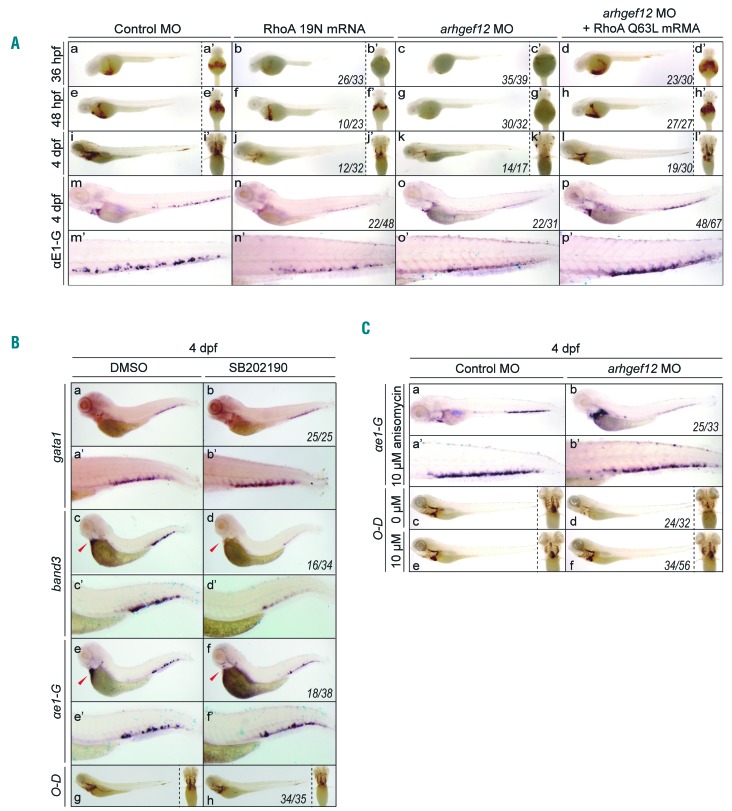
Figure 4.
arhgef12 regulates erythroid differentiation through RhoA and p38. (A) O-Dianisidine staining results at 36hpf, 48hpf and 4dpf of embryos injected with control morpholino (MO), RhoA 19N mRNA, arhgef12a and arhgef12b MO, RhoA Q63L mRNA co-injected with arhgef12a and arhgef12b MO (a-l). Yolk sac ventral views of the indicated microinjected embryos (a’-l’). Whole-mount in situ hybridization (WISH) results of ae1-globin in the indicated microinjected embryos at 4dpf (m-p) and the corresponding magnifications of CHT (m’-p’). (B) WISH results of gata1, band3, ae1-globin (a-f) and the corresponding magnifications of CHT (a’-f’) in control (dimethyl sulfoxide, DMSO) and SB202190 (the inhibitor of p38) treated embryos at 4 dpf. O-Dianisidine (O-D) staining results at 4dpf (g, h) with the corresponding ventral view on the right. (C) WISH results of ae1-globin in control or arhgef12a and arhgef12b MO injected embryos with anisomycin (activator of p38) treatment (a, b) and the corresponding magnifications of CHT (a’-b’). O-D staining results of control or arhgef12a and arhgef12b MO injected embryos with DMSO (c, d) or 10uM anisomycin (e, f) treatment (the corresponding ventral view on the right) showed anisomycin could rescue the blocked erythroid differentiation in the morphants at 4dpf. The indicated embryos were treated by DMSO (labeled by 0uM) and anisomycin (labeled by 10uM) for 24 hours (from 3dpf to 4dpf).