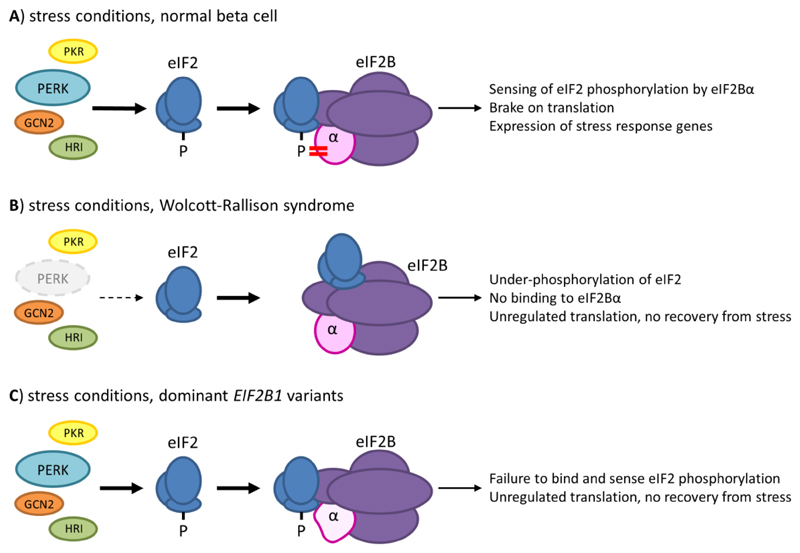
Figure 2. Different forms of monogenic neonatal diabetes affect steps in the Integrated Stress Response pathway.
A) Stress conditions induce activation of four kinases of the Integrated Stress Response (ISR); Pancreatic eIF2-alpha kinase (PERK) responds mainly to ER stress, and is of particular importance in maintaining liver and pancreatic β-cells; other kinases of the IRS are Protein kinase (PK) R, GCN2 and Heme-regulated eIF2α kinase (HRI), which respond to dsRNA, amino acid deprivation and heme deprivation respectively. Phosphorylation of Ser51 of eIF2α results in a tight interaction with eIF2Bα, which inhibits the GDP dissociation activity mediated primarily by the γ and ε subunits of eIF2B and thus arrests translation of most mRNAs, except for specific mRNAs associated with the stress response programme. B) In Walcott-Rallison syndrome, homozygous or compound heterozygous loss of function variants in EIF2AK3, the gene encoding PERK, prevent phosphorylation of eIF2α Ser51 in response to ER stress; the lack of an appropriate stress response ultimately leads to a prolonged unfolded protein response and cell death. C) The dominant eIF2B1 variants identified in neonatal patients all lie in the binding surface for phosphorylated eIF2α and likely prevent effective sensing of Ser51 phosphorylation by eIF2B. This defect would be expected to affect the response to all kinases of the ISR, potentially explaining differences in the phenotype compared to that of Wolcott Rallison syndrome and the dominant nature of the disease.