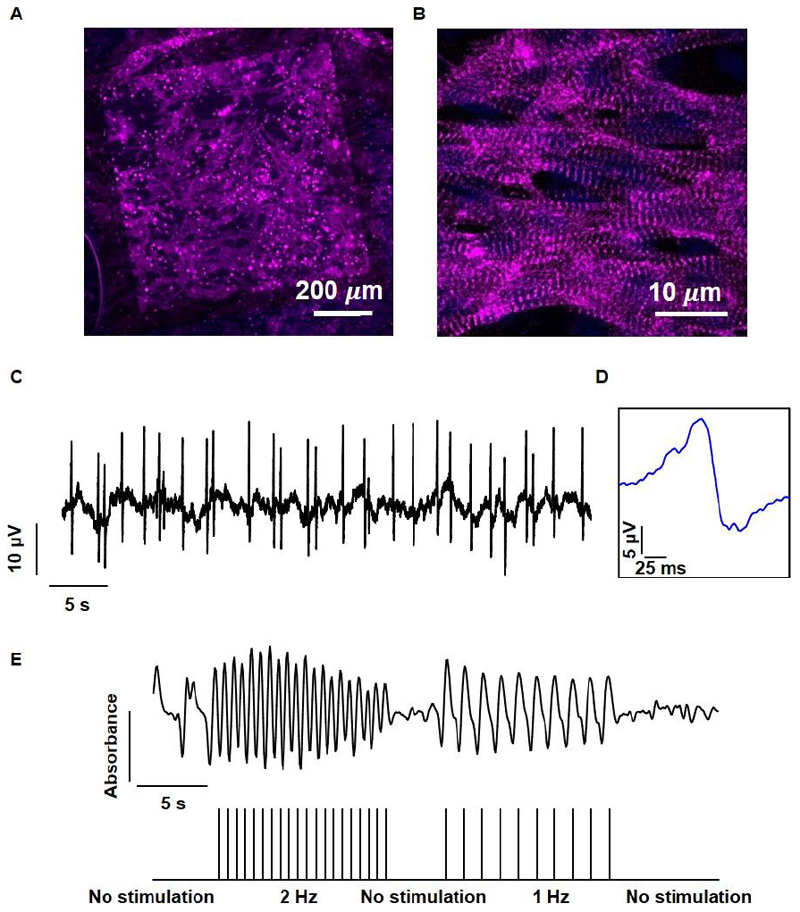
Figure 8. Tissue assembly and function within the microelectronic scaffold.
A. Confocal microscope image showing the assembled cardiac tissue within the biomaterial–electronics hybrid. A large drug release electrode can be seen in the background. B. A Zoomed-in image of cardiac cells revealing cell elongation and massive striation. Sarcomeric actinin in pink, nuclei in blue. C. Extracellular potential recordings collected from an electrode within the tissue. D. Zoomed-in extracellular potential recording, showing a typical signal recorded from ventricular cardiomyocytes. E. Quantification of tissue contraction as a function of stimulation through the microelectronic device. The stimulation pattern is presented in the lower part.