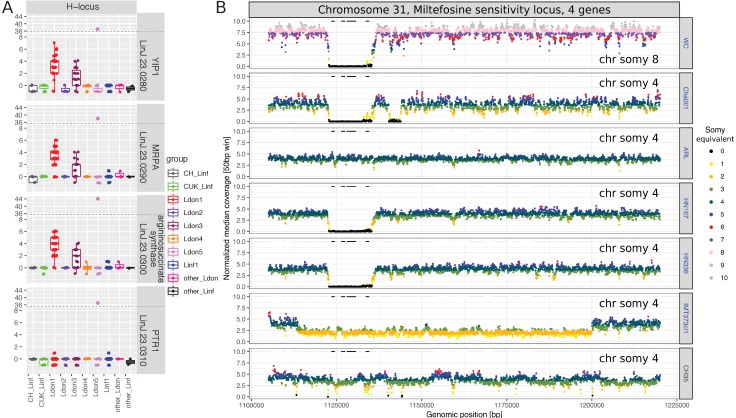
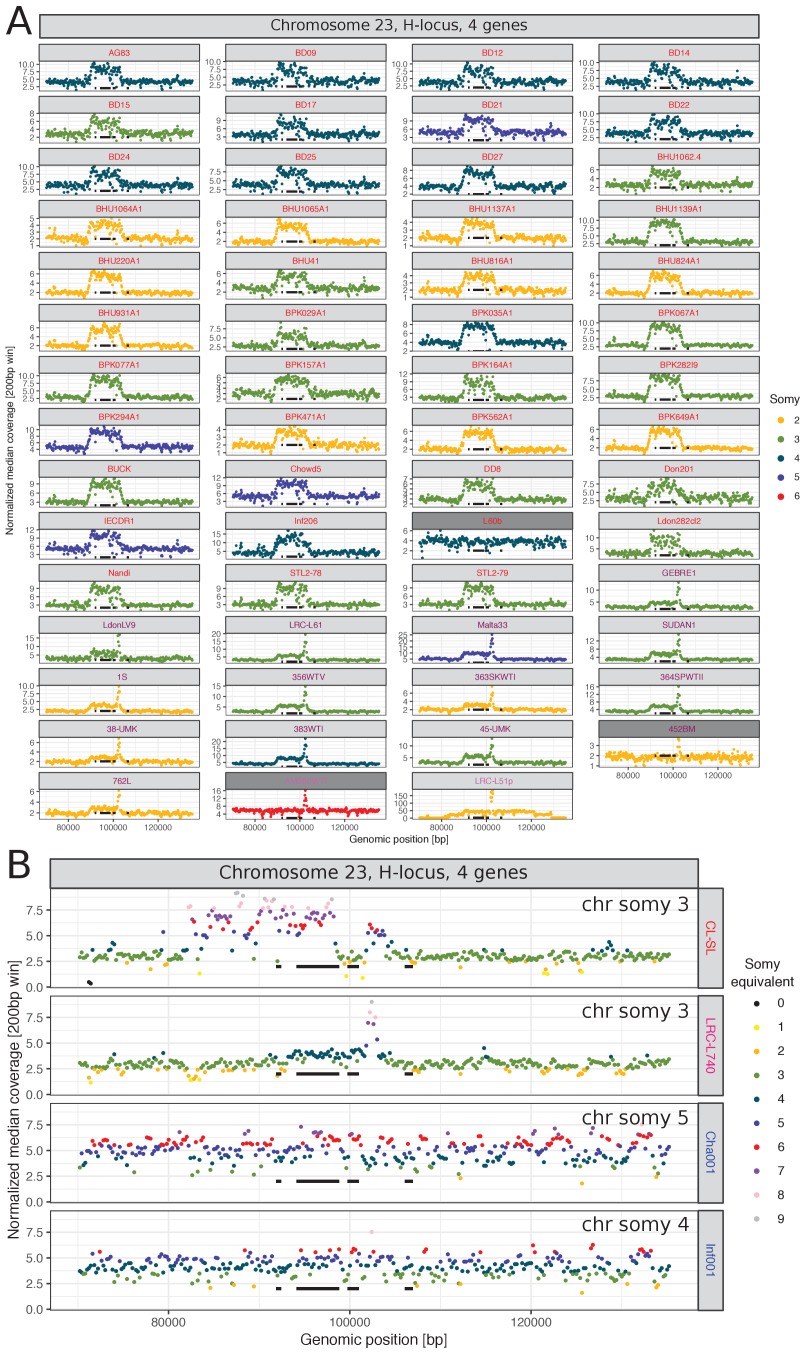
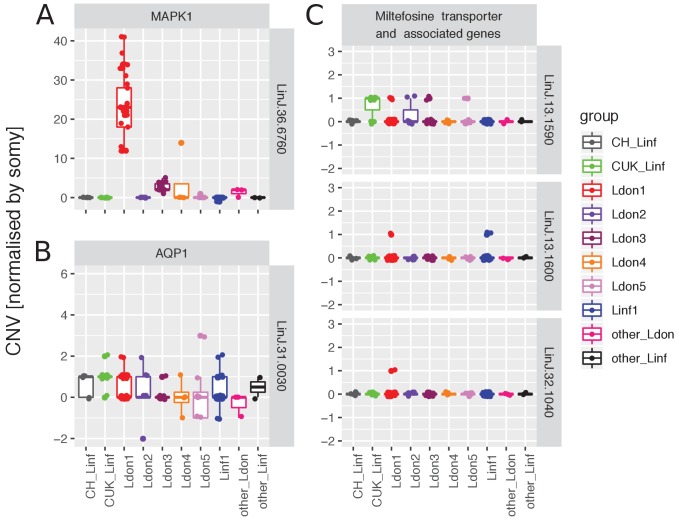
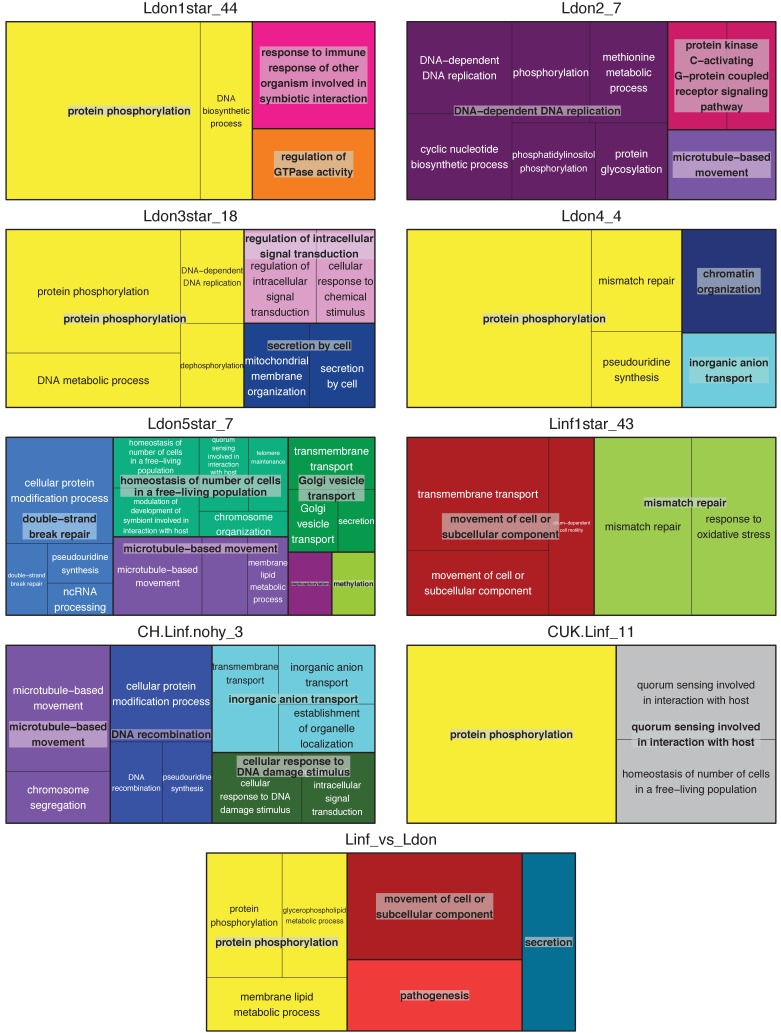
Figure 9. Copy number variation of putative drug resistance genes.
(A) Copy numbers (CNs) for all four genes on the H-locus are shown for all 151 samples across all 10 different (sub-)groups. (B) Genome coverage in the genomic regions surrounding the MSL in all six samples showing a deletion and one sample with no CN reduction. Genome coverage for 50 bp windows is normalised by the haploid chromosome coverage and colours indicate the somy equivalent coverage of the respective window. The genes, LinJ.31.2370, LinJ.31.2380, LinJ.31.2390 and LinJ.31.2400, are marked as black horizontal lines. Colours of the sample names indicate group colours used throughout this study.