Abstract
Background
Bronchiolitis is one of the most frequent causes of respiratory failure in infants; some infants will require intensive care and mechanical ventilation. There is lack of evidence regarding effective treatment for bronchiolitis other than supportive care. Abnormalities of surfactant quantity or quality (or both) have been observed in severe cases of bronchiolitis. Exogenous surfactant administration appears to favourably change the haemodynamics of the lungs and may be a potentially promising therapy for severe bronchiolitis. This is an update of a review published in Issue 9, 2012. We did not identify any new studies for inclusion, and our conclusions remain unchanged.
Objectives
To evaluate the efficacy of exogenous surfactant administration (i.e. intratracheal administration of surfactant of any type (whether animal‐derived or synthetic), at any dose and at any time after start of ventilation) compared to placebo, no intervention or standard care in reducing mortality and the duration of ventilation in infants and children with bronchiolitis requiring mechanical ventilation.
Search methods
We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Studies (CENTRAL; 2015, Issue 5) which contains the Cochrane Acute Respiratory Infections Group's Specialised Register; MEDLINE (1948 to June week 3, 2015); EMBASE (1974 to June 2015); CINAHL (1982 to June 2015); LILACS (1985 to June 2015); and Web of Science (1985 to June 2015).
Selection criteria
We considered prospective, randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi‐RCTs evaluating the effect of exogenous surfactant in infants and children with bronchiolitis requiring mechanical ventilation.
Data collection and analysis
Two review authors selected studies independently. We extracted the data using a predefined proforma, independently analysed the data, and performed meta‐analyses.
Main results
We included three small RCTs enrolling 79 participants. Two trials did not use a placebo in the control arms and the third trial used air placebo. Two included studies reported no mortality. We judged all three of the included studies to be at low risk or unclear risk across all risk of bias categories; we did not judge any of the studies to be at high risk of bias in any category. Our pooled analysis of the three trials revealed that duration of mechanical ventilation was not significantly different between the groups (mean difference (MD) ‐63.04, 95% confidence interval (CI) ‐130.43 to 4.35 hours) but duration of intensive care unit (ICU) stay was less in the surfactant group compared to the control group: MD ‐3.31, 95% CI ‐6.38 to ‐0.25 days. After excluding one trial which produced significant heterogeneity, the duration of mechanical ventilation and duration of ICU stay were significantly lower in the surfactant group compared to the control group: MD ‐28.99, 95% CI ‐40.10 to ‐17.87 hours; and MD ‐1.81, 95% CI ‐2.42 to ‐1.19 days, respectively. Use of surfactant had favourable effects on oxygenation and CO2 elimination. No adverse effects and no complications were observed in any of the three included studies. The level of evidence for duration of mechanical ventilation, duration of intensive care unit stay, oxygenation parameters, and carbon dioxide parameters was of moderate quality.
Authors' conclusions
Use of surfactant had favourable effects on duration of mechanical ventilation, duration of ICU stay, oxygenation, and CO2 elimination. However, the studies are few and small (n = 79) so available evidence is insufficient to establish the effectiveness of surfactant therapy for bronchiolitis in critically ill infants who require mechanical ventilation. There is a need for larger trials with adequate power and a cost‐effectiveness analysis to evaluate the effectiveness of exogenous surfactant therapy for infants with bronchiolitis who require intensive care management.
Keywords: Child, Preschool; Humans; Infant; Infant, Newborn; Bronchiolitis; Bronchiolitis/drug therapy; Critical Illness; Length of Stay; Pulmonary Surfactants; Pulmonary Surfactants/therapeutic use; Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic; Respiration, Artificial; Respiration, Artificial/statistics & numerical data; Time Factors
Plain language summary
Usefulness of surfactant for bronchiolitis in seriously ill infants and children
Review question Will use of exogenous surfactant (a material made of lipid and protein that is produced by the lungs) in infants and children with bronchiolitis, who require mechanical ventilation, decrease mortality and duration of mechanical ventilation?
Background Bronchiolitis (infection of small airways in the lungs) is one of the most common causes of respiratory failure in infants. There are no established treatment options for bronchiolitis. Surfactant may be useful in bronchiolitis because of its favourable effect on lung mechanics. We wanted to evaluate the efficacy of exogenous surfactant in reducing mortality and the duration of ventilation in infants and children with bronchiolitis, requiring mechanical ventilation.
Study characteristics The evidence is current to June 2015. Three small randomised controlled trials (RCTs) enrolling 79 participants were included in the review. All studies included children younger than 2.5 years with a diagnosis of bronchiolitis who required mechanical ventilation. Two studies did not include a placebo (a substance having no active effect) for comparison. None of the included studies provided a source of funding.
Key results Two included studies reported no mortality. Use of surfactant for mechanically ventilated infants and children with bronchiolitis did not decrease the duration of mechanical ventilation. However, the intervention decreased duration of stay in the intensive care unit and had favourable effects on oxygenation and carbon dioxide removal. No complications were observed in any of the three included studies.
Quality of the evidence The level of evidence for duration of mechanical ventilation, duration of intensive care unit stay, oxygenation parameters, and carbon dioxide parameters was of moderate quality. The limited number of studies with small numbers of participants was the reason for moderate quality, and are limitations of this review. There is a need for larger trials to establish any benefits of surfactant for bronchiolitis in critically ill infants and children.
Summary of findings
Summary of findings for the main comparison. Surfactant for critically ill infants with bronchiolitis.
| Surfactant for critically ill infants with bronchiolitis | ||||||
| Patient or population: critically ill infants with bronchiolitis Settings: intensive care unit Intervention: surfactant | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | No of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Surfactant | |||||
| Duration of mechanical ventilation (hours) | The mean duration of mechanical ventilation (hours) in the control groups was 170 to 213.61 | The mean duration of mechanical ventilation (hours) in the intervention groups was 63.04 lower (130.43 lower to 4.35 higher) | 79 (3 studies) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ moderate2 | Duration of mechanical ventilation was highest among controls in Luchetti 1998 where blinding was not mentioned | |
| Duration of ICU stay (days) | The mean duration of ICU stay (days) in the control group was 8.2 to 15.7 days1 | The mean duration of ICU stay (days) in the intervention groups was 3.31 lower (6.38 to 0.25 lower) | 79 (3 studies) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ moderate2 | Duration of ICU stay was highest among controls in Luchetti 1998 where blinding was not mentioned | |
| PO2/FiO2 ratio at 12 hours | The mean PO2/FiO2 ratio at 12 hours in the control group was 140 to 148.13 | The mean PO2/FiO2 ratio at 12 hours in the intervention groups was 99.08 higher (57.43 to 140.72 higher) | 60 (2 studies) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ moderate2 | SD was not available for Luchetti 2002; it was imported from Luchetti 1998 | |
| PO2/FiO2 ratio at 24 hours | The mean PO2/FiO2 ratio at 24 hours in the control group was 136 to 145.93 | The mean PO2/FiO2 ratio at 24 hours in the intervention group was 109.64 higher (63.29 to 155.99 higher) | 60 (2 studies) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ moderate2 | SD was not available for Luchetti 2002; it was imported from Luchetti 1998 | |
| PCO2 at 12 hours (mmHg) | The mean PCO2 at 12 hours (mmHg) in the control group was 42.2 to 45 mmHg3 | The mean PCO2 at 12 hours (mmHg) in the intervention group was 7.63 lower (8.99 to 6.28 lower) | 60 (2 studies) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ moderate2 | SD was not available for Luchetti 2002; it was imported from Luchetti 1998 | |
| PCO2 at 24 hours (mmHg) | The mean PCO2 at 24 hours (mmHg) in the control group was 42.6 to 45 mmHg3 | The mean PCO2 at 24 hours (mmHg) in the intervention group was 7.9 lower (9.42 to 6.38 lower) | 60 (2 studies) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ moderate2 | SD was not available for Luchetti 2002; it was imported from Luchetti 1998 | |
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% CI) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence High quality: Further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect. Moderate quality: Further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate. Low quality: Further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate. Very low quality: We are very uncertain about the estimate. | ||||||
1Range of means in control groups in all three studies. 2Total number of participants is less than 400. 3Range of means in control groups from two studies.
CI: confidence interval GRADE: Grading of Recommendations: Assessment, Development and Evaluation ICU: intensive care unit PO2/FiO2 ratio: ratio of partial pressure of arterial oxygen and fractional inspired oxygen SD: standard deviation PCO2: partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide
Background
Description of the condition
Bronchiolitis is one of the most frequent causes of respiratory failure in infants and yet no effective therapy is available except for supportive care. Acute bronchiolitis (inflammation of the small airways in the lung) is predominantly a viral disease and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the most common cause (CDC 2010). Bronchiolitis is more common in non‐breast fed male infants and in those living in crowded conditions (Meates‐Dennis 2005). In the USA, approximately 2% to 3% of all infants in the first 12 months of life are hospitalised (more than 125,000 hospitalisations annually) because of an RSV infection (Meissner 2009). From 1979 to 1997 there were 1806 (annual mean 95 deaths; range 66 to 127) bronchiolitis‐associated deaths in the USA (Shay 2001). Risk factors for severe morbidity and mortality in bronchiolitis are: low and very low birth weight infants, prematurity, chronic pulmonary disease (most often bronchopulmonary dysplasia), congenital heart disease, immune deficiency, increasing birth order, low five‐minute Apgar score, young maternal age, unmarried mother and tobacco use during pregnancy (Holman 2003; Navas 1992). Primary RSV infection occurs later in infants from higher socioeconomic groups and there is less risk of developing severe disease in these infants (Handforth 2000).
Clinical features of bronchiolitis begin as sneezing, rhinorrhoea and fever. It may than gradually progress to paroxysmal wheezy cough, respiratory distress and irritability. A physical examination will find wheezing, with or without fine crackles. Chest X‐ray usually reveals hyperinflated lungs with patchy atelectasis. The diagnosis of bronchiolitis is clinical, particularly in a previously healthy infant presenting with first‐time viral symptoms and wheezing. About 10% to 15% of infants and children hospitalised with bronchiolitis require intensive care for worsening respiratory distress and about half of these develop respiratory failure, requiring mechanical ventilation (Navas 1992). The case‐fatality rate is usually 0.5% to 1.5% in high‐income countries and causes may be apnoea, respiratory failure or severe dehydration (Levy 1997). There was a declining trend in post‐neonatal mortality rate due to bronchiolitis in the UK, where figures fell from 21.47 per 100,000 in 1979 to 1.82 per 100,000 live births in 2000 (Panickar 2005). There are limited epidemiological data from low‐income countries. A study from Bangladesh (Kabir 2003) reported a mortality rate of 2% in children admitted to hospital with a diagnosis of bronchiolitis.
Description of the intervention
The mainstay of bronchiolitis treatment is supportive measures, such as adequate fluid intake, antipyretics and oxygen supplement if necessary. Humidified oxygen is indicated for hospitalised infants with hypoxia (Davison 2004). Many therapeutic interventions other than supportive measures have been used to treat bronchiolitis but their effectiveness is not well documented.
Hypertonic nebulised saline may have a role in the management of bronchiolitis (Zhang 2013). In a recent review, nebulised adrenaline has been shown to be beneficial in acute bronchiolitis (Hartling 2011a; Hartling 2011b). Other adjunctive therapies for bronchiolitis, for example, bronchodilators (Gadomski 2014), heliox inhalation therapy (Liet 2010), chest physiotherapy (Roqué i Figuls 2012), nebulised recombinant human deoxyribonuclease (Mercus 2001; Nasr 2001) and steam inhalation (Umoren 2011) have no definitive role in the management of bronchiolitis.
Corticosteroids (Fernandes 2013) and antibiotics (Farley 2014) are usually not recommended for bronchiolitis. Ribavirin, an antiviral agent administered by aerosol, has no clear beneficial effect in bronchiolitis caused by RSV (Ventre 2007). There is no support for RSV immunoglobulin administration during acute episodes of RSV bronchiolitis (Davison 2004). Palivizumab, an intramuscular monoclonal antibody to the RSV F protein, is recommended for infants younger than two years of age with chronic lung disease (bronchopulmonary dysplasia), prematurity or symptomatic congenital heart disease, before and during the RSV season, to reduce the severity and incidence of acute bronchiolitis due to RSV (Meissner 2009).
Pulmonary surfactant is a highly surface active (preventing alveolar collapse) lipoprotein complex that is synthesised and secreted by type II alveolar cells and the airway Clara cell (Goerke 1998). A natural surfactant contains about 80% phospholipids (mainly dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine), 8% neutral lipids and 12% proteins (Wood 1993). There are four types of surfactant‐associated proteins: SP‐A, SP‐B, SP‐C and SP‐D (Griese 1999). Pulmonary surfactants reduce surface tension at the air‐liquid interface of the lung and prevent alveolar collapse (Possmayer 1990). There are two types of surfactants available for clinical use: animal surfactants (for example, beractant and poractant) and synthetic surfactants (for example, colfosceril palmitate) (Logan 2009; Ramanathan 2009; Appendix 1). Surfactants (especially SP‐A and SP‐D) also have some immunological functions and protect the lungs from injuries and infections caused by inhaled particles and micro‐organisms (Wright 2003). A genetic association has been reported between SP‐A (Löfgren 2002) and SP‐D (Lahti 2002) gene locus and severe RSV infection. Use of exogenous surfactants in preterm babies with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)/hyaline membrane disease (HMD) has been extensively studied and is now the standard management for this condition (Ardell 2015; Seger 2009; Soll 1998).
How the intervention might work
Dargaville 1996 reported deficiency of SP‐A and disaturated phosphatidylcholine and impaired surfactant functional activity during acute viral bronchiolitis that resolved as the disease improved. In another study, severe viral bronchiolitis requiring mechanical ventilation was associated with an absence of surfactant activity and phosphatidylglycerol which resolved by clinical recovery (Skelton 1999). These abnormalities may represent one of the pathophysiological mechanisms causing airway obstruction in acute bronchiolitis. Barr 2000 revealed that SP‐A enhanced binding and uptake of RSV by peripheral blood monocytes and U937 macrophages (a human macrophage cell line known to express SP‐A receptors) and, further, the SP‐A mediated uptake of RSV reversed the effects of RSV on TNF‐alpha and IL‐10 production by both monocytes and U937 macrophages). These findings suggest that RSV clearance from the human lung may be enhanced by SP‐A.
Why it is important to do this review
Acute bronchiolitis is one of the most frequent causes of hospitalisation in infants. A few of those affected require intensive care and mechanical ventilation. However, no effective treatment is available, except for supportive therapy. Abnormalities of surfactant have been observed in severe cases of bronchiolitis; exogenous surfactant administration appears to favourably change the haemodynamics of the lungs and may be a promising therapy for severe bronchiolitis.
Objectives
To evaluate the efficacy of exogenous surfactant administration (i.e. intratracheal administration of surfactant of any type (whether animal‐derived or synthetic), at any dose and at any time after start of ventilation) compared to placebo, no intervention or standard care in reducing mortality and the duration of ventilation in infants and children with bronchiolitis requiring mechanical ventilation.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
Prospective, randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi‐RCTs evaluating the effect of exogenous surfactant in infants and children with bronchiolitis, requiring mechanical ventilation.
Types of participants
Infants and children (0 to 60 months of age) in an intensive care unit (ICU) with a diagnosis of bronchiolitis, requiring mechanical ventilation. There is no standard diagnostic criteria for bronchiolitis; diagnosis is usually clinical. We included studies of children with a diagnosis of bronchiolitis.
Types of interventions
Comparison of exogenous surfactant with placebo, no intervention or standard care (humidified oxygen or adrenaline nebulisation, or both). We included intratracheal administration of surfactant of any type (for example, animal‐derived or synthetic), at any dose and at any time after start of ventilation.
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes
Mortality.
Duration of mechanical ventilation (hours).
Adverse effects (desaturation, change in heart rate, change in blood pressure and bronchospasm) or complications (pneumothorax) or both.
Secondary outcomes
Duration of ICU stay.
Duration of hospital stay.
Gas exchange [effects on oxygenation (pO2/FiO2 ratio) and CO2 elimination (pCO2)].
Respiratory mechanics (effects on pulmonary compliance and airways resistance).
Recurrent lower respiratory tract disease.
Search methods for identification of studies
Electronic searches
For this update we searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL; 2015, Issue 5) which contains the Cochrane Acute Respiratory Infections Group's Specialised Register; MEDLINE (January 2012 to June week 3, 2015); EMBASE (January 2012 to June 2015); CINAHL (January 2012 to June 2015); LILACS (2011 to June 2015); and Web of Science (2012 to June 2015).
Previously we searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL; 2012, Issue 4) which contains the Cochrane Acute Respiratory Infections Group's Specialised Register; MEDLINE (1948 to May week 1, 2012); EMBASE (1974 to May 2012); CINAHL (1982 to May 2012); LILACS (1985 to May 2012); and Web of Science (1985 to May 2012).
We used the search strategy in Appendix 2 to search CENTRAL and MEDLINE. We combined the MEDLINE search with the Cochrane Highly Sensitive Search Strategy for identifying randomised trials in MEDLINE: sensitivity‐ and precision‐maximising version (2008 revision); Ovid format (Lefebvre 2011). We adapted the search strategy to search EMBASE (Appendix 3), CINAHL (Appendix 4), LILACS (Appendix 5), and Web of Science (Appendix 6). We imposed no language or publication restrictions. We excluded non‐RCTs.
Searching other resources
We searched ClinicalTrials.gov (www.ClinicalTrials.gov) and the World Health Organization (WHO) trials portal (http://apps.who.int/trialsearch/) for completed and ongoing trials. We ran the latest search on 25 June 2015.
One review author (KRJ) contacted experts in the field to determine if they knew of any additional ongoing RCTs, or completed published or unpublished articles. KRJ contacted companies that supply surfactant in order to identify possible ongoing trials of surfactant in bronchiolitis.
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies
Two review authors (KRJ, DC) independently assessed the studies for inclusion. We independently reviewed the reference lists of all available review articles and primary studies to identify references not found in the computerised searches. Two review authors (KRJ, DC) independently screened the title and abstract of search results to identify studies which might be relevant to this review. We retrieved the full‐text of potentially relevant studies and independently assessed them for inclusion in the review. We recorded the selection process in a PRISMA flow diagram (Moher 2009) (Figure 1). We corresponded with investigators, where appropriate, to clarify study eligibility. We listed excluded studies with reason(s) for exclusion (see Characteristics of excluded studies). We resolved disagreements by discussion.
1.
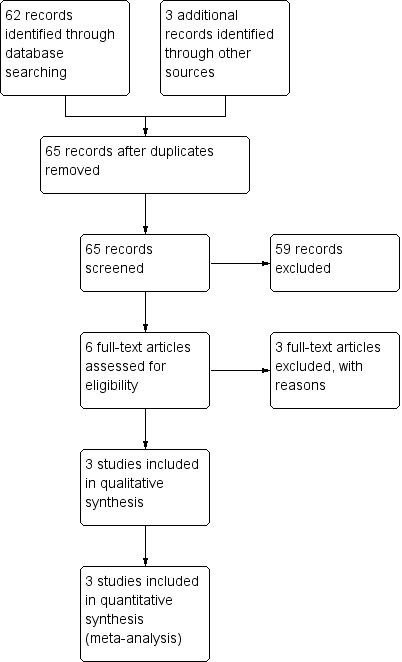
Study flow diagram.
Data extraction and management
Two review authors (KRJ, DC) independently extracted data using a standardised data collection form in accordance with the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Deeks 2011), which included the following data: source, eligibility, methods, participants and settings, interventions, outcomes, results, adverse outcomes and miscellaneous (funding source of the study, or potential conflicts of interest). We resolved disagreements by discussion.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
Two review authors (KRJ, DC) independently assessed the risk of bias in included studies using the criteria described in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011). This comprised a judgement for each specific feature of the study as 'low risk', 'high risk' or 'unclear risk' of bias ('unclear' indicating either lack of information or uncertainty over the potential for bias). The specific features were random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel, blinding of outcome assessment, incomplete outcome data, selective reporting, and other sources of bias. We created a ‘Risk of bias' graph (Figure 2) using Review Manager 5 software (RevMan 2014).
2.
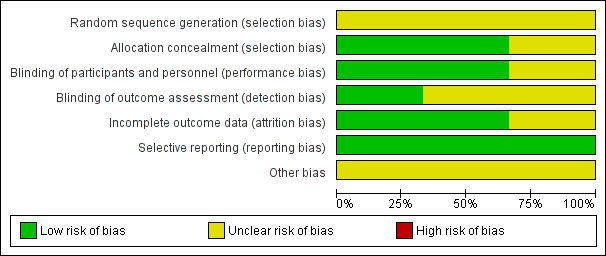
'Risk of bias' graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.
Measures of treatment effect
We analysed dichotomous outcomes by calculating the risk ratio (RR) and risk difference (RD). We analysed continuous outcome data as mean differences (MDs). We expressed the overall results with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Unit of analysis issues
We only included RCTs in the review. We found no quasi‐RCTs, cluster‐RCTs or cross‐over trials.
Dealing with missing data
We considered one or more of the following steps for any missing data.
We contacted the trial investigators to request missing data whenever possible.
We performed sensitivity analyses to assess how sensitive results were to reasonable changes in the assumptions that were made.
We addressed the potential impact of missing data on the findings of the review in the Discussion.
We calculated the standard deviation (SD) from study statistics (for example, standard errors and P values) for missing SDs of continuous outcome data. If SD calculation was still not possible, then we imputed from other studies in the meta‐analysis as per the recommendations in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Deeks 2011).
There were no losses to follow‐up in the included studies and we did not need to perform an intention‐to‐treat (ITT) analysis.
Assessment of heterogeneity
We assessed both clinical and methodological heterogeneity before pooling. We carried out assessment for statistical heterogeneity visually, using a Chi2 test and using the I2 statistic. Using the Chi2 test, a low P value (< 0.1) (or a large Chi2 test relative to its degree of freedom) provided evidence of heterogeneity of intervention effects (variation in effect estimates beyond chance). We interpreted the values of the I2 statistic as follows: 0% to 40% might not be important; 30% to 60% may represent moderate heterogeneity; 50% to 90% may represent substantial heterogeneity; and 75% to 100% represents considerable heterogeneity (Deeks 2011).
Assessment of reporting biases
There were an insufficient number of included studies to assess publication bias using funnel plots in RevMan 2014.
Data synthesis
We carried out the meta‐analyses using RevMan 2014. We used a fixed‐effect model for pooled data analysis unless there was important statistical heterogeneity among studies, in which case we considered a random‐effects meta‐analysis. We created Table 1 using GRADEproGDT software (GRADEproGDT 2015).
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
Insufficient data did not allow us to conduct a subgroup analysis for different age groups and for risk factors for severe bronchiolitis.
However, we performed subgroup analyses to investigate statistical heterogeneity to determine the possible reason(s) for this. Further, we performed subgroup analysis to explore whether the heterogeneity was a result of low quality trials or not.
Sensitivity analysis
We performed sensitivity analyses to test the robustness of the decisions if sufficient numbers of trials were found. We:
repeated meta‐analysis after exclusion of studies with inadequate concealment of allocation;
repeated meta‐analysis after exclusion of studies in which the outcome evaluation was not blinded;
repeated meta‐analysis, imputing missing data as best possible and worst possible outcome(s); and
compared the difference of pooled analysis results by using a fixed‐effect model and a random‐effects model.
Results
Description of studies
All the results are based on published data only. We attempted to contact study authors of included studies through emails to provide additional details but received no replies.
Results of the search
We retrieved records from CENTRAL (5), MEDLINE (12), EMBASE (21), CINAHL (15), LILACS (1), and Web of Science (24); after removing duplicates there was a total of 56 records. We identified three additional records through other sources. Thus, we screened a total of 59 records for eligibility (Figure 1). Out of these, we excluded 53 and assessed the remaining six full‐text articles for eligibility. We excluded three full‐text articles and included the remaining three trials for qualitative and quantitative synthesis.
Included studies
We included three studies, enrolling 79 participants. Details of these studies are provided in the Characteristics of included studies tables. All three studies were RCTs; two from Italy (Luchetti 1998; Luchetti 2002) and one from the UK (Tibby 2000). One study was multicentric (six centres) (Luchetti 2002). We summarised extracted data from included studies in Appendix 7. The age of included participants ranged from 1 week to 2.5 years, as provided in studies by Luchetti 1998 and Luchetti 2002. The children were younger in the Tibby 2000 study, with a median (inter‐quartile range, IQR) age of 2 (1.5 to 3.1) months and 1.4 (1 to 2.1) months in the surfactant and control group, respectively. The children in the Luchetti 1998 study were older with a mean (standard deviation, SD) age of 10.4 (1.8) and 11.2 (2.0) months in the surfactant and control group, respectively (Appendix 7). Overall there were 40 males and 39 females, with no major difference in sex distribution among the studies (Appendix 7). The majority of participants had RSV‐induced respiratory failure except for the Luchetti 1998 study where viral aetiology was known only in four out of a total 20 cases and these were RSV‐positive. The Luchetti 1998 study enrolled patients when they were on mechanical ventilation for 24 hours without significant improvement of their clinical status (used predefined oxygenation and PaCO2 (partial pressure of arterial CO2) criteria) and used surfactant 50 mg/kg in two to three doses. Luchetti 2002 included participants who had mechanical ventilation for at least 12 hours without significant improvement and used surfactant 50 mg/kg in two aliquots over about five minutes. The Tibby 2000 study enrolled participants who were ventilated for less than 24 hours with an oxygenation index above five and a ventilation index above 20 and surfactant was administered in two doses (100 mg/kg), 24 hours apart. Participants with uncorrected congenital heart disease and neuromuscular diseases were excluded by two studies (Luchetti 2002; Tibby 2000). The Luchetti 2002 study excluded children with chronic lung disease, whereas the Tibby 2000 study did not exclude children with chronic lung disease and with a history of prematurity. Intervention included porcine surfactant (Curosurf) in Luchetti 1998 and Luchetti 2002 trials and bovine surfactant (Survanta) in the Tibby 2000 trial. The exogenous surfactant was administered through an endotracheal tube in all studies. Luchetti 1998 and Luchetti 2002 used no placebo, whereas air placebo was used in Tibby 2000. The primary outcomes vary among the included studies as depicted in the Characteristics of included studies tables.
Excluded studies
We excluded three RCTs (Moller 2003; Willson 1999; Willson 2005) for the reasons given in the Characteristics of excluded studies table. All three studies used surfactants but none of them enrolled participants with bronchiolitis.
Risk of bias in included studies
The risk of bias rated for each criteria for included studies is shown in the Characteristics of included studies and 'Risk of bias' graph (Figure 2) and 'Risk of bias' summary (Figure 3).
3.
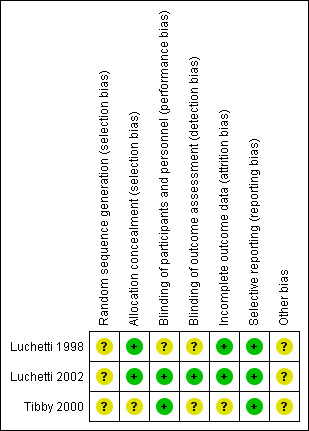
'Risk of bias' summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
Allocation
The method of random sequence generation was not described by any of the included studies (Characteristics of included studies). Sealed envelopes were used for allocation concealment in studies by Luchetti 1998 and Luchetti 2002 and it was not described in the study by Tibby 2000.
Blinding
Participants and health care providers were blinded in the study by Tibby 2000; blinding of health care providers was attempted in the study by Luchetti 2002 and it was not mentioned in the Luchetti 1998 study. Outcome assessors were blinded in the Luchetti 2002 trial, whereas it was not mentioned in the studies by Luchetti 1998 and Tibby 2000.
Incomplete outcome data
Mortality data were not reported in the Tibby 2000 study; apart from this study, there were no incomplete outcome data.
Selective reporting
None of the included studies had selective reporting based on the outcomes mentioned in the methods section; although a study protocol was not available for any of these studies.
Other potential sources of bias
None of the included studies mentioned funding or conflict of interest.
Effects of interventions
See: Table 1
Primary outcomes
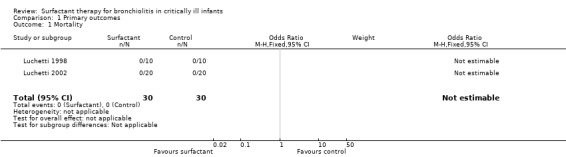
1. Mortality
Mortality data were described for 60 participants in two included studies; there was no mortality in either study (Luchetti 1998; Luchetti 2002).
2. Duration of mechanical ventilation (hours)
The data regarding duration of mechanical ventilation were available for 79 participants in all three included studies. Duration of mechanical ventilation was significantly less in two studies (Luchetti 1998; Luchetti 2002) but there was no significant difference in the study by Tibby 2000. When data from three studies were pooled, the duration of mechanical ventilation was no different in the surfactant group compared to the control group (mean difference (MD) ‐63.04 hours, 95% confidence interval (CI) ‐130.43 to 4.35) but there was a trend towards beneficial effects of surfactant (Analysis 1.2; Figure 4).
1.2. Analysis.
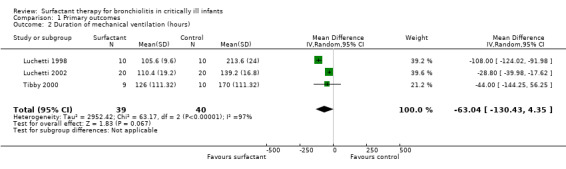
Comparison 1 Primary outcomes, Outcome 2 Duration of mechanical ventilation (hours).
4.
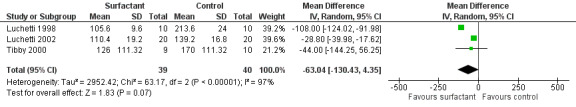
Forest plot of comparison: 1 Primary outcome: 1.2 Duration of mechanical ventilation (hours).
There was statistically significant heterogeneity for duration of mechanical ventilation (I2 statistic 97%) that was attributed to the Luchetti 1998 study, where blinding was not attempted and controls had comparatively higher duration of mechanical ventilation. After excluding the Luchetti 1998 study from the meta‐analysis, the duration of mechanical ventilation was significantly lower in the surfactant group (MD ‐28.99 hours, 95% CI ‐40.10 to ‐17.87).
3. Adverse effects (desaturation, change in heart rate, change in blood pressure and bronchospasm) or complications (pneumothorax) or both
Luchetti 1998 reported that no adverse haemodynamic effects (no significant change in heart rate and blood pressure) and no complications were noted. Luchetti 1998 reported no other specific adverse effects and complications. Luchetti 2002 stated that they observed no significant change in heart rate and no complications, without mentioning specific adverse effects and complications. Tibby 2000 stated that no complications were noted, again without mentioning specific adverse effects and complications.
Secondary outcomes
1. Duration of ICU stay
The data regarding duration of intensive care unit (ICU) stay were available from all three included studies (79 participants). The Tibby 2000 study had non‐significant difference in duration of ICU stay between the experimental and control group; duration of ICU stay in the control roup was just significantly less for the Luchetti 1998 and Luchetti 2002 studies (Analysis 2.1; Figure 5). After combining the data, the duration of ICU stay was significantly less in the surfactant group compared to the control group (MD ‐3.31 days, 95% CI ‐6.38 to ‐0.25) (Analysis 2.1; Figure 5). There was statistically significant heterogeneity for duration of ICU stay (I2 statistic = 94%), again attributable to the Luchetti 1998 study. The results were still significant after excluding the Luchetti 1998 study from the analysis (MD ‐1.81 days, 95% CI ‐2.42 to ‐1.19).
2.1. Analysis.
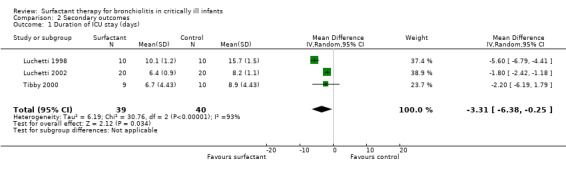
Comparison 2 Secondary outcomes, Outcome 1 Duration of ICU stay (days).
5.
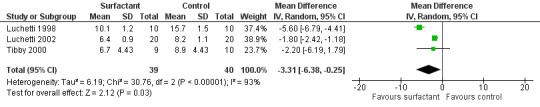
Forest plot of comparison: 2 Secondary outcome: 2.1 Duration of ICU stay (days).
2. Duration of hospital stay
Duration of hospital stay was available from Tibby 2000 only and it was not significantly different between the groups (13 days versus 17 days; P = 0.3).
3. Gas exchange (effects on oxygenation (pO2/FiO2 ratio) and CO2 elimination (pCO2))
The effect of oxygenation was measured as PO2/FiO2 ratio (ratio of partial pressure of arterial oxygen and fractional inspired oxygen) in two studies (Luchetti 1998; Luchetti 2002) and as oxygenation index (OI = mean airway pressure (cm H2O) x FiO2 x 100/arterial PO2(mm Hg)) and alveolar arterial gradient (Aa) by the third study (Tibby 2000). In the Luchetti 1998 and Luchetti 2002 studies, the PO2/FiO2 ratio was significantly higher in the surfactant group at 1, 3, 12 and 24 hours and at 1, 3, 6, 12, 24 and 48 hours, respectively. In the Tibby 2000 study, the mean OI and Aa gradient changed from 6.3 to 9.3 and 198 to 246, respectively, following the first dose, and from 6.8 to 7.6 and 191 to 225, respectively, after the second dose; but all changes were not significant. After combining the data from two studies (Luchetti 1998; Luchetti 2002), the PO2/FiO2 ratio at 12 and 24 hours of surfactant administration was significantly higher in the surfactant group (MD 99.08, 95% CI 57.43 to 140.72) (Analysis 2.2) and (MD 109.64, 95% CI 63.29 to 155.99) (Analysis 2.3; Figure 6), respectively. There was significant heterogeneity for the combined PO2/FiO2 ratio and we performed a random‐effects meta‐analysis.
2.2. Analysis.
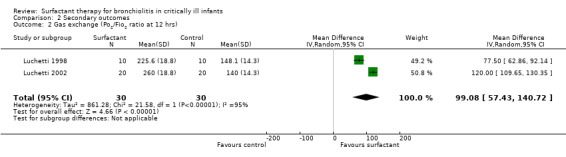
Comparison 2 Secondary outcomes, Outcome 2 Gas exchange (Po2/Fio2 ratio at 12 hrs).
2.3. Analysis.
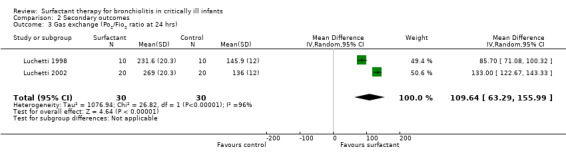
Comparison 2 Secondary outcomes, Outcome 3 Gas exchange (Po2/Fio2 ratio at 24 hrs).
6.
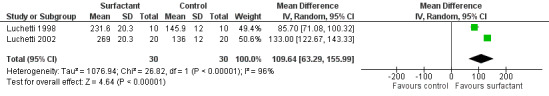
Forest plot of comparison: 2 Secondary outcome: 2.3 Po2/Fio2 ratio at 24 hrs.
The effect on CO2 elimination was measured as PCO2 (partial pressure of arterial CO2) values in two studies (Luchetti 1998; Luchetti 2002) and as ventilation index (VI = respiratory rate x peak‐inspiratory pressure (cm H2O) x arterial PCO2 (mm Hg)/1000) in the third study (Tibby 2000). A significant reduction of PCO2 in the surfactant group as compared to control group was observed in Luchetti 1998 and Luchetti 2002 at 12 and 24 hours and at 1, 3, 6, 12, 24 and 48 hours, respectively. The ventilation index did not significantly change in the Tibby 2000 study after surfactant administration. The pooled PCO2 values from two studies (Luchetti 1998; Luchetti 2002) were significantly less in the surfactant group at 12 and 24 hours (MD ‐7.63 mmHg, 95% CI ‐8.99 to ‐6.28) (Analysis 2.4) and (MD ‐7.90 mmHg, 95% CI ‐9.42 to ‐6.38) (Analysis 2.5; Figure 7), respectively; there was no heterogeneity (Figure 7).
2.4. Analysis.
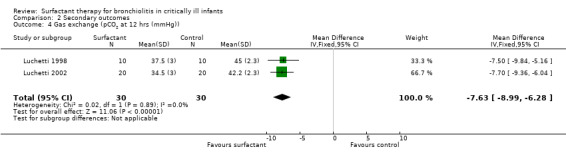
Comparison 2 Secondary outcomes, Outcome 4 Gas exchange (pCO2 at 12 hrs (mmHg)).
2.5. Analysis.
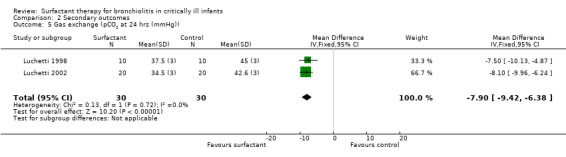
Comparison 2 Secondary outcomes, Outcome 5 Gas exchange (pCO2 at 24 hrs (mmHg)).
7.
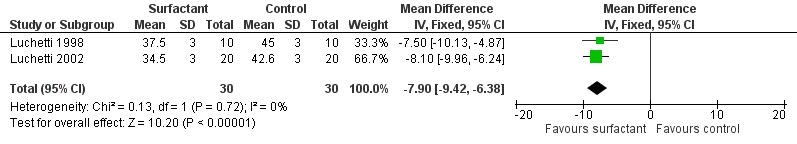
Forest plot of comparison: 2 Secondary outcome: 2.5 pCO2 at 24 hrs (mmHg).
4. Respiratory mechanics (effects on pulmonary compliance and airways resistance)
Data regarding compliance after surfactant administration were available from two studies (Luchetti 2002; Tibby 2000). The static compliance was significantly higher in the surfactant group at 1, 3, 6, 12, 24 and 48 hours in Luchetti 2002. In the Tibby 2000 study, compliance fell (0.36 to 0.27 mL/cm H2O/kg; P < 0.01) in the placebo group only at 30 hours post‐surfactant administration. Only the Tibby 2000 study provided data regarding airway resistance, where it increased (229 cm H2O/L/s to 391 cm H2O/L/s; P < 0.001) significantly in the placebo group only at 30 hours post‐surfactant administration.
5. Recurrent lower respiratory tract disease
No data were available regarding recurrent lower respiratory tract disease in follow‐up for enrolled participants.
Assessment of reporting bias
There were not a sufficient number of included studies to assess publication bias by funnel plot.
Subgroup analysis
There were insufficient data to perform subgroup analyses for different age groups (< 1 month, 1 to < 12 months and 12 to < 60 months) and participants with or without risk factors for severe bronchiolitis.
Sensitivity analysis
We repeated the analysis after excluding studies with unclear risk of biases. The duration of mechanical ventilation was not statistically different as a whole, but became significant after excluding the Luchetti 1998 study where no blinding was mentioned. For duration of ICU stay, the difference among the groups was still significant after excluding the Luchetti 1998 study from the analysis. We performed a random‐effects meta‐analysis for the duration of mechanical ventilation and duration of ICU stay while combining all three studies' data because of significant heterogeneity. Results were not much different in the meta‐analysis when using the fixed‐effect or random‐effects models. There were no incomplete outcome data to perform sensitivity analysis with best and worst possible outcomes.
Investigation of heterogeneity
There was statistically significant heterogeneity for outcomes of duration of mechanical ventilation, duration of ICU stay and PO2/FiO2 ratios. The heterogeneity was attributed to the Luchetti 1998 study (no blinding and higher values of different parameters in the control group) as there was no heterogeneity after excluding this study from analysis. We performed a random‐effects meta‐analysis for PO2/FiO2 ratios as only two studies (Luchetti 1998; Luchetti 2002) were included for analysis.
Level of evidence as per GRADE
The level of evidence for duration of mechanical ventilation, duration of intensive care unit stay, oxygenation parameters, and carbon dioxide parameters was of moderate quality (Table 1).
Discussion
Summary of main results
The review evaluated the effects of surfactant therapy for bronchiolitis in critically ill infants. The results of the review are summarised in Table 1. There was no mortality reported in two included studies. The duration of mechanical ventilation was significantly less in the surfactant group as compared to the control group in children with severe bronchiolitis. No adverse effects and no complications were reported with surfactant treatment. The results regarding duration of ICU stay, PO2/FiO2 ratio and PCO2 favoured surfactant treatment. The compliance was higher in the surfactant group in individual studies. Data were available from only one study for duration of hospital stay and airway resistance.
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
The limited available evidence suggests usefulness of surfactant therapy for bronchiolitis in critically ill infants. Overall, the total number of participants (79) in the identified studies was small. One of the included studies did not mention mortality. Data were not available from any of the three studies for most of the secondary outcomes, except for duration of ICU stay. Two included studies (Luchetti 2002; Tibby 2000) excluded participants with congenital heart disease and the other study (Luchetti 2002) excluded infants with chronic lung diseases, where bronchiolitis may be more severe. Currently there is a lack of evidence for effective therapy, except for nebulised adrenaline, in infants with bronchiolitis. The present review suggests that there is insufficient evidence of benefit of surfactant in children with bronchiolitis who require mechanical ventilation.
Quality of the evidence
The quality of evidence for each outcome is described in Table 1. The three included studies in the review enrolled a total of 79 participants. There was no high risk of bias but there was significant unclear risk, as shown in Figure 2. The duration of mechanical ventilation and duration of ICU stay were significantly lower in two studies (Luchetti 1998; Luchetti 2002), but these were not significantly different in the third study (Tibby 2000) where air placebo was used. Similary, results for oxygenation and CO2 elimination were significantly better for two studies (Luchetti 1998; Luchetti 2002), but not for the third one (Tibby 2000). The quality of evidence was moderate for all the objectives, as shown in Table 1. We downgraded the quality of the body of evidence for all the outcomes because of the small number of total participants in the included studies (Table 1). Patients were younger in Tibby 2000 compared to Luchetti 1998. Data regarding blinding of outcome assessors were not available from two studies: Luchetti 1998 had predefined criteria for discontinuation of ventilation, whereas Tibby 2000 did not. The ventilation strategy was also different between studies: Luchetti 1998 used tidal volume of 10 mL/kg, whereas Luchetti 2002 and Tibby 2000 allowed permissive hypercapnia.
Potential biases in the review process
The search strategy for this review was broad and it was performed by the Trials Search Co‐ordinator of the Cochrane Acute Respiratory Infections (ARI) Group, thus it is unlikely that any relevant study was missed. Study selection, data extraction and analysis were carried out independently by two review authors. The quality of included trials varied with many unclear risks of bias (Figure 2). Not all data related to assessment of bias were available from the published studies and there was no reply from study authors regarding these. There were other limitations in this review. For most of the secondary outcome measures, data were available from two of three included studies. The standard deviations (SDs) for Tibby 2000 were not available and we calculated them from P values or standard error of mean (SEM). Similarly, SD for PO2/FiO2 ratio and PCO2 were not available for Luchetti 2002 and we imported them from another study (Luchetti 1998).
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
We did not identify any additional relevant studies since the previous version of this review (Jat 2012). The results were similar for both reviews. In one of the excluded trials with 153 participants with acute respiratory failure from acute lung injury (nine were of RSV pneumonia but none with bronchiolitis), participants were randomised to receive surfactant or air placebo; the surfactant acutely improved oxygenation and significantly reduced mortality, although no significant reduction in duration of ventilator therapy, ICU or hospital stay was observed (Willson 2005). In a pilot study, part of the second excluded study (Moller 2003), where 19 children (two with RSV bronchiolitis) with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) received surfactant, there was a significant increase in PaO2/FIO2 at four hours and 48 hours after surfactant administration. In a RCT (part of Moller 2003) (there were no children with bronchiolitis), surfactant therapy in severe ARDS improved oxygenation immediately after administration. In a third excluded study, administration of surfactant in children with acute hypoxaemic respiratory failure (six children had RSV pneumonia but none had bronchiolitis) was safe and was associated with rapid improvement in oxygenation, earlier extubation and reduced requirement for intensive care (Willson 1999). There was variability in type, timing and dose of surfactant in included studies. Two studies (Luchetti 1998; Luchetti 2002) used porcine‐derived surfactant (Curosurf) and the third study (Tibby 2000) used bovine surfactant (Survanta). Similarly, out of three excluded studies, calfactant was used in two (Willson 1999; Willson 2005) and bovine surfactant (Alveofact) in the third (Moller 2003). There are different compositions of different types of surfactants (Appendix 1) and effects of different surfactants may differ. The surfactant was administered after 12 and 24 hours of ventilation in the Luchetti 2002 and Luchetti 1998 studies, respectively, and it was administrated within 24 hours of ventilation in Tibby 2000 (children with > 24 hours of ventilation were excluded). The surfactant was administered in two doses and two to three doses over about five minutes in Luchetti 1998 and Luchetti 2002, respectively, but it was administered in two doses at 24 hours apart in the third study (Tibby 2000). Luchetti 2002 and Tibby 2000 included only RSV bronchiolitis, whereas only 4 out of 20 participants had RSV bronchiolitis in the Luchetti 1998 study. The most surfactant protein deficiency had been demonstrated in RSV‐induced respiratory failure as compared to controlled ventilated children (Kerr 1999). It may be possible that surfactant may produce different effects in respiratory failure due to different aetiologies.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
In infants, the administration of surfactant did not reduce the duration of mechanical ventilation significantly compared with placebo or no treatment, irrespective of timing, although duration of intensive care unit (ICU) stay was shorter in the surfactant group and there was a better effect of surfactant on gas exchange. After excluding a study which produced significant heterogeneity, the duration of mechanical ventilation was also less in the surfactant group. However, it is difficult to suggest the usefulness of surfactant therapy for bronchiolitis in critically ill infants because of the small number of methodologically flawed included trials. Cost‐effectiveness is another concern. The use of surfactant for bronchiolitis in critically ill infants did not appear to have any adverse effects in the included studies. Thus, it is difficult to recommend for or against the use of surfactant in infants with bronchiolitis who require mechanical ventilation.
Implications for research.
The level of evidence for duration of mechanical ventilation, duration of intensive care unit stay, oxygenation parameters, and carbon dioxide parameters was of moderate quality. There is a need for larger trials with adequate power to evaluate the effectiveness of exogenous surfactant administration in infants with bronchiolitis who require mechanical ventilation. The type (animal‐derived or synthetic), dose (dose per aliquot and total number of aliquots) and timing (at the time of ventilation, after 12 hours of ventilation or after 24 hours of ventilation) of surfactant administration also need to be addressed in future trials. Finally, a cost‐effective analysis is worth considering regarding the cost of surfactant and cost of intensive care for critically ill infants with bronchiolitis.
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 25 June 2015 | New search has been performed | We did not identify any new studies for inclusion. |
| 25 June 2015 | New citation required but conclusions have not changed | Our conclusions remain unchanged. |
Notes
This review was previously published in 2006 and later withdrawn in 2010 as the authors were not able to update it (Ventre 2006).
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Clare Dooley, Liz Dooley, Sarah Thorning and Inge Axelsson for their support in performing the review. We also acknowledge Ventre K, Haroon M and Davison C for the first publication of this review in 2006 (Ventre 2006). We would also like to acknowledge José Luis Ferrero, Mathew Zacharias, Manal Kassab and Teresa Neeman for commenting on this review and providing useful suggestions.
Appendices
Appendix 1. Details of surfactants available for clinical use
| Animal‐derived | Preparation/composition |
Phospholipids conc. mg/ml (%) |
SP‐B (µg per µmol) |
SP‐C (µg per µmol) |
| Beractant (Survanta) | Minced bovine lung extract + DPPC + palmitic acid + tripalmitin | 25 (84 ) | 0 to 1.3 | 1 to 20 |
| Calfactant (Infasurf) | Bovine lung lavage + DPPC + cholesterol | 35 (95) | 5.4 | 8.1 |
| Poractant alfa (Curosurf) | Minced porcine lung extract (liquid gel chromatography) | 80 (99) | 2 to 3.7 | 5 to 11.6 |
| Synthetic | ||||
| Colfosceril palmitate (Exosurf) | DPPC, hexadecanol, tyloxapol | 13.5 | none | none |
| Pumactant (ALEC) | DPPC, PG | 40 | none | none |
| Lucinactant (Surfaxin) | DPPC, PG | 30 | KL‐4 19.8 | none |
| DPPC: dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine PG: phosphatidylglycerol | ||||
Appendix 2. MEDLINE and CENTRAL search strategy
1 exp Bronchiolitis/ 2 bronchiolit*.tw. 3 respiratory syncytial viruses/ or respiratory syncytial virus, human/ 4 Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections/ 5 (respiratory syncytial virus* or rsv).tw. 6 or/1‐5 7 exp Surface‐Active Agents/ 8 exp Pulmonary Surfactants/ 9 surfactant*.tw,nm. 10 tensides.tw. 11 amphiphilic agent*.tw. 12 poractant*.tw,nm. 13 beractant*.tw,nm. 14 calfactant*.tw,nm. 15 infasurf.tw,nm. 16 venticute*.tw,nm. 17 survanta.tw,nm. 18 curosurf.tw,nm. 19 exosurf.tw,nm. 20 alec.tw,nm. 21 or/7‐20 22 6 and 21
Appendix 3. EMBASE.com search strategy
#17. #13 AND #16 21 25 May 2011 #16. #14 OR #15 864,776 25 May 2011 #15. random*:ab,ti OR placebo*:ab,ti OR factorial*:ab,ti OR crossover*:ab,ti OR 'cross over':ab,ti OR 'cross‐over':ab,ti OR volunteer*:ab,ti OR assign*:ab,ti OR allocat*:ab,ti OR ((singl* OR doubl*) NEAR/1 blind*):ab,ti AND [embase]/lim 824,994 25 May 2011 #14. 'randomized controlled trial'/exp OR 'single blind procedure'/exp OR 'double blind procedure'/exp OR 'crossover procedure'/exp AND [embase]/lim 242,572 25 May 2011 #13. #5 AND #12 296 25 May 2011 #12. #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11 125,238 25 May 2011 #11. poractant*:ab,ti OR beractant*:ab,ti OR calfactant*:ab,ti OR infasurf:ab,ti OR venticute*:ab,ti OR survanta:ab,ti OR curosurf:ab,ti OR exosurf:ab,ti OR alec:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim 675 25 May 2011 #10. 'amphiphilic agent':ab,ti OR 'amphiphilic agents':ab,ti AND [embase]/lim 35 25 May 2011 #9. tensides:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim 126 25 May 2011 #8. surfactant*:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim 33,345 25 May 2011 #7. 'surface‐active agents':ab,ti OR 'surface‐active agent':ab,ti AND [embase]/lim 529 25 May 2011 #6. 'surfactant'/exp OR 'lung surfactant'/de AND [embase]/lim 116,054 25 May 2011 #5. #1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 20,018 25 May 2011 #4. 'respiratory syncytial virus':ab,ti OR 'respiratory syncytial viruses':ab,ti OR rsv:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim 9,335 25 May 2011 #3. 'respiratory syncytial pneumovirus'/de OR 'respiratory syncytial virus infection'/exp AND [embase]/lim 9,088 25 May 2011 #2. bronchiolit*:ab,ti AND [embase]/lim 6,772 25 May 2011 #1. 'bronchiolitis'/exp AND [embase]/lim 9,220 25 May 2011
Appendix 4. CINAHL (Ebsco) search strategy
S14 S6 and S13 15 S13 S7 or S8 or S9 or S10 or S11 or S12 1860 S12 TI (poractant* or beractant* or calfactant* or infasurf or venticute* or survanta or curosurf or exosurf or alec) or AB (poractant* or beractant* or calfactant* or infasurf or venticute* or survanta or curosurf or exosurf or alec) 61 S11 TI amphiphilic agent* or AB amphiphilic agent* 1 S10 TI tensides or AB tensides 1 S9 TI surfactant* or AB surfactant* 773 S8 (MH "Pulmonary Surfactants") 556 S7 (MH "Surface‐Active Agents+") 998 S6 S1 or S2 or S3 or S4 or S5 1583 S5 TI (respiratory syncytial virus* or rsv) or AB (respiratory syncytial virus* or rsv) 734 S4 (MH "Respiratory Syncytial Viruses") 236 S3 (MH "Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections") 695 S2 TI bronchiolit* or AB bronchiolit* 616 S1 (MH "Bronchiolitis+") 549
Appendix 5. LILACS (BIREME) search strategy
VHL > Search > (MH:Bronchiolitis OR bronchiolit$ OR Bronquiolitis OR Bronquiolite OR MH:C08.127.446.435$ OR MH:C08.381.495.146.135$ OR MH:C08.730.099.135$ OR MH:"Respiratory Syncytial Viruses" OR "Virus Sincitiales Respiratorios" OR "Vírus Sinciciais Respiratórios" OR "respiratory syncytial virus" OR "respiratory syncytial viruses" OR MH:"Respiratory Syncytial Virus, Human" OR "Virus Sincitial Respiratorio Humano" OR "Vírus Sincicial Respiratório Humano" OR "Virus Humano Respiratorio Sincitial" OR MH:"Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections" OR "Infecciones por Virus Sincitial Respiratorio" OR "Infecções por Vírus Respiratório Sincicial") AND (MH:"Surface‐Active Agents" OR Tensoactivos OR Tensoativos OR surfactant$ OR MH:D27.720.877$ OR MH:SP4.011.097.039.724$ OR MH:"Pulmonary Surfactants" OR "pulmonary surfactants" OR "pulmonary surfactant" OR "Surfactantes Pulmonares" OR surfactant$ OR tenside$ OR "amphiphilic agent" OR "amphillic agents" OR poractant OR beractant OR calfactant OR infasurf OR venticute OR survanta OR curosurf OR exosurf OR alec)
Appendix 6. Web of Science (ISI Thomson) search strategy
Topic=(bronchiolitis or respiratory syncytial virus* or rsv) AND Topic=(surfactant* or tensides or amphiphillic agent* or poractant or beractant or calfactant or infasurf or venticute or survanta or curosurf or exosurf or alec)
Refined by: Topic=(random* or placebo* or clinical trial* or singl* blind* or doubl* blind*)
Timespan = 1985‐2011. Databases = SCI‐EXPANDED, CPCI‐S.
Appendix 7. Data extraction from included studies
|
Study and group→ Parameters↓ |
Luchetti 1998 | Luchetti 2002 | Tibby 2000 | |||
| Surfactant group | Control group | Surfactant group | Control group | Surfactant group | Control group | |
| Number of participants | 10 | 10 | 20 | 20 | 09 | 10 |
| Age | 10.4 ± 1.8 months* | 11.2 ± 2.0 months* | 8.7 ± 8.1 months* | 7.4 ± 6.5 months* | 9 (7 to 14) weeks# | 6.5 (4.5 to 9.5) weeks# |
| Male:female | 6:4 | 5:5 | 8:12 | 11:9 | 6:3 | 4:6 |
| Mortality | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA | NA |
| Duration of mechanical ventilation (hrs); mean ± SD | 105.6 ± 9.6 | 213.6 ± 24 | 110.4 ± 19.2 | 139.2 ± 16.8 | 126 ± 111.32$ | 170 ± 111.32$ |
| Duration of ICU stay (days); mean ± SD | 10.1 ± 1.2 | 15.7 ± 1.5 | 6.4 ± 0.9 | 8.2 ± 1.1 | 6.7 ± 4.43$ | 8.9 ± 4.43$ |
| Duration of hospital stay (days) | NA | NA | NA | NA | 13 | 17 |
| PO2/FiO2 ratio at 12 hrs (mmHg); mean ± SD | 225.6 ± 18.8 | 148.1 ± 14.3 | 260 ± 18.8£ | 140 ± 14.3£ | NA | NA |
| PO2/FiO2 ratio at 24 hrs (mmHg); mean ± SD | 231.6 ± 20.3 | 145.9 ± 12.0 | 269 ± 20.3£ | 136 ± 12.0£ | NA | NA |
| PCO2 at 12 hrs (mmHg); mean ± SD | 37.5 ± 3.0 | 45.0 ± 2.3 | 34.5 ± 3.0£ | 42.2 ± 2.3£ | NA | NA |
| PCO2 at 24 hrs (mmHg); mean ± SD | 37.5 ± 3.0 | 45.0 ± 3.0 | 34.5 ± 3.0£ | 42.6 ± 3.0£ | NA | NA |
| Compliance at 12 hrs (ml/cm H2O/kg); mean ± SD | NA | NA | 0.79 ± NA | 0.59 ± NA | NA | NA |
| Compliance at 24 hrs (ml/cm H2O/kg); mean ± SD | NA | NA | 0.83 ± NA | 0.62 ± NA | NA | NA |
| Resistance at 12 hrs | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Resistance at 24 hrs (cm H2O/L/sec); mean ± SD | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| *mean ± SD; #median (IQR); NA: data not available; SD: standard deviation; $SD calculated from P value; £ SD imported from another study (Luchetti 1998); **SD calculated from SEM (standard error of mean); ## SD imported from another study (Tibby 2000). | ||||||
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. Primary outcomes.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Mortality | 2 | 60 | Odds Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2 Duration of mechanical ventilation (hours) | 3 | 79 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐63.04 [‐130.43, 4.35] |
1.1. Analysis.
Comparison 1 Primary outcomes, Outcome 1 Mortality.
Comparison 2. Secondary outcomes.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Duration of ICU stay (days) | 3 | 79 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐3.31 [‐6.38, ‐0.25] |
| 2 Gas exchange (Po2/Fio2 ratio at 12 hrs) | 2 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 99.08 [57.43, 140.72] |
| 3 Gas exchange (Po2/Fio2 ratio at 24 hrs) | 2 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 109.64 [63.29, 155.99] |
| 4 Gas exchange (pCO2 at 12 hrs (mmHg)) | 2 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐7.63 [‐8.99, ‐6.28] |
| 5 Gas exchange (pCO2 at 24 hrs (mmHg)) | 2 | 60 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐7.9 [‐9.42, ‐6.38] |
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Luchetti 1998.
| Methods | RCT | |
| Participants | 20 children; 20 days to 2.5 years of age at an ICU in Italy with diagnosis of severe bronchiolitis requiring mechanical ventilation with continuous positive pressure ventilation (CPPV) > 24 hrs without improvement; and PaO2/FiO2 < 21 kPa, FiO2 ≥ 0.6, PaCO2 > 5.6 kPa and PIP (peak inspiratory pressure) > 35 cm H2O at 24 hrs of ventilation. All received β2 agonist and antibiotics | |
| Interventions | CPPV plus surfactant (porcine‐derived, Curosurf, 50 mg/kg, in 2 to 3 doses) versus CPPV only. No placebo was used in control group | |
| Outcomes | Gas exchange, PIP (at 1, 3, 12, 24 hours) duration of mechanical ventilation and ICU stay | |
| Notes | The study was conducted in 2 winter seasons over 2 consecutive years | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Authors stated that participants were randomly assigned to one of the groups |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sealed envelope method was used |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | There were no incomplete outcome data |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No selective reporting |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Information regarding funding and conflict of interest was not provided |
Luchetti 2002.
| Methods | Multicentre (6 sites), RCT | |
| Participants | 40 children; 1 week to 2 years of age at an ICU in Italy with diagnosis of respiratory failure (PaO2/FiO2 ratio ≤ 150 mm Hg and PaCO2 ≥ 40 mm Hg) due to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) bronchiolitis; conventional mechanical ventilation (CMV) for at least 12 hours without significant improvement | |
| Interventions | Conventional mechanical ventilation (CMV) plus surfactant (50 mg/kg of porcine‐derived natural surfactant, Curosurf, in 2 aliquots over about 5 mins) versus CMV only. No placebo was used in control group | |
| Outcomes | Primary: days on mechanical ventilation and length of ICU stay Secondary: gas exchange, respiratory mechanics, haemodynamic stability, re‐treatment needed, incidence of complications and mortality | |
| Notes | Patients with severe head injury with Glasgow Coma Score < 8, brain death, chronic lung disease, pre‐existing airways disease, congenital heart diseases (CHD) and neuromuscular diseases were considered as exclusion criteria | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Authors stated that patients were randomly assigned |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sealed envelopes were used |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Blinding was attempted in controls by performing similar manoeuvres on them as per experimental group |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Data collector and outcome assessors were blinded |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No incomplete outcome data |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No selective reporting |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Information regarding funding and conflict of interest was not provided |
Tibby 2000.
| Methods | Randomised controlled pilot study | |
| Participants | 19 children with median corrected age of 4 weeks in paediatric ICU in UK requiring mechanical ventilation due to RSV‐induced respiratory failure | |
| Interventions | Bovine surfactant (Survanta, 2 doses, 100 mg/kg, 24 hours apart) versus air placebo. No steroids or bronchodilators were used | |
| Outcomes | Indices of gas exchange ‐ oxygenation index (OI), ventilation index (VI), alveolar arterial gradient (Aa); lung compliance and resistance at 1, 2, 6, 24, 30, 60 hours; and phospholipid molecular species composition in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) | |
| Notes | Patients with neuromuscular disease, uncorrected CHD, pre‐existing pneumothorax, ventilation for > 24 hours, oxygenation index (OI) < 5 and a ventilation index (VI) < 20 at enrolment were excluded from study | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Authors stated that infants were randomised to receive one of the interventions |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Participants and health care providers were blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Data regarding mortality were not mentioned |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No selective reporting |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Information regarding funding and conflict of interest was not provided |
Aa: alveolar arterial gradient BALF: bronchoalveolar lavage fluid CHD: congenital heart diseases CMV: conventional mechanical ventilation CPPV: continuous positive pressure ventilation ICU: intensive care unit FiO2: fractional inspired oxygen H2O: water kPa: unit of pressure mmHg: mm of mercury OI: oxygenation index PaCO2: partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide PIP: peak inspiratory pressure RCT: randomised controlled trial RSV: respiratory syncytial virus VI: ventilation index
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Moller 2003 | Included children with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) secondary to pneumonia and sepsis, but not bronchiolitis |
| Willson 1999 | Participants were children with acute hypoxaemic respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation with clinical and radiographic evidence of diffuse, bilateral parenchymal lung injury; not due to bronchiolitis |
| Willson 2005 | Included children with acute lung injury (respiratory failure due to radiographically evident bilateral parenchymal lung disease), not with bronchiolitis |
ARDS: acute respiratory distress syndrome
Contributions of authors
Dr Jat (KRJ) designed and co‐ordinated the review. KRJ and Dr Chawla (DC) collected and analysed data for the review. Both review authors approved the final version of the review.
Declarations of interest
Kana R Jat: none known. Deepak Chawla: none known.
New search for studies and content updated (no change to conclusions)
References
References to studies included in this review
Luchetti 1998 {published data only}
- Luchetti M, Casiraghi G, Valsecchi R, Galassini E, Marraro G. Porcine‐derived surfactant treatment of severe bronchiolitis. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 1998;42(7):805‐10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Luchetti 2002 {published data only}
- Luchetti M, Ferrero F, Gallini C, Natale A, Pigna A, Tortorolo L, et al. Multicenter, randomized, controlled study of porcine surfactant in severe respiratory syncytial virus‐induced respiratory failure. Pediatric Critical Care Medicine 2002;3(3):261‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tibby 2000 {published data only}
- Tibby SM, Hatherill M, Wright SM, Wilson P, Postle AD, Murdoch IA. Exogenous surfactant supplementation in infants with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2000;162(4 Pt 1):1251‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Moller 2003 {published data only}
- Moller JC, Schaible T, Roll C, Schiffmann JH, Bindl L, Schrod L, et al. Treatment with bovine surfactant in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome in children: a randomized multicenter study. Intensive Care Medicine 2003;29(3):437‐46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Willson 1999 {published data only}
- Willson DF, Zaritsky A, Bauman LA, Dockery K, James RL, Conrad D, et al. Members of the Mid‐Atlantic Pediatric Critical Care Network. Instillation of calf lung surfactant extract (calfactant) is beneficial in pediatric acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. Critical Care Medicine 1999;27(1):188‐95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Willson 2005 {published data only}
- Willson DF, Thomas NJ, Markovitz BP, Bauman LA, DiCarlo JV, Pon S, et al. Effect of exogenous surfactant (calfactant) in pediatric acute lung injury: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2005;293(4):470‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Additional references
Ardell 2015
- Ardell S, Pfister RH, Soll R. Animal derived surfactant extract versus protein free synthetic surfactant for the prevention and treatment of respiratory distress syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 5. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000144.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Barr 2000
- Barr FE, Pedigo H, Johnson TR, Shepherd VL. Surfactant protein‐A enhances uptake of respiratory syncytial virus by monocytes and U937 macrophages. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 2000;23(5):586‐92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
CDC 2010
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Respiratory Syncytial Virus. www.cdc.gov/rsv/ (accessed 15 February 2011).
Dargaville 1996
- Dargaville PA, South M, McDougall PN. Surfactant abnormalities in infants with severe viral bronchiolitis. Archives of Disease in Childhood 1996;75(2):133‐6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Davison 2004
- Davison C, Ventre KM, Luchetti M, Randolph AG. Efficacy of interventions for bronchiolitis in critically ill infants: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Pediatric Critical Care Medicine 2004;5(5):482‐9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Deeks 2011
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Farley 2014
- Farley R, Spurling GK, Eriksson L, Mar CB. Antibiotics for bronchiolitis in children under two years of age. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 10. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005189.pub4] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fernandes 2013
- Fernandes RM, Bialy LM, Vandermeer B, Tjosvold L, Plint AC, Patel H, et al. Glucocorticoids for acute viral bronchiolitis in infants and young children. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 6. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004878.pub4] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gadomski 2014
- Gadomski AM, Scribani MB. Bronchodilators for bronchiolitis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 6. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001266.pub4] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Goerke 1998
- Goerke J. Pulmonary surfactant: functions and molecular composition. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica 1998;1408(2‐3):79‐89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
GRADEproGDT 2015 [Computer program]
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime, Inc.). GRADEproGDT: GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool [www.guidelinedevelopment.org]. Version 25th June 2015. Hamilton: McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime, Inc.), 2015.
Griese 1999
- Griese M. Pulmonary surfactant in health and human lung diseases: state of the art. European Respiratory Journal 1999;13(6):1455‐76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Handforth 2000
- Handforth J, Friedland JS, Sharland M. Basic epidemiology and immunopathology of RSV in children. Paediatric Respiratory Reviews 2000;1:210‐4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hartling 2011a
- Hartling L, Bialy LM, Vandermeer B, Tjosvold L, Johnson DW, Plint AC, et al. Epinephrine for bronchiolitis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue 6. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003123.pub3] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hartling 2011b
- Hartling L, Fernandes RM, Bialy L, Milne A, Johnson D, Plint A, et al. Steroids and bronchodilators for acute bronchiolitis in the first two years of life: systematic review and meta‐analysis. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.) 2011;342:d1714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Holman 2003
- Holman RC, Shay DK, Curns AT, Lingappa JR, Anderson LJ. Risk factors for bronchiolitis‐associated deaths among infants in the United States. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2003;22(6):483‐90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kabir 2003
- Kabir ML, Haq N, Hoque M, Ahmed F, Amin R, Hossain A, et al. Evaluation of hospitalized infants and young children with bronchiolitis ‐ a multi centre study. Mymensingh Medical Journal 2003;12:128‐33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kerr 1999
- Kerr MH, Paton JY. Surfactant protein levels in severe respiratory syncytial virus infection. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 1999;159(4 Pt 1):1115‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lahti 2002
- Lahti M, Lofgren J, Marttila R, Renko M, Klaavuniemi T, Haataja R, et al. Surfactant protein D gene polymorphism associated with severe respiratory syncytial virus infection. Pediatric Research 2002;51(6):696‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lefebvre 2011
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Levy 1997
- Levy BT, Graber MA. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants and young children. Journal of Family Practice 1997;45(6):473‐81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Liet 2010
- Liet J‐M, Ducruet T, Gupta V, Cambonie G. Heliox inhalation therapy for bronchiolitis in infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006915.pub2] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Logan 2009
- Logan JW, Moya FR. Animal‐derived surfactants for the treatment and prevention of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome: summary of clinical trials. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management 2009;5(1):251‐60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Löfgren 2002
- Löfgren J, Rämet M, Renko M, Marttila R, Hallman M. Association between surfactant protein A gene locus and severe respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2002;185(3):283‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Meates‐Dennis 2005
- Meates‐Dennis M. Bronchiolitis. Archives of Disease in Childhood Education and Practice Edition 2005;90:81–6. [Google Scholar]
Meissner 2009
- Meissner HC, Bocchini JA. Reducing RSV hospitalizations AAP modifies recommendations for use of palivizumab in high‐risk infants, young children. AAP News 2009;30(7):1. [Google Scholar]
Mercus 2001
- Merkus PJ, de Hoog M, van Gent R, de Jongste JC. DNase treatment for atelectasis in infants with severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. European Respiratory Journal 2001;18(4):734‐7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Moher 2009
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta‐Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. BMJ 2009;339:2535. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nasr 2001
- Nasr SZ, Strouse PJ, Soskolne E, Maxvold NJ, Garver KA, Rubin BK, et al. Efficacy of recombinant human deoxyribonuclease I in the hospital management of respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Chest 2001;120(1):203‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Navas 1992
- Navas L, Wang E, Carvalho V, Robinson J. Improved outcome of respiratory syncytial virus infection in a high‐risk hospitalized population of Canadian children. Pediatric Investigators Collaborative Network on Infections in Canada. Journal of Pediatrics 1992;121(3):348‐54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Panickar 2005
- Panickar JR, Dodd SR, Smyth RL, Couriel JM. Trends in deaths from respiratory illness in children in England and Wales from 1968 to 2000. Thorax 2005;60:1035‐8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Possmayer 1990
- Possmayer F. The role of surfactant‐associated proteins. American Review of Respiratory Disease 1990;142(4):749‐52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ramanathan 2009
- Ramanathan R. Animal‐derived surfactants: where are we? The evidence from randomized, controlled clinical trials. Journal of Perinatology 2009;29(Suppl 2):38‐43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Roqué i Figuls 2012
- Roqué i Figuls M, Giné‐Garriga M, Granados Rugeles C, Perrotta C. Chest physiotherapy for acute bronchiolitis in paediatric patients between 0 and 24 months old. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004873.pub3] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Seger 2009
- Seger N, Soll R. Animal derived surfactant extract for treatment of respiratory distress syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007836] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Shay 2001
- Shay DK, Holman RC, Roosevelt GE, Clarke MJ, Anderson LJ. Bronchiolitis‐associated mortality and estimates of respiratory syncytial virus‐associated deaths among US children, 1979‐1997. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2001;183(1):16‐22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Skelton 1999
- Skelton R, Holland P, Darowski M, Chetcuti PA, Morgan LW, Harwood JL. Abnormal surfactant composition and activity in severe bronchiolitis. Acta Paediatrica 1999;88(9):942‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Soll 1998
- Soll R. Synthetic surfactant for respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1998, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001149] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Umoren 2011
- Umoren R, Odey F, Meremikwu MM. Steam inhalation or humidified oxygen for acute bronchiolitis in children up to three years of age. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006435.pub2] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ventre 2007
- Ventre K, Randolph AG. Ribavirin for respiratory syncytial virus infection of the lower respiratory tract in infants and young children. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000181.pub4] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wood 1993
- Wood AJJ, Jobe AH. Pulmonary surfactant therapy. New England Journal of Medicine 1993;328(12):861‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wright 2003
- Wright JR. Pulmonary surfactant: a front line of lung host defense. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2003;111(10):1453‐5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Zhang 2013
- Zhang L, Mendoza‐Sassi RA, Wainwright C, Klassen TP. Nebulised hypertonic saline solution for acute bronchiolitis in infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 7. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006458.pub3] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to other published versions of this review
Jat 2011
- Jat KR, Chawla D. Surfactant therapy for bronchiolitis in critically ill infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue 7. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009194] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Jat 2012
- Jat KR, Chawla D. Surfactant therapy for bronchiolitis in critically ill infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 9. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009194.pub2] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ventre 2006
- Ventre K, Haroon M, Davison C. Surfactant therapy for bronchiolitis in critically ill infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005150.pub3] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


