Key Points
Question
In patients with recent acute coronary syndrome, does apabetalone (a selective inhibitor of bromodomain and extraterminal proteins) reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events when added to standard care?
Finding
In this randomized clinical trial that included 2425 patients with acute coronary syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, treatment with apabetalone compared with placebo and added to standard therapy did not significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or stroke (10.3% vs 12.4%, respectively; hazard ratio, 0.82).
Meaning
Apabetalone did not significantly reduce major adverse cardiovascular events after acute coronary syndrome.
Abstract
Importance
Bromodomain and extraterminal proteins are epigenetic regulators of gene transcription. Apabetalone is a selective bromodomain and extraterminal protein inhibitor targeting bromodomain 2 and is hypothesized to have potentially favorable effects on pathways related to atherothrombosis. Pooled phase 2 data suggest favorable effects on clinical outcomes.
Objective
To test whether apabetalone significantly reduces major adverse cardiovascular events.
Design, Setting, and Participants
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, conducted at 190 sites in 13 countries. Patients with an acute coronary syndrome in the preceding 7 to 90 days, type 2 diabetes, and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels were eligible for enrollment, which started November 11, 2015, and ended July 4, 2018, with end of follow-up on July 3, 2019.
Interventions
Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive apabetalone, 100 mg orally twice daily (n = 1215), or matching placebo (n = 1210) in addition to standard care.
Main Outcomes and Measures
The primary outcome was a composite of time to the first occurrence of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or stroke.
Results
Among 2425 patients who were randomized (mean age, 62 years; 618 women [25.6%]), 2320 (95.7%) had full ascertainment of the primary outcome. During a median follow-up of 26.5 months, 274 primary end points occurred: 125 (10.3%) in apabetalone-treated patients and 149 (12.4%) in placebo-treated patients (hazard ratio, 0.82 [95% CI, 0.65-1.04]; P = .11). More patients allocated to apabetalone than placebo discontinued study drug (114 [9.4%] vs 69 [5.7%]) for reasons including elevations of liver enzyme levels (35 [2.9%] vs 11 [0.9%]).
Conclusions and Relevance
Among patients with recent acute coronary syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, the selective bromodomain and extraterminal protein inhibitor apabetalone added to standard therapy did not significantly reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events.
Trial Registration
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02586155
This randomized trial compares the effects of apabetalone (an inhibitor of bromodomain 2 and extraterminal protein, 2 epigenetic “readers”) vs placebo on major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS), type 2 diabetes, and low HDL cholesterol level.
Introduction
Epigenetics refers to a process whereby chromatin undergoes chemical modification in response to its environment, affecting transcription. One such modification is acetylation of lysine residues on histone proteins. Bromodomain and extraterminal proteins are a family of epigenetic “readers” that detect and bind to acetylated lysine residues, thereby forming molecular scaffolds between chromatin and transcriptional machinery.1,2,3,4 Recruitment of bromodomain and extraterminal proteins may enhance the expression of genes that drive maladaptive responses in atherosclerosis, including inflammation, oxidation, complement activation, and thrombogenesis.5,6
Small-molecule bromodomain and extraterminal protein inhibitors have therapeutic potential in disease states including atherosclerosis.6,7 These inhibitors bind to dual bromodomains within each bromodomain and extraterminal protein, displacing them from chromatin and thus attenuating maladaptive gene expression.1,2 Nonselective bromodomain and extraterminal inhibitors bind to bromodomains 1 and 2 with equal affinity and are in development for cancer indications.6 Apabetalone is an oral bromodomain and extraterminal inhibitor with selectivity for bromodomain 2, which may have particular relevance in atherothrombosis.7,8,9,10,11 Early clinical studies with apabetalone demonstrated modest effects on plasma lipoproteins12 and coronary atherosclerotic plaque volume and morphology.13,14 A pooled analysis of 3 placebo-controlled phase 2 trials including a total of 798 patients suggested a decrease in major adverse cardiovascular events with apabetalone, particularly among patients with conditions associated with increased bromodomain and extraterminal activity such as type 2 diabetes, elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels, and low high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels.15 This randomized trial was designed to test whether apabetalone compared with placebo on the background of standard of care reduces cardiovascular events in patients with a recent acute coronary syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and a low HDL cholesterol level.
Methods
The study protocol was approved by the institutional review board or independent ethics committee from each site. All participants provided written informed consent. All research procedures adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. The trial protocol and statistical analysis plan are available in Supplement 1.
Trial Oversight
The trial was designed by the academic steering committee and the sponsor, Resverlogix. Investigator-reported cardiovascular outcome events were prospectively captured and centrally adjudicated by a clinical events committee that was masked to treatment assignment. Statistical analyses were performed by PPD Ltd and validated by the independent academic statistician (K.A.B.), who had a complete copy of the trial database. The final analyses presented here were performed by the independent academic statistician.
Trial Design
The trial design and aggregate baseline characteristics have been published.16 In brief, BETonMACE was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial conducted at 190 sites in 13 countries. It tested whether apabetalone compared with placebo reduces cardiovascular events with an acceptable adverse event profile in patients with a recent acute coronary syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and low high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol level.
Trial Participants
Eligible patients were aged 18 years or older with type 2 diabetes, low HDL cholesterol level (<40 mg/dL in men or 45 mg/dL in women [to convert cholesterol values to mmol/L, multiply data by 0.0259]), and an acute coronary syndrome within the previous 7 to 90 days. The presence of diabetes was based on the medical history, use of glucose-lowering medication, or baseline hemoglobin A1c level of at least 6.5%. Standard laboratory test results and demographic characteristics were recorded at baseline, including self-reported race using fixed categories. A qualifying acute coronary syndrome included myocardial infarction or unstable angina, with the latter capped at 25% of the overall population. Criteria for qualifying myocardial infarction or unstable angina have been published.16
Patients were required to receive high-intensity statin therapy with atorvastatin (40-80 mg daily) or rosuvastatin (20-40 mg daily). Atorvastatin 20 mg or rosuvastatin 10 mg was allowed for recognized factors limiting the dose (advanced age, low body mass, or drug interactions). Exclusion criteria included planned further coronary revascularization within 90 days of the screening visit, estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2, fasting triglyceride levels greater than 400 mg/dL, evidence of cirrhosis or active hepatitis, liver transaminase levels greater than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal, total bilirubin level greater than the upper limit of normal, or a history of intolerance to either statin.
Trial Procedures
Participants were randomized (1:1) to receive either apabetalone 100 mg twice daily or matching placebo in a blinded fashion. Treatment allocation was stratified by country and background statin type, using block randomization with block size 4. Assignment was by interactive internet response system from a computer-generated randomization list. Follow-up visits occurred every 2 weeks through week 12, then every 4 weeks through week 28, and then every 12 weeks until the common study end date. At these visits, patients were assessed for end points and adverse events and had laboratory tests. Liver function tests were conducted every 2 weeks until week 12, then every 4 weeks from weeks 12 to 28, and then every 12 weeks thereafter. Other laboratory measurements were conducted at 6 months, 12 months, 18 months, 24 months, and the end of the study. Three to 4 weeks after the last visit during study treatment, a follow-up visit was conducted to ascertain any adverse events.
End Points
The primary efficacy end point was the time to first occurrence of cardiovascular death or nonfatal myocardial infarction or stroke. Deaths of undetermined cause were considered cardiovascular deaths in line with studies in similar populations.17 Key secondary end points, evaluated in hierarchic sequence, were time to first occurrence of the composite of the primary end point or hospitalization for unstable angina or an urgent or emergency coronary revascularization procedure; total (first and recurrent) primary end point events; cardiovascular death or nonfatal myocardial infarction; coronary heart disease death or nonfatal myocardial infarction; the individual components of the primary end point (nonfatal myocardial infarction, cardiovascular death, and stroke, in that order); all-cause death; and incidence of hospitalization for congestive heart failure.16 Other prespecified secondary end points included total (first and recurrent) hospitalization for congestive heart failure; the incidence of primary end point events, excluding deaths of undetermined cause from cardiovascular deaths; and changes within and between treatment groups in lipid levels, fasting serum glucose level, hemoglobin A1c level, alkaline phosphatase level, and estimated glomerular filtration rate overall and among the subset with baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Percentage change in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein was an exploratory end point. Adverse events reported by investigators were classified according to Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities terms and system organ class.
Statistical Analysis
We assumed a cumulative incidence of the primary end point of 10.5% in the placebo group at 18 months. Pooled analysis of phase 2 placebo-controlled trials15 suggested a favorable effect of apabetalone that was most pronounced in patients with type 2 diabetes (hazard ratio [HR], 0.43; P = .02), elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels (HR, 0.38; P = .02), or low high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol (HR, 0.43; P = .01). In this trial, we assumed a more conservative HR of 0.70 (7.47% incidence of the primary end point in the apabetalone group at 18 months). It was estimated that 250 primary end point events occurring in 2400 patients followed for a median of 18 months would provide 80% power to detect the expected difference in risk at a 2-sided significance level of .05.
Analyses were conducted in accordance with the prespecified statistical analysis plan (Supplement 1). The time-to-event analysis for the primary end point conducted on the full analysis set (described later) used a log-rank test for formal hypothesis testing and a Cox proportional hazards model to estimate the HR with 95% CI. Both analyses were stratified by statin and country. Because of the small numbers of patients randomized in Croatia, Germany, the Netherlands, and Taiwan, these countries were combined into a single stratum; this decision was based on a blinded review of data before database lock and unblinding. The proportional hazards assumption was tested with Schoenfeld residuals. For comparison, a post hoc analysis with a random site effect was conducted by replacing stratification by country with a γ frailty term for site. A prespecified sensitivity analysis that excluded deaths of undetermined cause was conducted. Events for which event dates could not be established were excluded from the primary time-to-event analyses; post hoc analyses including these events were conducted, using last contact date as the event date.
Prespecified subgroup analyses were conducted with Cox models with treatment-subgroup interaction terms; subgroup HRs and 95% CIs were calculated together with interaction P values. Secondary time-to-event end points were summarized as patient counts and percentages (for first events) and as event counts (for total first and recurrent events) by treatment; Kaplan-Meier curves for the primary and secondary time-to-event end points were also produced. Overall type I error control was provided by a sequential gatekeeping procedure that included testing of the primary end point followed by key secondary time-to-event end points in the order given earlier, with formal testing to stop with the first failed test. No formal interim analyses for early stopping for efficacy were performed. The percentage change from baseline of lipids and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and the absolute change from baseline of hemoglobin A1c, glucose, and alkaline phosphatase levels, as well as estimated glomerular filtration rate, were analyzed with analysis of covariance models with baseline biomarker value, statin, and country as covariates; these analyses were considered exploratory. In these analyses, the primary coefficient of interest was the between-group difference in change from baseline, referred to as the adjusted difference herein. In accordance with the statistical analysis plan, no missing results or outcomes were imputed.
Baseline, time-to-event, and biomarker analyses were conducted with the full analysis set, defined as the patients in the randomized subset who received any amount of study therapy, analyzed by assigned group. Adverse event analyses were conducted with the safety set, defined as patients receiving at least 1 dose of double-blind study therapy, analyzed according to actual treatment received. A threshold of P < .05 with 2-sided tests was used to determine statistical significance. Analyses were performed with SAS version 9.2 and R software version 3.5.1.
Results
Characteristics of the Patients
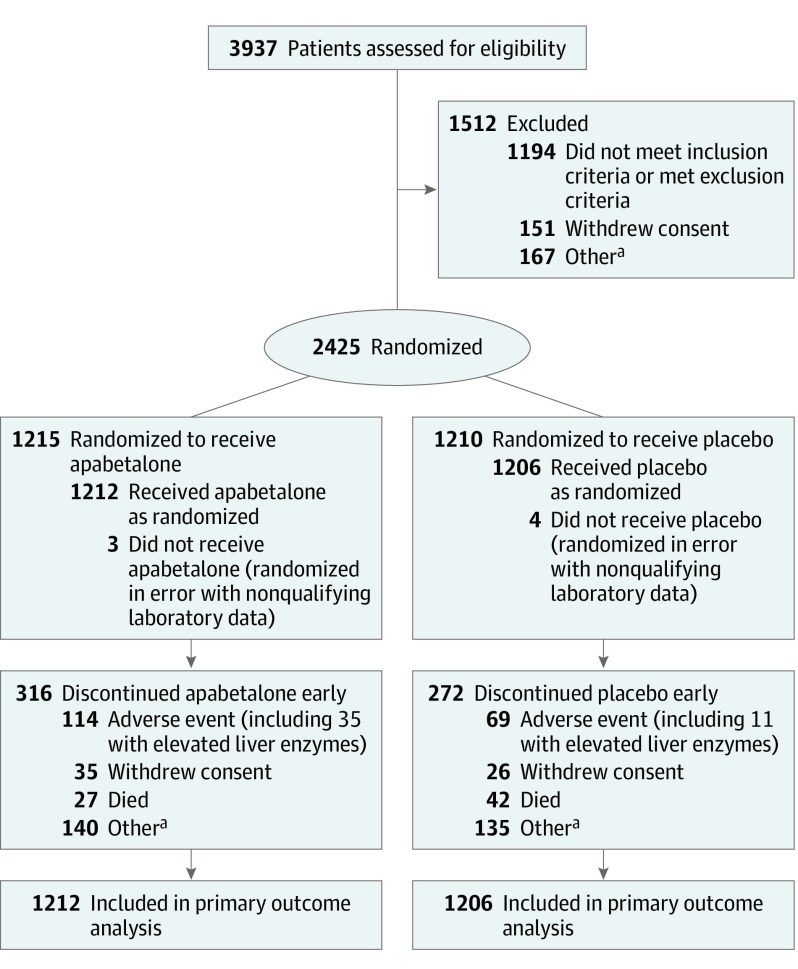
Between November 2015 and July 2018, 3937 patients were screened and 2425 were randomized. Efficacy analyses included 2418 patients (1212 assigned to apabetalone and 1206 to placebo) (Figure 1) and excluded 7 patients who did not receive a confirmed dose of study medication. Adverse event analyses (n = 2419) included an additional patient who withdrew without a confirmed dose of study medication and failed to return dispensed medication. Baseline characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1 and were well balanced between treatment groups. The median age was 62 years, 25.6% were women, 87.6% were white, mean duration of diabetes was 8.5 years, and median time from index acute coronary syndrome to randomization was 38 days. Most index events were acute myocardial infarction, approximately equally distributed between ST-segment elevation and non–ST-segment elevation subtypes.
Figure 1. Patient Recruitment, Randomization, and Flow in the BETonMACE Trial of Apabetalone for Reduction of Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes.
aReasons for exclusion varied, primarily failure to return for randomization visit. Reasons for discontinuation were due to patient preference.
Table 1. Baseline Patient Characteristics.
| Characteristic | Apabetalone (n = 1212) | Placebo (n = 1206) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, median (IQR), y | 62 (55-68) | 62 (56-68) |
| Sex, No. (%) | ||
| Women | 305 (25.2) | 313 (26.0) |
| Men | 907 (74.8) | 893 (74.0) |
| Race, No. (%) | ||
| White | 1063 (87.7) | 1056 (87.6) |
| Asian | 20 (1.7) | 19 (1.6) |
| Othera | 129 (10.6) | 131 (10.9) |
| Geographic region, No. (%) | ||
| Europe | 689 (56.8) | 686 (56.8) |
| Latin America | 315 (26.0) | 313 (26.0) |
| Israel | 188 (15.5) | 189 (15.7) |
| Taiwan | 20 (1.7) | 18 (1.5) |
| Body mass index, mean (SD) | 30.2 (4.8) [n = 1208] | 30.3 (5.0) [n = 1206] |
| Medical history before acute coronary syndrome | ||
| Hypertension, No. (%) | 1083 (89.4) | 1059 (87.8) |
| Current or former smoker, No. (%)b | 147 (12.1) | 125 (10.4) |
| Duration of diabetes, mean (SD), y | 8.4 (7.6) [n = 1211] | 8.7 (7.7) [n = 1205] |
| Previous myocardial infarction, No. (%) | 174 (14.4) | 177 (14.7) |
| Previous percutaneous coronary intervention or coronary artery bypass surgery, No. (%) | 259 (21.4) | 256 (21.2) |
| Index acute coronary syndrome, No. (%) | [n = 1208] | [n = 1195] |
| Myocardial infarction | 885 (73.3) | 893 (74.7) |
| STEMI | 466 (38.6) | 466 (39.0) |
| Non-STEMI | 413 (34.2) | 423 (35.4) |
| Unstable angina | 323 (26.7) | 302 (25.3) |
| Percutaneous coronary intervention for index acute coronary syndrome, No. (%) | 967 (79.8) | 955 (79.2) |
| Time from index acute coronary syndrome to randomization, median (IQR), d | 38 (25-63.5) | 38 (25-62) |
| Cardiovascular medications, No. (%) | ||
| Atorvastatin | 621 (51.2) | 620 (51.4) |
| Rosuvastatin | 591 (48.8) | 586 (48.6) |
| High-intensity statinc | 1089 (89.9) | 1092 (90.5) |
| Ezetimibe | 32 (2.6) | 35 (2.9) |
| PCSK-9 inhibitors | 0 | 0 |
| ACE inhibitors/angiotensin II blockers | 1119 (92.3) | 1110 (92.0) |
| β-Blockers | 1103 (91.0) | 1088 (90.2) |
| Antiplatelet agents | 1196 (98.7) | 1195 (99.1) |
| Dual antiplatelet agents | 1057 (87.2) | 1065 (88.3) |
| Diabetes medications, No. (%) | ||
| Metformin | 1009 (83.3) | 989 (82.0) |
| Insulin | 445 (36.7) | 464 (38.5) |
| Sulfonylureas | 363 (30.0) | 344 (28.5) |
| DPP4 inhibitors | 181 (14.9) | 178 (14.8) |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | 150 (12.4) | 148 (12.3) |
| GLP1 receptor agonists | 41 (3.4) | 45 (3.7) |
| Otherd | 52 (4.3) | 55 (4.6) |
| Biochemical parameters, mean (SD) | ||
| Hemoglobin A1c, median (IQR), % | 7.4 (6.4-8.7) [n = 1202] | 7.3 (6.4-8.6) [n = 1194] |
| Serum glucose, mg/dL | 152.2 (60.7) [n = 1210] | 150.7 (62.5) [n = 1205] |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2e | 104.9 (39.3) [n = 1208] | 101.7 (38.6) [n = 1205] |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 134.8 (35.3) [n = 1212] | 136.8 (38.2) [n = 1206] |
| LDL cholesterol, mg/dL | 69.7 (29.8) [n = 1212] | 70.9 (32.4) [n = 1203] |
| HDL cholesterol, mg/dL | 33.3 (5.1) [n = 1212] | 33.3 (5.1) [n = 1206] |
| Triglycerides, median (IQR), mg/dL | 146.1 (110.7-198.4) [n = 1212] | 151.5 (116.0-202.8) [n = 1205] |
| Alkaline phosphatase, U/L | 83.3 (38.2) [n = 1212] | 81.9 (34.8) [n = 1206] |
| Alanine aminotransferase, U/L | 25.3 (14.3) [n = 1209] | 25.4 (14.7) [n = 1204] |
| Total bilirubin, μmol/L | 9.8 (4.2) [n = 1211] | 9.9 (4.2) [n = 1205] |
| High-sensitivity C-reactive protein, median (IQR),f mg/L | 2.9 (1.3-5.9) [n = 244] | 2.7 (1.1-6.1) [n = 239] |
Abbreviations: ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme; DPP4, dipeptidyl peptidase 4; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; GLP1, glucagon-like peptide 1; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; IQR, interquartile range; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; STEMI, ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
SI conversion factors: To convert cholesterol to mmol/L, multiply by 0.0259; to convert triglycerides, multiply by 0.0113; to convert from μmol/L to mg/dL, divide by 17.1. Body mass index is calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared.
“Other” race includes fixed categories American Indian or Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander, and other. Ethnicity data were not collected.
Smoking status was not collected via a dedicated prospective question, and counts are based on free-form medical history data coded to “tobacco user” or “ex–tobacco user.” These counts likely underestimate actual prevalence, and current vs former smoking status cannot be reliably determined from the coded categories.
High-intensity statin is defined as 40 or 80 mg of atorvastatin or 20 or 40 mg of rosuvastatin.
Other diabetes medications include acarbose, pioglitazone, and repaglinide.
eGFR was calculated with the Cockcroft-Gault method, based on age and weight at baseline.
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein level was assessed in a subset of patients.
Patients received guideline-based treatment for management of the index acute coronary syndrome, with 79.5% undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, as well as 90.2% receiving high-intensity statins, 92.2% inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system, 90.6% β-blockers, and 87.8% dual antiplatelet therapy. Risk factors were well controlled, with mean baseline low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol level 70.3 mg/dL and mean blood pressure 129.3/76.4 mm Hg. The baseline HDL cholesterol level was low by design, at a mean 33.3 mg/dL. Median hemoglobin A1c level was 7.3% and mean body mass index was 30.3.
Efficacy
Overall, 2320 randomized patients (95.7%) had full ascertainment of the primary outcome through the planned observation period or else were known to be dead. Seven patients in the apabetalone group and 13 in the placebo group were lost to follow-up, and their data were censored at the last contact.
During a median follow-up of 26.5 months, there were a total of 274 primary end points, 125 (10.3%) in the apabetalone group and 149 (12.4%) in the placebo group, representing a Kaplan-Meier estimated event rate of 7.8% in the apabetalone group and 9.7% in the placebo group at 18 months. Apabetalone did not significantly reduce the primary end point of cardiovascular death or nonfatal myocardial infarction or stroke (HR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.65-1.04; P = .11) (Figure 2). No deviation from the proportional hazards assumption was detected (P = .40). In a post hoc analysis using a random effect for site, results were similar (HR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.65-1.05; P = .12).
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier Estimate of Time to First Occurrence of the Primary Efficacy End Point.
The primary end point was time to cardiovascular death or nonfatal myocardial infarction or stroke. Median observation time for the apabetalone group was 781 days (interquartile range [IQR], 566-967) and for the placebo group, 772 days (IQR, 560-960).
There were 26 deaths of undetermined cause (14 and 12 in the apabetalone and placebo groups, respectively) that were considered cardiovascular deaths in the primary and key secondary efficacy analyses. In a prespecified sensitivity analysis that included adjudicated cardiovascular deaths but excluded deaths of undetermined cause, the primary end point occurred in 113 patients (9.3%) in the apabetalone group and 140 (11.6%) in the placebo group (HR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.62-1.01; P = .06). For 2 deaths, both in the placebo group, a date of death could not be established. These events were excluded from all time-to-event analyses, including the primary analysis; a post hoc analysis including these deaths did not meaningfully alter the overall results (HR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.64-1.03).
Because there was no statistically significant difference in the primary end point between the apabetalone group and the placebo group, the prespecified sequential gatekeeping procedure precluded formal statistical testing of the key secondary end points and prespecified subgroups. Therefore, the data for these end points are presented in eFigures 1 to 3 in Supplement 2.
The effect of apabetalone vs placebo on biomarker levels over time is shown in eFigure 4 in Supplement 2. Apabetalone did not alter levels of LDL cholesterol, hemoglobin A1c, fasting glucose, or high-sensitivity C-reactive protein compared with placebo. At week 24, mean HDL cholesterol levels had increased from 33.3 mg/dL at baseline in each group to 38.0 mg/dL in the apabetalone group vs 36.6 mg/dL with placebo. In the apabetalone group, alkaline phosphatase level was reduced from 83.3 U/L at baseline to 76.5 U/L at 2 weeks and 74.3 U/L at 24 weeks. In the placebo group, alkaline phosphatase levels decreased from 81.9 U/L at baseline to 80.2 and 79.5 U/L, respectively, at 2 and 24 weeks. Levels of cholesterol and triglycerides are shown in eFigure 5 in Supplement 2.
Adverse Events
Adverse events and biomarkers of adverse effects are shown in Table 2 and the eTable in Supplement 2. The incidence of total adverse events or serious adverse events was similar in both treatment groups. Levels of alanine aminotransferase, γ-glutamyltransferase, and bilirubin are shown in eFigure 5 in Supplement 2. There were minimal differences between treatment groups in the median levels of these biomarkers. However, there were 40 cases (3.3%) vs 9 (0.7%) of alanine aminotransferase elevation exceeding 5 times the upper limit of normal in the apabetalone and placebo groups, respectively. Elevation of alanine aminotransferase level with apabetalone occurred most often between 4 and 16 weeks of treatment. On cessation of apabetalone, alanine aminotransferase level declined to normal values within 4 weeks unless there were other ongoing medical problems affecting liver function such as active hepatitis or cholelithiasis. At 24 weeks, bilirubin levels were higher than at baseline in both groups, having increased from 9.8 to 11.4 μmol/L (0.57 to 0.67 mg/dL) in the apabetalone group and from 9.9 to 10.5 μmol/L (0.58 to 0.61 mg/dL) in the placebo group, with an adjusted difference in change from baseline representing an 11.1% increase with apabetalone vs placebo. However, the numbers of individuals with bilirubin levels greater than twice the upper limit of normal were similar (7 [0.7%] vs 9 [0.7%] for apabetalone and placebo, respectively), and no case in either group fulfilled Hy’s law criteria for drug-induced liver injury (eFigure 6).18 Nausea occurred more often with apabetalone vs placebo (26 [2.1%] vs 7 [0.6%]).
Table 2. Adverse Events and Key Laboratory Findingsa.
| Variable | No. (%) | RR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apabetalone (n = 1212) | Placebo (n = 1207) | ||
| Adverse events | |||
| Patients with at least 1 adverse eventb | 830 (68.5) | 820 (67.9) | 1.01 (0.95-1.06) |
| Hepatobiliary disordersb | 24 (2.0) | 42 (3.5) | |
| Drug discontinuation caused by any adverse eventc | 114 (9.4) | 69 (5.7) | 1.65 (1.23-2.19) |
| Discontinuation caused by LFT elevationc | 35 (2.9) | 11 (0.9) | 3.17 (1.62-6.21) |
| Serious adverse events | |||
| Patients with at least 1 serious adverse eventb | 354 (29.2) | 339 (28.1) | 1.04 (0.92-1.18) |
| Deathd | 61 (5.0) | 71 (5.9) | 0.86 (0.61-1.19) |
| Cardiovascular deaths | 34 (2.8) | 42 (3.5) | 0.81 (0.52-1.26) |
| Cancer deaths | 5 (0.4) | 4 (0.3) | 1.24 (0.34-4.62) |
| New, worsening, or recurrent malignancyb | 24 (2.0) | 30 (2.5) | 0.80 (0.47-1.35) |
| Frequent adverse eventsb,e | |||
| Musculoskeletal | 143 (11.8) | 183 (15.2) | 0.78 (0.63-0.95) |
| Worsening diabetes | 95 (7.8) | 93 (7.7) | 1.02 (0.77-1.34) |
| Angina | 74 (6.1) | 76 (6.3) | 0.97 (0.71-1.32) |
| Hypertension | 72 (5.9) | 72 (6.0) | 1.00 (0.73-1.37) |
| Laboratory results | |||
| Liver function | |||
| ALT >3 times ULN | 78 (6.4) | 18 (1.5) | 4.32 (2.60-7.16) |
| ALT >5 times ULN | 40 (3.3) | 9 (0.7) | 4.43 (2.16-9.08) |
| Bilirubin >2 times ULN | 7 (0.6) | 9 (0.7) | 0.77 (0.29-2.07) |
| Hy’s lawf | 0 | 0 | |
| eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 22 (1.8) | 21 (1.7) | 1.04 (0.58-1.89) |
| Creatine kinase | |||
| >5 times ULN | 12 (1.0) | 6 (0.5) | 1.99 (0.75-5.29) |
| >10 times ULN | 3 (0.2) | 4 (0.3) | 0.75 (0.17-3.33) |
| Platelets | |||
| <LLN | 147 (12.1) | 135 (11.2) | 1.08 (0.87-1.35) |
| <0.5 LLN | 2 (0.1) | 3 (0.2) | 0.66 (0.11-3.97) |
Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate calculated with the Cockcroft-Gault formula using baseline age and weight; LFT, liver function test; LLN, lower limit of normal; RR, relative risk; ULN, upper limit of normal.
Safety population includes all patients who received at least 1 dose of study medication.
Includes treatment-emergent adverse events only, defined as those occurring after the first dose and within 14 days of the last dose of the study drug.
Based on the single primary reason for discontinuation of the drug. Discontinuations caused by elevations in LFT results are a subset of discontinuations because of adverse events.
One additional death occurred in a patient randomized to placebo who did not receive the first dose and was excluded from the analysis set assessing adverse events.
Defined as occurring with a frequency of 5% or more.
No cases fulfilled Hy’s law for severe drug-induced liver injury, which is defined by ALT level elevation, usually substantial, concurrent with bilirubin greater than 2 times the ULN. Hy’s law is used to identify drugs likely to cause liver injury that may be fatal or require transplantation. It assumes that other causes of hepatocellular injury (eg, other drugs, viral hepatitis) and an obstructive basis for elevated bilirubin level have been excluded so that alkaline phosphatase level should not be substantially elevated. There were 2 cases in which ALT or AST exceeded 3 times the ULN and total bilirubin level exceeded 2 times the ULN, 1 in each group. In the placebo case, the elevation of liver function test results was attributed to hepatitis B virus reactivation. In the apabetalone case, the elevation of liver function test results occurred 10 months after study treatment had been discontinued in a subject who received only 1 dose and was associated with serious adverse events of cholelithiasis and choledocholithiasis.
Discussion
In this trial among patients with diabetes, low HDL cholesterol level, and recent acute coronary syndrome, treatment with the selective bromodomain and extraterminal protein inhibitor apabetalone did not significantly reduce the incidence of a composite end point of cardiovascular death or nonfatal myocardial infarction or stroke compared with placebo.
Treatment-emergent adverse events were similar between apabetalone and placebo but discontinuation caused by adverse events was more frequent with apabetalone. Apabetalone was associated with a greater incidence of elevated results for liver function tests, as previously observed in phase 2 studies,15 but there were no cases of drug-induced liver injury as defined by Hy’s law.18 When alanine aminotransferase level greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal occurred with apabetalone, it resolved on protocol-specified treatment cessation. The frequency of serious adverse events was similar with apabetalone and placebo, including death from any cause, cardiovascular causes, or cancer; or new, worsening, or recurrent malignancy.
The evaluation of novel drugs that target pathways not directly reflected by conventional biomarkers presents a challenge for dose finding and gauging therapeutic effects. In the case of apabetalone, there were no significant effects on traditional biomarkers associated with cardiovascular benefit, such as low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, C-reactive protein, and hemoglobin A1c levels, and only modest absolute changes in HDL cholesterol and alkaline phosphatase levels compared with placebo. To date, no therapy that increases HDL cholesterol levels without decreasing low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol levels has shown reductions in clinical events. Levels of alkaline phosphatase (a biomarker) are associated with risk of major adverse cardiovascular events19; in phase 2 studies, reductions in alkaline phosphatase level with apabetalone were associated with a lower risk of such events.20 In the present trial, the absolute reductions in alkaline phosphatase level with apabetalone were modest. Thus, changes in HDL cholesterol and alkaline phosphatase levels under apabetalone treatment are likely qualitative markers of drug exposure, but to what extent the magnitude of these changes reflects the magnitude of bromodomain and extraterminal inhibition at the level of the chromatin is unknown.
Among patients with acute coronary syndrome, the presence of type 2 diabetes and low HDL cholesterol level identifies patients who remain at particularly high risk of recurrent cardiovascular events despite use of evidence-based therapies.21,22 Such patients have a high unmet need for further risk reduction23 and were included in this trial in accordance with previous analyses that suggested potential benefit from apabetalone treatment.15 In fact, for patients in the placebo group the incidence of the primary end point was high despite background care that included high rates of coronary revascularization for the index acute coronary syndrome; high use of intensive statin, dual antiplatelet therapies, β-blockers, and renin-angiotensin system inhibitors; and good control of low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol level, glycated hemoglobin level, and blood pressure. Few patients in the trial received glucagonlike peptide 1 receptor agonists or sodium-glucose–loop transporter 2 inhibitors. These drug classes have reduced cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,24,25 but neither these drugs nor any other glucose-level-decreasing treatment has demonstrated cardiovascular benefit in patients with acute coronary syndrome.26
Limitations
This study has several limitations. First, the observed Kaplan-Meier estimated event rate of 9.7% in the placebo group at 18 months was lower than the 10.5% rate assumed in the study design. Second, this study had 80% power to detect a 30% difference in treatment effect with apabetalone. This was based on previous analyses of pooled phase 2 data, in which apabetalone reduced cardiovascular event rates by approximately 60%. In the design of this moderately sized cardiovascular outcomes trial, a more conservative treatment effect than suggested in previous phase 2 studies was assumed, but nonetheless one that is comparable to effects observed in recent cardiovascular outcomes trials using agents with other novel mechanisms of action.24,27 It would be of interest to determine whether a study of a larger cohort would reveal a different result. Third, 7 patients in the apabetalone group and 13 in the placebo group were lost to follow-up. Fourth, there were few patients of nonwhite race in this trial, which may limit the generalizability of the findings.
Conclusions
Among patients with recent acute coronary syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and low HDL cholesterol level, the selective bromodomain and extraterminal protein inhibitor apabetalone compared with placebo and added to standard therapy did not significantly reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events.
Trial protocol
Study Committees and Investigators
Trial Registration
Laboratory Analytical Methods
eFigure 1. Kaplan-Meier estimates of pre-specified secondary end points
eFigure 2. Hazard ratios for primary and secondary end points
eFigure 3. Effect of apabetalone on the primary efficacy end point by pre-specified subgroup
eFigure 4. Effect of apabetalone versus placebo on biomarkers over time
eFigure 5. Effect of apabetalone versus placebo on additional selected biochemical measures over time
eFigure 6. eDISH plot assessing liver adverse event
eTable. System organ class treatment-emergent adverse events with at least 2% incidence in either group
Narratives of two cases of elevated alanine aminotransferase and bilirubin
Data Sharing Statement
References
- 1.Dhalluin C, Carlson JE, Zeng L, He C, Aggarwal AK, Zhou M-M. Structure and ligand of a histone acetyltransferase bromodomain. Nature. 1999;399(6735):491-496. doi: 10.1038/20974 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zeng L, Zhou M-M. Bromodomain: an acetyl-lysine binding domain. FEBS Lett. 2002;513(1):124-128. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(01)03309-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Devaiah BN, Case-Borden C, Gegonne A, et al. BRD4 is a histone acetyltransferase that evicts nucleosomes from chromatin. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016;23(6):540-548. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3228 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kanno T, Kanno Y, LeRoy G, et al. BRD4 assists elongation of both coding and enhancer RNAs by interacting with acetylated histones. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014;21(12):1047-1057. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2912 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brown JD, Lin CY, Duan Q, et al. NF-κB directs dynamic super enhancer formation in inflammation and atherogenesis. Mol Cell. 2014;56(2):219-231. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hajmirza A, Emadali A, Gauthier A, Casasnovas O, Gressin R, Callanan MB. BET family protein BRD4: an emerging actor in NFκB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Biomedicines. 2018;6(1):16. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines6010016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tsujikawa LM, Fu L, Das S, et al. Apabetalone (RVX-208) reduces vascular inflammation in vitro and in CVD patients by a BET-dependent epigenetic mechanism. Clin Epigenetics. 2019;11(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s13148-019-0696-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wasiak S, Gilham D, Tsujikawa LM, et al. Data on gene and protein expression changes induced by apabetalone (RVX-208) in ex vivo treated human whole blood and primary hepatocytes. Data Brief. 2016;8:1280-1288. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2016.07.047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wasiak S, Gilham D, Tsujikawa LM, et al. Downregulation of the complement cascade in vitro, in mice and in patients with cardiovascular disease by the BET protein inhibitor apabetalone (RVX-208). J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2017;10(4):337-347. doi: 10.1007/s12265-017-9755-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gilham D, Wasiak S, Tsujikawa LM, et al. RVX-208, a BET-inhibitor for treating atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, raises ApoA-I/HDL and represses pathways that contribute to cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis. 2016;247:48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.01.036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jahagirdar R, Zhang H, Azhar S, et al. A novel BET bromodomain inhibitor, RVX-208, shows reduction of atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemic ApoE deficient mice. Atherosclerosis. 2014;236(1):91-100. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.06.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nicholls SJ, Gordon A, Johansson J, et al. Efficacy and safety of a novel oral inducer of apolipoprotein a-I synthesis in statin-treated patients with stable coronary artery disease: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57(9):1111-1119. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.11.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nicholls SJ, Puri R, Wolski K, et al. Effect of the BET protein inhibitor, RVX-208, on progression of coronary atherosclerosis: results of the phase 2b, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, ASSURE trial. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2016;16(1):55-65. doi: 10.1007/s40256-015-0146-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shishikura D, Kataoka Y, Honda S, et al. The effect of bromodomain and extra-terminal inhibitor apabetalone on attenuated coronary atherosclerotic plaque: insights from the ASSURE trial. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2019;19(1):49-57. doi: 10.1007/s40256-018-0298-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nicholls SJ, Ray KK, Johansson JO, et al. Selective BET protein inhibition with apabetalone and cardiovascular events: a pooled analysis of trials in patients with coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2018;18(2):109-115. doi: 10.1007/s40256-017-0250-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ray KK, Nicholls SJ, Ginsberg HD, et al. Effect of selective BET protein inhibitor apabetalone on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome and diabetes: rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of the BETonMACE trial. Am Heart J. 2019;217:72-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2019.08.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fanaroff AC, Clare R, Pieper KS, et al. Frequency, regional variation, and predictors of undetermined cause of death in cardiometabolic clinical trials: a pooled analysis of 9259 deaths in 9 trials. Circulation. 2019;139(7):863-873. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037202 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Robles-Diaz M, Lucena MI, Kaplowitz N, et al. ; Spanish DILI Registry; SLatinDILI Network; Safer and Faster Evidence-based Translation Consortium . Use of Hy’s law and a new composite algorithm to predict acute liver failure in patients with drug-induced liver injury. Gastroenterology. 2014;147(1):109-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tonelli M, Curhan G, Pfeffer M, et al. Relation between alkaline phosphatase, serum phosphate, and all-cause or cardiovascular mortality. Circulation. 2009;120(18):1784-1792. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.851873 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Haarhaus M, Ray KK, Nicholls SJ, et al. Apabetalone lowers serum alkaline phosphatase and improves cardiovascular risk in patients with cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis. 2019;290:59-65. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.09.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ray KK, Colhoun HM, Szarek M, et al. ; ODYSSEY OUTCOMES Committees and Investigators . Effects of alirocumab on cardiovascular and metabolic outcomes after acute coronary syndrome in patients with or without diabetes: a prespecified analysis of the ODYSSEY OUTCOMES randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(8):618-628. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30158-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Barter P, Gotto AM, LaRosa JC, et al. ; Treating to New Targets Investigators . HDL cholesterol, very low levels of LDL cholesterol, and cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(13):1301-1310. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa064278 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ridker PM. How common is residual inflammatory risk? Circ Res. 2017;120(4):617-619. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.310527 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, et al. ; EMPA-REG OUTCOME Investigators . Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(22):2117-2128. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504720 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, et al. ; LEADER Steering Committee; LEADER Trial Investigators . Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(4):311-322. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1603827 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pfeffer MA, Claggett B, Diaz R, et al. ; ELIXA Investigators . Lixisenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute coronary syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(23):2247-2257. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1509225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bhatt DL, Steg PG, Miller M, et al. ; REDUCE-IT Investigators . Cardiovascular risk reduction with icosapent ethyl for hypertriglyceridemia. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):11-22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1812792 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Trial protocol
Study Committees and Investigators
Trial Registration
Laboratory Analytical Methods
eFigure 1. Kaplan-Meier estimates of pre-specified secondary end points
eFigure 2. Hazard ratios for primary and secondary end points
eFigure 3. Effect of apabetalone on the primary efficacy end point by pre-specified subgroup
eFigure 4. Effect of apabetalone versus placebo on biomarkers over time
eFigure 5. Effect of apabetalone versus placebo on additional selected biochemical measures over time
eFigure 6. eDISH plot assessing liver adverse event
eTable. System organ class treatment-emergent adverse events with at least 2% incidence in either group
Narratives of two cases of elevated alanine aminotransferase and bilirubin
Data Sharing Statement