Abstract
Escaping programmed cell death is a hallmark of cancer. NF-κB transcription factors are key regulator of cell survival and aberrant NF-κB signaling has been involved in the pathogenesis of most human malignancies. Although NF-κB is best known for its antiapoptotic role, other processes regulating the life/death balance, such as autophagy and necroptosis, seem to network with NF-κB. This review discusses how the reciprocal regulation of NF-κB, autophagy and programmed cell death affect cancer development and progression.
Subject terms: Cancer, Cell death
Facts
NF-κB transcription factors are key regulator of cell survival and aberrant NF-κB signaling has been involved in the pathogenesis of most human malignancies.
NF-κB is well known for providing cancer cells with a survival advantage by upregulating antiapoptotic genes.
There is a reciprocal crosstalk between NF-κB and autophagy in cancer, where it can either promote or repress tumorigenesis, depending on the stimulus and the context.
NF-κB proinflammatory signaling downstream of RIPK1/RIPK3 activation is required for the immunogenicity of necroptotic cells in the tumor-microenvironment (TME).
Open questions
Targeting autophagy and NF-κB as a strategy for improving anticancer therapy and bypass drug-resistance.
The controversial role of endogenous necroptotic signaling within the tumor cell and its crosstalk with NF-κB pathway.
The reciprocal interplay between autophagy and programmed cell death (PCD) in cancer and how these processes intersect with NF-κB signaling.
Introduction—historical background
The choice of whether to live or die for the cell may depend on the activation of NF-κB transcription factors. The antiapoptotic function of NF-κB has long been established, since Beg and Baltimore described that RelA-deficient mice succumbed during embryogenesis due to massive apoptosis of hepatocytes1. Beyond its role in liver, the NF-κB pro-survival function is also crucial for the physiology of the immune system, where the constitutive activation of NF-κB pathway is needed for differentiation and maintenance of B lymphocytes, the development of thymocytes, as well as for immune response to antigens by mature B and T lymphocytes2,3.
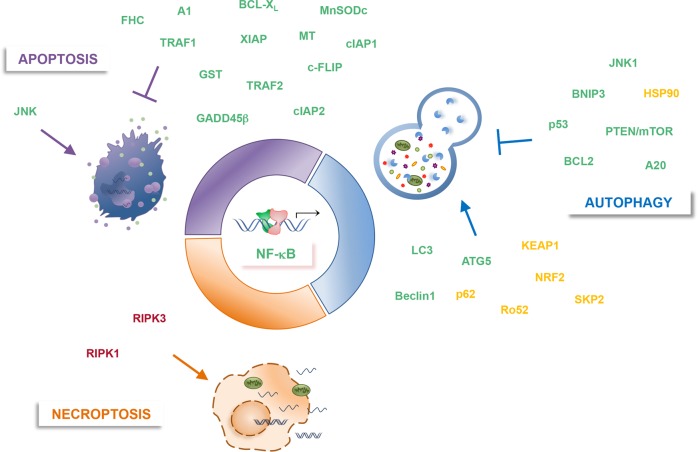
The suppression of apoptosis by NF-κB could be viewed as a transcriptional event. NF-κB exerts its pro-survival activity by inducing the transcription of several antiapoptotic genes, and this transcriptional program seems to be specifically tailored depending on the tissues involved and the biological contexts. The NF-κB-mediated resistance to tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)-induced apoptosis has been associated to the upregulation of several pro-survival genes, including cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1 (cIAP1) and 2 (cIAP2), X chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP), TNF-R associated factor 1 (TRAF1) and 2 (TRAF2), cellular FLICE inhibitor protein (c-FLIP) and several Bcl-2 family members (i.e., Bcl-XL and A1/Bfl-1), mainly implicated in the inhibition of the apoptotic signaling4–6. However, these factors are not sufficient to account for the complete NF-κB-dependent blockade of apoptotic pathway. Over the past decades, NF-κB’s role in dampening JNK activation, both downstream of TNFR1 and other death stimuli, has been extensively investigated7–10. Indeed, the blockage of NF-κB pathway, by either ablation of RelA or IKKβ or overexpression of the super repressor IκBαM, caused the sustained and prolonged activation of JNK in response to TNF-α or concavalin A, and the persistence of this induction was responsible for cell death7,8,10. NF-κB represses sustained JNK activation both directly, by upregulating the expression of critical JNK inhibitors, and indirectly, via opposing oxidative stress. The NF-κB target gene encoding for Growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible (Gadd45)β protein is one of the best-known suppressor of JNK pathway. Gadd45β antagonizes TNF-α-induced cytotoxicity by targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MKK)7, which in turn is responsible for JNK activation7,11. NF-κB also blocks JNK-dependent cell death by counteracting reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation, which in turn triggers JNK activation. Indeed, well established targets of NF-κB are several antioxidant factors, such as Ferritin heavy chain (FHC), manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), Glutathione -S-transferase (GST) and metallothionein (MT)12–16.
Malignant cells often hijack key pathways and the same molecular networks that control normal development, and NF-κB pathway is no exception to the rule. Malignant cells are “addicted” to NF-κB signaling, which drives oncogenesis, disease recurrence and therapy resistance in both solid and haematological malignancies, where it induces transcriptional programmers sustaining all hallmarks of cancer6,17–23.
Multiple studies revealed that in the bulk of tumors in which NF-κB is constitutively active, it frequently provides cancer cells with a survival advantage by upregulating antiapoptotic genes17,21. Several evidence, both in vitro and in vivo, demonstrated that NF-κB antiapoptotic signaling is required for RAS-induced transformation6,20,24,25. In addition, seminal papers reported how the suppression of IKK/NF-κB signaling in mouse models of inflammation-driven colorectal (CRC) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) resulted in apoptosis of preneoplastic cells and failure of tumor progression, thus establishing a key role for NF-κB as a linchpin between inflammation and cancer26,27. NF-κB pro-survival function is also critical in inflammation-driven tumor progression, as demonstrated in syngeneic colon and breast cancer xenograft models, where inflammation-associated NF-κB activation mediates tumor growth by conferring resistance to TRAIL death cytokine28. NF-κB constitutive activation is considered to be a signature also in several haematological malignancies, and in many of them, including activated B‐cell‐like (ABC)-diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and multiple myeloma (MM), it promotes cancer cell survival17,21,29. Recently, we furthered the understanding in MM, where we showed that oncogenic NF-κB signaling mediates cancer cell survival by upregulating GADD45B, which, in turn, suppresses apoptosis ensuing from JNK/MAPK-pathway activation by inhibiting MKK7 (Fig. 1)30–32.
Fig. 1. NF-κB involvement in autophagy and PCD.
Shown are key positive (↑) or negative (⊥) modulators of autophagic, apoptotic and necroptotic processes, which are regulated by (green, red), or regulator of (yellow, red) NF-κB.
While the role of NF-κB signaling in evading cancer cell apoptosis has been well-established, increasing evidence are pointing out for a broader role for NF-κB in balancing life and death. Autophagy and necroptosis play a key part in this scenario, and accordingly, NF-κB has been involved in their regulation. This review will focus on the role of this transcription factor in controlling autophagy and necroptosis in the context of cancer.
Autophagy and NF-κB
Autophagy or “self-eating” is a physiological tightly conserved multistep process for recycling endogenous or exogenous cytoplasmatic materials like misfolded proteins, lipids, organelles (mitochondria, ribosomes), cellular components, peroxisomes and viruses or bacteria, that culminates with lysosomal degradation33–35. Three different types of autophagy co-exist in most cell types: microautophagy and endosomal microautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) and macroautophagy34. The best characterized form of autophagy is macroautophagy, that relies on the formation of the autophagosome, a double-membraned vesicle able to take up the autophagic cargo, including protein aggregates and entire organelles. Depending on the specific autophagic substrate and initiating stimulus, macroautophagy can be defined selective (i.e., mitophagy, lysophagy) or non-selective (intracellular materials)34. The selective recognition and recruitment of cargoes is driven by autophagic receptors, like sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1 or p62) autophagy-related proteins (ATG) and nuclear receptor binding factor 2 (NRBF2)34. The autophagic mechanism is highly regulated. Each phase involves specific regulatory molecules and complexes, such as mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (MTORC1), ubiquitin-like conjugation systems (i.e., ULK1/Atg13/FIP200 and Beclin-1/Vps34/Atg14), microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3), ATG7 and lysosomal-associated membrane proteins (i.e., LAMP)33,34,36.
In addition to regulating cell survival, apoptosis and activation of inflammation, the NF-κB family of transcription factors are also involved in the control of autophagy19,22,23,37–39. There is a lot of evidence indicating the reciprocal crosstalk between NF-κB and autophagy, both in physiological and pathological processes. IKK/NF-κΒ signaling axis regulates autophagy in a stimulus- and context-dependent manner and vice versa6,40,41. In fact, it has been demonstrated that IKK/NF-κΒ could trigger autophagy by directly inducing the expression of genes or proteins involved in the autophagosome machine, such as Beclin 1, BAG3-HspB8 complex, ATG5, and LC340,42,43. Studies conducted by Comb et al. demonstrated that IKK is also able to induce autophagy, independently of NF-κΒ signaling44–46. On the other hand, NF-κΒ can also inhibit autophagocytosis by either increasing the expression of autophagy repressors, like A20, Bcl-2 family members, phosphatase and tensin homolog/mammalian target of rapamycin (PTEN/mTOR) and nitric oxide (NO), or suppressing autophagy inducers, such as BCL-2 interacting protein 3 (BNIP3), JNK1, p53 and ROS40,47–49. In turn, autophagy has been shown to regulate NF-κB pathway, mainly by degrading IKK components and NF-κΒ-inducing kinase (NIK) (Fig. 1)50–54.
Autophagy and NF-κB in cancer
In response to different cellular stresses, autophagy plays a pivotal cytoprotective role in maintaining metabolic and cellular homeostasis. Indeed, autophagy substrates are recognized, isolated and degraded in order to meet the energy demand and avoid the accumulation of damaged proteins and organelles33,34,55. Paradoxically, recent evidence indicates that autophagy can be also considered itself a mechanism of cell death, hence the term “autophagic cell death”56,57. Several in vitro and in vivo studies clarified that this dual biological outcome of autophagy is tissue-specific and it is tightly dependent on the nature of the autophagy substrates58,59.
This context-dependent function has been also reported in cancer, where autophagy shows both tumor suppressor and tumor promoter activities34,60. In the early phases of cancer development, autophagy has been reported to have a tumor suppressive role, mainly through the blockade of ROS-induced damage and the preservation of cellular homeostasis. Additional mechanisms by which autophagy suppresses carcinogenesis include the preservation of genetic/genomic stability, the maintenance of a normal stem cell compartment, the elicitation of anticancer immune response, and the restraint of inflammation. On the other hand, during tumor promotion, progression and metastasis, autophagy exerts a pro-tumoral activity by both dampening cytotoxic ROS-induced metabolic stress and providing nutrients required for cancer cell survival. In addition, autophagy exerts its tumor-supporting function by increasing the resistance of cancer cells to stressful conditions (i.e. loss of attachment, hypoxia and nutrient deprivation) and therapy-induced dormancy or senescence33.
NF-κB regulates autophagy in cancer cells
The role of NF-κΒ and autophagy in cancer has been well investigated and the impairment of this crosstalk establishes the fate of the cell.
Djavaheri-Mergny et al. reported that in response to TNF-α, NF-κΒ activation represses autophagy in different cancer cell lines including Edwing sarcoma, breast and promyelocytic leukemia49,61 via activation of mTOR pathway, a major negative regulator of autophagy. Accordingly, TNF-α treatment induced an increased accumulation of autophagic vacuoles and LC3-II, the conjugated form of LC-3, only in cells lacking NF-κΒ activity. Unsurprisingly, the TNF-α-dependent enhanced autophagy observed in absence of NF-κB occurred via ROS accumulation and a rapid increase in Beclin1 expression49,62. Several other studies pointed out the role of NF-κΒ in suppressing the autophagic machinery upon TNF-α treatment, via inhibition of PTEN-mediated suppression of insulin/Akt pathways, which in turn is a potent activator of mTOR pathway63.
Recent evidence highlighted the pro-tumorigenic role of NF-κB-induced autophagy in most human cancer. Zhang et al. demonstrated that under stress conditions, transglutaminase (TG2)/NF-κΒ-mediated interleukin-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (IL-6/STAT3) signaling promotes increased autophagy in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), thus supporting cell survival. The enhanced macroautophagy in turn, positively regulates TG2/NF-κΒ/IL-6 signaling, thereby implying a potential positive feedback loop required for cancer cell survival. Since increased TG2 levels are associated with poor prognosis in MCL patients, breaking TG2/NF-κΒ/IL-6/autophagy might be a potential therapeutic target for MCL64.
In recent years, signalphagy, defined as the termination of cytosolic signaling events by selective autophagy, is catching on in the context of tumorigenesis65. Newman and collaborators highlighted that autophagy contributes to carcinogenesis in Ras-mutant cancer cells in vivo through reprogramming gene expression65. Selective autophagy of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3) via the cargo receptor nuclear dot protein (NDP52) protein drives nuclear translocation of RelB. Once in the nucleus, RelB represses SMAD-mediated transcription of antitumoral genes downstream transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling. Accordingly, autocrine and/or paracrine sources of TGF-β dampen tumorigenesis when autophagy is loss in vivo, and this antitumor effect is abrogated by SMAD knockdown65. Despite this area is largely unexplored, increased understanding of the mechanisms are needed for targeting signalphagy in cancer.
It is known that in some circumstances IKK complex promotes autophagy, with or without any involvement of NF-κΒ, by inducing the expression of autophagy-regulated genes (i.e., Atg5, BECN1, LC3), activating 5' adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK), and/or inhibiting mTOR and p53.
Comb and colleagues demonstrated that IKK activity is required for initiation of autophagy in response to nutrient deprivation, identifying p85α, a regulator subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K), as mediator of IKK function, both in vitro and in vivo. p85α phosphorylation by IKK results in decreased affinity for tyrosine phosphorylated proteins and PI3K membrane localization, leading to Akt and mTOR inhibition6,44,45. Moreover, they also demonstrated that IKK induces autophagic genes, such as Beclin1, Atg5 and LC3, and its ability does not require NF-κΒ45. In contrast with these findings, it has been demonstrated that IKKα plays an important role in mediating mTOR kinase activation in Akt-active, PTEN-null prostate cancer cells, thus suppressing autophagy66,67.
While it is true that NF-κB can regulate the autophagic process, it is also true that autophagy can modulate the NF-κB signaling.
A recent study reported a key role of Beclin1-mediated autophagy in maintaining NF-κΒ and STAT3 constitutively active in human T cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1)-mediated tumorigenesis. Knockdown of Beclin1 and selective inhibition of IKK in HTLV-1-transformed T cells reduced growth, due to diminished Tax-induced activities of both transcription factors68. In accordance with these roles of autophagy in regulating NF-κB in cancer, Yoon and colleagues demonstrated that enhanced autophagic process and NF-κΒ and STAT3 activation in starved cancer cells caused an increased production of various cytokines and factors including IL-6, interleukin 9 (IL-9), ADAM metallopeptidase domain 12 (ADAM12) and FRAS1 related extracellular matrix 1 (FREM1). In turn, the secretion of these factors led to proliferation, survival and metastasis of cancer cells and migration of endothelial cells contributing to the inflammatory microenvironment surrounding the tumor. Notably, genetic inhibition of autophagic machinery, via Beclin-1 and Atg5 silencing, abrogated IL-6 expression, STAT3 phosphorylation, and NF-κΒ activation, suggesting that in this model, NF-κΒ is affected by autophagy69.
It has been reported that autophagy can impact NF-κB activity by mediating either IKKs or IκBα autophagocytosis, thus inhibiting or activating the NF-κB signaling6,45,46. The autophagic targeting of NF-κB core pathway components occurs via specific partners, such as Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1), E3 ubiquitin ligase Ro52, heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90), S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (SKP2) and sequestome-1 (SQSTM1/p62) (Fig. 2)41,70.
Fig. 2. Autophagy regulates IKK/NF-κΒ signaling in cancer cells.
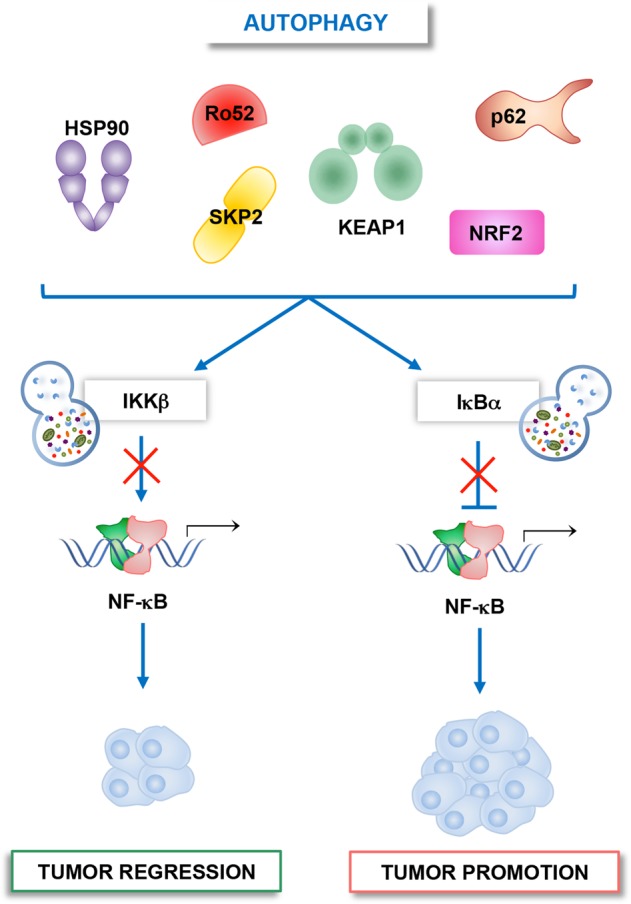
Autophagy modulates NF-κΒ pathway by mediating the degradation of either IKKs or IκBα. If IKK is degraded, pro-tumoral NF-κB signaling is inhibited, while the autophagic degradation of IκBα causes NF-κB activation and tumor promotion. The autophagic targeting of core elements of NF-κB pathway involves specific cargo receptors, such as KEAP1, Ro52, Hsp90, SKP2, p62, and NRF2.
KEAP1 is a ubiquitin ligase, which interacts with nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a transcription factor involved in the inflammatory and antioxidant response. KEAP1 fosters IKKβ ubiquitination and autophagic degradation, thus allowing the downregulation of NF-κΒ signaling53,71. Accordingly, with the cytoprotective role of Nrf2 in tumor cells72,73, Lee and colleagues demonstrated that proteasome inhibitors favored IκBα degradation by triggering Nrf2-mediated autophagy. Interestingly, proteasome inhibitors induced the upregulation of Nrf2 by both inducing its de novo synthesis and KEAP1 degradation. These events promote NF-κΒ-mediated upregulation of antiapoptotic genes leading to the suppression of apoptotic cell death in lung cancer cells74.
Recently Liu and colleagues demonstrated that SKP2, an lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-inducible gene, is able to inhibit NF-κΒ through the degradation of active IKKβ via autophagy. The complex IKKβ−SKP2 is recognized and recruited by the cargo receptor p62. Since SKP2 can be induced by NF-κΒ, this finding suggests that autophagy-mediated SKP2-IKKβ-NF-κΒ axis is modulated through a negative feedback loop70. Further evidence demonstrated that autophagy can degrade IKK complex, in particular IKKβ, also following Ro52-mediated mono-ubiquitination52.
Another important partner involved in the control of IKK/NF-κΒ axis is Hsp90, a well-known pro-survival cytosolic chaperone involved in the activation of IKK and the switch between autophagy and apoptosis. The study conducted by Qing and colleagues reported that treatment with geldanamycin, an inhibitor of Hsp90, promoted both IKK and NIK degradation via autophagy, resulting in the suppression of NF-κΒ-driven transcription in most cancer cells50,51,75. However, under stress conditions, Hsp90 hyperactivation stabilizes its partners and protects cells from cell death76.
Moreover, there is some evidence on the role of the autophagy cargo receptor SQSTM1/p62 in modulating NF-κΒ in cancer77,78. p62 is a multifunctional protein that exerts its function depending on stimulus and context. Recently, p62 has been identified as a key component required for cancer development and progression, both in vitro and in vivo, and accumulation of p62 is a common event in most human cancer. Accordingly, p62 knockdown reduced both the proliferation of cancer cells and tumor growth. Although the regulation of mitochondrial integrity by mitophagy seems to be the principal mechanism by which p62 promotes cancer cell survival, it remains to be clarified the impact of p62 in the regulation of important signaling pathway in cancer, such as NF-κΒ60,77,79–81. p62 alters IKK/NF-κΒ signaling by promoting IκΒα phosphorylation and its autophagy-dependent degradation20,82,83. In several human tumors and cancer cell lines increased Ras-mediated p62 overexpression is essential for cell survival and tumorigenesis78. In agreement with this, Duran et al. showed that the pro-survival NF-κΒ activation in mouse model of Ras-induced lung adenocarcinoma was dependent on p62. Genetic deletion of p62 impaired NF-κΒ activation, at the level of IKK, and abrogated Ras-driven tumorigenesis, due to increased ROS production and cell death. In addition, the author demonstrated that the lack of p62 enhanced the activation of stress-activated MAPKs, like JNK, and reduced the expression of NF-κΒ-dependent genes, such as ROS scavenger FHC, identifying p62 as a key target in Ras-mediated transformation77. p62/NF-κB axis plays also a key role in tumor cell resistance to anticancer drugs. Recently, Yang et al. demonstrated that chloroquine (CQ), an autophagic blocker, triggers the activation of NF-κΒ and its target genes, such as hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α), interleukin-8 (IL-8) and antiapoptotic genes like BCL-2 and BCL-XL, in both squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma cells. Additionally, the authors showed that CQ-induced NF-κΒ activation required autophagosome activation, upregulation of p62 and JNK activation. Knockdown of either p62 or JNK prevented CQ-induced IKK phosphorylation, p62 expression, and NF-κΒ activation. Notably, CQ creates a positive feed-forward loop between p62 and NF-κΒ, the CQ-induced upregulation of p62 actives NF-κΒ, which, in turn, induces p62 expression. Nevertheless, blocking either p62 or NF-κΒ pathway sensitized cancer cells to CQ-mediated apoptotic cell death, suggesting the important role of p62/NF-κΒ axis in mediating cell survival and resistance to CQ in cancer84. In keeping with the role of autophagy in drug resistance, Jia and collaborators reported that Bortezomib, a novel anticancer agent used for the treatment of MM, induced autophagy of IκBα in DLBCL, thus promoting cell drug resistance. In this study the authors showed that proteasome inhibitor bortezomib induced canonical NF-κB activation by favouring the accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins, like IκBα, which are subsequently recruited to autophagosomes by p62 carrier. Increased autophagy and ER stress were observed, as demonstrated by elevated LC3-II accumulation, a hallmark of autophagy activation and CHOP, an indicator of ER stress respectively. Treatment with autophagic blocker, CQ, prevented IκBα degradation and bortezomib-induced pro-survival NF-κB signaling, leading to cancer cell death (Fig. 2). Based on these results, a potential way to overcome drug resistance and induce apoptosis of DLBCL cancer cells may be blocking both autophagy and NF-κB pathways85.
NF-κΒ, autophagy, and TME
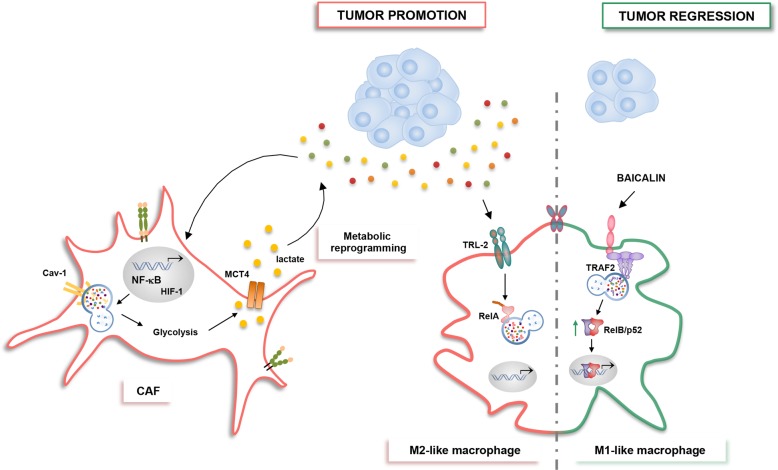
The complex role of the tumor-microenvironment (TME) in promoting cancer cell survival and immune evasion has been characterized as a new hallmark of cancer86. The dynamic crosstalk between TME and tumor cells affects cell survival and tumor progression, but it remains hard to fully understand how the autophagy fosters the cross talk between tumor and inflammatory cells. It is known that NF-κΒ is an important player during inflammatory response and tumorigenesis as well as in the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs)23,87–91. Recently, has been reported that autophagy has both anti- and pro-inflammatory effects in the TME by modulating NF-κΒ pathway92. Chang et al. demonstrated that Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) promoted the M2-like phenotype of hepatoma-derived macrophages. In addition, they showed that NF-κΒ activation was inhibited by TLR2-dependent selective autophagic degradation of NF-κΒ/p65-containing aggresome-like structures (ALS), through the autophagy cargo receptor, SQSTM1/p62. This event occurred in hepatoma-derived M2-macrophages, but not in M1-polarized macrophages, both in vivo and in vitro. The inhibition of autophagy by lysosomal inhibitor bafilomycin A1 or knockdown of Atg5 restored NF-κΒ activity and induced pro-inflammatory cytokines, switching macrophages from M2 to M1 phenotype. These data suggest that autophagy is a player in “re-educating” macrophages and regulating macrophage-associated antitumor immune response93,94. Recently, it has been demonstrated that after treatment with Baicalin, a natural flavonoid, autophagy-induced RelB/p52 activation, a constituent of the alternative NF-κΒ pathway, induced TAMs repolarization towards M1-like phenotype, resulting in the suppression of HCC in vivo. Importantly, Tan et al. showed that Baicalin acted specifically on M2 macrophages, while no affecting M1 phenotype in the TME. They also observed that downregulation of TRAF2 via lysosomal degradation regulated macrophage polarization towards pro-inflammatory phenotype and increased transcriptional activation of RelB/p52 pathway. Inhibition of both autophagy and RelB rescued the effects of baicalin, suggesting that this natural compound might be a potential immune therapeutic candidate for cancer therapy, with particular regard to HCC (Fig. 3)95.
Fig. 3. NF-κΒ and autophagy crosstalk in the TME-associated cells can either suppress or promote tumorigenesis.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by cancer cells promotes NF-κΒ and HIF-1 activation in CAFs. In turn, these two transcription factors induce the autophagic degradation of caveolin 1 (Cav-1). Consequently, loss of Cav-1 amplifies oxidative stress and triggers glycolytic catabolism and lactate extrusion, thus promoting the anabolic growth of adjacent cancer cells. In TAMs, the autophagic degradation of RELA/p65 induced by TLR2 activation promotes the M2-like phenotype in the context of HCC. On the contrary, the lysosomal degradation of TRAF2 induced by baicalin treatment determines the transcriptional activation of RelB/p52 pathway, thus reprogramming TAMs towards the pro-inflammatory M1-like phenotype and counteracting HCC.
Recently, Sun et al. demonstrated that Atg5 loss in Kupffer cells, the liver resident macrophages, at early stages of tumorigenesis speeded up fibrosis, inflammation and finally HCC. This pro-tumoral effect associated with autophagy impairment was due to increased ROS production and NF-κB/interleukin-1 alpha/beta (IL-1α/β) signaling, resulting in inflamed TME, thus demonstrating an antitumorigenic role of Kupffer cell-associated autophagy in HCC tumor initiation96.
In accordance with the relevance of TME-associated autophagy in cancer, Martinez-Outschoorn et al. showed that, under oxidative stress and hypoxia, cancer cells induced autophagic degradation of caveolin 1 (Cav-1) in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) by upregulating NF-κB and HIF-1. Importantly, the authors demonstrated that cancer cells promoted NF-κΒ and HIF-1 activation in adjacent fibroblasts in a paracrine manner, and that the pharmacological inactivation of both HIF-1 and NF-κΒ prevented Cav-1 degradation. In addition, as an important structural protein and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor, loss of Cav-1 in the stroma triggered glycolytic catabolism and lactate extrusion, via HIF-1 stabilization and upregulation of monocarboxylate transporter 4 (MCT4). This catabolic phenotype of stroma cells, in turn, promotes anabolic growth of adjacent cancer cells, thus highlighting the importance of this metabolic synergy in driving cancer (Fig. 3)97,98.
Although further investigations are needed to best characterize the roles of NF-κΒ and autophagy during tumorigenesis, its involvement in both cancer cells and TME might have profound implications to oncogenesis and anticancer therapy.
Necroptosis and NF-κB
Cells react to cellular stress, pathogen infection, and organismal development undergoing distinct forms of cell death99. Research on the mechanisms of PCD induced following the interaction of a death ligand with its death receptors (DRs) expressed on the cell surface has revealed a signaling pathway that triggers programmed necrotic cell death or necroptosis. These receptors, including tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1), Fas (CD95/APO-1) and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), show a cytoplasmic death domain (DD) through which a regulated death signal could be transduced, resulting in apoptotic or necroptotic cell death100,101. Although the necroptosis outcome is phenotypically similar to necrosis, as the final event leads to a lytic cell death, it is defined by a dedicated signaling cascade. Unlike extrinsic apoptosis, which causes caspase activation, death via canonical necroptosis is induced by the activation of the receptor-interacting protein kinases RIPK1-RIPK3 and the pseudokinase mixed lineage kinase domain-like (MLKL).
Classically, under apoptosis-deficient conditions, e.g. inactivation of Caspase-8 activity, or pharmacological inhibitors, the activated RIPK1 interacts with RIPK3 through RHIM domains forming the heteroamyloid complex called necrosome102–104. This platform is considered to be important, as it can sustains and amplifies key signals that otherwise might be decreased by protein degradation. The RIPK1-RIPK3 oligomerization leads to RIPK3 auto-activation that, in turn, phosphorylates MLKL. MLKL phosphorylation is the important execution step of necroptosis downstream of DR ligation and it is required for its translocation to the membrane, where it generates cation channels causing plasma membrane rupture, induces phosphatidylserine (PS) externalization and release of pro-inflammatory intracellular components105–107. The release of the cellular content into the extracellular space exposes several molecules that function as damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) to the immune system through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), thus promoting, perpetuating, and potentiating the inflammatory response. Such DAMPs include lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), mitochondrial DNA, N-formyl peptides, interleukin-1 (IL-1) and interleukin-33 (IL-33)108,109.
The current model is that necroptosis can function as an alternative cell death pathway which eliminates caspase-deficient cells in the event of infection, while, at same time, releases endogenous molecules and newly inflammatory signals generated during cell death to recruit and activate immune cells at site of necroptotic cell110,111.
As previously discussed, NF-κB pathway plays crucial role in regulating both inflammatory processes and programmed cell death, and, unsurprisingly, it is also involved in necroptosis.
Yatim et al. formally demonstrated for the first time that the release of endogenous DAMPs (ATP and HMGB1) induced by RIPK3/MLKL-mediated cell lysis was not sufficient for CD8+ T cell priming, but the transcriptional NF-κB activation in the dying cell was necessary to achieve T cell priming. The NF-κΒ regulates the expression of many pro-inflammatory genes that may actively contribute to immunogenicity of dying cells. Although the mechanism whereby NF-κB activation within dying cells actively regulates cross prime and the molecular signals involved in this process remain to be elucidated, it has become apparent that this regulation contributes to the immunogenicity of necroptotic cells108.
Moreover, NF-κB signaling can be triggered by RIPK1, which acts as molecular switch that can induce inflammation and cell survival, as well as apoptosis or necroptosis, depending on the context. Indeed, as a scaffold molecule, RIPK1 mediates the activation of NF-κB downstream of DR ligation by recruiting key activators of NF-κB pathway, such as the TGF-β-activated kinase 1 binding protein 1/2 (TAB1/2) and NEMO, to promote the activation of TAK1 and IKK complex112,113. The consequent NF-κB-mediated expression of pro-survival genes, such as cFLIP, prevents extrinsic apoptosis by inducing the formation of inhibitory cFLIP/caspase-8 heterodimers, thus inhibiting caspase-8 activation114,115. In the absence of NF-κB, active dimers of caspase-8 are formed driving extrinsic apoptosis116,117. Active caspase-8 not only initiates the apoptotic program, but also negatively regulates necroptosis by cleaving and inactivating essential necroptosis mediators such as RIPK1 and RIPK3117. However, depending on the context, RIPK1 can also promote the activation of caspase-8. Complex post-translational modifications tightly regulate the integration of RIPK1 into distinct multiprotein signaling complexes that will ultimately decide the cell fate118–120. Such modifications include ubiquitination and phosphorylation but also caspase-mediated cleavage. However, the possibility that RIPK1 shifts from pro-survival to pro-apoptotic and -necroptotic signaling depends on the intracellular RIPK3 levels. Since RIPK3 expression is cell-type restricted and a high intracellular concentration of this factor is required for initiating the necroptotic program, RIPK3 represents a key determinant to transduce necroptosis signal through the canonical RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL axis (Fig. 1)103,121.
NF-κB and necroptosis in cancer
Evading cell death is considered one of the characteristics of cancer cell. The apoptotic evasion or downregulation of the apoptotic regulators contributes to the disease progression of many cancers122. Instead, there is less knowledge regarding the role of endogenous necroptotic signaling within the tumor cell, mostly because the study of necroptosis has been complicated by the absence of specific markers that can be used in vivo123. Transient events such as phosphorylation of RIPK3 and MLKL are not easily detectable in the context of human or murine tumor models.
The TNF-α-induced pro-survival function of NF-κΒ in cancer cells is recognized as a main feature in most human cancers27,124–126. Defective activation of NF-κΒ (i.e., genetic deletion or pharmacological inactivation) can promote apoptosis or, under caspase-8-deficiency, necroptosis99,127–129. In this context, Hernandez et al. demonstrated that blocking NF-κB in OVCAR3 cells, one of the few ovarian cancer cell lines expressing RIPK3, resulted in TNF-α-dependent cell death. While cancer cells proficient for caspase-8 died by apoptosis, the depletion of caspase 8 promoted necroptosis by stabilizing RIPK1. Of note, although the authors proposed a potential role of necroptosis to overcome resistance to apoptosis and improve survival of those patients exhibiting low caspase-8 expression, it is now clear that a limit could be the absence of functional necroptotic machinery too130.
The role of necroptosis in mediating cell death has been well characterized in many human diseases131, although is not well defined the interaction between IKK/NF-κΒ and RIPK1 in apoptosis and necroptosis. Several data prompt at the existence of organ-specific ways in cell-death inducing stimuli that could be dependent from the levels of expression of the proteins mainly implicated in cell survival or cell death induction.
Recently, Bozec and colleagues demonstrated that necroptosis, in particular RIPK3, suppressed inflammation-driven CRC132. Accordingly, tumor cells lacking RIPK3 were more invasive, both in vitro and in vivo. The authors showed that RIPK3 loss induced tumorigenesis via upregulation of NF-κΒ, STAT3, AKT, and Wnt-β-catenin pathways activation, thus in turn leading to aberrant tumor cell proliferation, colon inflammation, immune cell infiltration and finally CRC. The upregulation of NF-κΒ in RIPK3-deficient mice induced the expression of cytokines (i.e., IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β) and chemokines (i.e., CCL2, CXCL1, CXCL2), as well as the transcription of genes involved in survival, cell cycle progression. This pro-tumorigenic milieu fosters the transition from inflammation to CRC malignancy. The capability of RIPK3 to negatively regulate the activation of different signaling pathways, such as NF-κΒ, together with its antitumoral function identified RIPK3 as a tumor suppressor in CRC. Accordingly, reduced expression levels of RIPK3 observed in CRC patients support the idea that RIPK3 plays a pivotal role in CRC pathogenesis but further studies are needed to clarify the tumor suppressor function of RIPK3-dependent necroptosis in CRC tumorigenesis (Fig. 4a)132.
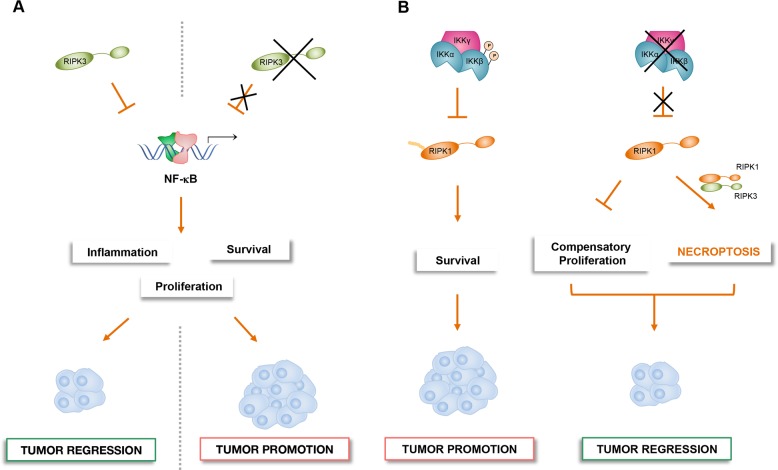
Fig. 4. The role of NF-κΒ and RIPK1/RIPK3-mediated signaling in tumorigenesis.
a RIPK3 activation in intestinal epithelial cells induces necroptosis, thus counteracting CRC development. On the contrary, RIPK3 loss in the same cells leads to excessive activation of several pathways including NF-κΒ, which result in abnormal proliferation and occurrence and development of CRC. b In the liver, activated IKKα and IKKβ directly phosphorylates RIPK1 and inhibits RIPK1-dependent PCD, thus promoting hepatocarcinogenesis. By contrast loss of IKKα/β-dependent RIPK1 phosphorylation prevents carcinogenesis by suppressing compensatory proliferation of hepatocytes and increasing necroptosis cell death.
In the liver, the IKK/NF-κB signaling pathway has emerged as a principal regulator of homeostasis and disease. Complete deletion of NF-κB-mediated transcription in liver parenchymal cells (LPCs) in mice (RelALPC-KO or RelA/RelB/c-RelLPC-KO mice) did not cause spontaneous liver damage133,134, in contrast NEMO deletion induced liver damage with massive compensatory proliferation and spontaneous development of HCC135.
In human, NEMO expression is completely absent in 40% of HCC biopsies studied (85 samples) when compared with adjacent normal tissue. Indeed, the correlation between the loss or low protein expression of NEMO and poor prognosis for patients has been reported136, emphasizing the idea that NEMO-dependent survival functions may be critical for the prevention of chronic liver damage and HCC in at least a certain group of patients.
The expression of a kinase inactive mutant of RIPK, in a contest of NEMOLPC deletion, prevented cell death and HCC in mice, this evidence strongly suggested the interplay between NEMO and RIPK1 kinase-activity-dependent apoptosis in liver disease, whereas the role of the necroptosis remains controversial133.
In according with the antitumoral function of necroptosis, Koppe and colleagues demonstrated that IKKα and IKKβ deletion in LPC (IKKα/βLPC-KO) induced cholestasis and, at the same time, inhibited HCC, due to increased intrahepatic necrosis and reduced compensatory proliferation in vivo. They also showed that both RIPK1 and RIPK3 promoted necroptosis in IKKα/βLPC-KO mice, as demonstrated by reduced necrotic foci in livers after additional deletion of Ripk3 and Ripk1, suggesting that these two kinases play a role in mediating necroptosis in these mice. Furthermore, Koppe et al. demonstrated that RIPK1 is the main players of the NF-κΒ-independent IKKα/βLPC-KO phenotype of mice characterized by cholestasis, reduced compensatory proliferation and then carcinogenesis, underlying a role of the catalytic IKKs in controlling RIPK1 activity independently of NF-κΒ (Fig. 4b)137. In a recent study, Koppe et al. showed that the additional deletion of NEMO in the IKKα/βLPC-KO mice (IKKα/β/NEMOLPC-KO) prevented necroptosis of LPCs and supported apoptosis and compensatory proliferation of both hepatocytes and cholangiocytes thus inducing HCC138. This study would support the idea that NEMO protein alone can directly inhibit the activation of apoptosis mediated by RIP1 Kinase activity in a context of NF-κB inhibition.
Although previous studies demonstrated that NEMO induces necroptosis by promoting RIPK1/RIPK3 necrosome139,140, further studies are needed to better understand the IKK/NF-κΒ-independent role of NEMO in controlling PCD in the liver. Nevertheless, based on these studies, the use of small molecule inhibitors of RIPK1 Kinase, also blocking necroptosis, would be an effective therapeutic option for patients with liver damages and HCC.
In the last few years, the immunogenicity of necroptotic cancer cells and its possible role in antitumor immune responses has attracted enormous attention as an alternative strategy for eliminating cancerous cells. As previously said, necroptosis induces adaptive immune responses by releasing DAMPs in the TME which in turn stimulate DCs and macrophages to secrete pro-inflammatory cytokine important to activate cytotoxic CD8+ T cells as well as interferon-gamma (INF-γ) in response to tumor antigen stimulation108,141–143. One of the specific characteristics of a cell undergoing necroptosis is that, apart DAMPs release, it can synthesize proteins and secrete antigens and pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6. Hence, the necroptotic environment becomes enriched also in pro-inflammatory cytokines/chemokines which might lead to immunostimulation and immunogenicity of necroptotic cancer cells. In keeping with these findings, Schmidt et al. showed that RIPK3-dependent-necroptotic cervical cancer cells induced the expression of IL-1α which stimulate the activation of DCs. As a result, activated DCs, in turn, promote the upregulation of DC surface markers as well as the release of interleukin-12 (IL-12) leading to antitumor effects144.
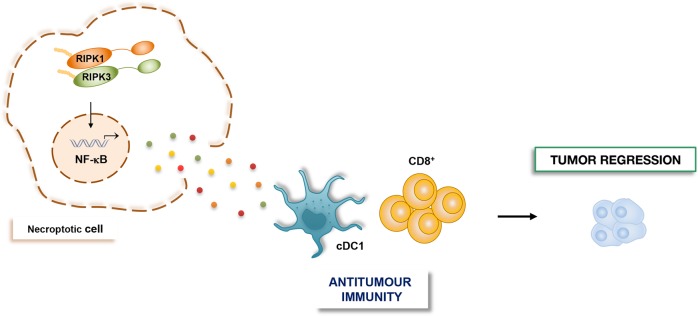
Recently, the role of RIPK1 and RIPK3 within the TME has been described by Snyder et al. The authors demonstrated that ectopic injection of necroptotic cells into tumors induced RIPK1/RIPK3-mediated production of NF-κΒ-dependent cytokines. These factors, together with conventional dendritic cells 1 (cDC1s) and CD8+ T cells, promoted in situ and systemic antitumor immune response and tumor regression. Importantly, inhibition of NF-κΒ activation via BAY-117085, significantly reduced both the tumor control effects and the survival advantage, demonstrating that intact NF-κΒ transcriptional signaling downstream of RIPK1/RIPK3 activation is required for the immunogenicity of necroptotic cells in the TME (Fig. 5). Furthermore, immune-mediated tumor control occurred independently of MLKL, cell lysis, and DAMPs release. They also suggest that necroptosis in the TME can synergize with α-prohrammed cell death protein 1(PD-1) to promote durable tumor clearance in vivo145.
Fig. 5. NF-κΒ and necroptosis control antitumor immune response within the TME.
RIPK1/RIPK3 necrosome complex induces NF-κΒ-dependent cytokines production in necroptotic cells. These NF-κΒ-dependent paracrine signals, in turn, promote antitumor immunity by activating cDC1 and CD8+ cells within the TME.
Taken together, these studies indicate that necroptosis is immunogenic, extending the current concept of immunogenic cell death, and open ways for the development of new cancer therapy strategies.
Conclusion and perspectives
Apoptosis, autophagy, and necroptosis are interconnected processes, which intersect with NF-κB signaling in response to different stimuli. This interplay exists also in cancer, thus opening the door to new therapeutic opportunities. It has been demonstrated that autophagy modulates the sensitivity to anticancer drugs146 and is able to switch its function upon the context147. Over the last few years several studies showed that combination of inhibitors of autophagy and survival pathways as NF-κB could be an important therapeutic option to sensitize tumor cells to apoptotic cell death148–150, thus improving cancer patient survival. Although the role of necroptosis in cancer is controversial, the fact that many tumors cells lack key necroptotic components132,151–154 suggests that restoring necroptosis might provide an intriguing opportunity for developing new anticancer treatments to bypass apoptosis resistance and promote strong antitumoral response in cancer therapy.
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the MIUR PRIN grant no 2017WLKYAM_1 to F.Z., MIUR PRIN grant no 2017WLKYAM_3 to A.P., Medical Research Council (MRC) Biomedical Catalyst grant MR/L005069/1, Bloodwise project grant 15003 and NIHR Imperial (BRC) Push for Impact Award WIIS_P81135 to G.F.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Edited by G. Melino
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Beg AA, Sha WC, Bronson RT, Ghosh S, Baltimore D. Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the RelA component of NF-kappa-B. Nature. 1995;376:167–170. doi: 10.1038/376167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bonizzi G, Karin M. The two NF-kappa B activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:280–288. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2004.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Siebenlist U, Brown K, Claudio E. Control of lymphocyte development by nuclear factor-kappa B. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005;5:435–445. doi: 10.1038/nri1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Karin M, Lin A. NF-kappa B at the crossroads of life and death. Nat. Immunol. 2002;3:221–227. doi: 10.1038/ni0302-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Luo JL, Kamata H, Karin M. IKK/NF-kappaB signaling: balancing life and death-a new approach to cancer therapy. J. Clin. Invest. 2005;115:2625–2632. doi: 10.1172/JCI26322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Baldwin AS. Regulation of cell death and autophagy by IKK and NF-kappa B: critical mechanisms in immune function and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012;246:327–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.De Smaele E, et al. Induction of gadd45 beta by NF-kappa B downregulates pro-apoptotic JNK signalling. Nature. 2001;414:308–313. doi: 10.1038/35104560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tang GL, et al. Inhibition of JNK activation through NF-kappa B target genes. Nature. 2001;414:313–317. doi: 10.1038/35104568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen LF, Greene WC. Shaping the nuclear action of NF-kappa B. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2004;5:392–401. doi: 10.1038/nrm1368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Maeda S, et al. IKK beta is required for prevention of apoptosis mediated by cell-bound but not by circulating TNF alpha. Immunity. 2003;19:725–737. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(03)00301-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Papa S, et al. Gadd45 beta mediates the NF-kappa B suppression of JNK signalling by targeting MKK7/JNKK2. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004;6:146. doi: 10.1038/ncb1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pham CG, et al. Ferritin heavy chain upregulation by NF-kappa B inhibits TNF alpha-induced apoptosis by suppressing reactive oxygen species. Cell. 2004;119:529–542. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.10.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Delhalle S, Deregowski V, Benoit V, Merville MP, Bours V. NF-kappa B-dependent MnSOD expression protects adenocarcinoma cells from TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. Oncogene. 2002;21:3917–3924. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bernard D, Quatannens B, Begue A, Vandenbunder B, Abbadie C. Antiproliferative and antiapoptotic effects of cRel may occur within the same cells via the up-regulation of manganese superoxide dismutase. Cancer Res. 2001;61:2656–2664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Papa S, et al. The NF-kappa B-mediated control of the JNK cascade in the antagonism of programmed cell death in health and disease. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:712–729. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sasazuki T, et al. Genome wide analysis of TNF-inducible genes reveals that antioxidant enzymes are induced by TNF and responsible for elimination of ROS. Mol. Immunol. 2004;41:547–551. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2004.03.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.DiDonato JA, Mercurio F, Karin M, NF-kappa B. and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012;246:379–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Xia L, et al. Role of the NFkappaB-signaling pathway in cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:2063–2073. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S161109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Capece D, et al. Cancer secretome and inflammation: the bright and the dark sides of NF-kappaB. Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 2018;78:51–61. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Taniguchi K, Karin M. NF-kappaB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018;18:309–324. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Staudt LM. Oncogenic activation of NF-kappaB. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010;2:a000109. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bennett J, et al. NF-kappaB in the crosshairs: Rethinking an old riddle. Int J. Biochem Cell Biol. 2018;95:108–112. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2017.12.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Begalli F, et al. Unlocking the NF-kappaB Conundrum: embracing complexity to achieve specificity. Biomedicines. 2017;5:E50. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines5030050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mayo MW, et al. Requirement of NF-kappaB activation to suppress p53-independent apoptosis induced by oncogenic Ras. Science. 1997;278:1812–1815. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5344.1812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Basseres DS, Ebbs A, Levantini E, Baldwin AS. Requirement of the NF-kappaB subunit p65/RelA for K-Ras-induced lung tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2010;70:3537–3546. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Greten FR, et al. IKKbeta links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer. Cell. 2004;118:285–296. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.07.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pikarsky E, et al. NF-kappaB functions as a tumour promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nature. 2004;431:461–466. doi: 10.1038/nature02924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Luo JL, Maeda S, Hsu LC, Yagita H, Karin M. Inhibition of NF-kappaB in cancer cells converts inflammation- induced tumor growth mediated by TNFalpha to TRAIL-mediated tumor regression. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:297–305. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Davis RE, Brown KD, Siebenlist U, Staudt LM. Constitutive nuclear factor kappaB activity is required for survival of activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001;194:1861–1874. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.12.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tornatore L, et al. Cancer-selective targeting of the NF-kappaB survival pathway with GADD45beta/MKK7 inhibitors. Cancer Cell. 2014;26:495–508. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.07.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tornatore L, et al. Preclinical toxicology and safety pharmacology of the first-in-class GADD45beta/MKK7 inhibitor and clinical candidate, DTP3. Toxicol. Rep. 2019;6:369–379. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.04.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tornatore L, et al. Clinical proof of concept for a safe and effective NF-kappaB-targeting strategy in multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2019;185:588–592. doi: 10.1111/bjh.15569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Galluzzi L, et al. Essential versus accessory aspects of cell death: recommendations of the NCCD 2015. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22:58–73. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Galluzzi L, Buque A, Kepp O, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. Immunogenic cell death in cancer and infectious disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017;17:97–111. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Choi AM, Ryter SW, Levine B. Autophagy in human health and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013;368:651–662. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1205406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yun CW, Lee SH. The roles of autophagy in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018;19:3466. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ben-Neriah Y, Karin M. Inflammation meets cancer, with NF-kappaB as the matchmaker. Nat. Immunol. 2011;12:715–723. doi: 10.1038/ni.2060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hayden MS, Ghosh S. NF-kappaB, the first quarter-century: remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev. 2012;26:203–234. doi: 10.1101/gad.183434.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Verzella D, et al. Targeting the NF-kappaB pathway in prostate cancer: a promising therapeutic approach? Curr. Drug Targets. 2016;17:311–320. doi: 10.2174/1389450116666150907100715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Salminen A, Hyttinen JM, Kauppinen A, Kaarniranta K. Context-dependent regulation of autophagy by IKK-NF-kappaB signaling: impact on the aging process. Int J. Cell Biol. 2012;2012:849541. doi: 10.1155/2012/849541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Trocoli A, Djavaheri-Mergny M. The complex interplay between autophagy and NF-kappaB signaling pathways in cancer cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2011;1:629–649. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nivon M, Richet E, Codogno P, Arrigo AP, Kretz-Remy C. Autophagy activation by NFkappaB is essential for cell survival after heat shock. Autophagy. 2009;5:766–783. doi: 10.4161/auto.8788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Copetti T, Bertoli C, Dalla E, Demarchi F, Schneider C. p65/RelA modulates BECN1 transcription and autophagy. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009;29:2594–2608. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01396-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Comb WC, Hutti JE, Cogswell P, Cantley LC, Baldwin AS. p85alpha SH2 domain phosphorylation by IKK promotes feedback inhibition of PI3K and Akt in response to cellular starvation. Mol. Cell. 2012;45:719–730. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.01.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Comb WC, Cogswell P, Sitcheran R, Baldwin AS. IKK-dependent, NF-kappaB-independent control of autophagic gene expression. Oncogene. 2011;30:1727–1732. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Criollo A, et al. The IKK complex contributes to the induction of autophagy. Embo. J. 2010;29:619–631. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sarkar S, et al. Complex inhibitory effects of nitric oxide on autophagy. Mol. Cell. 2011;43:19–32. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.04.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Balaburski GM, Hontz RD, Murphy ME. p53 and ARF: unexpected players in autophagy. Trends Cell Biol. 2010;20:363–369. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.02.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Djavaheri-Mergny M, et al. NF-kappaB activation represses tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced autophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:30373–30382. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602097200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Qing G, Yan P, Xiao G. Hsp90 inhibition results in autophagy-mediated proteasome-independent degradation of IkappaB kinase (IKK) Cell Res. 2006;16:895–901. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Qing G, Yan P, Qu Z, Liu H, Xiao G. Hsp90 regulates processing of NF-kappa B2 p100 involving protection of NF-kappa B-inducing kinase (NIK) from autophagy-mediated degradation. Cell Res. 2007;17:520–530. doi: 10.1038/cr.2007.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Niida M, Tanaka M, Kamitani T. Downregulation of active IKK beta by Ro52-mediated autophagy. Mol. Immunol. 2010;47:2378–2387. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2010.05.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kim JE, et al. Suppression of NF-kappaB signaling by KEAP1 regulation of IKKbeta activity through autophagic degradation and inhibition of phosphorylation. Cell Signal. 2010;22:1645–1654. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Colleran A, et al. Autophagosomal IkappaB alpha degradation plays a role in the long term control of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2011;286:22886–22893. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.199950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Singh R, Cuervo AM. Autophagy in the cellular energetic balance. Cell Metab. 2011;13:495–504. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.04.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kroemer G, Levine B. Autophagic cell death: the story of a misnomer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008;9:1004–1010. doi: 10.1038/nrm2529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Yu L, et al. Autophagic programmed cell death by selective catalase degradation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2006;103:4952–4957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0511288103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Mizushima N. Autophagy in protein and organelle turnover. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2011;76:397–402. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2011.76.011023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Rabinowitz JD, White E. Autophagy and metabolism. Science. 2010;330:1344–1348. doi: 10.1126/science.1193497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.White E. The role for autophagy in cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 2015;125:42–46. doi: 10.1172/JCI73941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Djavaheri-Mergny M, et al. Regulation of autophagy by NFkappaB transcription factor and reactives oxygen species. Autophagy. 2007;3:390–392. doi: 10.4161/auto.4248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Huang J, Lam GY, Brumell JH. Autophagy signaling through reactive oxygen species. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011;14:2215–2231. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Salminen A, Ojala J, Kaarniranta K, Kauppinen A. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress activate inflammasomes: impact on the aging process and age-related diseases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2012;69:2999–3013. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-0962-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Zhang H, Chen Z, Miranda RN, Medeiros LJ, McCarty N. TG2 and NF-kappaB signaling coordinates the survival of mantle cell lymphoma cells via IL6-mediated autophagy. Cancer Res. 2016;76:6410–6423. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Newman AC, Kemp AJ, Drabsch Y, Behrends C, Wilkinson S. Autophagy acts through TRAF3 and RELB to regulate gene expression via antagonism of SMAD proteins. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:1537. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00859-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Dan HC, Adli M, Baldwin AS. Regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin activity in PTEN-inactive prostate cancer cells by I kappa B kinase alpha. Cancer Res. 2007;67:6263–6269. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Levine B, Kroemer G. Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 2008;132:27–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Chen L, Liu D, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Cheng H. The autophagy molecule Beclin 1 maintains persistent activity of NF-kappaB and Stat3 in HTLV-1-transformed T lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015;465:739–745. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.08.070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Yoon S, et al. NF-kappaB and STAT3 cooperatively induce IL6 in starved cancer cells. Oncogene. 2012;31:3467–3481. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Liu K, et al. SKP2 attenuates NF-kappaB signaling by mediating IKKbeta degradation through autophagy. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018;10:205–215. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjy012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Lee DF, et al. KEAP1 E3 ligase-mediated downregulation of NF-kappaB signaling by targeting IKKbeta. Mol. Cell. 2009;36:131–140. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.07.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.van der Wijst MG, Huisman C, Mposhi A, Roelfes G, Rots MG. Targeting Nrf2 in healthy and malignant ovarian epithelial cells: protection versus promotion. Mol. Oncol. 2015;9:1259–1273. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2015.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Leinonen HM, Kansanen E, Polonen P, Heinaniemi M, Levonen AL. Role of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2014;122:281–320. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-420117-0.00008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Lee KH, Lee J, Woo J, Lee CH, Yoo CG. Proteasome inhibitor-induced IkappaB/NF-kappaB activation is mediated by Nrf2-dependent light chain 3B induction in lung cancer cells. Mol. Cells. 2018;41:1008–1015. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2018.0277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Xiao G. Autophagy and NF-kappaB: fight for fate. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007;18:233–243. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2007.04.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Zuehlke A, Johnson JL. Hsp90 and co-chaperones twist the functions of diverse client proteins. Biopolymers. 2010;93:211–217. doi: 10.1002/bip.21292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Duran A, et al. The signaling adaptor p62 is an important NF-kappaB mediator in tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:343–354. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Moscat J, Diaz-Meco MT. p62 at the crossroads of autophagy, apoptosis, and cancer. Cell. 2009;137:1001–1004. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Ren F, et al. Knockdown of p62/sequestosome 1 attenuates autophagy and inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2014;385:95–102. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1818-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Nguyen TD, et al. Loss of the selective autophagy receptor p62 impairs murine myeloid leukemia progression and mitophagy. Blood. 2019;133:168–179. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-02-833475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Su J, et al. p62 participates in the inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling and apoptosis induced by sulfasalazine in human glioma U251 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015;34:235–p243. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Sanz L, Sanchez P, Lallena MJ, Diaz-Meco MT, Moscat J. The interaction of p62 with RIP links the atypical PKCs to NF-kappaB activation. Embo. J. 1999;18:3044–3053. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.11.3044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Wooten MW, et al. The p62 scaffold regulates nerve growth factor-induced NF-kappaB activation by influencing TRAF6 polyubiquitination. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:35625–35629. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C500237200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Yang S, Qiang L, Sample A, Shah P, He YY. NF-kappaB signaling activation induced by chloroquine requires autophagosome, p62 protein, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling and promotes tumor cell resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2017;292:3379–3388. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.756536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Jia L, Gopinathan G, Sukumar JT, Gribben JG. Blocking autophagy prevents bortezomib-induced NF-kappaB activation by reducing I-kappaBalpha degradation in lymphoma cells. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e32584. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Karin M. Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer development and progression. Nature. 2006;441:431–436. doi: 10.1038/nature04870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Hoesel B, Schmid JA. The complexity of NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer. 2013;12:86. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Mancino A, Lawrence T. Nuclear factor-kappaB and tumor-associated macrophages. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010;16:784–789. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Verzella D, et al. GADD45beta loss ablates innate immunosuppression in cancer. Cancer Res. 2018;78:1275–1292. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Capece D, et al. Turning an old GADDget into a troublemaker. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:640–642. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0087-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Monkkonen T, Debnath J. Inflammatory signaling cascades and autophagy in cancer. Autophagy. 2018;14:190–198. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1345412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Chang CP, Su YC, Lee PH, Lei HY. Targeting NFKB by autophagy to polarize hepatoma-associated macrophage differentiation. Autophagy. 2013;9:619–621. doi: 10.4161/auto.23546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Chang CP, Su YC, Hu CW, Lei HY. TLR2-dependent selective autophagy regulates NF-kappaB lysosomal degradation in hepatoma-derived M2 macrophage differentiation. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20:515–523. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2012.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Tan HY, et al. Autophagy-induced RelB/p52 activation mediates tumour-associated macrophage repolarisation and suppression of hepatocellular carcinoma by natural compound baicalin. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1942. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Sun K, et al. Autophagy-deficient Kupffer cells promote tumorigenesis by enhancing mtROS-NF-kappaB-IL1alpha/beta-dependent inflammation and fibrosis during the preneoplastic stage of hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2017;388:198–207. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Capece D, et al. NF-kappaB and mitochondria cross paths in cancer: mitochondrial metabolism and beyond. Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 2020;98:118–128. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2019.05.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Lisanti MP, Sotgia F. Catabolic cancer-associated fibroblasts transfer energy and biomass t.o anabolic cancer cells, fueling tumor growth. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;25:47–60. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Weinlich R, Oberst A, Beere HM, Green DR. Necroptosis in development, inflammation and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017;18:127–136. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Park HH, et al. The death domain superfamily in intracellular signaling of apoptosis and inflammation. Annu Rev. Immunol. 2007;25:561–586. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Dickens LS, Powley IR, Hughes MA, MacFarlane M. The ‘complexities’ of life and death: death receptor signalling platforms. Exp. Cell Res. 2012;318:1269–1277. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Cho YS, et al. Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation. Cell. 2009;137:1112–1123. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Mompean M, et al. The structure of the necrosome RIPK1-RIPK3 core, a human hetero-amyloid signaling complex. Cell. 2018;173:1244–1253 e1210. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.He S, et al. Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell. 2009;137:1100–1111. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Wang H, et al. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein MLKL causes necrotic membrane disruption upon phosphorylation by RIP3. Mol. Cell. 2014;54:133–146. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Cai Z, et al. Plasma membrane translocation of trimerized MLKL protein is required for TNF-induced necroptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014;16:55–65. doi: 10.1038/ncb2883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Quarato G, et al. Sequential engagement of distinct MLKL phosphatidylinositol-binding sites executes necroptosis. Mol. Cell. 2016;61:589–601. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.01.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Yatim N, et al. RIPK1 and NF-kappaB signaling in dying cells determines cross-priming of CD8(+) T cells. Science. 2015;350:328–334. doi: 10.1126/science.aad0395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Yatim N, Cullen S, Albert ML. Dying cells actively regulate adaptive immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017;17:262–275. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Daniels BP, et al. RIPK3 Restricts Viral Pathogenesis via Cell Death-Independent Neuroinflammation. Cell. 2017;169:301–313 e311. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.03.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Nailwal H, Chan FK. Necroptosis in anti-viral inflammation. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26:4–13. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0172-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Ea CK, Deng L, Xia ZP, Pineda G, Chen ZJ. Activation of IKK by TNFalpha requires site-specific ubiquitination of RIP1 and polyubiquitin binding by NEMO. Mol. Cell. 2006;22:245–257. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.03.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Kanayama A, et al. TAB2 and TAB3 activate the NF-kappaB pathway through binding to polyubiquitin chains. Mol. Cell. 2004;15:535–548. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Micheau O, Lens S, Gaide O, Alevizopoulos K, Tschopp J. NF-kappaB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001;21:5299–5305. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.16.5299-5305.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Kreuz S, Siegmund D, Scheurich P, Wajant H. NF-kappaB inducers upregulate cFLIP, a cycloheximide-sensitive inhibitor of death receptor signaling. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001;21:3964–3973. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.12.3964-3973.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Micheau O, Tschopp J. Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell. 2003;114:181–190. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00521-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Feng S, et al. Cleavage of RIP3 inactivates its caspase-independent apoptosis pathway by removal of kinase domain. Cell Signal. 2007;19:2056–2067. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.05.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Degterev A, et al. Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of necrostatins. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008;4:313–321. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Ofengeim D, Yuan J. Regulation of RIP1 kinase signalling at the crossroads of inflammation and cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013;14:727–736. doi: 10.1038/nrm3683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Weinlich R, Green DR. The two faces of receptor interacting protein kinase-1. Mol. Cell. 2014;56:469–480. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.11.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Li J, et al. The RIP1/RIP3 necrosome forms a functional amyloid signaling complex required for programmed necrosis. Cell. 2012;150:339–350. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Fernald K, Kurokawa M. Evading apoptosis in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2013;23:620–633. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.He S, Huang S, Shen Z. Biomarkers for the detection of necroptosis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016;73:2177–2181. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2192-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Kagoya Y, et al. Positive feedback between NF-kappaB and TNF-alpha promotes leukemia-initiating cell capacity. J. Clin. Invest. 2014;124:528–542. doi: 10.1172/JCI68101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Chu WM. Tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Lett. 2013;328:222–225. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.10.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Gentle IE, Silke J. New perspectives in TNF-R1-induced NF-kappaB signaling. Adv. Exp. Med Biol. 2011;691:79–88. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-6612-4_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Laster SM, Wood JG, Gooding LR. Tumor necrosis factor can induce both apoptic and necrotic forms of cell lysis. J. Immunol. 1988;141:2629–2634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Sawai H. Characterization of TNF-induced caspase-independent necroptosis. Leuk. Res. 2014;38:706–713. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2014.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Vanden Berghe T, et al. Necroptosis, necrosis and secondary necrosis converge on similar cellular disintegration features. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17:922–930. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Hernandez L, et al. A dual role for Caspase8 and NF-kappaB interactions in regulating apoptosis and necroptosis of ovarian cancer, with correlation to patient survival. Cell Death Disco. 2015;1:15053. doi: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2015.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Shan B, Pan H, Najafov A, Yuan J. Necroptosis in development and diseases. Genes Dev. 2018;32:327–340. doi: 10.1101/gad.312561.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Bozec D, Iuga AC, Roda G, Dahan S, Yeretssian G. Critical function of the necroptosis adaptor RIPK3 in protecting from intestinal tumorigenesis. Oncotarget. 2016;7:46384–46400. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Kondylis V, et al. NEMO prevents steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting RIPK1 kinase activity-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis. Cancer Cell. 2015;28:830. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.11.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Geisler F, Algul H, Paxian S, Schmid RM. Genetic inactivation of RelA/p65 sensitizes adult mouse hepatocytes to TNF-induced apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2489–2503. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Luedde T, et al. Deletion of NEMO/IKKgamma in liver parenchymal cells causes steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2007;11:119–132. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Aigelsreiter A, et al. NEMO expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma and its association with clinical outcome. Hum. Pathol. 2012;43:1012–1019. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2011.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Koppe C, et al. IkappaB kinasealpha/beta control biliary homeostasis and hepatocarcinogenesis in mice by phosphorylating the cell-death mediator receptor-interacting protein kinase 1. Hepatology. 2016;64:1217–1231. doi: 10.1002/hep.28723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Koppe C, et al. An NF-kappaB- and IKK-independent function of NEMO prevents hepatocarcinogenesis by suppressing compensatory liver regeneration. Cancers. 2019;11:E999. doi: 10.3390/cancers11070999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Pescatore A, Esposito E, Draber P, Walczak H, Ursini MV. NEMO regulates a cell death switch in TNF signaling by inhibiting recruitment of RIPK3 to the cell death-inducing complex II. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2346. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Irrinki KM, et al. Requirement of FADD, NEMO, and BAX/BAK for aberrant mitochondrial function in tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced necrosis. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011;31:3745–3758. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05303-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Pasparakis M, Vandenabeele P. Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature. 2015;517:311–320. doi: 10.1038/nature14191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Biswas SK, Lewis CE. NF-kappaB as a central regulator of macrophage function in tumors. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010;88:877–884. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0310153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Aaes TL, et al. Vaccination with necroptotic cancer cells induces efficient anti-tumor immunity. Cell Rep. 2016;15:274–287. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.03.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Schmidt SV, et al. RIPK3 expression in cervical cancer cells is required for PolyIC-induced necroptosis, IL-1alpha release, and efficient paracrine dendritic cell activation. Oncotarget. 2015;6:8635–8647. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Snyder AG, et al. Intratumoral activation of the necroptotic pathway components RIPK1 and RIPK3 potentiates antitumor immunity. Sci. Immunol. 2019;4:eaaw2004. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aaw2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Maycotte P, Thorburn A. Autophagy and cancer therapy. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011;11:127–137. doi: 10.4161/cbt.11.2.14627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Gewirtz DA. Autophagy and senescence in cancer therapy. J. Cell Physiol. 2014;229:6–9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Papademetrio DL, et al. Inhibition of survival pathways MAPK and NF-kB triggers apoptosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells via suppression of autophagy. Target Oncol. 2016;11:183–195. doi: 10.1007/s11523-015-0388-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Papademetrio DL, et al. Interplay between autophagy and apoptosis in pancreatic tumors in response to gemcitabine. Target Oncol. 2014;9:123–134. doi: 10.1007/s11523-013-0278-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Ravikumar B, Rubinsztein DC. Role of autophagy in the clearance of mutant huntingtin: a step towards therapy? Mol. Asp. Med. 2006;27:520–527. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2006.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Koo GB, et al. Methylation-dependent loss of RIP3 expression in cancer represses programmed necrosis in response to chemotherapeutics. Cell Res. 2015;25:707–725. doi: 10.1038/cr.2015.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Feng X, et al. Receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 is a predictor of survival and plays a tumor suppressive role in colorectal cancer. Neoplasma. 2015;62:592–601. doi: 10.4149/neo_2015_071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Geserick P, et al. Absence of RIPK3 predicts necroptosis resistance in malignant melanoma. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1884. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.He L, Peng K, Liu Y, Xiong J, Zhu FF. Low expression of mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein is associated with poor prognosis in ovarian cancer patients. Onco Targets Ther. 2013;6:1539–1543. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S52805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]