BACKGROUND
In 2008, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) enacted the Public Access Policy requiring all NIH-funded investigators to submit accepted, peer-reviewed manuscripts to the National Library of Medicine’s digital repository PubMed Central. The purpose of the policy is to “ensure the public has access to the published results of NIH-funded research.” (Accessed Jan. 14, 2020 at https://www.nih.gov/health-information/nih-clinical-research-trials-you/what-is-nih-public-access-policy). Historically, the burden of cost to access manuscripts was on readers; however, the policy shifted the responsibility to researchers. Publishing a manuscript costs on average between $1,500 – $3,000, but these costs can be included in grant proposal budgets.
The NIH’s National Library of Medicine (NLM), established in 1836, originated with a few books in the office of the Surgeon General of the Army. Over the next century the NLM amassed millions of publications related to medicine, public health and the allied sciences for use by physicians and health professionals throughout the United States. The computer and technology era enhanced the reach of literature and produced numerous NIH online resources including the National Center for Biotechnology Information, MEDLINE, ClinicalTrials. gov, PubMed and PubMed Central (PMC). The NLM continues to maintain an immense amount of medical publications and biomedical clinical research manuscripts, primarily in online databases.
Why it is Important to Comply with the NIH Public Access Policy
Medical and public health researchers have a shared goal of developing innovative strategies to improve population health and of utmost importance is translating the effective discoveries to individuals. One approach to accelerate research findings to improve population health is to ensure the scientific and lay community has access to published research outcomes in a timely manner.
While translating effective strategies to improve population health is important to investigators, it is also imperative researchers comply with the NIH Public Access Policy to avoid interruption to scientific discovery. Any NIH Institute or Center can withhold future funding from the primary author of a manuscript and the principal investigator of acknowledged funding support, including non-competitive renewals and new grant proposals in non-compliance with the policy.
What Non-Compliance to the NIH Public Access Policy Means
Manuscripts are required to be publicly available no later than 12 months following original publication date depending on the embargo period of the publisher; however, manuscripts are non-compliant if the PubMed Central Identification (PMCID) number has not been acquired 90 days after the original publication date. Steps to acquire a PMCID are provided below. Embargo periods for each journal in PMC can be found in the “Free Access” column on the PMC Journal List. The exact release date for each article under embargo is displayed in PMC search results, on the table of contents for the issue, or in the corresponding PubMed record. To obtain access to an article prior to its availability in PMC, individuals must contact the respective journal publisher directly.
NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF HEALTH MANUSCRIPT SUBMISSION (NIHMS) PROCESS OVERVIEW
Step-by-Step Guide to Move Manuscripts through the NIH’s Databases to Acquire a PubMed Central Identification (PMCID) Number
Step 1: Deposit Files into the NIHMS
-
Select Submit New Manuscript - Primary Author or Principal Investigator (PI; or a delegate assigned in eRA Commons) of funding mechanism that supported the research can process manuscripts through the NIHMS database. The individual that initiates the process will need to complete all remaining steps. Delegates cannot serve as a Reviewer for the Initial or Final Approvals.
-
This process should be initiated immediately following official publication. Some journals may deposit the paper into the NIHMS for authors, but have a 12-month timeframe for submission, which is not within the 90 day compliance window.
-
-
Select submission method. Recommend using PubMed, as most journals submit abstracts to PubMed upon publication. Enter in the PubMed Identification (PMID) number or manuscript title in the PubMed search field.
PubMed is an online, free database comprised of over 30 million published biomedical abstracts and citations. PubMed’s aim is to support retrieval of abstracts and citations to improve population health. PubMed was created by and is sustained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) of the NLM.
-
Many journals provide abstracts and citations to NCBI, which then populates PubMed. While some links to full text articles are provided, PubMed is not a full-text repository. PMC was developed to be a full-text repository for biomedical and life science literature to ensure the public has free access to research outcomes. The NIH Manuscript Submission System (NIHMS) was developed to “facilitate the submission of peer-reviewed manuscripts for inclusion in PMC in support of the NIH Public Access Policy” (Accessed Jan. 6, 2020 at https://www.nihms.nih.gov/db/sub.cgi?page=overview).
-
Manuscript data will populate into the NIHMS. Select Next.
-
-
Select “My Funding” to open a list of grant awards. Choose the “Award ID(s)” associated with the manuscript. Select Next.
-
Selecting funding links this manuscript to the PI(s) of the funding mechanism. The citation will be added to the PIs “MyNCBI”, the NCBI investigator-specific dashboard for researchers to manage and track their publications. NCBI maintains a series of databases containing biomedical and genomic data for use by scientists, contributing to the mission of the NIH to “uncover new knowledge”.
-
-
Upload all files associated with the manuscript. The manuscript must be the final, published PDF. Naming convention: PILastName_et_al_year published_Journal name. Confirm that all figures, tables, videos and/or supplemental materials are included in the PDF. Some online publishers link to these items instead of including them with the manuscript. If not included, upload materials. Select Next.
-
Assign Reviewer and Release Delay (Embargo)
When an article is under an embargo it means that there is a delay, as specified by the publisher, between when the article is published and when its full version can be made freely available in PMC. The default embargo for each journal in PMC can be found under the “Free Access” column on the PMC Journal List. The exact release date for each article under embargo is displayed in PMC search results, on the table of contents for the issue, or in the corresponding PubMed record.
Step 2: Initial Approval
1. Review Submission Statement. Select Agree.
Step 3: NIHMS Conversion
The NIHMS conversion typically takes two-three weeks. NIHMS converts the deposited manuscript files into archival XML format. In this way, NIHMS makes papers publicly available in a format that ensures the permanent preservation of these research findings and makes the results of this research more readily accessible to the public, healthcare providers, educators, and the scientific community (Accessed Jan. 31, 2020 at https://www.nihms.nih.gov/about/publicaccess/).
Step 4: Final Approval
The individual that initiated the process in Step 1 will receive an email from nihms-help@ncbi.nlm.nih.gov with the subject line reading [nihms] Manuscript #1031896: Please review the PMC-ready Documents. *See Appendix A. Log into NIHMS to Review and Approve the submission for it to be rerouted to undergo conversion to PMC documents.
Step 5: PMCID Assigned
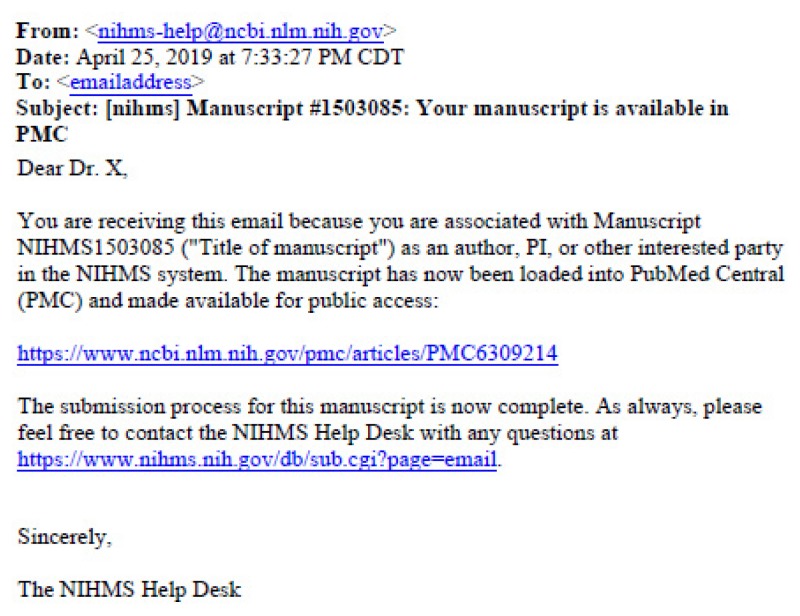
Once approved by the NIHMS the manuscript undergoes conversion to PMC documents. After file conversion the individual that initiated the process will receive an email from nihms-help@ncbi.nlm.nih.gov with the subject line: [nihms] Manuscript #1503085: Your manuscript is available in PMC. *See Appendix B. PI or primary author must again APPROVE the PMC-ready or final manuscript.
Note: PMCID is assigned when the following two criteria are met:
Converted materials (i.e., the PMC-ready documents) have been approved by the Reviewer.
The manuscript has been matched to a PubMed record for one of the following: a final print publication date or an electronic publication date for a journal that is an electronic publication only or an electronic publication date for a journal where PubMed has not received the final print publication date within six months of the electronic publication date
Steps for Processing Non-compliant Manuscripts Associated with Funding
The following three steps are provided to assist investigators with processing a non-compliant publication linked to their funding. Following completion of the three steps below, proceed to Step 1 above.
Step 1.i: Select Manage my Bibliography
Step 2.i: Select Edit Status
Step 3.i: Select Begin sfubmission in the NIHMS. Save
Step 4.i: Follow Steps 1–5
Step 1: Deposit Files into the NIHMS
Step 2: Initial Approval
Step 3: NIHMS Conversion
Step 4: Final Approval
Step 5: PMCID Assigned
APPENDIX A.
APPENDIX B.
Footnotes
FUNDING SUPPORT
This work was supported by a CTSA grant from NCATS awarded to the University of Kansas for Frontiers: University of Kansas Clinical and Translational Science Institute (# UL1TR002366). The contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH or NCATS.