Abstract
Objective
Health literacy has become a global issue, and it is important that patients and individuals are able to use information technology to access health information and educational services. The research objective is to develop a Saudi e-health literacy scale (SeHL) for measuring e-health literacy among Saudis suffering from non-communicable diseases (NCD).
Methods
Overall, 14 relevant papers in related interdisciplinary fields were reviewed to select the most useful literacy dimensions. From these articles, we extracted the most common dimensions used to measure e-health literacy across the disciplines. Multiple workshops with multidisciplinary team members reviewed and evaluated items for SeHL.
Results
Four key aspects of e-health literacy—use of technology/media, information-seeking, usefulness and confidence—were identified and integrated as e-health literacy dimensions. These will be used to measure e-health literacy among Saudi patients with NCDs. A translation from Arabic to English was performed in order to ensure that translation process was accurate. A SeHL scale was developed to measure e-health literacy among Saudi patients. By understanding e-health literacy levels, we will be able to create a patient-education system to be used by patients in Saudi Arabia.
Conclusions
As information technology is increasingly used by people of all ages all over the world, e-health literacy has been identified as a key factor in determining health outcomes. To date, no comprehensive scale exists to assess e-health literacy levels among speakers of Arabic, particularly among people with NCD such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and hypertension.
Keywords: health literacy, e-health, chronic diseases
Introduction
Literacy is defined as the ability to read and write, whereas health literacy refers to the ability to understand and use health-related information to achieve good health [1]. E-health literacy refers to the ability to use information technology (IT) to improve health outcomes. This study focuses on e-health literacy among patients with non-communicable diseases (NCDs). Worldwide, 48 million people have died from NCDs. In Saudi Arabia, NCDs accounted for 73% of the national mortality rate [2]. A major public health problem is diabetes, which is one of the four NCDs prioritized by the World Health Organization (WHO) [3]. The prevalence of diabetes has almost doubled globally since 1980, and affecting 8.5% of the world’s population in 2014 [3]. Prevention requires patients to understand steps and procedures for monitoring their diabetes, and management of diabetes may involve taking insulin or other medication in a consistent manner. Therefore, WHO recommends addressing the key gaps in patients’ knowledge in the disease and related health issues. With technology being available literally in everyone’s hand, e-health literacy is a key component for disseminating knowledge and ensuring that patients maintain good health.
No studies have explored e-health literacy among patients in the Middle East. Among Middle Eastern countries, Saudi Arabia has the highest number of people with Internet access: 68.5% of the population [4]. Saudis, especially the younger generation, are increasingly using IT to access health information [5], and health practitioners and institutions are frequently accessing the Internet for information. During the MERS corona-virus outbreak in 2014–15, for example, the Ministry of Health used an e-platform, namely Twitter, to alert the public about the epidemic as well as to promote health programs.
In high-income countries, healthcare efforts can be maximized using IT. There are numerous studies on the use of e-health or health IT for prevention, treatment, health maintenance and wellness. For example, mobile applications (apps) have been developed to provide information on how to treat cardiovascular issues and diabetes. Well-known websites such as WebMD [6] and the US Centers for Disease Control (CDC) [7] offer education and information regarding a wide range of health topics. Other health portals that are focused on individual health issues, such as the Diabetes Center, demonstrate the positive impact of IT on health maintenance for diabetes patients. Despite evidence of high IT use, there is no published evidence about whether the Saudi population is using IT to obtain health information or make decisions, especially regarding NCDs such as diabetes, cardiovascular issues and hypertension. Further, no studies have measured Saudis’ e-health literacy. The study was thus carried out to fill the gap in research in this particular area.
Literature review
Illiteracy is still a major problem worldwide, especially as it relates to health and healthcare. Many studies have found that almost half of the world’s adult population is deficient in reading, writing, and computing skills. Roughly 48% of English-speaking patients have inadequate health literacy skills, resulting in poor healthcare, inadequate medical information, and consequently, lack of treatment. This increases the prevalence of diseases, affects patients’ overall health and increases patients’ chances of hospitalization [8].
Literacy in e-health involves a variety of skills, from choosing which program to use (Internet-based or stand-alone), knowing how to use a search engine, and being able to read and evaluate an article or blog post. Furthermore, it is helpful to know how to find and use widgets and utilities available on the Web, stay up-to-date on health news, understand medical terminology and jargon, and know how to interpret graphs, charts and statistics.
One recently proposed framework for literacy [9] shows different sets of core skills that can be measured in e-health users and divides literacy into traditional (reading and numerical) literacy, health literacy, science literacy, computer literacy, information literacy and media literacy. Science literacy means that a person can understand accounts of scientific experiments in healthcare like what is meant by ‘a randomized trial’. Health literacy is also needed for a person to interpret health outcomes independently, without professional help. According to another study by Chew [10], having computing and engineering skills is also a measure of health literacy.
Nutbeam [11] defined health literacy from both personal and social aspects and proposed several dimensions such as functional, critical and communicative literacy. Paakkari and Paakkari [12], divided health literacy into theoretical knowledge, practical knowledge, critical thinking, self-awareness and citizenship. Ishikawa's et al. [8] work was an extension of Nutbeam’s work [11] and Paakkari and Paakkari [12], recommended that researchers use multiple criteria to evaluate health literacy. Similarly, Chan et al. [9] suggested that health literacy should encompass multiple forms of literacy, including traditional, health, science, computer, information and media literacies.
Many previous studies have explored how health literacy affects patients with chronic illness. Low literacy is associated with adverse health outcomes and is common, especially in elderly patients. Poor health status is more closely associated with low health literacy than with education, income, ethnic background or any other variables. In addition, patients with low health literacy may become ill or be hospitalized more frequently than patients with high or adequate health literacy [1]. The relationship between low health literacy and illness has been supported in studies about acute and chronic diseases, which show that health literacy skills have a direct impact on health status outcomes [4]. The ability to read is, all by itself, a predictor of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular death among the elderly. Reading fluency is a more powerful variable than education for examining the association between socioeconomic status and health. Chang et al. [13] posited a relationship between health literacy and two outcome measurements: knowledge and prevention behavior. The most recent study by Kim and Lee [14] concluded that diabetes management that is sensitive to health literacy is more effective in reducing HbA1c levels in patients. All evidence indicates that health literacy can have a strong impact on patient care. The more literate the patient, the better he or she will take care of himself or herself. Health literacy is an independent variable in this study.
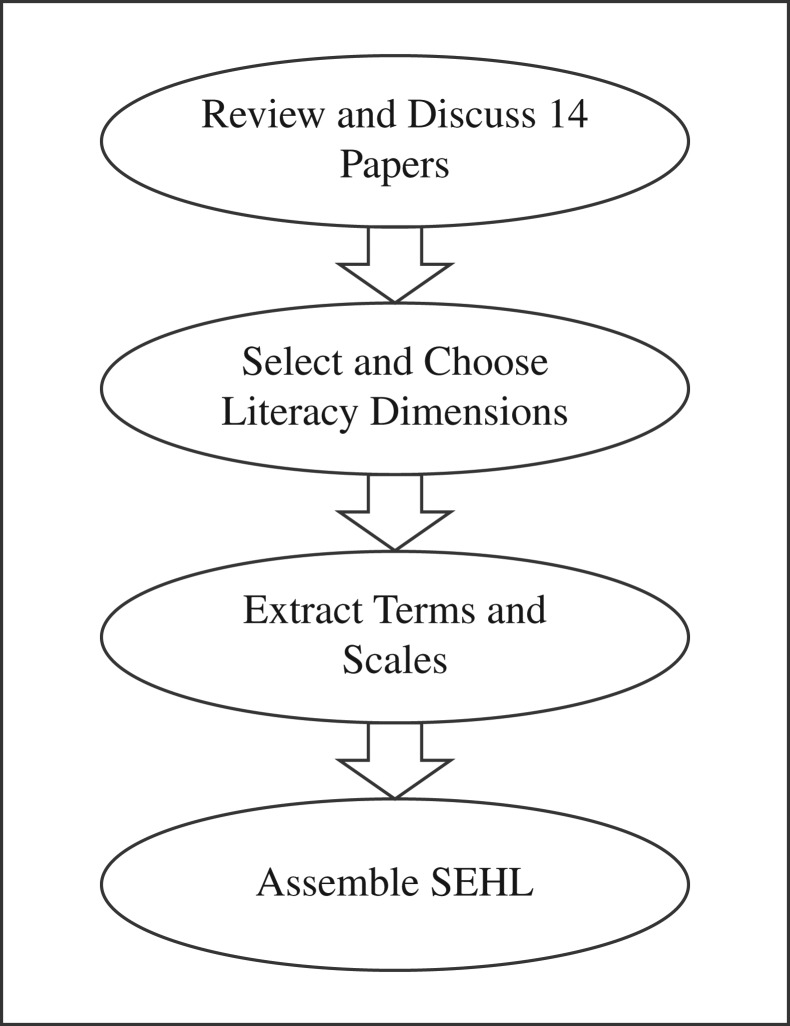
In this study, we describe the development of a Saudi e-health literacy scale (SeHL) for measuring e-health literacy among Saudis suffering from NCDs, especially diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Such a scale could be used to assess e-health literacy levels to assist healthcare providers in creating effective e-health interventions for these patients (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Workflow for development of SeHL.
Methodology
We began with a literature review, using Pubmed and Google Scholar to retrieve papers on literacy, health literacy and e-health literacy scales. The search was done from October 2014 till June 2015 and the list of search terms is listed in Table 1. We eventually pared down the selection from 145 papers to 14. These 14 papers met our inclusion criteria which were: (i) the topic must be either health literacy or e-health literacy, (ii) the paper must have been cited three or more times and (iii) all 14 papers were included in systematic reviews by Ishikawa et al., AlSayah and Boren [8, 15, 17]. The AlSayah et al.'s paper [15] included all the gold standards in health literacy such as Test of Functional Health Literacy in Adults (TOFHLA), Rapid Estimates of Adult Literacy in Medicine (REALM), Single Item Literacy Scales (SILS) and Newest Vital Signs (NVS). We also looked at the most recent publications by AlSayah et al. [15] and current papers on e-health literacy such as Watkins [17]. We revisited Health Literacy Skills Instruments (HLSI) [18] and the e-health literacy scale (e-heals) [19] to understand e-health literacy in depth. We decided that we could not use the e-heals scale because it only looks at literacy on the Internet, and because most e-heals work must be accompanied by an IT skills test [17, 20, 21]. Therefore, the e-heals scale was deemed unsuitable for the Saudi nationwide study.
Table 1.
List of keywords during searching the database
| Searching date from 1990 to 2015 | |
|
|
We conducted two workshops, in January and May 2015, respectively, to gain a better understanding of the selected studies and make sense of the e-health literacy and health literacy dimensions discussed in them. The process of selecting dimensions, extracting items and scales, and assembling a SeHL is illustrated in Figure 1. The workshop attendees were health informatics professionals, health educators and clinicians. A matrix (Table 1) was created to extract the dimensions used in each paper. As we tried to match the papers with the dimensions, we found that some overlapping concepts were used in similar ways; thus, similar concepts were merged into single dimensions. For example, under ‘Decision Making,’ we found four areas: Understanding, Usefulness, Remembering and Communication. Communication was further subdivided into pronunciation and verbalization, reading comprehension, numeracy, decision making, confidence, health-information seeking, navigation and need for assistance.
The dimensions for our SeHL scale were finalized as follows: (i) usefulness/understanding, (ii) confidence/needs assistance, (iii) information seeking and (iv) use of technology and media. We then list all the related items and scales, and conducted another workshop to clarify the meanings of the items in each category. During this workshop, we also revisited the reasons behind SeHL. We considered the following: how patients sought information, how well they understood it, how useful the information was, how comfortable patients were with new health information, and how they used media and technology for health information. The research group felt that it was important that the logistics of collecting data be straightforward and that the scale be easy to be read. It was presented in a language simple enough to suit the culture and context of our study (Table 2).
Table 2.
Identifying relevant dimensions across selected papers in health literacy and e-health literacy
| Literacy dimensions | [22] | [23] | [28] | [13] | [29] | [30] | [31] | [8] | [21] | [19] | [32] | [25] | [33] | [34] | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decision making Remembering |
× | × | 2 | ||||||||||||
| Decision making Understanding |
× | × | × | × | × | 5 | |||||||||
| Decision making Usefulness |
× | × | × | × | 4 | ||||||||||
| Decision making Applying |
× | × | 2 | ||||||||||||
| Decision making Analyzing |
× | × | x | × | 4 | ||||||||||
| Confidence Self-efficacy |
× | × | x | × | × | × | × | 7 | |||||||
| Health information Seeking |
× | × | × | × | 5 | ||||||||||
| Navigation | × | × | 2 | ||||||||||||
| Communication | × | × | × | × | 4 | ||||||||||
| Accessing | × | × | × | × | × | 5 | |||||||||
| Content | × | × | × | 3 | |||||||||||
| Interpreting | × | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Numeracy | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| ‘How to use’ | × | × | 2 | ||||||||||||
| Evaluating | × | × | 2 | ||||||||||||
| Word processing | × | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Reading | × | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Functional (reading and understanding) | × | × | × | 3 | |||||||||||
| Needs for assistance | × | × | 2 | ||||||||||||
| Total dimensions | 6 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 7 | 2 | 2 |
Results
In reviewing the 14 papers for Table 1, we discovered some common literacy dimensions used in both health literacy and e-health literacy assessment. For example, the Chinese Health Literacy Scale for Diabetes (CHLSD), developed by Leung et al. [22] for China’s population, adapted other gold-standard scales such TOFHLA to measure the ‘understanding’ and ‘applying’ aspects of literacy. Another study by Garcia-Marcinkiewicz et al. [23] measured health literacy among patients who had undergone anesthesia, in terms of confidence, usefulness and understanding. Garcia-Marcinkiewicz used a variety of Likert scales, such as ‘disagree/agree’ and ‘never/frequently’.
Our selected papers also included a study done in Taiwan by Chang et al. [13], which measured media literacy as it related to tobacco and alcohol use. We adapted the media literacy dimension used by Chang et al., since patients may receive health information from media content such as YouTube, educational videos or WebTV.
An important study in health literacy by Nutbeam, Paakkari and Paakkari, and Ishikawa [11, 12] used three literacy dimensions: functional, communicative and critical. Functional literacy deals with word recognition and comprehension, communicative literacy deals with how patients understand and communicate information about their disease to others, and critical literacy refers to how patients analyze information and make decisions about their disease.
Xie [21] investigated the use of the e-heals scale to measure e-health literacy. E-heals was introduced by Skinner [24] as the gold standard for measuring e-health literacy. The e-heals scale measures patients’ perceived skills and level of comfort using the Internet for health information. Follow-up studies by Watkins, van der Vaart et al. and Xie [17, 20, 21] expanded the exploration of e-health literacy into various health specialties. Another gold standard in health literacy, the single item literacy skills (SILS), was adapted by Peiravian et al. [25] to measure drug literacy among the Iranian public.
Discussions
Based on the selected papers, we chose four literacy dimensions for our SeHL scale:
Use of technology/media: This dimension asks patients how fast they learn to navigate websites and how often they make mistakes when using a web page. Follow-up questions measure how often they see chronic illnesses represented in various media on the Internet.
Information seeking: This dimension explores what information patients find, how and where they find it, and asks their preferences regarding obtaining information about health. Many of the items included in this section come from the e-heals scale.
Understanding/usefulness: This dimension asks patients how useful the information is to them and whether they have difficulty understanding the information given.
Confidence/needs assistance: This dimension measures how confident patients are in filling out forms and whether they need any assistance with reading and understanding the materials given to them at the hospital.
Our effort to develop SeHL is consistent with a recent study by Bautista and Wee [26] that suggests researchers should define the operational measure for e-health literacy and measure the validity and reliability of e-health literacy scales.
Conclusions and Future Research
To conduct a large-scale study on health education regarding NCDs in Saudi Arabia and other Arabic-speaking countries, we needed to develop an e-health literacy scale suitable for our objectives and context. We were able to aggregate a scale that measures e-health literacy based on four dimensions: decision making, information seeking, confidence, and use of media and technology. We did this by reviewing previous studies in health literacy and e-health literacy and by conducting workshops to propose a new scale suitable for measuring e-health literacy levels among the Saudi population. This study may later be extended to other Arabic-speaking countries, in which no e-health literacy research has been previously done. There are 25 Arabic-speaking countries, which represent a total population of ~400 million.
One study published by Giacaman et al. [27] found a high level of health literacy in Israeli-occupied Palestinian areas as compared to several Arab countries, but no measurements of e-health literacy were conducted. Besides the research noting the lack of an available scale, no major work has been done towards measuring e-health literacy at the population level in Saudi Arabia. The World Fact Website states that basic literacy (reading and writing) levels in Saudi Arabia are 87% (compared to the United States with 99%). However, e-health literacy—defined as the ability to read, write and understand health information using the Internet and other IT—is only 8% in the USA [10]. No other nation has reported its e-health literacy at the population level. The development of SeHL will contribute to our knowledge of e-health literacy as it relates to NCDs in the Saudi population. The national study that will be conducted in Saudi Arabia can help determine the prevalence of e-health literacy among patients with NCD. In terms of the public health field, this e-health literacy research can help organization build a better patient education system that would promote prevention of NCDs.
This study also analyzed literacy dimensions identified in other well-known scales in AlSayah et al. [15] and found that some of these tools cannot be applied directly in our context. The integration of several available scales was important to ensure that we accurately measure technology, information, and uses of health information for patients.
The limitation of the study is that our literature review looked only at publications and scales written in English. We may have therefore missed some important scales created in other languages. Future work will involve conducting focus groups with experts to finalize the SeHL, and test the new scale’s validity and reliability with patients suffering from NCDs at King Khalid University Hospital, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Appendix
Saudi E-health literacy (SeHL) prototype in English
Decision making (understanding and usefulness)
a. How useful is it for you to receive information about chronic illness?
Extremely
Quite a bit
Somewhat
A little bit
Not at all
b. It would be useful to receive information about chronic illness provided through an educational website.
Strongly agree
Agree
Neutral
Disagree
Strongly disagree
c. It would be useful to receive information about chronic illness provided in video format.
Strongly agree
Agree
Neutral
Disagree
Strongly disagree
d. How often do you have difficulty understanding written information about your medical condition on the Internet?
Always
Often
Sometimes
Occasionally
Never
Confidence/need for assistance
a. How confident are you in filling out medical forms?
Extremely
Quite a bit
Somewhat
A little bit
Not at all
b. How confident are you that you are able to follow the instructions given on a medication label?
Extremely
Quite a bit
Somewhat
A little bit
Not at all
c. How often do you have someone else (a family member, friend, hospital or clinic worker, or caregiver) help you read health materials, such as written information given to you about your health or care?
Always
Often
Sometimes
Occasionally
Never
d. How often do you need to have someone help you read instructions, pamphlets, or other written material from your doctor or pharmacy?
Always
Often
Sometimes
Occasionally
Never
Health information seeking
a. Do you know how to find specific web pages or helpful health resources on the Internet?
Yes
No
b. Do you know how to search [diabetes]?
Yes
No
c. Do you know how to find the symptoms for [diabetes]?
Yes
No
d. How do you prefer to read health information?
Media (e.g. audio, video) (film)
Print material
Internet
Lecture/seminar/workshop
Medical professionals
Using technology and use of media
a. How quickly can you learn to use a website?
Very quickly
Quickly
Neither quickly nor slowly
Slowly
Very slowly
b. How often do you make mistakes when using computer?
Always
Often
Sometimes
Occasionally
Never
C. During the past year, how often did you see the following:
i. advertisement for medication for chronic illness (diabetes, cardiovascular or hypertension) on TV?
Always
Often
Sometimes
Occasionally
Never
ii. advertisement for medication for chronic illness (diabetes, cardiovascular or hypertension) in newspapers or magazines?
Always
Often
Sometimes
Occasionally
Never
iii. Public health campaign for chronic illness (diabetes, cardiovascular or hypertension) on talk shows, or on outdoor billboards?
Always
Often
Sometimes
Occasionally
Never
iv. Characters with chronic illnesses (diabetes, cardiovascular or hypertension) on television or in movies or films?
Never
Always
Often
Sometimes
Occasionally
Never
v. Discussions of chronic illnesses (diabetes, cardiovascular or hypertension) on the Internet?
Always
Often
Sometimes
Occasionally
Never
Saudi E-health literacy (SeHL) prototype in Arabic
اتخاذ القرار (الفهم, الاستفادة)
ا. ما مدى الاستفادة بالنسبة لك عند تلقي معلومات عن الامراض المزمنة
مرتفعة جدا
مرتفعة
متوسطة
قليلة
لا يوجد
ب. سيكون من المفيد تلقي معلومات عن الامراض المزمنة من خلال موقع الكتروني تعليمي
اتفق بشدة
اتفق
محايد
لا اتفق
لا اتفق بشدة
ج. سيكون من المفيد تلقي معلومات عن الامراض المزمنة من خلال عرضها على شريط الفيديو
اتفق بشدة
اتفق
محايد
لا اتفق
لا اتفق بشدة
د. هل واجهت صعوبات في فهم معلومات مكتوبة عن حالتك الطبية علي الأنترنت
دائما
غالبا
احيانا
نادرا
ابدا
ثقه بالنفس – الحاجة لمساعدة
ا. ما مدى ثقتك بنفسك عند تعبئة نموذج طبي
مرتفعة جدا
مرتفعة
متوسطة
قليلة
لا يوجد
ب. ما مدى ثقتك بقدرتك على اتباع التعليمات الموجودة على طابع الدواء
مرتفعة جدا
مرتفعة
متوسطة
قليلة
لا يوجد
ج. الى أي مدى احتجت مساعدة شخص اخر (مثال: فرد من العائلة، صديق، موظف في عيادة او مستشفى، مسؤول صحي) لقراءة المواد الصحية، مثل المعلومات المكتوبة عن حالتك الصحية
دائما
غالبا
احيانا
نادرا
ابدا
د. الى أي مدى تطلب مساعدة شخص اخر لقراءة التعليمات، كتيبات او أي محتوى كتابي من طبيبك المعالج او الصيدلي
دائما
غالبا
احيانا
نادرا
ابدا
البحث عن المعلومات الصحية
ا. هل تعلم كيف تجد صفحة الكترونية معينة او موارد صحية مفيدة من (الانترنت)
نعم
لا
ب. هل تعلم كيف تبحث عن مرض (السكري)
نعم
لا
ج. هل تعلم كيف تبحث عن الاعراضالخاصة بمرض السكري
نعم
لا
د .من خلال أي من الطرق التالية تفضل قراءة المعلومات الصحية
المجال الاعلامي (مثال راديو او فيلم)
مواد مطبوعة
الإنترنت
محاضرات/ مؤتمرات/ ورش عمل
مباشرة من خلال الاخصائ الصحي
استخدام تقنيه المعلومات و المجال الاعلامي
ا. ما مدى سرعتك في تعلم استخدام المواقع الكترونية علي الانترنت
سريع جدا
سريع
متوسط
بطئ
بطئ جدا
ب. ما مدى ارتكابك للأخطاء عند استخدام الحاسب الألي (الكمبيوتر)
دائما
غالبا
احيانا
نادرا
ابدا
ج. خلال السنه الماضية إلى أي مدى شاهدت التالي:
اعلانات عن أدوية للأمراض المزمنة (سكري، امراض القلب او ارتفاع ضغط الدم) على التلفاز
دائما
غالبا
احيانا
نادرا
ابدا
اعلانات عن أدوية للأمراض المزمنة (سكري، امراض القلب او ارتفاع ضغط الدم) على الصحف او المجلات
دائما
غالبا
احيانا
نادرا
ابدا
حملات صحية عامة عن أدوية للأمراض المزمنة (سكري، امراض القلب او ارتفاع ضغط الدم) على البرامج الحوارية او اللوحات الإعلانية
دائما
غالبا
احيانا
نادرا
ابدا
شخصيات تمثيلية مصابة بالأمراض المزمنة (سكري، امراض القلب او ارتفاع ضغط الدم) على التلفاز او في الأفلام
دائما
غالبا
احيانا
نادرا
ابدا
نقاشات عن الأمراض المزمنة (سكري، امراض القلب او ارتفاع ضغط الدم) في الإنترنت
دائما
غالبا
احيانا
نادرا
ابدا
Funding
This Project was funded by the National Plan for Science, Technology and Innovation (MAARIFAH), King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Award Number (Med 2121-02-11)
References
- 1. Haun J. What Skills Should be Included when Assessing Health Literacy?2003; Online lecture. Available from: http://www.bumc.bu.edu/healthliteracyconference/files/2012/08/Haun_10_22_2012.pdf
- 2. WHO Noncommunicable Diseases (NCD) Country Profiles 2014.
- 3. WHO Global Report on Diabetes Executive Summary [Internet] 2016. Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/204874/1/WHO_NMH_NVI_16.3_eng.pdf?ua=1
- 4. Technology T and I. ICT Indicators in KSA [Internet] 2015. Available from: http://www.mcit.gov.sa/En/aboutmcit/sectordevelopment/pages/sectorindices.aspx
- 5. Albarrak AI, Mohammed R, Zakaria N et al. The impact of obesity related websites on decision making among students in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Pharm J [Internet] 2015. Available from: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1319016415000791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. WebMD [Internet] 2016. Available from: http://www.webmd.com/
- 7. Center for Disease Control and Prevention [Internet] 2016. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/
- 8. Ishikawa H, Takeuchi T, Yano E. Measuring functional, communicative, and critical health literacy among diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2008;31:874–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Chan CV. A framework for characterizing eHealth literacy demands and barriers. J Med Internet Res [Internet] 2011;13:e94 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22094891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Chew F. Developing a new scale for e-health literacy. Medicine 2014;20. [Google Scholar]
- 11. Nutbeam D. Health literacy as a public health goal: a challenge for contemporary health education and communication strategies into the 21st century. Health Promot Int [Internet]. 2000;15:259–67. Available from: http://heapro.oxfordjournals.org/content/15/3/259. [Google Scholar]
- 12. Paakkari L, Paakkari Olli. Health literacy as a learning outcome in schools. Health Educ 1992;112:133–52. [Google Scholar]
- 13. Chang FC, Miao NF, Lee CM et al. The association of medical exposure and media literacy with adolescent alcohol and tobacco use. J Health Psychol [Internet]. 2014; http://hpq.sagepub.com/cgi/doi/10.1177/1359105314530451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Kim SH, Lee A. Health-literacy-sensitive diabetes self-management interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World Views Evid based Nurs 2016;13:324–33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. AlSayah F, Williams B, Johnson J. Measuring health literacy in individuals with diabetes: a systematic review and evaluation of available measures. Health Educ Behav [Internet] 2012;40:42–55. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22491040. Feb [cited 2014 Dec 5]. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Boren S. A review of health literacy and diabetes: opportunities for technology. J Diabetes Sci Technol [Internet] 2009;3:202–9. Available from: http://dst.sagepub.com/lookup/doi/10.1177/193229680900300124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Watkins BBX. eHealth literacy interventions for older adults: a systematic review of the literature [Internet]. J Med Internet Res 2014;16:e225 Available from: http://www.jmir.org/2014/11/e225#ref16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. McCormack L, Bann C, Squiers L et al. Measuring health literacy: a pilot study of a new skills-based instrument. J Heal Commun [Internet] 2010;15:51–71. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20845193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Xie B. Experimenting on the impact of learning methods and information presentation channels on older adults’ e-health literacy. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol [Internet] 2011;62:1797–807. Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/asi.21575. [Google Scholar]
- 20. van der Vaart R, van Deursen AJ, Drossaert CH et al. Does the eHealth Literacy Scale (eHEALS) measure what it intends to measure? Validation of a Dutch version of the eHEALS in two adult populations. J Med Internet Res [Internet] 2011;13:e86 Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3222202&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract. [cited 2014 Dec 5]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Xie B. Older adults, e-health literacy, and collaborative learning: an experimental study. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol [Internet] 2011;62:933–46. Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/asi.21507. [Google Scholar]
- 22. Leung AYM, Lou VWQ, Cheung MKT et al. Development and validation of Chinese Health Literacy Scale for Diabetes. J Clin Nurs [Internet] 2013;22:2090–9. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23186320. [cited 2015 Jan 17]. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Garcia-Marcinkiewicz AG, Long TR, Danielson DR et al. Health literacy and anesthesia: patients’ knowledge of anesthesiologist roles and information desired in the preoperative visit. J Clin Anesth 2014;26:375–82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Cameron N, Skinner H. eHealth literacy: essential skills for consumer health in a networked world. J Med Internet Res 2006;8:e9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Peiravian F, Rasekh HR, Hashemi HJ et al. Drug literacy in Iran: the experience of using ‘the single item health literacy screening (SILS) tool. Iran J Pharm Res 2014;13:217–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Bautista JR, Wee WK. From solving a health problem to achieving quality of life: redefining eHealth literacy. J Lit Technol [Internet] 2015;16:33–54. Available from: http://www.literacyandtechnology.org/uploads/1/3/6/8/136889/jlt_v16_2_bautista.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 27. Giacaman R, Khatib R, Shabaneh L et al. Health status and health services in the occupied Palestinian territory. Lancet 2009;373:837–49. [Google Scholar]
- 28. Lee SD, Tsai T, Tsai Y et al. Health literacy and women’s health-related behaviors in Taiwan. Heal Educ Behav 2012;39:210–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. van der Vaart R, Drossaert CHC, de Heus M et al. Measuring actual eHealth literacy among patients with rheumatic diseases: a qualitative analysis of problems encountered using Health 1.0 and Health 2.0 applications. J Med Internet Res [Internet] 2013;15:e27 Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3636295&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract. [cited 2015 Jan 5]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Xie B. Effects of an eHealth literacy intervention for older adults. J Med Internet Res 2011;13:1–26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Park H, Moon M, Baeg JH. Association of eHealth literacy with cancer information seeking and prior experience with cancer screening. Comput Inform Nurs [Internet] 2014;32:458–63. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25105588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Kim S, Love F, Quistberg D et al. Association of health literacy with self-management behavior in patients with. Diabetes Care 2004;27:2980–2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Nath C. Literacy and diabetes self-management. Am J Nurs 2007;107:43–9. quiz 49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. AlSayah F, Williams B, Pederson JL et al. Health literacy and nurses’ communication with type 2 diabetes patients in primary care settings. Nurs Res [Internet] 2014;63:408–17. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25350540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]