm Hg, and respiratory rate was 24 breaths/min. There were markedly diminished breath sounds throughout the left lung with scattered bilateral crackles. A room air arterial blood gas revealed a pH of 7.47, Paco 2of 31 mm Hg, Pao 2 of 55 mm Hg, and an oxygen saturation of 88%. The chest radiograph was normal. Treatment with IV ceftriaxone, 1 g every 12 h, and erythromycin, 500 mg every 6 h, was initiated. A ventilation-perfusion lung scan revealed a marked decrease in both ventilation and perfusion on the left (Fig 3 ). On the right, there were several matched ventilation and perfusion defects. A pulmonary arteriogram was normal. Pulmonary function testing revealed FEV1 of 1.87 L (43%), FVC of 2.44 L (44%), FEV1/FVC ratio of 77%, functional residual capacity of 1.85 L (50%), residual volume of 1.64 L (74%), total lung capacity of 4.19 L (54%), and diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide corrected for alveolar volume of 6.88 mL/min/mm Hg/L (127%), consistent with a severe restrictive defect. The high-resolution CT (HRCT) scan revealed fine centrilobular nodules throughout the left lung (Fig 4 ). A similar pattern was observed in the superior segment of the right lower lobe consistent with an inflammatory bronchiolitis. Gram's stain, routine bacterial and fungal cultures, and viral cultures of BAL fluid were negative. Sputum cytology and BAL fluid were negative for viral inclusion bodies. A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) determination for M pneumoniae from the BAL fluid was positive. PCR amplification was performed at the Diagnostic Virology Laboratory at the University of Colorado School of Medicine and was based on a method previously described.17 The pair of primers used were MP4A (5′-AGG CTC AGG TCA ATC TGG CGT GGA-3′) and MP4B (5′-GGA TCA AAC AGA TCG GTG ACT GGG T-3′), both of which are specific for the M pneumoniae P1 adhesion gene. Once the results of the PCR were known, prednisone, 60 mg/d, was added to the erythromycin regimen, with significant improvement in the patient's symptoms.
Figure 3.
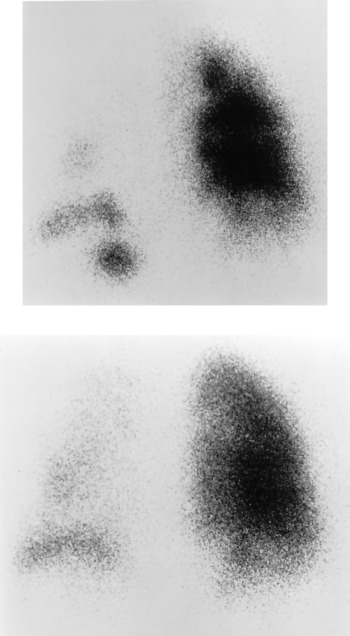
Top: Posterior view of 99mTc-DTPA aerosol ventilation scan of patient 2 showing severely reduced ventilation to the left lung, with a more patchy decrease in ventilation of the right lung. Bottom:corresponding image of 99mTc-MAA perfusion scan shows matching areas of decrease in perfusion.
Figure 4.
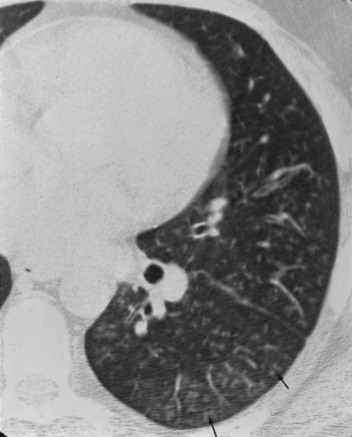
HRCT scan of patient 2, retargeted to the left lung, shows fine centrilobular nodules (arrows) compatible with an inflammatory bronchiolitis.
Case 3
A 64-year-old man with well-controlled type 2A diabetes mellitus presented with a 6-week history of shortness of breath, cough intermittently productive of yellow sputum, chest pain, and sore throat. He was a never-smoker. He was treated with cefaclor 1 week prior to hospital admission, without relief. On examination, his temperature was 37.1˚C, pulse rate was 106 beats/min, BP was 158/80 mm Hg, and respiratory rate was 22 breaths/min. On lung examination, there were bilateral crackles and inspiratory squeaks. There was no clinical evidence of myocardial dysfunction. Room air arterial blood gas revealed a pH of 7.39, a Paco 2 of 36 mm Hg, a Pao 2 of 44 mm Hg, and an oxygen saturation of 79%. Chest radiograph demonstrated a mild increase in interstitial markings with peribronchial thickening. HRCT of the chest revealed multiple tiny and indistinct nodular opacities with a branching pattern (“tree in bud”) in the periphery, consistent with bronchiolitis (Fig 5 ). In addition, scattered areas of ground-glass opacities were present bilaterally. A ventilation-perfusion lung scan showed multiple ventilatory defects that were either greater than or matched to perfusion defects. A spirometry revealed an FEV1 of 1.17 L (52%), FVC of 1.40 L (36%), and an FEV1/FVC ratio of 83%. Sputum culture grew mixed oral flora. The acute cold agglutinin titer was 1:2,048, and a convalescent titer obtained 3 weeks later was 1:16. The level of M pneumoniae IgG fell from 260 to 170 U/mL during the same period. The patient was treated with azithromycin, with progressive improvement of his symptoms.
Figure 5.
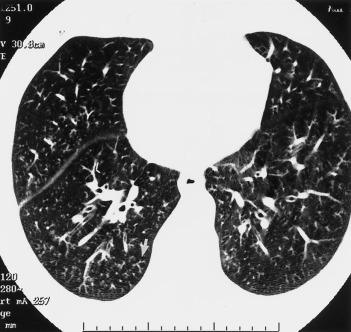
HRCT scan of chest of patient 3 shows diffuse centrilobular nodularity (“tree in bud” appearance, arrow) consistent with inflammatory bronchiolitis.
Discussion
Bronchiolitis refers to an inflammatory disease primarily involving the terminal and respiratory bronchioles, but in some cases, extending to the adjacent alveolar ducts and alveolar spaces.18 19 The histologic appearance of bronchiolitis includes an inflammatory (cellular) bronchiolitis, constrictive bronchiolitis obliterans, or a proliferative bronchiolitis.20 21 Known causes of bronchiolitis include toxic fume inhalation, tobacco smoke, mineral dust inhalation, penicillamine, collagen vascular diseases, and infections.22 23 24 25 26 Bone marrow, heart-lung, and lung transplantation have also been associated with this complication.27 28 29 Clinically apparent infectious bronchiolitis is generally considered to be a pediatric disease, rarely being recognized in adults.16 Although most pediatric cases are associated with respiratory syncytial virus, other viruses such as parainfluenza, influenza, rhinovirus, rubeola, mumps, parvovirus, enterovirus, coronavirus, coxsackie virus, and varicella zoster are occasionally isolated.15 19 In adults, there are occasional reports of viral- or bacterial (M pneumoniaeand Legionella pneumophila)-induced bronchiolitis.14 30 31
Bronchiolitis is subdivided according to specific histologic features. Infectious bronchiolitis is an acute, cellular bronchiolitis with epithelial necrosis, inflammation of the bronchiolar walls, and an intraluminal exudate.32 33 Proliferative bronchiolitis, characteristically seen in the setting of BOOP, consists of polypoid masses of new granulation tissue (Masson's bodies) within the lumina of bronchioles and alveolar ducts, often extending into the alveolar spaces.34 In addition, there is an interstitial cellular response comprised of neutrophils, eosinophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes that can be followed by fibroblast proliferation and collagen deposition.33 35 36 BOOP is a common nonspecific histologic finding occurring in a variety of unrelated lung diseases, including an idiopathic form.34 36 37 38 39 Obliterative or constrictive bronchiolitis is recognized by submucosal and peribronchiolar inflammation and fibrosis of the membranous and respiratory bronchioles, leading to concentric bronchiolar luminal narrowing.22 Bronchiolar lesions comprised of both intraluminal granulation tissue and peribronchiolar fibrosis have been described, which suggest that in some cases, constrictive and proliferative bronchiolitis may be expressions of the same disease process.25 40 Although alveolar wall fibrosis may occur in both proliferative and constrictive bronchiolitis, these entities are clinically and histologically distinct from usual interstitial pneumonitis.41 Constrictive bronchiolitis may demonstrate a variety of radiographic findings, including a normal chest radiograph, hyperinflation, or diffuse nodular opacities. The radiographic pattern in BOOP typically consists of patchy ground-glass opacities, although interstitial and small rounded opacities may be observed.42 Functionally, BOOP and inflammatory bronchiolitis are characterized by a restrictive ventilatory defect with a loss of diffusing surface area. Constrictive bronchiolitis, however, shows progressive obstructive physiologic findings.22
The incidence of proven infections that cause bronchiolitis requiring hospitalization in adults is low. Ham43 described seven adults with acute infectious bronchiolitis with obstructive physiologic processes. In one fatal case in which lung tissue was available for examination, findings were more consistent with fatal asthma with evidence of mucus plugging of primary and secondary bronchi, basement membrane thickening, marked eosinophilic infiltration, and Leyden crystal deposition. In another patient, an acute obstructive defect with hyperinflation, a diffuse and fine granular pattern on chest radiograph, and a cold agglutinin titer of 1:1,024 were found, consistent with constrictive bronchiolitis due to either a viral or Mycoplasma infection.43 The patient's dyspnea improved over 3 weeks after inhaled isoproterenol. In the remaining cases, evidence for bronchiolitis was not convincing.43Constrictive bronchiolitis with obstructive physiologic condition was also described in an adult with varicella pneumonia.44O’Reilly45 described an adult with bronchiolitis due to parainfluenza type 2. Despite a normal chest radiograph, there was significant hypoxemia and hypercarbia. Although symptoms and moderate airflow obstruction improved with bronchodilator and corticosteroid treatment, airflow limitation persisted.45 Seggev et al46 reported three cases of bronchiolitis obliterans in which detailed physiologic studies were available. One, a 69-year-old nonsmoking woman, developed a postviral respiratory illness characterized by shortness of breath, airflow limitation, and hypoxemia. Open lung biopsy specimen revealed narrowing of the bronchiolar lumina due to subepithelial deposition of fibrous connective tissue. Although the airway obstruction initially improved with corticosteroid therapy, the patient developed refractory respiratory failure and died. Both the histopathologic condition and the lack of significant improvement with corticosteroids in this patient are consistent with a diagnosis of constrictive bronchiolitis obliterans.
It is unusual to see the pattern of BOOP following infection. A 28-year-old woman developed fatal respiratory failure as a result of a progressive acute interstitial pneumonitis.47 Autopsy indicated a proliferative bronchiolitis (BOOP) with connective tissue plugs within the lumina of respiratory bronchioles that extended to the alveolar ducts and alveoli. Moreover, the presence of multinucleated giant cells and smudge cells suggested adenovirus as the etiologic agent.47 In a previously healthy elderly man with subacute Nocardia asteroides pneumonia, lung biopsy specimen revealed extensive proliferative bronchiolitis.48 His condition improved after treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole alone.
Pyogenic bacteria causing bronchiolitis without an associated pneumonia, to the best of our knowledge, has not been described. Goldstein et al49 described BOOP in four patients with nosocomial Serratia marcescens pneumonia. However, in all cases, the BOOP reaction was not the predominant feature but rather accompanied a necrotizing bronchopneumonia. Sato et al31described a case of bronchiolitis resulting from L pneumophila, diagnosed by a fourfold rise in indirect fluorescent antibody titer. The patient presented with radiographic bilateral diffuse infiltrates and severe hypoxemia that dramatically responded to corticosteroids. Based on the pathologic description of the polypoid masses of intraluminal connective tissue and the favorable response to corticosteroids, this lesion should be classified as BOOP. Miyagawa et al50 described two elderly patients with postinfectious BOOP. One had serologic evidence of L pneumophila infection and the other, M pneumoniae infection. Interestingly, circulating immune complexes were found in both patients prior to treatment with corticosteroids and were undetectable after treatment. A 57-year-old woman was recently reported to have BOOP due to M pneumoniae infection.51 Similar to our patient 1 with BOOP, there was significant improvement with corticosteroid treatment. In a patient with IgA deficiency due to ataxia-telangiectasia, BOOP occurred due to M pneumoniae infection.52
Rollins and coworkers14 described six patients with open lung biopsy specimen-proved inflammatory (cellular) bronchiolitis due to M pneumoniae. In three of the cases, there was an accompanying bronchopneumonia. A lymphoplasmocytic bronchiolar wall infiltrate with a neutrophil-rich intraluminal exudate was present. Ultrastructurally, there was extensive injury to the respiratory mucosa, causing loss of cilia and ciliated cells. Also noted was edema, fibrosis, and plasma cells infiltrating the bronchial and bronchiolar walls with extension of the inflammatory exudate from the bronchiolar lumen into the alveolar spaces. This histologic pattern is distinct from both constrictive bronchiolitis and BOOP. Although most patients with acute infectious inflammatory bronchiolitis recover without significant sequelae, some may develop constrictive bronchiolitis or reactive airways disease.33 53 Based on this and the few reports of constrictive bronchiolitis evolving from BOOP, we speculate that acute inflammatory bronchiolitis could also be an earlier stage of proliferative bronchiolitis (BOOP). Fraley et al12described a patient with respiratory failure from M pneumoniae pneumonia who had both acute necrotizing pneumonitis with consolidation and “bronchiolitis obliterans” on open lung biopsy specimen. Although the type of bronchiolitis was not described further,12 the restrictive changes noted on pulmonary function tests would argue against constrictive bronchiolitis obliterans and would be more representative of BOOP or inflammatory bronchiolitis. In another patient with respiratory failure due to M pneumoniae, a nodular infiltrate on chest radiograph correlated with a lung biopsy specimen that showed a confluent infiltrate in a bronchiolocentric distribution.13 The inflammatory infiltrate consisted of plasma cells, lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils in addition to basophilic connective tissue obliterating the lumen of the small airways and alveolar ducts. Pulmonary function testing in this patient revealed a mixed obstructive and restrictive defect.
The aforementioned clinical cases correlate with a hamster model of M pneumoniae infection, in which intratracheal inoculation of the organism produced a bronchiolitis characterized by peribronchiolar and perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate and a neutrophil and macrophage exudate in the bronchiolar lumen.54 Thus, it is likely that cases of severe pulmonary infections caused by M pneumoniae are due to an exuberant cell-mediated immune response, accounting for the favorable response to corticosteroids in the cases cited above.55
Herein we describe three adults with M pneumoniae pulmonary infections who presented with small airways disease as their only manifestation. One (patient 1) had postinfectious bronchiolitis with organizing pneumonia (BOOP), and two had an acute inflammatory bronchiolitis. Although patient 1 had BOOP, his chest radiograph was atypical. Patients 1 and 3 had subtle findings on chest radiograph despite severe gas exchange abnormalities, and patient 2 had striking ventilatory and perfusion defects despite a normal chest radiograph. These cases are unusual because both BOOP and inflammatory bronchiolitis are uncommon presentations of M pneumoniaeinfections, especially in the absence of lobar or patchy alveolar pneumonia. Moreover, acute infectious bronchiolitis requiring hospitalization is unusual in adults. In patient 1, open lung biopsy specimen demonstrated a proliferative bronchiolitis. The restrictive physiology, crackles on lung examination, and response to corticosteroids in this individual are consistent with the diagnosis of BOOP.34 Although it is possible that constrictive bronchiolitis may follow BOOP, this patient, after 2 years of follow-up, has not developed progressive airflow limitation. One notable finding in patient 2 was the marked asymmetric and extensive involvement by bronchiolitis of the left lung, as evinced by physical examination, ventilation-perfusion lung scanning, and HRCT. The bronchiolitis present in patients 2 and 3 is not consistent with either constrictive bronchiolitis obliterans because of the lack of obstructive physiology or of BOOP based on the HRCT scan, but it rather is characteristic of an inflammatory (cellular) bronchiolitis.56 The HRCT findings are similar to other inflammatory bronchiolar diseases such as diffuse panbronchiolitis.32 In two of the patients in whom full pulmonary physiologic testing was done, severe restrictive lung disease was present in both patients. Although restrictive physiologic condition is to be expected in the patient with BOOP,18 we postulate that the matched ventilatory and perfusion defects that were present in the left lung of the second patient with inflammatory bronchiolitis indicated a poorly functioning left lung, resulting in low lung volumes. The third patient did not have lung volumes measured, but the FEV1 to FVC ratio of > 100% predicted suggests a restrictive pattern.
Footnotes
Supported by National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute training grant HL07085 (Drs. Kalayanamit, Arndt, and Winn). Dr. Chan is recipient of Career Investigational Development Award, National Institutes of Health grant 1K08HL03625-01.
References
- 1.Leong MA, Nachajon R, Ruchelli E. Bronchitis obliterans due to Mycoplasma pneumonia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1997;23:375–381. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-0496(199705)23:5<375::aid-ppul10>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Halal F, Brochu P, Delage G. Severe disseminated lung disease and bronchiectasis probably due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Can Med Assoc J. 1977;117:1055–1056. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kawata K, Sumino Y, Kikuchi Y. Two cases of Mycoplasma pneumoniae with cavity formation. Jpn J Med. 1978;17:144–147. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stokes D, Sigler A, Khouri NF. Unilateral hyperlucent lung (Swyer-James syndrome) after severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978;117:145–152. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Solanki DL, Berdoff RL. Severe mycoplasma pneumonia with pleural effusions in a patient with sickle cell-hemoglobin C (SC) disease—case report and review of the literature. Am J Med. 1979;66:707–710. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)91189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Koletsky RJ, Weinstein AJ. Fulminant Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980;122:491–496. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tablan OC, Reyes MP. Chronic interstitial pulmonary fibrosis following Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Am J Med. 1985;79:268–270. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kaufman JM, Cuvelier CA, Van der Straeten M. Mycoplasma pneumonia with fulminant evolution into diffuse interstitial fibrosis. Thorax. 1980;35:140–144. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.2.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Siegler DIM. Lung abscess associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Br J Dis Chest. 1973;67:123–127. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(73)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Busse WW. The precipitation of asthma by upper respiratory infections. Chest. 1985;87:44S–48S. doi: 10.1378/chest.87.1_supplement.44s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zoratti EM, Busse WW. The role of respiratory infections in airway responsiveness and the pathogenesis of asthma. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 1990;10:449–461. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(90)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fraley DS, Ruben FL, Donnelly EJ. Respiratory failure secondary to Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. South Med J. 1979;72:437–440. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197904000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Coultas DB, Samet JM, Butler C. Bronchiolitis obliterans due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. West J Med. 1986;144:471–474. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rollins S, Colby T, Clayton F. Open lung biopsy in Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986;110:34–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Henderson FW, Clyde WA, Collier AM. The etiologic and epidemiologic spectrum of bronchiolitis in pediatric practice. J Pediatr. 1979;95:183–190. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80647-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wohl MEB, Chernick V. Bronchiolitis: state of the art. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978;118:759–781. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.4.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cadieux N, Lebel P, Brousseau R. Use of a triplex polymerase chain reaction for the detection and differentiation of Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Mycoplasma genitalium in the presence of human DNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1993;139:2431–2437. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-10-2431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.King TE., Jr Overview of bronchiolitis. Clin Chest Med. 1993;14:607–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.King TE., Jr Bronchiolitis obliterans. Lung. 1989;167:69–93. doi: 10.1007/BF02714935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Colby TV, Myers JL. Clinical and histologic spectrum of bronchiolitis obliterans, including bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Semin Respir Med. 1992;13:119–133. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Garg K, Lynch DA, Newell JD. Proliferative and constrictive bronchiolitis: classification and radiologic features. Am J Radiol. 1994;162:803–808. doi: 10.2214/ajr.162.4.8140994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wright JL, Cagle P, Churg A. Diseases of the small airways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992;146:240–262. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.1.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yousem SA, Colby TV, Carrington CB. Lung biopsy in rheumatoid arthritis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985;131:770–777. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.5.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.King TE., Jr . Bronchiolitis. In: Schwarz MI, King TE Jr, editors. Interstitial lung disease. 2nd ed. Mosby-Year Book; St Louis, MO: 1993. pp. 463–495. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Epler GR, Colby TV. The spectrum of bronchiolitis obliterans. Chest. 1983;83:161–162. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Churg A. Small airways disease associated with mineral dust exposure. Semin Respir Med. 1992;13:140–148. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yousem SA. Small airway injury in heart-lung transplant recipients. Semin Respir Med. 1992;13:85–93. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Epler GR. Bronchiolitis obliterans and airways obstruction associated with graft-versus-host disease. Clin Chest Med. 1988;9:551–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Burke CM, Theodore J, Dawkins KD. Post-transplant obliterative bronchiolitis and other late lung sequelae in human heart-lung transplantation. Chest. 1984;86:824–829. doi: 10.1378/chest.86.6.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hall WJ, Hall CB, Speers DM. Respiratory syncytial virus in adults: clinical, virologic, and serial pulmonary function studies. Ann Intern Med. 1978;88:203–205. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-2-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sato P, Madtes DK, Thorning D. Bronchiolitis obliterans caused by Legionella pneumophila. Chest. 1985;87:840–842. doi: 10.1378/chest.87.6.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Muller NL, Miller RR. Diseases of the bronchioles: CT and histopathologic findings. Radiology. 1995;196:3–12. doi: 10.1148/radiology.196.1.7784583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Myers JL, Colby TV. Pathologic manifestations of bronchiolitis, constrictive bronchiolitis, cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, and diffuse panbronchiolitis. Clin Chest Med. 1993;14:611–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Epler GR, Colby TV, McCloud TC. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1985;312:152–158. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501173120304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Myers JL, Katzenstein ALA. Ultrastructural evidence of alveolar epithelial injury in idiopathic bronchiolitis obliterans-organizing pneumonia. Am J Pathol. 1988;132:102–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kindt GC, Weiland JE, Davis WB. Bronchiolitis in adults: a reversible cause of airway obstruction associated with airway neutrophils and neutrophil products. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989;140:483–492. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.2.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Guerry-Force ML, Muller NL, Wright JL. A comparison of bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia, usual interstitial pneumonia, and small airways disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987;135:705–712. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.3.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Grinblat J, Mechlis S, Lewitus Z. Organizing pneumonia-like process: an unusual observation in steroid responsive cases with features of chronic interstitial pneumonia. Chest. 1981;80:259–263. doi: 10.1378/chest.80.3.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cordier JF, Loire R, Brune J. Idiopathic bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia: definition of characteristic clinical profiles in a series of 16 patients. Chest. 1989;96:999–1004. doi: 10.1378/chest.96.5.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hawley PC, Whitcomb ME. Bronchiolitis fibrosa obliterans in adults. Arch Intern Med. 1981;141:1324–1327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Katzenstein ALA, Myers JL, Prophet WD. Bronchiolitis obliterans and usual interstitial pneumonia. Am J Surg Pathol. 1986;10:373–381. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198606000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.McLoud TC, Epler GR, Colby TV. Bronchiolitis obliterans. Radiology. 1986;159:1–8. doi: 10.1148/radiology.159.1.3952294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ham JC. Acute infectious obstructing bronchiolitis: a potentially fatal disease in the adult. Ann Intern Med. 1964;60:47–60. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-60-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nikki P, Meretoja O, Valtonen V. Severe bronchiolitis probably caused by varicella-zoster virus. Crit Care Med. 1982;10:344–346. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198205000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.O'Reilly JF. Adult bronchiolitis and parainfluenza type 2. Postgrad Med J. 1980;56:787–788. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.56.661.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Seggev JS, Mason UG, Worthen S. Bronchiolitis obliterans: report of three cases with detailed physiologic studies. Chest. 1983;83:169–174. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Marinopoulos GC, Huddle KRL, Wainwright H. Obliterative bronchiolitis: virus induced? Chest. 1991;99:243–245. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.1.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Camp M, Mehta JB, Whitson M. Bronchiolitis obliterans and Nocardia asteroides infection of the lung. Chest. 1987;92:1107–1108. doi: 10.1378/chest.92.6.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Goldstein JD, Godleski JJ, Balikian JP. Pathologic patterns of Serratia marcescens pneumonia. Hum Pathol. 1982;13:479–484. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(82)80031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Miyagawa Y, Nagata N, Shigematsu N. Clinicopathological study of migratory lung infiltrates. Thorax. 1991;46:233–238. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.4.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Llibre JM, Urban A, Garcia E. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia associated with acute Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;25:1340–1342. doi: 10.1086/516124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ito M, Nakagawa A, Hirabayashi N. Bronchiolitis obliterans in ataxia telangiectasia. Virchows Arch. 1997;430:131–137. doi: 10.1007/BF01008034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hardy KA, Schidlow DV, Zaeri N. Obliterative bronchiolitis in children. Chest. 1988;93:460–466. doi: 10.1378/chest.93.3.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.McGee ZA, Taylor-Robinson D. Mycoplasmas in medical microbiology and infectious diseases. In: Braude AI, editor. Medical microbiology and infectious diseases. WB Saunders; Philadelphia, PA: 1981. pp. 522–528. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Chan ED, Welsh CH. Fulminant Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. West J Med. 1995;162:133–142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Worthy SA, Muller NL. Small airway diseases. Radiol Clin North Am. 1998;36:163–173. doi: 10.1016/s0033-8389(05)70012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


