Abstract
The Spectrum-STI model, structured by sub-groups within a population, was used in a workshop in Yunnan, China, to estimate provincial trends in active syphilis in 15 to 49-year-old adults. Syphilis prevalence data from female sex workers (FSW), men who have sex with men (MSM), and lower-risk women and men in Yunnan were identified through literature searches and local experts. Sources included antenatal care clinic screening, blood donor screening, HIV/STI bio-behavioural surveys, sentinel surveillance, and epidemiology studies. The 2017 provincial syphilis prevalence estimates were 0.26% (95% confidence interval 0.17–0.34%) in women and 0.28% (0.20–0.36%) in men. Estimated prevalence was 6.8-fold higher in FSW (1.69% (0.68–3.97%) than in lower-risk women (0.25% (0.18–0.35%)), and 22.7-fold higher in MSM (5.35% (2.74–12.47%) than in lower-risk men (0.24% (0.17–0.31%). For all populations, the 2017 estimates were below the 2005 estimates, but differences were not significant. In 2017 FSW and MSM together accounted for 9.3% of prevalent cases. These estimates suggest Yunnan’s STI programs have kept the overall prevalence of syphilis low, but prevalence remains high in FSW and MSM. Strengthening efforts targeting FSW and MSM, and identification of other risk populations e.g. among heterosexual men, are critical to reduce syphilis.
Subject terms: Epidemiology, Population screening
Introduction
Spectrum-STI is a statistical trend-fitting model designed for countries to estimate trends over time in the prevalence and incidence of three sexually transmitted infections (STIs): syphilis (etiologic agent: Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum); gonorrhea (Neisseria gonorrhoeae); and chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis) from available prevalence data after standardizing for diagnostic test, location and age and weighted to reflect representativeness. The model builds on the Spectrum suite of health policy planning and surveillance models developed by Avenir Health1. The latest version of Spectrum-STI, the Spectrum-STI Groups model, allows for estimates to be generated for different higher-risk and lower-risk groups in a population and for these to be combined to form an overall population estimate. In November 2018, Spectrum-STI Groups was piloted in a 3-day workshop held in Kunming, Yunnan’s capital, organized by the Yunnan provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
Yunnan province is located in the south-west of China and in 2017 had a population of just under 46 million (3.4% of China’s population). It is one of three provinces chosen by China’s National Health and Family Commission and UNICEF to pilot validating elimination of mother-to-child transmission of HIV, syphilis and Hepatitis B. STI control in Yunnan is focused primarily on Female Sex Workers (FSW), Men who have Sex with Men (MSM), Intravenous Drug Users (IDU), and STI clinic attendees and includes health education, condom promotion, free testing for HIV, syphilis and gonorrhea, and free treatment. The STI control budget doubled between 2000 and 20172 and syphilis prevention and treatment efforts have been expanded. Screening has been scaled-up using HIV testing facilities, methadone substitution and detoxification centers, antenatal care clinics (ANC) and hospitals. Syphilis partner notification and referral, and standardized treatment, have been incentivized by performance-based compensation to clinics. This has resulted in a five-fold increase in the number of FSW, MSM, individuals using HIV voluntary counselling and testing facilities and methadone maintenance clients tested for syphilis between 2010 and 2017, reaching 7.83 million people including 20,400 higher-risk individuals screened in 2017 alone. By 2015 testing rates were estimated to be 80% in FSW and 95% in VCT and ANC clients2. Among those diagnosed with syphilis, the rate of standard treatment has been above 80% since 20142.
STI surveillance in Yunnan includes etiological case reporting by hospitals and all other institutions that provide STI diagnosis to China’s infectious disease prevention and control information system. These data are collated and reported electronically, on a continuous basis. In addition, in collaboration with the HIV department, there is a sentinel surveillance system measuring syphilis serology annually in FSW and MSM. The surveillance in FSW focuses on women who self-identify as FSW and around 6,000 FSW have been sampled annually since 2005 from 16 sites across the 16 prefectures in Yunnan. Surveillance in MSM focuses on self-identified MSM and around 3,000 men have been sampled annually since 2010 from 14 sites (Table 1). These surveillance data are complemented by ad hoc, typically smaller-scale research studies done in specific population groups.
Table 1.
Syphilis prevalence data from Yunnan province.
| Population group | Population type | Year, midpoint | Diagnostic test | N positive | N tested | Prevalence (%) | Weight (%) | Location/Sites | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower-risk women | ANC: Survey | 2005 | RPR & TPHA | 4 | 3,242 | 0.12 | 25 | 4 national surveillance sites within Yunnan province (Kunming, Qilin, Longyang and Gejiu) | 16 |
| 2006 | 15 | 3,241 | 0.46 | 25 | |||||
| 2007 | 3 | 2,702 | 0.11 | 25 | |||||
| 2008 | 12 | 3,215 | 0.37 | 25 | |||||
| 2009 | 0 | 3,041 | 0.00 | 25 | |||||
| 2010 | 4 | 1,599 | 0.25 | 25 | |||||
| 2011 | 5 | 1,600 | 0.31 | 25 | |||||
| 2012 | 5 | 1,600 | 0.31 | 25 | |||||
| 2013 | 1 | 1,600 | 0.06 | 25 | |||||
| 2014 | 9 | 1,600 | 0.56 | 25 | |||||
| 2015 | 4 | 1,600 | 0.25 | 25 | |||||
| 2016 | 6 | 1,600 | 0.38 | 25 | |||||
| 2017 | 6 | 1,596 | 0.38 | 25 | |||||
| ANC: Routine screening | 2011 | RPR & TPHA | 239 | 637,241 | 0.04 | 0 | All 16 prefectures and 129 counties | 2 | |
| 2012 | 690 | 786,334 | 0.09 | 0 | |||||
| 2013 | 1,032 | 753,696 | 0.14 | 0 | |||||
| 2014 | 1,338 | 761,945 | 0.18 | 0 | |||||
| 2015 | 1,360 | 730,474 | 0.19 | 99.66 | |||||
| 2016 | 1,879 | 888,171 | 0.21 | 99.92 | (Unpublished) program data, Yunnan CDC, Kunming, Yunnan | ||||
| 2017 | 1,974 | 814,401 | 0.24 | 99.95 | |||||
| Blood Donor Screening | 2008 | TPHA alone | 120 | 29,584 | 0.41 | 43.75 | 7 prefectures (Chuxiong, Nujiang, Wenshan, Xishuangbanna, Yuxi, Diqing and Qujing) | 17,18 | |
| 2009 | 132 | 32,465 | 0.41 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2010 | 139 | 34,310 | 0.41 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2011 | 141 | 35,771 | 0.39 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2012 | 165 | 39,956 | 0.41 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2013 | 159 | 38,165 | 0.42 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2014 | 142 | 42,835 | 0.33 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2015 | 179 | 45,849 | 0.39 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2016 | 241 | 52,006 | 0.46 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2017 | 238 | 55,471 | 0.43 | 43.75 | |||||
| Premarital Screening | 2001 | TPHA alone | 24 | 3,742 | 0.34 | 6.25 | 1 site (urban and rural) | 19 | |
| Lower-risk men | Blood Donor Screening | 2008 | TPHA alone | 217 | 43,020 | 0.50 | 43.75 | 7 prefectures (Chuxiong, Nujiang, Wenshan, Xishuangbanna, Yuxi, Diqing and Qujing) | 17,18 |
| 2009 | 244 | 47,547 | 0.51 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2010 | 220 | 52,385 | 0.42 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2011 | 229 | 56,517 | 0.41 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2012 | 297 | 62,171 | 0.48 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2013 | 236 | 56,320 | 0.42 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2014 | 252 | 61,675 | 0.41 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2015 | 275 | 65,825 | 0.42 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2016 | 339 | 73,984 | 0.46 | 43.75 | |||||
| 2017 | 317 | 76,685 | 0.41 | 43.75 | |||||
| Premarital Screening | 2001 | TPHA alone | 24 | 3,742 | 0.34 | 6.25 | 1 site (urban and rural) | 19 | |
| Lower-risk Women + Men pooled | Blood Donor Screening | 2008 | TPHA alone | 39 | 9,102 | 0.43 | 6.25/0* | 1 prefecture (Dehong) | 20 |
| 2009 | 29 | 10,034 | 0.29 | 6.25/0* | |||||
| 2010 | 36 | 11,622 | 0.31 | 6.25/0* | |||||
| 2011 | 35 | 13,302 | 0.26 | 6.25/0* | |||||
| 2012 | 53 | 13,164 | 0.40 | 6.25/0* | |||||
| 2013 | 39 | 12,295 | 0.32 | 6.25/0* | |||||
| FSW | FSW: Study | 2006 | RPR & TPHA | 55 | 737 | 7.46 | 10 | 1 site (Kaiyuan City) | 21 |
| FSW: Study | 2006 | RPR & TPHA | 12 | 96 | 12.50 | 20 | 2 sites (Kafang & Laochang towns) | 50 | |
| FSW: Study | 2007 | RPR & TPHA | 27 | 397 | 6.80 | 10 | 1 site (Kaiyuan City) | 26 | |
| FSW: Study | 2007 | RPR & TPHA | 32 | 270 | 11.85 | 10 | Detaining education centre, urban | 28 | |
| FSW | FSW: Study | 2010.5 | RPR & TPHA | 3 | 201 | 1.49 | 10 | 1 site (Kaiyuan City) | 27 |
| FSW: Study | 2011 | RPR & TPHA | 113 | 1,775 | 6.37 | 10 | 1 site (Kaiyuan City) | 53 | |
| FSW: Study | 2012 | RPR & TPHA | 62 | 734 | 8.45 | 10 | 1 site (Kaiyuan City) | 23 | |
| FSW: Study | 2012.5 | RPR & TPHA | 44 | 225 | 19.56 | 40 | 4 sites (Dali, Jinghong, Kaiyuan and Menghai cities) | 24 | |
| FSW: Study | 2017 | RPR & TPHA | 13 | 423 | 3.07 | 10 | 1 site (Kunming City) | 29 | |
| FSW: Sentinel | 2005 | RPR & TPHA | 107 | 5,849 | 1.83 | 100 | All 16 prefectures | 16 | |
| 2006 | 50 | 5,396 | 0.93 | 100 | |||||
| 2007 | 92 | 5,782 | 1.59 | 100 | |||||
| 2008 | 77 | 5,909 | 1.30 | 100 | |||||
| 2009 | 71 | 6,225 | 1.14 | 100 | |||||
| 2010 | 135 | 5,960 | 2.27 | 100 | |||||
| 2011 | 113 | 6,026 | 1.88 | 100 | |||||
| 2012 | 146 | 6,047 | 2.41 | 100 | |||||
| 2013 | 88 | 6,464 | 1.36 | 100 | |||||
| 2014 | 68 | 5,495 | 1.24 | 100 | |||||
| 2015 | 54 | 5,836 | 0.93 | 100 | |||||
| 2016 | 104 | 6,336 | 1.64 | 100 | |||||
| MSM | MSM: Sentinel | 2010 | RPR & TPHA | 44 | 1,169 | 3.76 | 87.5 | 14 prefectures | 16 |
| 2011 | 21 | 1,556 | 1.35 | 87.5 | |||||
| 2012 | 65 | 2,613 | 2.49 | 87.5 | |||||
| 2013 | 83 | 2,992 | 2.77 | 87.5 | |||||
| 2014 | 91 | 3,206 | 2.84 | 87.5 | |||||
| 2015 | 103 | 2,983 | 3.45 | 87.5 | |||||
| 2016 | 106 | 2,863 | 3.70 | 87.5 | |||||
| MSM: Study | 2009 | TPHA alone | 62 | 825 | 7.52 | 10 | 1 site (Kunming City) | 30 | |
| MSM: Study | 2010 | RPR & TPHA | 6 | 305 | 1.97 | 10 | 1 site (Dali prefecture) | 33 | |
| MSM: Study | 2014 | RPR & TPHA | 34 | 300 | 11.33 | 10 | 1 site (Kunming City) | 32 | |
| MSM: Study | 2008 | RPR & TPHA | 37 | 266 | 13.91 | 10 | 1 site (Kunming City) | 31 | |
| 2009 | 40 | 307 | 13.03 | 10 | |||||
| 2010 | 36 | 258 | 13.95 | 10 |
Pre-2015 ANC routine screening data were not included in the default estimation owing to a change in the ANC screening algorithm in 2015 from Treponema pallidum particle agglutination assay (TPPA) and RPR with an RPR threshold of 1:8, to a positive result from a Treponema-based rapid point-of-care test followed by RPR confirmation with no threshold, and an expansion in the number of sites tested from 2011 to 2015.
A number of the studies in FSW venues were cohort studies with repeated measurements and where later rounds probably resampled the same individuals after they had been treated. For these studies only the 1st round of data were included in the Spectrum estimations.
*6.25% is the default weight for men. These data were not included in default the estimate for women, owing to the large number of other women-specific data points.
Abbreviations: RPR = Rapid Plasma Reagin test; TPHA = Treponema pallidum hemagglutination assay; RPR&TPHA = dual positivity on both RPR and TPHA.
This paper presents the syphilis prevalence trend estimates for 2005 to 2017 generated using Spectrum-STI, for four population groups in Yunnan: Lower-risk women, Lower-risk men, FSW and MSM. These four estimates were then combined into provincial syphilis estimates for all 15–49 year old women and men. Findings are discussed with a view to how Spectrum-STI can be used by national and provincial HIV/STI programs to inform surveillance, evaluation and planning.
Methods
Prevalence data
Syphilis prevalence data were identified through a PubMed search of studies published in 2000 or later with the key words ‘China’ AND (‘sexually transmitted infection’ OR ‘sexually transmitted disease’ OR ‘syphilis’), a search of the Chinese scientific literature using these and related key words (using the search systems: www.cnki.net, www.cqvip.com and wanfangdata.com.cn), and back-tracking references of relevant English and Chinese language articles. These data were supplemented by published and unpublished/program data identified by STI experts during and in the 4 months after the November 2018 workshop (Table 1). Only studies where the majority of samples were from Yunnan Province and collected in 2000 or later were included in the analysis.
Data were collected for the following populations:
Lower-risk women: ANC routine screening (program data), ANC sentinel surveillance surveys, blood donor screening, community surveys, obstetrics & gynaecology patients and pre-marriage screening;
Lower-risk men: Blood donor screening, pre-marriage screening;
FSW: Annual sentinel surveillance surveys, ad hoc research studies. Data from FSW seeking care in STD clinics and re-education centers were not included;
MSM: Annual sentinel surveillance surveys and ad hoc studies.
Spectrum-STI model
Spectrum-STI is a statistical model that fits time trends in national or provincial adult STI prevalence and incidence, based on STI prevalence data3,4. In the fall of 2018, the model was expanded to incorporate different population groups (Spectrum-STI versions 5.73 and onwards) and is available online (https://avenirhealth.org/software-spectrum.php). The updated model was piloted in Yunnan province at a workshop in November 2018.
Provincial estimates were generated for four populations – Lower-risk women, lower-risk men, FSW and MSM. The estimates for the four populations were combined, based on their estimated contribution to the provincial population, to form provincial estimates. The adult (15–49 years) female and male population sizes for Yunnan province were created by the Division of Epidemiology, National Center for AIDS/STD Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention and Avenir Health, based on China’s 2000 and 2010 national population censuses5 and Statistical Yearbooks6 with their year-on-year projections extrapolated through 2017.
FSW were assumed to account for 0.30% of women 15–49 years of age and MSM for 0.80% of men 15–49, and these percentages were assumed to remain constant over time. The FSW size estimate was based on service statistics of outreach to FSW over 2016–2017 reported to China’s disease prevention and control information system by all 129 counties in Yunnan and is in line with the UNAIDS estimate for Asia of FSW representing an average of 0.35% of adult women7–9. The MSM size estimate was based on a community household survey conducted in 2 prefectures of Yunnan in 201410 and is similar to results from two cluster-sampled surveys in male students from all 16 prefectures in Yunnan in 2005 and 2015 in which 0.7% and 0.9% self-reported MSM behavior11. Lower-risk women and men population sizes estimates were then derived by subtracting the estimated FSW and MSM populations from the total population (Table 2).
Table 2.
Population sizes, estimated syphilis prevalence (default estimates) and share of provincial prevalent cases in 4 adult (15–49 years) sub-populations in Yunnan province, 2005 and 2017.
| Population group | Population size | Prevalence % (95% Confidence Interval) | Share of all prevalent cases | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 2017 | 2005 | 2017 | 2017 | |
| Lower-risk women | 12,077,922 | 12,148,877 | 0.26 (0.11–0.47) | 0.25 (0.18–0.35) | 45% |
| Lower-risk men | 12,893,877 | 13,135,136 | 0.26 (0.18–0.37) | 0.24 (0.17–0.31) | 46% |
| FSW | 36,343 | 36,556 | 1.93 (1.34–2.77) | 1.69 (0.68–3.97) | 0.91% |
| MSM | 103,983 | 105,929 | 6.84 (1.78–13.82) | 5.35 (2.74–12.47) | 8.4% |
| All women | 12,114,265 | 12,185,433 | 0.26 (0.18–0.35) | 0.26 (0.17–0.34) | 46% |
| All men | 12,997,860 | 13,241,065 | 0.32 (0.24–0.40) | 0.28 (0.20–0.36) | 54% |
| All women and men | 25,112,125 | 25,544,343 | 0.29 (0.22–0.36) | 0.29 (0.22–0.36) | 100% |
Standardizing and weighting prevalence data
Prevalence data from each study were standardized before trend fitting to ensure that they reflected active syphilis, the stage relevant for disease transmission, defined as concurrent positivity on both a non-treponemal (e.g., Rapid Plasma Reagin (RPR) or Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) test) and a treponemal test. This adjustment used the same approach and parameters as the WHO 2016 STI estimates4,12,13. For lower-risk men and women each study was assigned a weight reflecting how representative it was of the particular population group (Table 1). For FSW and MSM, prevalence trends were estimated separately for the provincial sentinel surveillance system data and for the ad-hoc studies. The two trend estimates were then combined, with the provincial surveillance trend assigned a weight of 94% (reflecting an average 15 out of the province’s 16 prefectures sampled) to account for the greater reliability of these data and the ad hoc studies trend a weight of 6% (reflecting a typical 1 of 16 prefectures sampled).
Syphilis trend estimates
Prevalence trends were estimated for each population group by fitting the standardized and weighted prevalence data using segmented polynomial regression. Segmented polynomials were fitted to the incidence underlying prevalence, assuming an average duration of infection for syphilis in both women and men of 4.1 years13. The fitted incidence curve was a second-order spline with a maximum of 2 knots, selected using the Akaike Information Criterion4.
Uncertainty intervals
Uncertainty bounds for each population group were calculated by bootstrapping3. When combining the results to generate the provincial estimates we assumed there was no uncertainty in population sizes. Differences between years were considered statistically significant if the respective 95% confidence intervals did not overlap.
Sensitivity analysis
Univariate sensitivity analyses looked at the impact of restricting the eligible data by altering the weights attached to individual data points and to data types available within each group. We also looked at the effect of changing the relative population sizes of FSW and MSM, using UNAIDS regional estimates for Asia or all low- and middle-income countries9,14 instead of Yunnan’s population size estimates. More general assumptions underlying the Spectrum-STI model have been addressed in sensitivity analyses in earlier publications3,4,15.
Results
Prevalence data
Table 1 presents the identified data that met the study entry criteria, and the default weights assigned to each data point. A total of 82 syphilis data points from Yunnan province were identified between 2000 and 2017 from ANC women, blood donors, pre-marital screening, FSW and MSM.
Lower-risk women
31 data points were identified from ANC routine screening (2011 to 2017), ANC sentinel screening in four cities that were part of China’s national STI surveillance (2005 to 2017)16, blood donor screening (7 prefectures from 2008 to 2017, a period when donor eligibility criteria were stable)17,18, and pre-marriage compulsory syphilis screening (1 prefecture in 2001, covering urban and rural areas within 1 prefecture19).
Lower-risk men
11 data points were identified from blood donor screening (7 prefectures from 2008 to 2017, a period when donor eligibility criteria were stable)17,18, and pre-marriage compulsory syphilis screening (1 prefecture in 2001, covering urban and rural areas19).
Lower-risk men and women
6 data points were identified from blood donors where no breakdown by sex was provided (1 prefecture from 2008 to 2013)20.
FSW
21 data points were identified from the annual sentinel surveillance surveys (16 prefectures from 2005 to 201616) and studies (9 studies conducted between 2006 and 201721–29).
MSM
13 data points were identified from the annual sentinel surveillance surveys (14 prefectures from 2010 to 201616) and studies (6 studies conducted between 2009 and 201430–33).
For both FSW and MSM, prevalence in the research studies were more diverse and, on average, higher than in the sentinel surveillance. This may reflect a bias in the sentinel surveillance data towards lower prevalence if FSW and MSM tested and treated in previous rounds are re-sampled. Or it may be that the research studies over-sampled populations in ‘hot-spot’ areas where prevalence is unrepresentatively high.
Spectrum-STI estimates
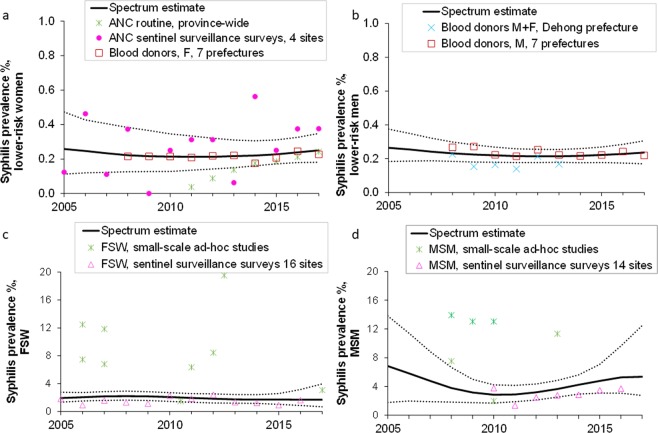
Figure 1 shows the Spectrum-STI estimations for 2005 to 2017 based on the default weightings for the four population groups. The Spectrum-STI trend estimates were restricted to 2005 to 2017, as only one study was identified between 2000 and 200519. In 2017 the estimated prevalence in lower-risk women was 0.25% (0.18–0.35%) and in lower- risk men 0.24% (0.17–0.31%). The prevalence in FSW in 2017, 1.69% (0.68–3.97%) was 6.8-fold greater than in lower- risk women and the prevalence in MSM 5.35% (2.74–12.47%) was 22.7-fold greater than in lower- risk men (see Table 2). Comparing the prevalences in 2005 and 2017, the 2017 estimates were lower than the 2005 estimates for all four population groups, but the 95% confidence intervals overlapped suggesting the differences were not significant.
Figure 1.
Prevalence data and estimates for active syphilis, Yunnan province, 2005–2017: (a) Lower-risk women; (b) Lower-risk men: (c) Female Sex Workers; (d) Men who have sex with men. Prevalence estimates shown are after adjustment for diagnostic test performance. Solid lines are the best estimates; dotted lines the corresponding 95% confidence interval. The blood donor screening data that could not be disaggregated by sex; Table 1) were used in the estimation for lower-risk men, as this group had few other data available (panel b) and the majority of donors in this dataset (56%) were men. In contrast, they were not used in the estimation for lower-risk women, for whom there were many more data points (panel a).
The estimated prevalence for all women between the ages of 15 and 49 in Yunnan province is almost identical to the estimate for lower-risk women (Table 2) reflecting the small proportion of FSW in Yunnan’s overall women’s population (0.30%). FSW and MSM together accounted for 0.9% and 8.4% of prevalent cases, respectively, totaling 9.3% of all prevalent cases (Table 2).
In 2017, 46% of prevalent cases were in women and 54% in men. The larger share of men primarily reflects the relative contribution of FSW and MSM. FSW accounted for 0.9% of prevalent cases (Table 2), whilst MSM, with their larger share of the male population and higher prevalence, accounted for 8.4%.
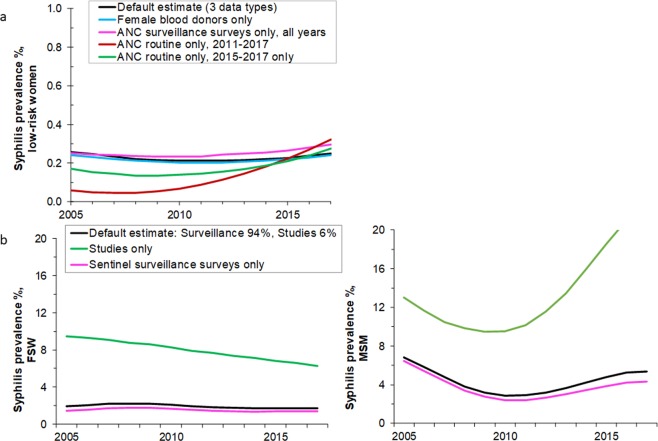
Sensitivity analysis
The effect of altering the prevalence data included in the trend analysis are illustrated in Fig. 2. Figure 2a is for lower-risk women and compares the default estimate that combined three data types, with an estimate based only on (i) routine ANC data, (ii) ANC sentinel surveillance data, or (iii) female blood donor data. The trend estimates for ANC surveillance data and for blood donor data are both similar to the default estimate, with a fairly stable prevalence (Fig. 2a). The ANC routine data only, however, suggest prevalence has increased but this is based on only 3 years of data (2015 to 2017) as the pre-2015 routine ANC measurements used a stricter case definition (threshold titer for RPR test) and covered fewer sites. If the 2011–2014 routine ANC data are added to the analysis (Fig. 1a), the increase is more marked (Fig. 2a).
Figure 2.
Syphilis prevalence estimates under alternative data inclusion criteria, for (a) Lower-risk women, (b) FSW and (c) MSM. Series titles shown in panel b also apply to panel c.
For FSW (Fig. 2b) and MSM (Fig. 2c) the trend estimates based on the ad hoc studies were much higher than those based on sentinel surveillance surveys alone. For FSW, the estimates based on the sentinel surveillance surveys suggest that between 2005 and 2017 prevalence was stable, whilst those based on the ad hoc studies suggest a steady decline.
For MSM, the estimates based on the sentinel surveillance surveys suggest that prevalence fell between 2005 and 2010 but has been stable or increasing slightly since then. The trend estimate based on the ad-hoc studies, in contrast, shows a strong decline in prevalence followed by a partial more recent increase.
In the default estimates presented above, we assumed 0.30% of the female population were FSW, which is in line with the UNAIDS’ median estimate for the Asian region of 0.35%8,9. If the FSW group size is increased to the UNAIDS median across all low- and middle-income countries8,9 of 0.67%, the share of FSW in overall adult syphilis prevalence in 2017 increased from 0.91% to 2.0%, and overall female prevalence from 0.256% to 0.263%. If the group size is increased to UNAIDS’ upper limit estimate for the Asian region of 2.33%8,9, then FSW account for 6.2% of the overall adult syphilis prevalence in Yunnan, and overall female prevalence would increase to 0.28%.
Finally, increasing the proportion of MSM from the Yunnan estimate of 0.80% to the UNAIDS’ median regional estimate for Asia9,14 of 1.69% of the overall male population, the share of MSM in overall adult syphilis prevalence increased from 8.4% to 16%, and the male prevalence estimate from 0.28% to 0.31%.
Discussion
This study illustrates the functionality and relevance of the Spectrum-STI Groups model for estimating trends in syphilis prevalence across distinct population groups. The model was piloted at a workshop in Yunnan Province that brought together individuals from different implementing and supporting organizations to discuss the strengths and limits of the available local prevalence data and to identify additional data sources. The workshop looked at three infections but, owing to a lack of historical data for gonorrhea and chlamydia for which a prevalence study was just ongoing, we decided to focus this analysis on syphilis.
The 2017 syphilis prevalence estimate in Yunnan for women 15 to 49 was 0.26% (0.17–0.34%) and for men 0.28% (0.20–0.36%). These levels are low compared to other East and Central Asia countries15, and relative to countries with similar per capita incomes34–36. Given the low prevalence, Yunnan is in a position where it could meet the WHO criteria for eliminating congenital syphilis, provided coverages of ANC attendance, of ANC-based syphilis screening and of syphilis treatment among women diagnosed during ANC are all 95% or higher37.
The estimates for all four population groups were lower in 2017 than in 2005, although the differences were not significant. This suggests that the province’s targeted HIV/STI response, which includes free syphilis (and HIV) screening, alongside free counselling and prevention services has helped contain the spread of syphilis during a time of social and economic change and liberalization. For FSW, the estimated decline is consistent with the national FSW surveillance data from sites in other provinces of China followed since 200538. For MSM the results are consistent with the overall decline in syphilis prevalence observed among male patients of STD clinics in Yunnan2. The decline is also consistent with the drop in test positivity rates in routine provincial syphilis case reporting, from 0.20% in 2012 to 0.14% in 2017, while numbers tested annually increased 3-fold2. Still, based on the estimated trends, Yunnan province is not on track to reach the strong decline required to meet the global target in the WHO Global Health Sector Strategy for STI control, of a 90% reduction in the incidence of syphilis between 2018 and 203039.
For FSW and MSM there were marked differences between the estimates based on the provincial sentinel surveillance data and those based on the small-scale ad hoc studies. The former was, on average, much lower, which may reflect the fact that individuals who are part of the sentinel surveillance system are more likely to be screened and treated and as a result have, on average, a shorter duration of infection.
FSW and MSM together accounted for 9.3% of Yunnan’s estimated prevalent cases in 2017. This is lower than the share of these key groups in past Spectrum-STI estimates35,36,40, and in HIV incidence estimates41–44, which reflects that both the estimated prevalence of syphilis in FSW and Yunnan’s key population size estimates are lower than in other countries7,9,45,46. The size estimate of FSW was based on self-identified sex workers; and almost certainly is an under-estimate of the total number of women who engage in transactional sex work. As a result, the relative share of FSW and MSM in incident cases is likely greater than 9.3% − and for MSM closer to their share in national case notifications in China and other countries47,48. In addition, FSW and MSM, by having on average relatively many partners, contribute more newly transmitted infections per episode, than lower-risk individuals.
The strengths of this study lie in the large number of data points identified from different populations and sources in Yunnan, the engagement of the Yunnan CDC in interpreting data and assigning weights to the prevalence studies used, and the use of Spectrum-STI to generate trend estimates. Spectrum-STI provided a unified coherent approach for synthesizing data from different sources, taking into account varying diagnostic tests, data collection methods and possible biases in sampling.
The provincial results, however, are very dependent on the underlying prevalence data, which vary in quantity, quality and representativeness. The sensitivity analysis showed how the trends were influenced by the data sources included, and the benefits from combining and triangulating multiple data types. The trend estimations for Yunnan show the benefits of extracting and reviewing data from different population groups and collected for different purposes. For lower-risk women the data from ANC sentinel surveillance and blood donor screening are similar. The routine ANC data suggested an increase, but this trend may have been biased by the change in testing regimen and expansion in coverage of screening service. For FSW and MSM there were marked differences between the estimates based on the provincial sentinel surveillance data and those based on the small-scale ad hoc studies. The former was, on average, much lower, which may reflect the fact that individuals who are part of the sentinel surveillance system are more likely to be screened and treated and as a result have, on average, a shorter duration of infection.
Our analysis focused on four population groups - however, this is a simplification of the real world and ignores other key populations (e.g., Intravenous drug users) and populations at intermediate risk of infection (e.g., truck drivers, migrants and mining workers and male clients of FSW49–52), and even with the identified risk groups of FSW and MSM, there are sub-groups with different risk profile and prevalence. As additional data become available (both prevalence data and population size) the model for Yunnan should be expanded. Incorporating other groups – e.g., an intermediate-risk groups, who were likely under-sampled in the studies we have included (e.g. of ANC women), would likely increase the prevalence estimates compared to those currently presented.
Yunnan has a strong sentinel surveillance system focused on FSW and MSM and on syphilis in ANC women. Future estimates would benefit from an expansion of these efforts to collate additional data from lower-risk men and populations at intermediate risk of infection, and from assessing how representative the sentinel surveillance data are of the overall FSW and MSM populations. In addition, estimates would benefit from additional studies looking at the relative size of the different population groups modelled.
Tools like Spectrum-STI have a role to play in helping program managers interpret surveillance data and monitor progress towards reducing the public health burden of STIs and the elimination of mother-to-child transmission of syphilis. Spectrum-STI provided a constructive framework for collating and analyzing data in Yunnan from a variety of different data sources and encouraged dialogue between the key players. The resulting estimates suggests that the prevalence of syphilis in the general population in Yunnan is low, under 0.30% in men and women 15 to 49 years. Syphilis, nevertheless, continues to pose a public health challenge, and prevention, screening and surveillance efforts would benefit from additional strengthening and expansion beyond the current target groups.
Acknowledgements
The views expressed in this paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official position of Avenir Health, the World Health Organization, the United States of America Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or other affiliated organization. Financial support for this work was provided by the WHO’s Department of Reproductive Health and Research/Human Reproduction Programme, the Department for International Development (DFID), United Kingdom and the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US CDC).
Author contributions
E.K., J.R., M.J. and M.Y. conceived the paper. X.Z., W.Z., Y.M., M.J., X.G., E.K., M.T. and J.R. compiled and analyzed data. E.K., J.R., K.H., G.M., J.L. and F.C. tested the modelling software. E.K., J.R., G.M. and M.Y. performed estimations. G.M. developed the statistical estimation method. K.H. programmed the software. E.K. and J.R. wrote the paper. All authors reviewed the final results and the paper.
Data availability
All data analyzed and used, and all estimates generated during this study are included in this published article and its Tables.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Eline L. Korenromp, Wanyue Zhang and Xiujie Zhang.
References
- 1.Stover J, McKinnon R, Winfrey B. Spectrum: a model platform for linking maternal and child survival interventions with AIDS, family planning and demographic projections. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010;39:i7–i10. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyq016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhang W, et al. Monetary incentives for provision of syphilis screening, Yunnan, China. Bull. World Health Organ. 2017;95:657–662. doi: 10.2471/BLT.17.191635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Korenromp, E. L. et al. Estimating prevalence trends in adult gonorrhoea and syphilis prevalence in low- and middle-income countries with the Spectrum-STI model: results for Zimbabwe and Morocco from 1995 to 2016. Sex Transm Infect sextrans-2016-052953, 10.1136/sextrans-2016-052953 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Korenromp, E. L. et al. Syphilis prevalence trends in adult women in 132 countries – estimations using the Spectrum Sexually Transmitted Infections model. Scientific Reports8, 10.1038/s41598-018-29805-9 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2010 Populatoin Census, http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/statisticaldata/censusdata/ (2012).
- 6.National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbooks, 1999 to 2016, http://data.stats.gov.cn/english/publish.htm?sort=1 (2019).
- 7.Sabin K, et al. Availability and Quality of Size Estimations of Female Sex Workers, Men Who Have Sex with Men, People Who Inject Drugs and Transgender Women in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0155150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Vandepitte, J. et al. Estimates of the number of female sex workers in different regions of the world. Sex Transm Infect 82 Suppl 3, iii18–25, 82/suppl_3/iii18 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 9.UNAIDS. Quick Start Guide for Spectrum 2018. (Geneva, 2018).
- 10.Yunnan Provincial Centre for Disease Control and Prevention. Community household survey conducted in Honghe and Dali prefectures in 2014 (Yunnan Provincial Centre for Disease Control and Prevention, Kunming, 2019).
- 11.Yunnan Provincial Centre for Disease Control and Prevention. Cluster sample surveys of male students in 16 prefectures of Yunnan province, 2005 and 2015 (Yunnan Provincial Centre for Disease Control and Prevention, Kunming, 2015).
- 12.Korenromp EL, et al. Global burden of maternal and congenital syphilis and associated adverse birth outcomes – estimates for 2016 and progress since 2012. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0211720. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rowley JTF, et al. Chlamydia, gonorrhoea, trichomoniasis and syphilis: global prevalence and incidence estimates, 2016. Bull. WHO. 2019;97:548–562P. doi: 10.2471/BLT.18.228486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Caceres C, Konda K, Pecheny M, Chatterjee A, Lyerla R. Estimating the number of men who have sex with men in low and middle income countries. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2006;82(Suppl 3):iii3–9. doi: 10.1136/sti.2005.019489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Enkhbat E, et al. Estimating adult female syphilis prevalence, Congenital Syphilis case incidence and adverse birth outcomes due to Congenital Syphilis using the Spectrum Sexually Transmitted Infection surveillance tool, Mongolia 2000–2016. Infect. Dis. Model. 2018;3:13–22. doi: 10.1016/j.idm.2018.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yunnan Centers for Disease Control. Sentinel surveillance of syphilis, in pregnant women in antenatal care, in Female Sex Workers and in Men having Sex with Men in Yunnan province of China. (2018).
- 17.Pan B, Wu L, Huang C, Liu Y, Zhang Y. Analysis of Syphilis Screening among Voluntary Blood Donors in Yuxi City from 2007 to 2014. Chin. J. AIDS STD. 2016;22:290–291. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Blood banks of Chuxiong & Nujiang & Wenshan & Xishuangbanna & Yuxi & Diqing & Qujing prefectures. Syphilis prevalence in blood donors screened in the blood banks of Chuxiong, Nujiang, Wenshan, Xishuangbanna, Yuxi, Diqing and Qujing prefectures of Yunnan province, 2008 to 2017–data reported to the Yunnan Centers for Disease Control (Yunnan Centers for Disease Control, Kunming, 2018).
- 19.Hesketh T, et al. HIV and syphilis in young Chinese adults: implications for spread. Int. J. STD AIDS. 2005;16:262–266. doi: 10.1258/0956462053420257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yuan G, Wang Q. The serum analysis of Dehong blood donors. Chin. J. Dermatology Venereology. 2015;37:91–93. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang H, et al. Prevalence and predictors of HIV infection among female sex workers in Kaiyuan City, Yunnan Province, China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2009;13:162–169. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2008.05.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lin L, et al. Study on genital tract Chlamydia trachomatis and gonococcal infection in Han and minority (Naxi and Dai) women in China’s two provinces. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1999;3:221–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0756.1999.tb01151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Luo L, et al. Prevalence and correlates of Trichomonas vaginalis infection among female sex workers in a city in Yunnan Province, China. Int. J. STD AIDS. 2016;27:469–475. doi: 10.1177/0956462415585449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhou C, et al. High prevalence of HIV and syphilis and associated factors among low-fee female sex workers in mainland China: a cross-sectional study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014;14:225. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pan S-F, et al. Analysis on the prevalence of HIV and syphilis among female sex workers with low fee in four counties of Yunnan province. J. Kunming Med. Univ. 2015;36:150–153. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yao Y, et al. Associations between drug use and risk behaviours for HIV and sexually transmitted infections among female sex workers in Yunnan, China. Int. J. STD AIDS. 2012;23:698–703. doi: 10.1258/ijsa.2012.011346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhang XD, Temmerman M, Li Y, Luo W, Luchters S. Vulnerabilities, health needs and predictors of high-risk sexual behaviour among female adolescent sex workers in Kunming, China. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2013;89:237–244. doi: 10.1136/sextrans-2012-050690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gao, L., Che, Z. & Lu, Y. A cross-sectional study on STDs/AIDS and HIV of 270 female sex workers. Chinese J Dematology and Venereology03 (2008).
- 29.Yang, C. et al. Successive/Snowball sampled survey among FSWs in Kunming of the prevalence of syphilis, gonorrhea and chlamydia. (Submitted to Chin J. AIDS STD (2019)).
- 30.Wu Z, et al. HIV and syphilis prevalence among men who have sex with men: a cross-sectional survey of 61 cities in China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013;57:298–309. doi: 10.1093/cid/cit210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chen H, Luo W, Li Y, Al E. Prevalence of HIV and syphilis infection in 831 MSM [article in Chinese] Dermatology Venereology. 2011;33:236–237. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhang X, et al. Prevalence and the associated risk factors of HIV, STIs and HBV among men who have sex with men in Kunming, China. Int. J. STD AIDS. 2017;28:1115–1123. doi: 10.1177/0956462416688818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yang G-Z, Wang H, Shi J-C. Survey of HIV/TP infection of gay in Dali prefecture. Chin. J. Health Laboratory Technol. 2011;21:995–996. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kularatne R, et al. Adult gonorrhea, chlamydia and syphilis prevalence, incidence, treatment and syndromic case reporting in South Africa: estimates using the Spectrum-STI model, 1990–2017. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0205863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Korenromp EL, et al. Adult syphilis, chlamydia and gonorrhea prevalence and incidence, and congenital syphilis incidence in Colombia, 1995–2016 – estimates using the Spectrum-STI model. Pan-American J. Public. Health. 2018;42:e118. doi: 10.26633/RPSP.2018.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rowley, J. & Korenromp, E. L. A pilot application of the Spectrum-STI model in a low-prevalence setting: Estimation of STI prevalence and incidence trends in Georgia. Technical Report, based on a workshop in Tbilisi, Georgia, August 23–24th 2017. (London, 2017).
- 37.World Health Organization. Elimination of mother-to-child transmission (EMTCT) of HIV and syphilis. Global guidance on criteria and processes for validation. (Geneva, 2014).
- 38.China National Center for STD control & Centers for Disease Control. Syphilis surveillance in women in Antenatal Care and in Female Sex Workers (2018).
- 39.World Health Organization. Global health sector strategy on sexually transmitted infections 2016–2021. Towards ending STIs. Report No. WHO/RHR/16.09 (Geneva, 2016).
- 40.Bennani A, et al. The prevalence and incidence of active syphilis in Morocco, 1995–2016: model-based estimation and implications for STI surveillance. PLoS one. 2017;12:e0181498. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kouyoumjian, S. P. et al. National and Souss Massa Draa HIV Modes of Transmission analysis in Morocco 2013. (Kingdom of Morocco Ministry of Health Department of Epidemiology and Disease Control National STI/AIDS Programme, Weill Cornell Medical College in Qatar, Qatar Foundation, ONUSIDA, Rabat, 2014).
- 42.Mumtaz GR, et al. The distribution of new HIV infections by mode of exposure in Morocco. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2013;89(Suppl 3):iii49–56. doi: 10.1136/sextrans-2012-050844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Shubber Z, Mishra S, Vesga JF, Boily MC. The HIV Modes of Transmission model: a systematic review of its findings and adherence to guidelines. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2014;17:18928. doi: 10.7448/IAS.17.1.18928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mukandavire C, et al. Estimating the contribution of key populations towards the spread of HIV in Dakar, Senegal. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2018;21(Suppl 5):e25126. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bennani, A. et al. National and Souss Massa Draa: HIV modes of transmission analysis in Morocco 2013. (Morocco Ministry of Health & Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS, 2014).
- 46.Sulaberidze L, et al. Population Size Estimation of Men Who Have Sex with Men in Tbilisi, Georgia; Multiple Methods and Triangulation of Findings. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0147413. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tucker JD, Cohen MS. China’s syphilis epidemic: epidemiology, proximate determinants of spread, and control responses. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2011;24:50–55. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e32834204bf. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mohammed H, et al. Increase in Sexually Transmitted Infections among Men Who Have Sex with Men, England, 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016;22:88–91. doi: 10.3201/eid2201.151331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhang G, et al. HIV-1 and STIs prevalence and risk factors of miners in mining districts of Yunnan, China. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2010;53(Suppl 1):S54–60. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181c7d8d2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Xu JJ, et al. HIV and STIs in clients and female sex workers in mining regions of Gejiu City, China. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2008;35:558–565. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e318165926b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Reilly KH, et al. HIV and associated risk factors among male clients of female sex workers in a Chinese border region. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2012;39:750–755. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31825f7af7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zhao R, et al. Sexually transmitted disease/HIV and heterosexual risk among miners in townships of Yunnan Province, China. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2005;19:848–852. doi: 10.1089/apc.2005.19.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Luo L, Li X, Zhang LL. Neisseria gonorrhoeae prevalence, incidence and associated risk factors among female sex workers in a high HIV-prevalence area of China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2015;38:115–120. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2015.07.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data analyzed and used, and all estimates generated during this study are included in this published article and its Tables.