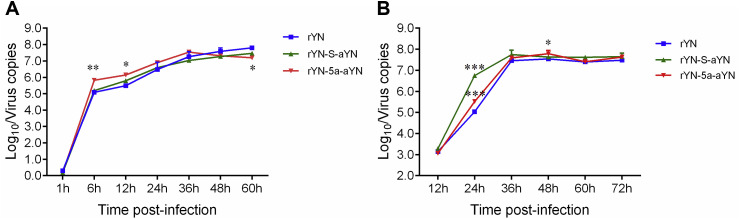
Fig. 2.
Growth characteristics of IBV-rYNs. (A) Comparison of the replication kinetics of rYNs in CEK cells. The rescued viruses (0.2 ml of 103 TCID50) were inoculated onto CEK cells in 24-well plates, and the supernatants from three wells from each group were harvested at various time-points post-infection for real-time PCR detection of IBV N gene. (B) Comparison of the replication kinetics of rYNs in ovo. The rescued viruses (0.2 ml of 102 EID50) were inoculated into the allantoic cavities of 10-day-old embryonated eggs, and the allantoic fluids of five eggs from each group were harvested at the time points 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, and 72 hpi and pooled for real-time PCR detection of IBV N gene. All of the assays were run in triplicate and calculated according to a standard curve. Data were statistically evaluated by the two-way ANOVA test adjusted for post-hoc analysis, followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparison tests. Statistically significant differences between groups are highlighted; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.