Abstract
Viral replication and capsid assembly in the viruses in the order Picornavirales requires polyprotein proteolytic processing by 3C or 3C-like (3CL) proteases. We identified and characterized the 3CL protease of Ectropis obliqua virus (EoV) of the newly established family Iflaviridae (order Picornavirales). The bacterially expressed EoV 3CL protease domain autocatalytically released itself from larger precursors by proteolytic cleavage, and cleavage sites were determined via N-terminal sequencing of the cleavage products. This protease also mediated trans-proteolytic activity and cleaved the polyprotein at the same specific positions. Moreover, we determined the critical catalytic residues (H2261, D2299, C2383) for the protease activity, and characterized the biochemical properties of EoV 3CL and its responses to various protease inhibitors. Our work is the first study to identify an iflaviral 3CL protease and further characterize it in detail and should foster our understanding of EoV and other iflaviruses.
Keywords: Ectropis obliqua virus, Iflavirus, Picornavirales, 3C-like protease, Autocatalytic polyprotein processing, Cleavage sites, Trans cleavage
Introduction
The order Picornavirales comprises five families of positive-strand RNA viruses (Dicistroviridae, Picornaviridae, Marnaviridae, Secoviridae, and Iflaviridae) that share several common features. Their polyproteins contain a conservative helicase–protease–polymerase (Hel–Pro–Pol) module of core replication domains and capsid proteins (CPs) (Le Gall et al., 2008). These groups of small single-stranded RNA viruses infect different vertebrate, invertebrate, and plant hosts and are responsible for a variety of human, animal, and plant diseases.
The proteolytic processing of viral polyproteins is a crucial step in genome replication and CPs assembly in the order Picornavirales, whose genome generally translates a large precursor polyprotein. After translation, the viral precursor polyprotein is proteolytically cleaved to generate mature functional viral proteins (Dougherty and Semler, 1993). This maturation process is usually mediated by (more than one) proteases, and a 3C (for the family Picornaviridae) or 3C-like (3CL) protease (for other families) plays a central role in the cleavage of the viral precursor polyprotein (Le Gall et al., 2008, Palmenberg, 1990). To date, 3C and 3CL proteases have been extensively studied in several viruses in the order Picornavirales, particularly hepatitis A virus (HAV), poliovirus (PV), human rhinovirus (HRV), encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV), human enterovirus 71 (EV71), and foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) in the family Picornaviridae (Bablanian and Grubman, 1993, Bonderoff et al., 2008, de Breyne et al., 2008, Ghildyal et al., 2009, Goodwin et al., 2009, Harmon et al., 1992, Lawson et al., 1999, Lu et al., 2011, Rivera and Lloyd, 2008). Furthermore, the crystallographic structures of picornaviral 3C proteases from HRV, HAV, FMDV, and EV71 have been determined, which facilitates the identification of the active sites of these 3C proteases. The functional and structural studies of 3C or 3CL proteases have revealed that most of them are cysteine proteases and contain the chymotrypsin (two β-barrel) fold; therefore, they are also called “chymotrypsin-like proteases” (CHLPro) (Allaire et al., 1994, Cui et al., 2011, Gorbalenya et al., 1986, Malcolm, 1995, Matthews et al., 1994, Sweeney et al., 2007).
Within the order Picornavirales, the family Iflaviridae is a new member classified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2009) (http://www.ictvonline.org/virusTaxonomy.asp?version=2009) and this family currently includes the sole genus Iflavirus (Christian et al., 2005, van Oers, 2010). In addition, the viral structure and genomic organization of iflaviruses are quite similar to those of the viruses of the family Picornaviridae (Le Gall et al., 2008). Ectropis obliqua virus (EoV) was initially identified by our group in 2000 and was classified as a member of the Iflaviridae family in January 2010 (van Oers, 2010, Wang et al., 2004). EoV is an insect positive-strand RNA virus that leads to a lethal granulosis infection in the larvae of the tea looper (Ectropis obliqua), which is an important agricultural pest that can seriously damage tea leaves. To date, the genomic RNA of EoV has been cloned as full-length cDNA and completely sequenced. The genome of EoV consists of 9394 nucleotides (nts) excluding the poly(A) tail and contains a single large open reading frame (nt 391–9351) encoding a polyprotein of 2987 amino acids. In this polyprotein, structural and nonstructural proteins are located at its N- and C-terminal regions respectively, and the conservative Hel–Pro–Pol and CPs domains have been identified as well ( Fig. 1A) (Wang et al., 2004). In the 5′ untranslated region (5′ UTR), an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) has been shown to play an essential role in mediating EoV cap-independent translation (Lu et al., 2007, Lu et al., 2006). The RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) activity of EoV has also been identified (Lin et al., 2010). In addition to EoV, the family Iflaviridae comprises other invertebrate viruses, such as infectious flacherie virus (IFV) of the silkworm, Sacbrood virus (SBV) of the honeybee, Perina nuda virus (PnV), deformed wing virus (DWV), and Varroa destructor virus-1 (VDV-1), as well as some tentative members like slow bee paralysis virus (SBPV) and Nasonia vitripens virus (NvV) (Christian et al., 2005, van Oers, 2010).
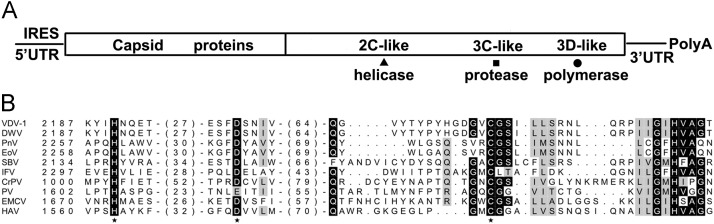
Fig. 1.
(A) The map of the EoV genome. The long box represents the single open reading frame with different conserved protein domains as indicated. (B) The amino acid sequence alignment of the putative 3CL protease domain of EoV compared with those of the other iflaviruses (VDV-1, DWV, SBV, PnV, and IFV), cripavirus (CrPV), and three picornaviruses (PV, ECMV, and HAV) Multiple sequence alignments were generated using ClustalX. The genomic position of the first amino acid of each aligned sequence is indicated, with those of partial sequences shown in brackets and the conserved amino acids identified by asterisks.
On the basis of the amino acid sequences, putative cysteine 3CL protease domains have been predicted in all the members of the family Iflaviridae (Ghosh et al., 1999, Isawa et al., 1998, Lanzi et al., 2006, Ongus et al., 2004, Wang et al., 2004, Wu et al., 2002). The putative EoV cysteine protease motif GXCG is located in the C-terminal half of the polyprotein precursor, upstream of the RdRp domain, and the putative catalytic triad of H2261, D2299, and C2383 is also conserved in EoV and other iflaviruses (Fig. 1B) (Wang et al., 2004). Despite the importance of 3C and 3CL proteases in viruses in the order Picornavirales (Le Gall et al., 2008), 3CL protease activity in iflaviruses has not been formally determined, and consequently, the molecular mechanisms of 3CL-mediated cleavage of iflaviral polyproteins have not yet been studied, which significantly limits our understanding of this new family.
In this study, we identified EoV 3CL as a cysteine protease and confirmed that the EoV 3CL protease can be released autocatalytically from the polyprotein in the form of a 34 kDa protein and exhibits specific trans-cleavage activity. Moreover, via N-terminal sequencing and mutational analyses, we have defined the cleavage sites of the EoV 3CL protease, determined the catalytic residues that are critical for its activity, and characterized its biochemical properties and responses to various protease inhibitors. Our study not only represents a crucial step toward understanding the mechanism of EoV polyprotein proteolytic processing, but also suggests future directions for the study of 3CL proteases, polyprotein processing, and viral replication of other iflaviruses.
Results
Autocatalytic processing activity of EoV 3CL protease in E. coli
To determine whether the putative EoV 3CL protease domain can autocatalytically release itself from flanking domains, we expressed the two fusion proteins, His-Pro2160–2680-Flag and His-Pro2026–2738-Flag, which contain amino acids 2160–2680 and 2026–2738 of the EoV polyprotein, respectively ( Fig. 2A). Both fragments covered the entire putative 3CL protease region as well as various portions of the neighboring domains. They were linked to the pET32a vector with a His-tag at the N-terminus and an inserted Flag-tag at the C-terminus. After being expressed in E. coli, the proteins were then subjected to Western blot analyses with various antibodies.
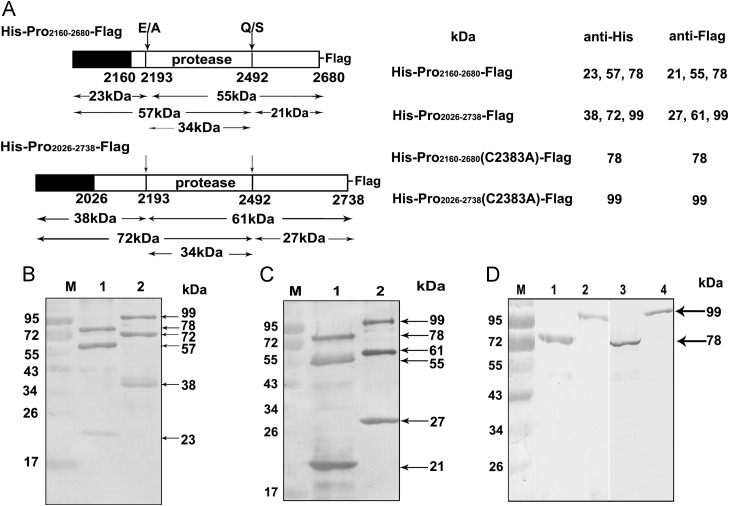
Fig. 2.
Cleavage activity of the putative EoV 3CL protease. (A) Left: Schematic illustrations of the recombinant fusion proteins His-Pro2160–2680-Flag and His-Pro2026–2738-Flag and their site-specific mutants His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(C2383A) and His-Pro2026–2738-Flag(C2383A). The fusion proteins are depicted as bars. Arrows point to the putative boundaries of each cleavage product, and amino acid pairs probably forming processing sites with the numbers representing the positions indicated below the bars. The molecular weights of the cleavage products are indicated between the arrows. Right: The fusion proteins and their cleavage products were subjected to 12% SDS-PAGE and then Western blot analysis with anti-His or anti-Flag monoclonal antibody. The molecular weights of the detected cleavage products are indicated below the primary antibodies (anti-His and anti-Flag). (B) Western blots with anti-His antibody. Lane M, molecular weight marker; Lane 1, His-Pro2160–2680-Flag; Lane 2, His-Pro2026–2738-Flag. (C) Western blots with anti-Flag antibody. Lane M, molecular weight marker; Lane 1, His-Pro2160–2680-Flag; Lane 2, His-Pro2026–2738-Flag. (D) Western blots with the mutants. Lane M, molecular weight marker; Lane 1, His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(C2383A); Lane 2, His-Pro2026–2738-Flag(C2383A); Lane 3, His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(C2383A); Lane 4, His-Pro2026–2738-Flag (C2383A). Lanes 1 and 2 were blotted with anti-His antibody, and lanes 3 and 4 were blotted with anti-Flag antibody.
Western blotting with anti-His monoclonal antibody revealed an approximately 78-kDa band corresponding to the intact His-Pro2160–2680-Flag in addition to two cleavage products of around 23 kDa and 57 kDa (Fig. 2B, lane 1). Meanwhile, we observed an approximately 99-kDa band corresponding to the intact His-Pro2026–2738-Flag fusion protein as well as two more bands around 38 kDa and 72 kDa (Fig. 2B, lane 2). The cleavage products of His-Pro2160–2680-Flag and His-Pro2026–2738-Flag with molecular weights of around 23 kDa and 38 kDa, respectively, were presented in relatively smaller amounts than other proteins, and are believed to be the products that were autocatalytically cleaved from the N-terminal of the putative 3CL protease region in both His-Pro2160–2680-Flag and His-Pro2026–2738-Flag fusion proteins. Of note, both fusion proteins included a 19-kDa amino acid sequence from the pET32a vector (Fig. 2A, black box). On the other hand, the 57-kDa and 72-kDa protein bands should correspond to the C-terminal cleavage products of both fusion proteins. The detection of intact His-Pro2160–2680-Flag and His-Pro2026–2738-Flag proteins (around 78 kDa and 99 kDa, respectively) in these experiments indicates that cleavage of the proteins was not completed.
The cleavage products were also examined via Western blotting with anti-Flag monoclonal antibody. In addition to the intact fusion proteins (around 78 kDa and 99 kDa), two cleavage products of around 55 kDa and 21 kDa were observed for His-Pro2160–2680-Flag (Fig. 2C, Lane 1), while for His-Pro2026–2738-Flag, two cleavage products of around 61 kDa and 27 kDa were clearly detected (Fig. 2C, lane 2). The 21-kDa and 27-kDa bands should be the C-terminal cleavage products of His-Pro2160–2680-Flag and His-Pro2026–2738-Flag, respectively, whereas the 55-kDa and 61-kDa bands should be the cleavage products from the N-terminal of the putative 3CL protease region (Fig. 2A).
Moreover, to exclude the possibility that the cleavage of both fusion proteins was mediated by any bacterially derived protease, the putative core conserved active residue GXC(2383)G (Fig. 1B) was mutated to GXA(2383)G, which was expected to abolish the processing activity of a 3CL protease. The mutants His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(C2383A) and His-Pro2026–2738-Flag(C2383A) could not undergo any autocatalytic cleavage, as the Western blots with both anti-His and anti-Flag antibodies revealed only the intact fusion proteins at their expected molecular weights (i.e., 78 kDa and 99 kDa respectively) (Fig. 1D, lanes 1–4). Taken together, these results indicate that EoV 3CL can release itself from neighboring domains via the localization of 3CL protease activity in the putative EoV 3CL region, and the predicted catalytic residue C(2383) is indispensable for the proteolytic activity.
Further confirmation of the cleavage activity of EoV 3CL via anti-3CL polyclonal antibodies
To further confirm the cleavage activity of EoV 3CL, we examined its autocatalytic processing using antibodies that specifically recognized the EoV 3CL protease. The EoV 3CL-specific polyclonal antibodies were obtained by immunizing rabbit with purified His-tagged 3CL-His fusion protein, which contains the C-terminal 6xHis tag and the predicted complete EoV 3CL region without any extra amino acids ( Fig. 3A, upper portion: 3CL-His). As shown in Fig. 3B (lane 3), the purity of 3CL-His fusion protein purified via nickel–nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni–NTA) was also assessed via sodium dodecyl polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE).
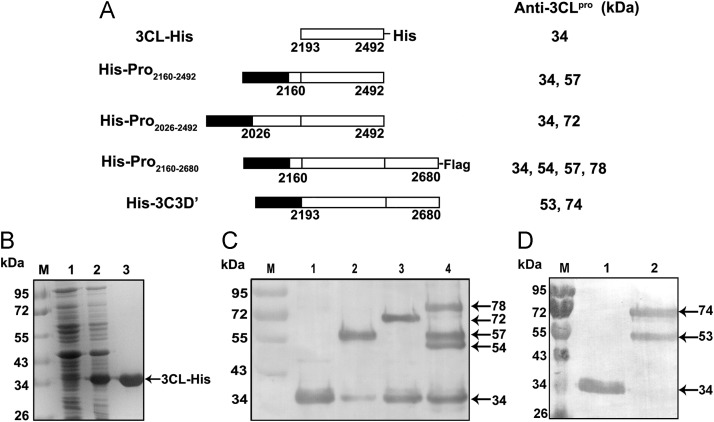
Fig. 3.
Expression and purification of 3CL-His and confirmation of the cleavage activity of EoV 3CL via anti-3CL polyclonal antibodies. (A) Schematic illustrations of the recombinant fusion proteins 3CL-His, His-Pro2160–2492, His-Pro2026–2492, His-Pro2160–2680-Flag and His-3C3D′. The fusion proteins are depicted as bars. The molecular weights of the cleavage products detected with anti-3CL polyclonal antibodies are indicated. (B) Expression and purification of 3CL-His. Lane M, molecular weight markers; Lane 1, uninduced cell lysate; Lane 2, induced cell lysate; Lane 3, purified 3CL-His. The position of overexpressed 34-kDa 3CL-His is shown. (C) The different fusion proteins 3CL-His (Lane 1), His-Pro2160–2492 (Lane 2), His-Pro2026–2492 (Lane 3), and His-Pro2160–2680-Flag (Lane 4) were subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-3CL polyclonal antibodies. Lane M, molecular weight marker. (D) The fusion proteins 3CL-His (Lane 1) and His-3C3D′ were subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-3CL polyclonal antibodies. Lane M, molecular weight marker.
To examine the cleavage activity of EoV 3CL, we expressed four different fusion proteins, His-Pro2160–2492, His-Pro2026–2492, His-3C3D′ and His-Pro2160–2680-Flag in E. coli. All four fusion proteins contained the entire 3CL region; both His-Pro2160–2492 and His-Pro2026–2492 included one predicted cleavage site at the N-terminal of EoV 3CL, His-3C3D′ included one predicted cleavage site at the C-terminal of EoV 3CL, whereas His-Pro2160–2680-Flag contained the two predicted cleavage sites at both N- and C-terminals (Fig. 3A). Western blot analyses using anti-3CL polyclonal antibodies revealed that His-Pro2160–2492 was processed into two products, a 57-kDa band corresponding to the intact His-Pro2160–2492 and a 34-kDa band corresponding to the predicted 3CL protease (Fig. 3C, lane 2). Similarly, His-Pro2026–2492 was processed into two products that corresponded to the intact His-Pro2026–2492 (72 kDa) and the 3CL protease (34 kDa) (Fig. 3C, lane 3).
On the other hand, the bacterial expression of His-Pro2160–2680-Flag yielded four protein bands. In addition to the intact fusion protein (78 kDa), the 54-kDa and 57-kDa band corresponded to the cleavage product generated from the single cleavage at the N- or C-terminal of the 3CL domain, respectively, and the 34-kDa band corresponded to the cleavage product generated from the double cleavage at both the N- and C-terminals of the 3CL domain (Fig. 3C, lane 4). The bacterial expression of all three recombinant fusion proteins yielded the 34-kDa products that apparently corresponded to 3CL protease. In addition, the His-3C3D′ was processed into two products. The 74-kDa band corresponded to the intact His-3C3D′, while the 53-kDa band corresponded to the cleavage product generated from the single cleavage at the C-terminal of the 3CL domain (Fig. 3D, lane 2). Taken together, these results confirm the autocatalytic processing activity of the EoV 3CL protease and further indicate the size of EoV 3CL.
Critical catalytic sites of the EoV 3CL protease as determined via mutational analyses
The EoV 3CL protease has been proposed to be a cysteine protease containing the catalytic triad of H2261, D2299, and C2383, which is conserved in the Iflaviridae family (Fig. 1B). To determine whether these conserved residues are responsible for the autocatalytic processing of the EoV polyprotein, we expressed the wild-type fusion protein His-Pro2026–2492 and its mutants His-Pro2026–2492(H2261A), His-Pro2026–2492(C2383A), and His-Pro2026–2492(D2299A) in E. coli ( Fig. 4A) and then subjected them to Western blot analyses with anti-3CL polyclonal antibodies.
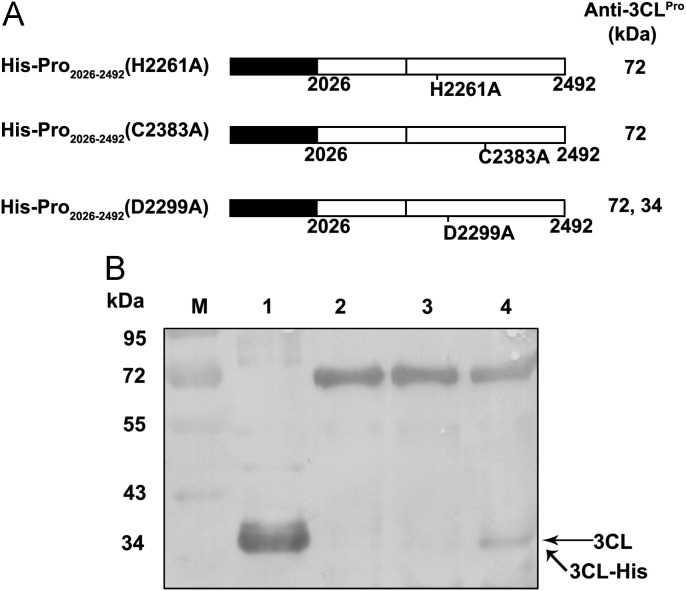
Fig. 4.
Mutational analysis of the predicted catalytic sites for EoV 3CL protease activity. (A) The fusion proteins are depicted as bars. The sites for point mutations are indicated. (B) The fusion proteins were subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-3CL polyclonal antibodies. Lane M, molecular weight marker; Lane 1, 3CL-His; Lane 2, His-Pro2026–2492(C2383-A); Lane 3, His-Pro2026–2492(H2261-A); Lane 4 His-Pro2026–2492(D2299-A). The positions for 3CL and 3CL-His are indicated.
Compared with the wild-type His-Pro2026–2492 (Fig. 3C, lane 3), only one 72-kDa band at the expected molecular weight of the intact His-Pro2026–2492(H2261A) or His-Pro2026–2492(C2383A) was observed (Fig. 4B, lanes 2 and 3), indicating that the substitution of H2261 or C2383 with alanine (A) could abolish the cleavage activity of the EoV 3CL protease. These experiments were independently repeated several times with extended reaction or exposure time, and the same results were obtained (data not shown). Interestingly, the autocatalytic processing activity of His-Pro2026–2492(D2299A) was much weaker than that of wild-type His-Pro2026–2492 (Fig. 4B, lane 4 vs. Fig. 3C, lane 3), indicating that the D2299A substitution inhibits but does not abolish the protease activity of EoV 3CL. The mutagenesis analyses of the EoV 3CL protease showed that the conserved H2261, D2299, and C2383 play critical roles in EoV 3CL protease activity and provided further confirmation of the cleavage activity of EoV 3CL.
Determination of the cleavage sites of EoV 3CL via N-terminal sequencing analyses
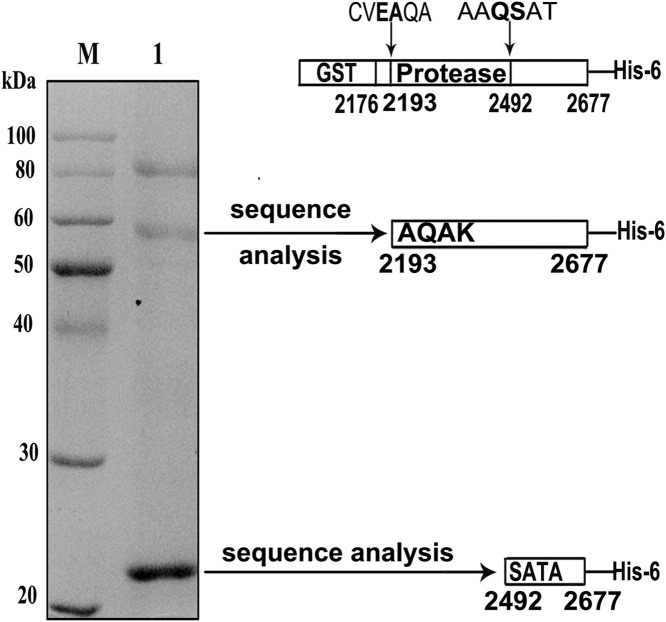
To further characterize the proteolytic activity of the EoV 3CL protease, we sought to determine the exact location of its cleavage sites. To this end, the fusion protein GST-Pro2176–2677-His, which contains amino acids 2176–2677 and covers the complete 3CL domain and flanking sequences with both cleavage sites, was expressed ( Fig. 5). After bacterial expression and purification for His fusion protein via Ni–NTA, the purified products were separated via SDS-PAGE. Three proteins with molecular weights of 82 kDa, 56 kDa, and 21 kDa were readily detected (Fig. 5, lane 1). The 82-kDa band corresponded to the intact fusion protein GST-Pro2176–2677-His, whereas the 56-kDa and 21-kDa bands corresponded to the products cleaved at the N- and C-terminals of the 3CL protease domain, respectively. The purified cleavage products were then subjected to N-terminal amino acid sequencing analyses.
Fig. 5.
Determination of the cleavage sites of the EoV 3CL protease via N-terminal sequencing. The fusion protein GST-Pro2176–2677-His was expressed in E. coli and then purified. The fusion protein and its cleavage products were separated on 12% SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. Lane M, molecular weight marker; Lane 1, GST-Pro2176–2677-His and cleavage products. The fusion protein and cleavage products are depicted as a bar. The cleavage products were subsequently subjected to N-terminal amino acid sequencing analyses, and the positions of the determined cleavage sites are indicated below the bars.
The N-terminal amino acids of the 56-kDa cleavage product were determined to be AQAK, which are mapped to amino acids 2193–2196 of the EoV polyprotein, indicating that N-terminal cleavage takes place in the E/A dipeptide at positions 2192 and 2193 (Fig. 5). On the other hand, N-terminal sequencing of the autoprocessed 21-kDa product revealed that the sequence was SATA, which corresponds to the amino acids 2492–2495, indicating that C-terminal cleavage occurs in the Q/S dipeptide at positions 2491 and 2492. Of note, a faint band less than 56 kDa was detected; however, N-terminal sequencing of this band was unsuccessful, and this band may represent a bacterial contaminant. Taken together, these results indicate that the N- and C-terminal boundaries of the EoV 3CL protease are amino acids 2193 and 2491.
Trans-cleavage activity of the EoV 3CL protease
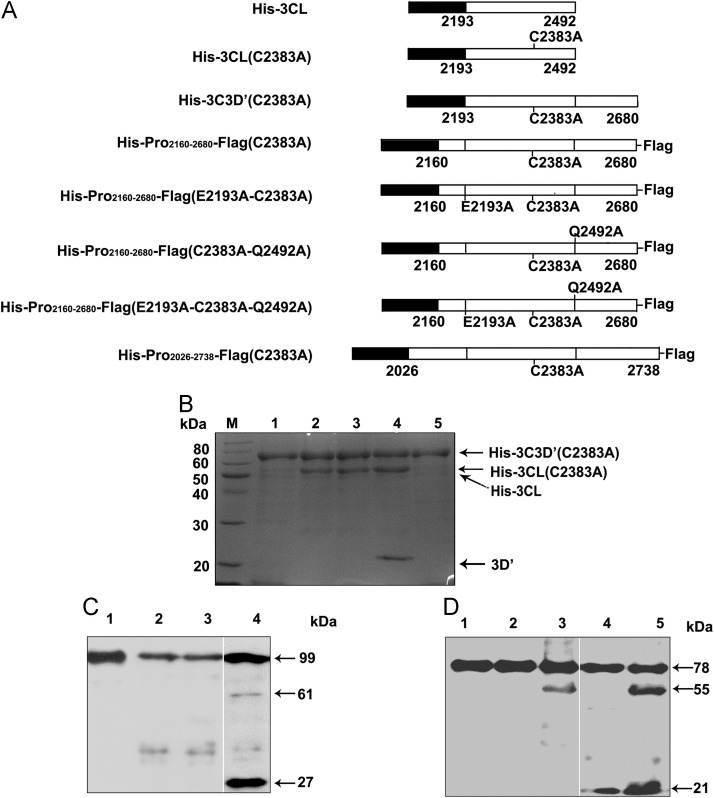
Various viral proteases have been showed to be able to cleave viral polyproteins in an intermolecular manner (in trans) (Blakeney et al., 2003, Carrier et al., 1999, Harmon et al., 1992, Lin et al., 2004, Robel et al., 2008, Tian et al., 2009). Therefore, we sought to determine whether EoV 3CL could intermolecularly cleave its natural substrate, the EoV polyprotein, in trans. His-tagged EoV 3CL protease (His-3CL) was bacterially expressed and purified as the functional enzyme, and the protease-defective His-3CL(C2383A) mutant was used as the negative control ( Fig. 6A). On the other hand, the purified fusion protein His-3C3D′(C2383A) contains a cleavage site between the 3CL region and partial 3D-like/RdRp domain and was used as the trans-cleavage substrate. The C2383A substitution completely abolished the 3CL protease activity in the fusion protein, thereby excluding the possibility of any intramolecular cleavage. The trans-cleavage products were analyzed via 12% SDS-PAGE (Fig. 6B). After 6 h of incubation, wild-type His-3CL efficiently cleaved His-3C3D′(C2383A), as the level of the 53-kDa band corresponding to both His-3CL and the trans-cleavage product His-3CL(C2383A) was increased and an additional ∼21-kDa band corresponding to 3D′ appeared (Fig. 6B, lane 4), when compared with the levels of the same reaction mix before incubation (Fig. 6B, lane 2). As expected, the reaction of the substrate with the active site mutant His-3CL(C2383A) did not exhibit any cleavage (Fig. 4B, lane 3).
Fig. 6.
Trans-cleavage of the EoV 3CL protease. (A) Schematic illustrations of the wild-type and mutant 3CL proteases and various substrates. (B) The substrate His-3CD′(C2383A) was expressed in E. coli, purified via Ni–NTA chromatography, and then mock-treated for 0 h (Lane 5) or 6 h (Lane 1), incubated with His-3CL (active protease) for 0 h (Lane 2) or 6 h (Lane 4), or incubated with His-3CL(C2383A) (inactive protease) for 6 h (Lane 3). Then, the reaction mix was subjected to 12% SDS-PAGE, and the proteins were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R250. Lane M, molecular weight marker. (C) The substrate His-Pro2026–2738-Flag(C2383A) was incubated with His-3CL (active) for 0 h (Lane 1) or 6 h (Lane 4), incubated with His-3CL(C2383A) (inactive) for 6 h (Lane 3), or mock-treated for 6 h (Lane 2). The reaction mixtures were separated via 12% SDS-PAGE and then subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-Flag antibody. The arrow indicates the position of the fusion protein or cleavage products. (D) Active His-3CL was used to treat different substrates, including His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(C2383A) for 0 h (Lane 1) and for 6 h (Lane 5) and His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(E2193A-C2383A-Q2492A) (Lane 2), His-Pro2160–2680-Flag (C2383A-Q2492A) (Lane 3), and His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(E2193A-C2383A) (Lane 4) for 6 h. The reaction mixtures were separated via 12% SDS-PAGE and then subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-Flag antibody.
To further confirm the trans-cleavage activity of EoV 3CL, we used His-Pro2026–2738-Flag(C2383A), which contains the cleavage sites at both the N- and C-terminals of the 3CL domain, as the substrate. Western blot analyses with anti-Flag antibody revealed that wild-type His-3CL efficiently cleaved the fusion protein in trans after 6 h of incubation (Fig. 6C, lane 4), whereas negative controls (Fig. 6C, lanes 1–3) did not exhibit any cleavage products. Of note, faint bands of about 34 kDa were observed in the reaction in the presence or absence of wild-type His-3CL or His-3CL(C2383A) (Fig. 4C, lanes 2–4), but these were non-specific bands, not cleavage products. Taken together, these results indicate that our bacterially expressed recombinant EoV His-3CL protease was enzymatically active and able to mediate trans-cleavage activity.
After determining the trans-cleavage activity of the EoV 3CL protease, we sought to determine whether the cleavage sites in trans cleaved the polyprotein at the same specific positions identified in Fig. 5. To this end, we used wild-type His-3CL as the protease, and we used the fusion proteins His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(C2383A), His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(E2193A-C2383A), His-Pro2160–2680-Flag (C2383A-Q2492A), and His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(E2193A-C2383A-Q2492A) as the trans-cleavage substrates. All four fusion proteins are protease defective (C2383A), and the last three fusion proteins contain the point mutation(s) in one or both of the identified cleavage sites of EoV 3CL.
The trans-cleavage products of His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(C2383A) were subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-Flag antibody (Fig. 6D, lane 5), revealing two cleavage products of about 55 kDa and 21 kDa, a result similar to the cleavage results obtained previously (Fig. 2C, lane 1). The trans-cleavage assay using His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(C2383A-Q2492A) or His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(E2193A-C2383A) as the substrate revealed only one cleavage product of about 55 kDa (Fig. 6D, lane 3) or 21 kDa respectively (Fig. 6D, lane 4) besides the intact fusion protein. Moreover, for His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(E2193A-C2383A-Q2492A), both the cleavage sites determined via N-terminal sequencing were mutated, and no trans-cleavage was observed when this fusion protein was used as the substrate (Fig. 6D, lane 2). On the basis of these results, we can conclude that the EoV 3CL protease is active in trans, and the trans-cleavage occurs at the same positions determined via the N-terminal sequencing analyses.
Optimal reaction conditions and the effects of protease inhibitors for the processing activity of EoV 3CL
The data reported in the preceding sections confirm that EoV 3CL is a protease and demonstrate its processing activities. To further characterize the biochemical properties of EoV 3CL, we examined the 3CL protease activities under varying reaction conditions, such as pH, temperature, and salt content, or after treatment with various protease inhibitors. Of note, the protease activities were examined using the previously described trans-cleavage assay with His-3CL (2 μM) as the enzyme and His-3C3D′(C2383A) (5 μM) as the substrate and were assessed by measuring the ratio of cleavage products/precursor after each reaction.
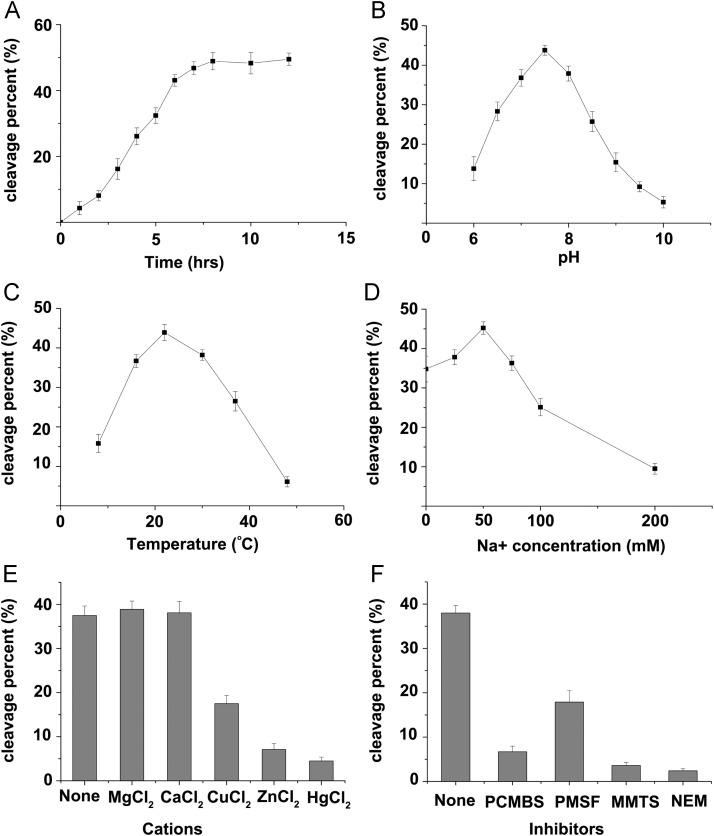
The cleavage reactions were firstly performed at the different time points from 0 to 12 h, and measured the ratios of cleavage products/precursor ( Fig. 7A). We then chose the time point of 6 h, which is in the linear phase of the cleavage activity (Fig. 7A), for the following experiments. The optimal pH was around 7.5, and either a lower or higher pH impaired 3CL protease activity (Fig. 7B), indicating that the EoV 3CL protease has a relatively low tolerance for pH variation. The trans-cleavage assays were conducted at different temperatures, such as 8 °C, 16 °C, 22 °C, 30 °C, 37 °C, and 48 °C. The optimal temperature was determined to be about 22 °C (Fig. 7C).
Fig. 7.
Optimal reaction conditions and effects of protease inhibitors for the processing activity of EoV 3CL and the ratio of cleavage products/precursor. (A) Cleavage activity at different reaction time points (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12 h). Enzyme His-3CL and substrate His-3C3D′(C2383A) were incubated in a buffer of 25 mM Tris–HCl and 50 mM NaCl (pH, 7.5) at 22 °C. (B) Effects of pH on protease activity. Enzyme His-3CL and substrate His-3C3D′(C2383A) were incubated in a buffer of 25 mM Tris–HCl and 50 mM NaCl with various pH (6.0, 6.5, 7.0, 7.5, 8.0, 8.5, 9.0, and 10.0) at 22 °C for 6 h. (C) Effects of temperature on protease activity. Enzyme His-3CL and substrate His-3C3D′(C2383A) were reacted in a buffer of 25 mM Tris–HCl and 50 mM NaCl (pH, 7.5) for 6 h at the indicated temperatures (8°, 16°, 22°, 30°, 37°, and 48 °C). (D) Effects of NaCl concentration on protease activity. Enzyme His-3CL and substrate His-3C3D′(C2383A) were reacted in the 25-mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH, 7.5) containing the indicated concentrations (0, 25, 50, 75, 100, and 200 mM) of NaCl at 22 °C for 6 h. (E) Effects of various divalent cations (5 mM) on protease activity in the 25-mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH, 7.5) at 22 °C for 6 h. None: reaction without extra cations. (F) Effects of various protease inhibitors on 3CL protease activity. Enzyme His-3CL and substrate His-3C3D′(C2383A) were incubated in the 25 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.5) with 50 μM of each indicated inhibitor at 22 °C for 6 h. None: no inhibitor. The standard errors of the means of results from three independent experiments are shown.
The results of the trans-cleavage assays with different Na+ concentrations indicated that the optimal concentration was around 50 mM (Fig. 7D) and that the enzyme is relatively sensitive to Na+. A high concentration of Na+ (about 200 mM) strongly inhibited 3CL protease activity, but a concentration lower than 50 mM was also not ideal for enzyme activity. Then, we examined the effects of various divalent cations on the protease activity. To this end, the reaction was supplemented with 5 mM of HgCl2, CuCl2, MgCl2, CaCl2, or ZnCl2. Although MgCl2 or CaCl2 did not affect protease activity, Cu2+, Zn2+, and Hg2+ decreased protease activity remarkably relative to the level of activity before the extra cations were added.
Finally, we examined a group of known inhibitors of cysteine or serine protease to determine their effects on the activity of the EoV 3CL protease (Fig. 7F). The cysteine 3C and 3CL proteases were previously reported to be sensitive to sulfhydryl reagents (Someya et al., 2005). As expected, 50 μM p-chloromercuribenzenesulfonate (PCMBS), which contains an Hg2+ within each compound, strongly inhibited the 3CL activity. Moreover, 50 μM methyl methanethiosulfonate (MMTS) or N-ethylmaleimide (NEM), either of which could form a covalent bond with a sulfur atom of the cysteine residue, almost completely abolished the protease activity of EoV 3CL. On the other hand, phenyl methylsulfonylfluoride (PMSF), which is known as an inhibitor of serine proteases, also inhibited EoV 3CL activity, but in a much less efficient way than did PCMBS, MMTS, and NEM, which are specific for cysteine proteases. All these experiments were independently repeated for three times.
Discussion
Polyprotein processing is a common strategy used by many viruses to generate functional protein products from a single open reading frame (Palmenberg, 1990). For iflaviruses, such as EoV, viral replication also involves the proteolytic processing of viral polyprotein, and a 3CL domain was predicted to be the critical protease in this process (Wang et al., 2004). In this study, we determined that EoV 3CL is a protease and revealed its ability to autocatalytically release itself from flanking sequences and to mediate proteolytic processing in trans. Moreover, via N-terminal sequencing and mutational analyses, we have defined the two cleavage sites of the EoV 3CL protease. Furthermore, we have determined the catalytical residues that are critical for EoV 3CL protease activity and characterized the biochemical properties of EoV 3CL.
We have identified the N- and C-terminal cleavage sites for EoV 3CL as Q/S and E/A, which are consistent with the typical characteristics of the polyprotein substrates of many other picornaviral 3C and 3CL proteases, namely, cleavage at Q, E/G, S, or A (Dougherty and Semler, 1993, Palmenberg, 1990). We also observed that proteolytic processing efficiency was higher at the C-terminal site Q/S than at the N-terminal site E/A. In the cleavage assay, the C-terminal (Q/S) cleavage products were obviously much more prominent than the N-terminal (E/A) cleavage products (Figs. 2B and 5); likewise, in the trans-cleavage assay, cleavage in Q/S was more effective than in E/A (Fig. 6C, lane 4). Consistently, most 3C and 3C-like proteases appear to prefer glutamine (Q) to glutamic acid (E) for cleavage (Palmenberg, 1990). The specificity for glutamine has been attributed to the ability of the carboxamide group of the glutamine to form hydrogen bonds with two conserved amino acids (threonine, histidine) in the substrate binding pocket of 3C and 3CL proteases (Matthews et al., 1994).
In addition to the primary conserved amino acid sequences, the secondary structure around the cleavage site may also be important for the specificity of cleavage (Ypma-Wong et al., 1988). Interestingly, we found several additional Q–S (Q–G or Q–A) and E–A (E–G) dipeptides in the EoV polyproteins; however, none of them could serve as cleavage sites for EoV 3CL, a finding similar to observations reported for 3CL protease of a coronavirus, infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) (Liu et al., 1997). Although the mechanism for this discrimination is still unclear, unfavorable secondary structures might be involved. The observation that cleavage occurs more efficiently at certain sites might represent a possible regulatory mechanism for protease activity during viral replication.
Similar to chymotrypsin, most of the 3C and 3CL proteases have a catalytic triad consisting of His, Asp/Glu, and Cys/Ser. (Dougherty and Semler, 1993, Gorbalenya et al., 1989). The data presented here suggest that the residues Cys-2383 and His-2261 are essential for protease activity, and the substitution of Asp-2299 with Ala reduced but did not abolish the processing activity of EoV 3CL. This finding suggests that Asp-2299 plays a supportive but not an essential role. One possibility is that this residue is close to the substrate-binding pocket and interacts with essential amino acids (like His-2261) instead of directly binding to the cleavage sites (Craik et al., 1987, Sprang et al., 1987).
The non-essential roles of Asp were previously reported for other chymotrypsin-like proteases, such as equine arteritis virus nsp4 (Asp-1129), equine torovirus Mpro (Glu-3347), and white bream virus MPro (Asp-3518) (Smits et al., 2006, Snijder et al., 1996, Ulferts et al., 2011). Further structural studies should be able to reveal the exact role of Asp-2299 in the EoV 3CL protease.
Like many picornaviral proteases, the EoV 3CL protease contains a cysteine residue as a nucleophile of the active site, and thus should be sensitive to sulfhydryl reagents (Ryan and Flint, 1997). As expected, the addition of Hg2+, Zn2+, and sulfhydryl reagents such as PCMBS, MMTS, and NEM strongly inhibited EoV 3CL protease activity thereby confirming the finding that Cys-2383 is required for the catalysis of polyprotein processing and that EoV 3CL is a cysteine protease. On the other hand, the serine protease inhibitor PMSF also reduced the activity of EoV 3CL, but to a lesser extent (Fig. 7F). Similarly, several other 3C and 3CL cysteine proteases, such as Chiba virus 3CL protease and poliovirus 3C protease have also been reported to be inhibited by PMSF (Baum et al., 1991, Someya et al., 2005). This phenomenon may exist because 3C and 3CL proteases share the structural homology of chymotrypsin-like folds and have a proteolytic mechanism similar to that of serine proteases.
Like the 3CL proteases of norovirus and EAV, the EoV 3CL protease is relatively sensitive to varying Na+ ionic concentrations (Someya et al., 2005, van Aken et al., 2006), because high concentrations of Na+ strongly inhibited the proteolytic activity of EoV 3CL. In contrast, the 3CL proteases of mouse hepatitis virus and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) are insensitive to 100–500 mM of Na+ (Seybert et al., 1997, Xu et al., 2010). Moreover, the presence of Mg2+ or Ca2+ did not visibly affect the proteolytic activity of EoV 3CL. In addition, we found that the optimal pH for EoV 3CL is about 7.5 rather than the acidic pH we previously expected based on the physiological environment in insect cells. These biochemical features suggest that the EoV 3CL protease is localized and functions in a limited environment such as an intracellular organelle within infected cells. Moreover, instead of the optimal temperature of 27 °C for insect cell culture, the optimal temperature for the protease activity of EoV 3CL is around 22 °C, which corresponds well to the appropriate environments for the growth of the natural host of EoV, the tea looper (Ectropis oblique, 20–24 °C). In nature, the growth and reproduction of tea loopers are greatly affected by various meteorologic factors, and the temperature is one of the most important factors (Xue et al., 2009).
For viruses in the order Picornavirales, 3C or 3CL proteases play essential roles in processing the single open reading frame-encoded large precursor polyproteins into mature functional viral proteins. In Iflaviridae, which is a novel family in the order Picornavirales, the complete nucleotide sequences of several iflaviruses have been determined and the presence of putative 3CL protease domains have been predicted on the basis of sequence analysis, but no data have been reported concerning the characteristics of the putative 3CL proteases and the processing of iflaviral polyproteins.
To our knowledge, our study is the first to identify an iflaviral 3CL protease, EoV 3CL, and to provide a detailed characterization of this novel 3CL protease, which not only represents an important step toward understanding the mechanism of EoV polyprotein proteolytic processing but also gives direction for future studies of 3CL proteases, polyprotein processing, and viral replication of other members of the family Iflaviridae. For instance, on the basis of sequence analysis and our findings, future studies could find conservative residues similar to those at EoV cleavage sites in other iflaviruses, such as the potential cleavage sites E2192/A2193 and Q2491/S2492 in PnV and Q2178/S2179 and E2446/G2447 in IFV.
As a newly established family within the order Picornavirales, the family Iflaviridae comprises invertebrate viruses belonging to the picornavirus “superfamily.” Iflaviruses share a number of features, such as virion structure and genomic organization, with the viruses in the families Picornaviridae and Dicistroviridae but still form a distinct group of viruses according to phylogenetic analyses (Le Gall et al., 2008). Thus, detailed molecular studies of iflaviruses like the current study of EoV 3CL might provide novel insights into biological features of different viruses in the order Picornavirales and, possibly, help uncover evolutional driving forces in this group of positive-strand RNA viruses.
Materials and methods
Construction of recombinant plasmids and site-directed mutagenesis
The construction of recombinant plasmids was done according to our standard cloning procedures (Lin et al., 2010). The EoV full-length genomic cDNA clone obtained previously was used as the template. The corresponding cDNA sequences were amplified via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and subsequently subcloned into plasmids such as pET32a, pET28a (Novagen), and pGEX-6p-1 (GE Healthcare) to generate the bacterial expression vectors for various fusion proteins. The inserted cDNA sequences, PCR primers, restriction endonuclease sites, and generated fusion proteins are listed in Supplementary Table 1. The point mutations were introduced into the corresponding templates via PCR-mediated mutagenesis, with appropriate primers containing the desired nucleotide changes (Table 1).
Tablee 1.
List of the primers.
| Primers | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| His-Pro2160–2680-Flag-For | CCGGAATTCATGTCATTTATTTTTAGTAACAT (EcoRI) |
| His-Pro2160–2680-Flag-Rev | CCGCTCGAGTTACTTGTCATCGTCGTCCTTGTAGTCATCTATACCTACGGCAATTTTATTG (XhoI) |
| His-Pro2026–2738-Flag-For | CCGGAATTCAAGGTGATTCTTCCAGTTGTGTG (EcoRI) |
| His-Pro2026–2738-Flag-Rev | CCGCTCGAGTTACTTGTCATCGTCGTCCTTGTAGTCAACCACATCCTCATACTCCTTGTCT (XhoI) |
| GST-Pro2176–2677-His-For | CCGGAATTCTTGGCCTATAAGGTATATCGTT (EcoRI) |
| GST-Pro2176–2677-His-Rev | CCGCTCGAGTTAGTGATGATGATGATGATGTACGGCAATTTTATTGTTGATGGTG (XhoI) |
| His-Pro2160–2492-For | CCGGAATTCATGTCATTTATTTTTAGTAACAT (EcoRI) |
| His-Pro2160–2492-Rev | CCGCTCGAGTTACTGTGCAGCAGGGATCCGAAAG (XhoI) |
| His-Pro2026–2492-For | CCGGAATTCAAGGTGATTCTTCCAGTTGTGTG (EcoRI) |
| His-Pro2026–2492-Rev | CCGCTCGAGTTACTGTGCAGCAGGGATCCGAAAG (XhoI) |
| His-3C3D′-For | CCGGAATTCGCGCAAGCAAAGGATTACGACCAG (EcoRI) |
| His-3C3D′-Rev | CCGCTCGAGTTAATCTATACCTACGGCAATTTTA (XhoI) |
| His-3CL-For | CCGGAATTCGCGCAAGCAAAGGATTACGACCAG (EcoRI) |
| His-3CL-Rev | CCGCTCGAGTTACTGTGCAGCAGGGATCCGAAAG (XhoI) |
| 3CL-His-For | CATGCCATGGGCGCGCAAGCAAAGGATTACGA (NcoI) |
| 3CL-His-Rev | CCGCTCGAGTTAGTGATGATGATGATGATGCTGTGCAGCAGGGATCCGAAAGG (XhoI) |
| ⁎C2383A-For | GGGGGCCCAATCCGTAAGGgctGGC |
| ⁎C2383A-Rev | CTCATGATGAGGGAGCCagcCCTTA |
| ⁎H2261A-For | CTTTGTTTTGGCCCCCCAGgctTTA |
| ⁎H2261A-Rev | CGCCGGGCACCCAAGCTAAagcCTG |
| ⁎D2299A-For | CTCTTGTGTTAAAGGATTTgctTAT |
| ⁎D2299A-Rev | CGAACCGGTAGACTGCATAagcAAA |
| ⁎Q2492A-For | CTTTCGGATCCCTGCTGCAgctTCT |
| ⁎Q2492A-Rev | CGCCTTTCGCTGTTGCAGAagcTGC |
| ⁎E2193A-For | TAATTCATCAGAGTGCGTTgctGCG |
| ⁎E2193A-Rev | CGTAATCCTTTGCTTGCGCagcAAC |
Sequence-specific primers are designed according to GenBank accession numbers AY365064 (EoV), and primers with asterisks are designed for overlapping PCR. Underlined characters indicate restriction endonuclease sites, and the types are shown in parentheses. Substituted nucleotides for mutagenesis are shown with lowercase characters. Stop code are shown in bold faced characters and the His-tag and Flag-tag are shown in italics.
Production of EoV 3CL-specific polyclonal antibodies
Recombinant 3CL-His was produced and purified according to our standard procedures as previously described (Lin et al., 2010) with minor modifications. As the expressed 3CL-His was found in the insoluble fraction of the bacterial lysates, the insoluble material was collected via centrifugation. The pellet was washed with 2 M urea and then extracted with the buffer containing 25 mM Tris–HCl, 50 mM NaCl and 8 M urea (pH 7.5) by stirring at room temperature for 1 h. The resulting supernatant was purified using affinity chromatography on Ni–NTA columns (GE Healthcare) according to the manufacturer's protocol (Fig. 3B). This purified protein was used to raise EoV 3CL-specific polyclonal rabbit antisera. 3CL-specific antisera were obtained after subcutaneous immunization of New Zealand white rabbits. The detailed method was previously described (Satheshkumar et al., 2004).
Proteolytic reaction and trans-cleavage assays
For the proteolytic reaction assay, corresponding recombinant proteins were expressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3) at 37 °C, and the cells were harvested after 6 h of incubation in the presence of 1 mM IPTG at 30 °C. The pellet was resuspended in lysis buffer (25 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 50 mM NaCl, 0.2% TritonX-100, and 5% glycerol) and then subjected to sonication to generate a total bacterial lysate. The lysate was then subjected to 12% SDS-PAGE and Western blotting according to our standard procedures (Lin et al., 2010, Qiu et al., 2011). For Western blotting, monoclonal anti-His and anti-Flag antibodies were used as primary antibodies at a 1:2000 dilution, and a rabbit anti-3CL polyclonal antiserum that was described above was used at a dilution of 1:1000. The secondary antibody, alkaline phosphatase-linked goat anti-mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG), was used at a 1:2000 dilution, or goat anti-mouse IgG-HRP was used at a 1:10000 dilution (Roche).
For the trans-cleavage assay, recombinant His-3CL, His-3C3D′(C2383A), and His-3CL(C2383A) were expressed and purified as previously described (Lin et al., 2010). Purified proteins were then concentrated using Amicon Ultra-30 filters (Millipore) and stored in 50 mM NaCl and 25 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.5) at −70 °C (Qi et al., 2011, Qi et al., 2012). All proteins were quantified using a UV–visible spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The recombinant His-Pro2026–2738-Flag(C2383-A) and His-Pro2160–2680-Flag(C2383-A) polyproteins were expressed in E. coli BL21 in an insoluble fraction, which was then resuspended in 50 mM NaCl and 25 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.5) after centrifugation. The purified His-3CL or negative control His-3CL(C2383A) was incubated with corresponding substrates at a ratio of 2:5. The cleavage reactions were performed for 6 h at 22 °C in a total volume of 20 μl buffer (25 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.5), 50 mM NaCl, and 0.25 mM DTT). The reaction was stopped by boiling with SDS-PAGE loading dye, and the proteins were then analyzed via 12% SDS-PAGE. Then the gels were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R-250. To estimate the efficiency of proteolytic cleavage, the density of the respective stained bands was scanned and calculated using Bio-Rad Quantity One software.
N-terminal sequencing analysis of cleavage products
The fusion protein GST-Pro2176–2677-His was purified from inclusion bodies under denatured conditions according to our standard method described for production of EoV 3CL-specific polyclonal antibodies. The purified proteins were separated via 12% SDS-PAGE, and the gels were soaked in Western blotting transfer buffer (10 mM 3-cyclohexylamino-1-propanesulfonic acid (pH 11), 20% methanol) for 20 min, and then subjected to eletroblotting via polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (Millipore). After transfer, the membrane were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R250 for 1 min and washed with 30% (vol/vol) methanol–10% (vol/vol) acetic acid. The two appropriate membrane segments were cut out and subjected to Edman degradation using a 492 PROCISE protein sequencer (Shanghai GeneCore Bio Technologies).
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Huihui He for his help in protein alignment analysis.
This work was supported by the Chinese 111 project (Grant B06018), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 30670084) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (Grant 2011CDB444).
Contributor Information
Xi Zhou, Email: zhouxi@whu.edu.cn.
Yuanyang Hu, Email: yyhu@whu.edu.cn.
Referencces
- Allaire M., Chernaia M.M., Malcolm B.A., James M.N. Picornaviral 3C cysteine proteinases have a fold similar to chymotrypsin-like serine proteinases. Nature. 1994;369:72–76. doi: 10.1038/369072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bablanian G.M., Grubman M.J. Characterization of the foot-and-mouth disease virus 3C protease expressed in Escherichia coli. Virology. 1993;197:320–327. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum E.Z., Bebernitz G.A., Palant O., Mueller T., Plotch S.J. Purification, properties, and mutagenesis of poliovirus 3C protease. Virology. 1991;185:140–150. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90762-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeney S.J., Cahill A., Reilly P.A. Processing of Norwalk virus nonstructural proteins by a 3C-like cysteine proteinase. Virology. 2003;308:216–224. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(03)00004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonderoff J.M., Larey J.L., Lloyd R.E. Cleavage of poly(A)-binding protein by poliovirus 3C proteinase inhibits viral internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation. J. Virol. 2008;82:9389–9399. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00006-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrier K., Hans F., Sanfacon H. Mutagenesis of amino acids at two tomato ringspot nepovirus cleavage sites: effect on proteolytic processing in cis and in trans by the 3C-like protease. Virology. 1999;258:161–175. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.9729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian P., Carstens E., Domier L., Johnson K., Nakashima N., Scotti P., van der Wilk F. Iflavirus. In: Fauquet C.M., Mayo M.A., Maniloff J., Desselberger U., Ball. L.A., editors. Virus Taxonomy: Eighth Report of the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses. Academic Press; San Diego, USA: 2005. pp. 779–782. [Google Scholar]
- Craik C.S., Roczniak S., Largman C., Rutter W.J. The catalytic role of the active site aspartic acid in serine proteases. Science. 1987;237:909–913. doi: 10.1126/science.3303334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui S., Wang J., Fan T., Qin B., Guo L., Lei X., Wang J., Wang M., Jin Q. Crystal structure of human enterovirus 71 3C protease. J. Mol. Biol. 2011;408:449–461. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.03.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Breyne S., Bonderoff J.M., Chumakov K.M., Lloyd R.E., Hellen C.U. Cleavage of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF5B by enterovirus 3C proteases. Virology. 2008;378:118–122. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.05.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty W.G., Semler B.L. Expression of virus-encoded proteinases: functional and structural similarities with cellular enzymes. Microbiol. Rev. 1993;57:781–822. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.4.781-822.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghildyal R., Jordan B., Li D., Dagher H., Bardin P.G., Gern J.E., Jans D.A. Rhinovirus 3C protease can localize in the nucleus and alter active and passive nucleocytoplasmic transport. J. Virol. 2009;83:7349–7352. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01748-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh R.C., Ball B.V., Willcocks M.M., Carter M.J. The nucleotide sequence of sacbrood virus of the honey bee: an insect picorna-like virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1999;80(Pt 6):1541–1549. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-80-6-1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin S., Tuthill T.J., Arias A., Killington R.A., Rowlands D.J. Foot-and-mouth disease virus assembly: processing of recombinant capsid precursor by exogenous protease induces self-assembly of pentamers in vitro in a myristoylation-dependent manner. J. Virol. 2009;83:11275–11282. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01263-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A.E., Blinov V.M., Donchenko A.P. Poliovirus-encoded proteinase 3C: a possible evolutionary link between cellular serine and cysteine proteinase families. FEBS Lett. 1986;194:253–257. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A.E., Donchenko A.P., Blinov V.M., Koonin E.V. Cysteine proteases of positive strand RNA viruses and chymotrypsin-like serine proteases. A distinct protein superfamily with a common structural fold. FEBS Lett. 1989;243:103–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon S.A., Updike W., Jia X.Y., Summers D.F., Ehrenfeld E. Polyprotein processing in cis and in trans by hepatitis A virus 3C protease cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. J. Virol. 1992;66:5242–5247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5242-5247.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isawa H., Asano S., Sahara K., Iizuka T., Bando H. Analysis of genetic information of an insect picorna-like virus, infectious flacherie virus of silkworm: evidence for evolutionary relationships among insect, mammalian and plant picorna(-like) viruses. Arch. Virol. 1998;143:127–143. doi: 10.1007/s007050050273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzi G., de Miranda J.R., Boniotti M.B., Cameron C.E., Lavazza A., Capucci L., Camazine S.M., Rossi C. Molecular and biological characterization of deformed wing virus of honeybees (Apis mellifera L.) J. Virol. 2006;80:4998–5009. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.10.4998-5009.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson T.G., Gronros D.L., Evans P.E., Bastien M.C., Michalewich K.M., Clark J.K., Edmonds J.H., Graber K.H., Werner J.A., Lurvey B.A., Cate J.M. Identification and characterization of a protein destruction signal in the encephalomyocarditis virus 3C protease. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:9904–9980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Gall O., Christian P., Fauquet C.M., King A.M., Knowles N.J., Nakashima N., Stanway G., Gorbalenya A.E. Picornavirales, a proposed order of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses with a pseudo-T=3 virion architecture. Arch. Virol. 2008;153:715–727. doi: 10.1007/s00705-008-0041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C.W., Tsai C.H., Tsai F.J., Chen P.J., Lai C.C., Wan L., Chiu H.H., Lin K.H. Characterization of trans- and cis-cleavage activity of the SARS coronavirus 3CLpro protease: basis for the in vitro screening of anti-SARS drugs. FEBS Lett. 2004;574:131–137. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.08.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M., Ye S., Xiong Y., Cai D., Zhang J., Hu Y. Expression and characterization of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of Ectropis obliqua virus. BMB Rep. 2010;43:284–290. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2010.43.4.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D.X., Xu H.Y., Brown T.D. Proteolytic processing of the coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus 1a polyprotein: identification of a 10-kilodalton polypeptide and determination of its cleavage sites. J. Virol. 1997;71:1814–1820. doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.3.1814-1820.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu G., Qi J., Chen Z., Xu X., Gao F., Lin D., Qian W., Liu H., Jiang H., Yan J., Gao G.F. Enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 3C proteases: binding to rupintrivir and their substrates and anti-hand, foot, and mouth disease virus drug design. J. Virol. 2011;85:10319–10331. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00787-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J., Hu Y., Hu L., Zong S., Cai D., Wang J., Yu H., Zhang J. Ectropis obliqua picorna-like virus IRES-driven internal initiation of translation in cell systems derived from different origins. J. Gen. Virol. 2007;88:2834–2838. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.83201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J., Zhang J., Wang X., Jiang H., Liu C., Hu Y. In vitro and in vivo identification of structural and sequence elements in the 5′ untranslated region of Ectropis obliqua picorna-like virus required for internal initiation. J. Gen. Virol. 2006;87:3667–3677. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.82090-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm B.A. The picornaviral 3C proteinases: cysteine nucleophiles in serine proteinase folds. Protein Sci. 1995;4:1439–1445. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560040801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D.A., Smith W.W., Ferre R.A., Condon B., Budahazi G., Sisson W., Villafranca J.E., Janson C.A., McElroy H.E., Gribskov C.L. Structure of human rhinovirus 3C protease reveals a trypsin-like polypeptide fold, RNA-binding site, and means for cleaving precursor polyprotein. Cell. 1994;77:761–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ongus J.R., Peters D., Bonmatin J.M., Bengsch E., Vlak J.M., van Oers M.M. Complete sequence of a picorna-like virus of the genus Iflavirus replicating in the mite Varroa destructor. J. Gen. Virol. 2004;85:3747–3755. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.80470-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A.C. Proteolytic processing of picornaviral polyprotein. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1990;44:603–623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi N., Cai D., Qiu Y., Xie J., Wang Z., Si J., Zhang J., Zhou X., Hu Y. RNA binding by a novel helical fold of b2 protein from Wuhan. Nodavirus mediates the suppression of RNA interference and promotes b2 dimerization. J. Virol. 2011;85:9543–9554. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00785-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi N., Zhang L., Qiu Y., Wang Z., Si J., Liu Y., Xiang X., Xie J., Qin C.F., Zhou X., Hu Y. Targeting of Dicer-2 and RNA by a viral RNA silencing suppressor in Drosophila cells. J. Virol. 2012 doi: 10.1128/JVI.07229-11. (Epub, 10.1128/jvi.07229-11) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu Y., Cai D., Qi N., Wang Z., Zhou X., Zhang J., Hu Y. Internal initiation is responsible for synthesis of Wuhan nodavirus subgenomic RNA. J. Virol. 2011;85:4440–4451. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02410-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera C.I., Lloyd R.E. Modulation of enteroviral proteinase cleavage of poly(A)-binding protein (PABP) by conformation and PABP-associated factors. Virology. 2008;375:59–72. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.02.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robel I., Gebhardt J., Mesters J.R., Gorbalenya A., Coutard B., Canard B., Hilgenfeld R., Rohayem J. Functional characterization of the cleavage specificity of the sapovirus chymotrypsin-like protease. J. Virol. 2008;82:8085–8093. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00693-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M.D., Flint M. Virus-encoded proteinases of the picornavirus super-group. J. Gen. Virol. 1997;78(Pt 4):699–723. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-78-4-699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satheshkumar P.S., Lokesh G.L., Savithri H.S. Polyprotein processing: cis and trans proteolytic activities of Sesbania mosaic virus serine protease. Virology. 2004;318:429–438. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2003.09.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seybert A., Ziebuhr J., Siddell S.G. Expression and characterization of a recombinant murine coronavirus 3C-like proteinase. J. Gen. Virol. 1997;78(Pt 1):71–75. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-78-1-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smits S.L., Snijder E.J., de Groot R.J. Characterization of a torovirus main proteinase. J. Virol. 2006;80:4157–4167. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.8.4157-4167.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snijder E.J., Wassenaar A.L., van Dinten L.C., Spaan W.J., Gorbalenya A.E. The arterivirus nsp4 protease is the prototype of a novel group of chymotrypsin-like enzymes, the 3C-like serine proteases. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:4864–4871. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.9.4864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Someya Y., Takeda N., Miyamura T. Characterization of the norovirus 3C-like protease. Virus Res. 2005;110:91–97. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2005.02.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprang S., Standing T., Fletterick R.J., Stroud R.M., Finer-Moore J., Xuong N.H., Hamlin R., Rutter W.J., Craik C.S. The three-dimensional structure of Asn102 mutant of trypsin: role of Asp102 in serine protease catalysis. Science. 1987;237:905–909. doi: 10.1126/science.3112942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney T.R., Roque-Rosell N., Birtley J.R., Leatherbarrow R.J., Curry S. Structural and mutagenic analysis of foot-and-mouth disease virus 3C protease reveals the role of the beta-ribbon in proteolysis. J. Virol. 2007;81:115–124. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01587-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian X., Lu G., Gao F., Peng H., Feng Y., Ma G., Bartlam M., Tian K., Yan J., Hilgenfeld R., Gao G.F. Structure and cleavage specificity of the chymotrypsin-like serine protease (3CLSP/nsp4) of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus (PRRSV) J. Mol. Biol. 2009;392:977–993. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.07.062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulferts R., Mettenleiter T.C., Ziebuhr J. Characterization of Bafinivirus main protease autoprocessing activities. J. Virol. 2011;85:1348–1359. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01716-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Aken D., Benckhuijsen W.E., Drijfhout J.W., Wassenaar A.L., Gorbalenya A.E., Snijder E.J. Expression, purification, and in vitro activity of an arterivirus main proteinase. Virus Res. 2006;120:97–106. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2006.01.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oers M.M. Genomics and biology of Iflaviruses. In: Asgari S., Johnson K., editors. Insect Virology. Caister Academic Press; Norflok, UK: 2010. pp. 231–250. [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Zhang J., Lu J., Yi F., Liu C., Hu Y. Sequence analysis and genomic organization of a new insect picorna-like virus, Ectropis obliqua picorna-like virus, isolated from Ectropis obliqua. J. Gen. Virol. 2004;85:1145–1151. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.19638-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C.Y., Lo C.F., Huang C.J., Yu H.T., Wang C.H. The complete genome sequence of Perina nuda picorna-like virus, an insect-infecting RNA virus with a genome organization similar to that of the mammalian picornaviruses. Virology. 2002;294:312–323. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu A.T., Zhou Y.J., Li G.X., Yu H., Yan L.P., Tong G.Z. Characterization of the biochemical properties and identification of amino acids forming the catalytic center of 3C-like proteinase of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010;32:1905–1910. doi: 10.1007/s10529-010-0370-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue D., Wu Y., Cao L., Wang J. The relationship between the growth of Ectropis oblique and the natural environment condition. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2009:146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M.F., Filman D.J., Hogle J.M., Semler B.L. Structural domains of the poliovirus polyprotein are major determinants for proteolytic cleavage at Gln–Gly pairs. J. Biol. Chem. 1988;263:17846–17856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]