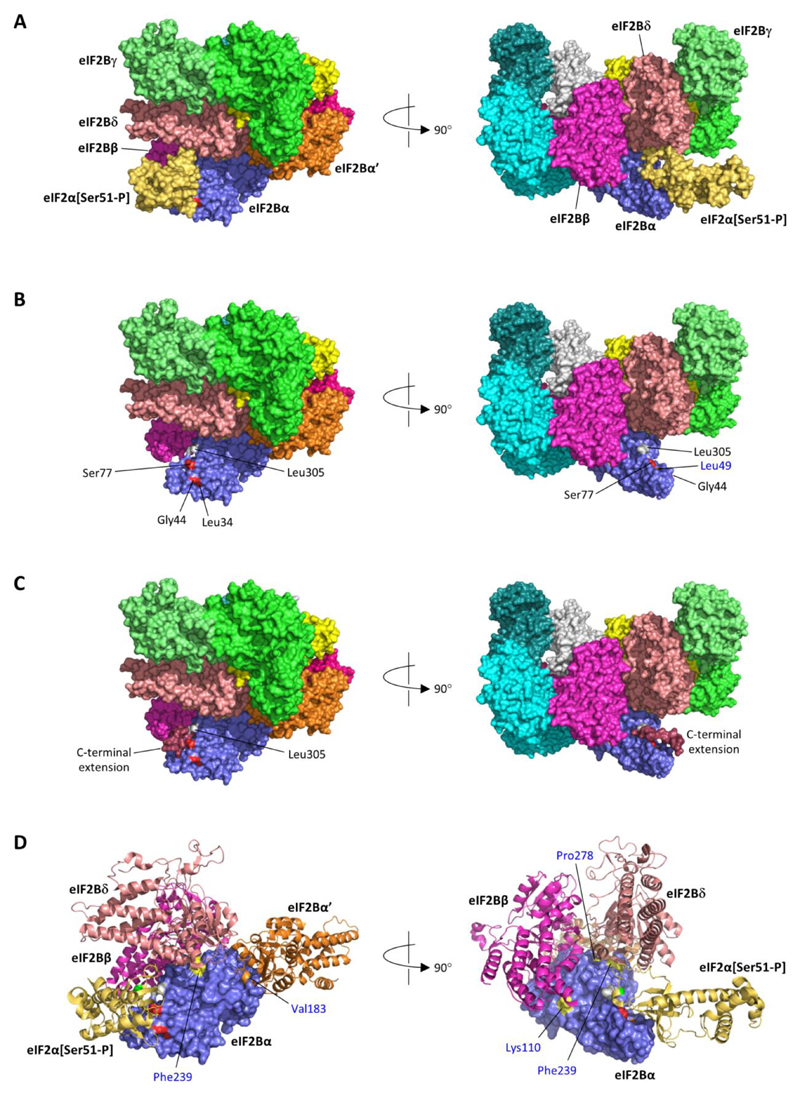
Figure 1. Heterozygous EIF2B1 variants in neonatal diabetes lie in the binding surface for phosphorylated eIF2α.
A) Structure of human eIF2B in complex with phosphorylated eIF2α (Ser51-P) (PDB id 6o9z (12)); the eIF2B complex is a heterodecamer comprised of two molecules each of subunits α, β, γ, δ and ε. B) As A, but shown without eIF2α (Ser51-P); positions of heterozygous missense variants in eIF2Bα identified in neonatal diabetes patients are coloured red and labelled in black font; the position of the homozygous p.(Leu49Arg) variant reported in a VWM patient is coloured orange and labelled in blue font; Leu305 (grey) is the C-terminal residue of eIF2Bα. C) The stop-loss variant c.915_916del, p.(*306Thrext*12) is expected to result in the addition of 12 novel amino acids (Thr-Cys-Glu-Pro-Phe-Pro-Ala-Lys-Val-Gln-Leu-Thr) to the C-terminal of eIF2B; this C-terminal extension (dark red) was predicted to form a short helix extending from Leu305 lying across the surface bound by eIF2α[Ser51-P]. D) As A, but zoomed and showing selected subunits (eIF2α[Ser51-P]; eIF2B subunits β, δ and α’) in ribbon format; surface positions of heterozygous missense variants identified in neonatal diabetes patients are coloured red, and the position of the homozygous p.(Leu49Arg) VWM variant orange, as in part B; positions of other homozygous variants identified in VWM patients are coloured yellow and labelled in blue font (Tyr275, the site of the p.Tyr275Cys variant, is not visible in these views but is surface-accessible at the junction of the interfaces with subunits δ and α’; Asn208, which was substituted by glutamate in a case of VWM, is not accessible at the eIF2Bα surface). The light green residue in the eIF2α ribbon indicates the position of phosphoserine 51.