Abstract
The cell cycle, as a basic cellular process, is conservatively regulated. Consequently, subversion of the host cell replication cycle is a common strategy employed by many viruses to create a cellular environment favorable for viral replication. Newcastle disease virus (NDV) causes disease in poultry and is also an effective oncolytic agent. However, the effects of NDV infection on cell cycle progression are unknown. In this study, we showed that NDV replication in asynchronized cells resulted in the accumulation of infected cells in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle, which benefitted the proliferation of NDV. Examination of various cell cycle-regulatory proteins showed that expression of cyclin D1, was significantly reduced following NDV infection. Importantly, the decreased expression of cyclin D1 was reversed by inhibition of CHOP expression, indicating that induction of the PERK-eIF-2a-ATF4-CHOP signaling pathway was involved in the G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest observed following NDV infection.
Keywords: Cell cycle arrest, Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV), Cyclin D1, Viral replication
1. Introduction
Appropriate regulation of the cell cycle is important for cell proliferation, differentiation, and cell homeostasis. The primary regulatory proteins controlling cell cycle progression are the cyclins and the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). The cyclins and CDKs form complexes (Cook et al., 2000) that, upon activation, are responsible for phosphorylation of downstream targets, including cell cycle repressors.
During cell cycle progression, the expression levels of specific cyclins vary. For example, cyclins D and E are crucial in the G1 phase, cyclin A is required in the S phase, and both cyclin B and cyclin A are important in the G2 and mitotic phases (Obaya and Sedivy, 2002). Cyclin D1-Cdk4/6 complexes regulate G1-phase progression by phosphorylation of the downstream retinoblastoma (Rb) protein (Blomen and Boonstra, 2007, Shafer, 1998). Later in the G1 phase, cyclin E is induced and it associates with Cdk2 to form active complexes that phosphorylate Rb. Hyper-phosphorylation of Rb deactivates it, causing the release of E2F transcription factors and facilitating the transcription of genes essential for DNA synthesis, so that the cells then progress into the S phase (Lundberg and Weinberg, 1998, Vermeulen et al., 2003, Bagga and Bouchard, 2014). The activities of cyclin-Cdk complexes are regulated by cellular Cdk inhibitors (CKIs) (Vermeulen et al., 2003, Harper and Brooks, 2005), which can be grouped into two families. The CKIs of the INK4 family bind to Cdk4 and Cdk6 and block cyclin D-Cdk4/6 activities (Harper and Brooks, 2005, Sherr, 1994). The CKIs of the Cip/Kip family, which include P21Cip1 and P27Kip1, are potent inhibitors of cyclin E-and A-dependent Cdk2 (Sherr and Roberts, 1999).
Many viruses, including DNA, RNA, and retroviruses, modulate the cell cycle to benefit their own replication. DNA viruses, whose primary site of replication is the nucleus, have been studied most extensively in terms of cell cycle control. Some small DNA tumorigenic viruses, including human papillomavirus (Reinson et al., 2015), simian virus (Rohaly et al., 2010, Lin and Lamb, 2000), and adenovirus, encode proteins that promote entry into the S phase, thereby avoiding competition for cellular DNA replication resources (Jiang et al., 2015). This virus-mediated alteration to the cell cycle may ultimately contribute to cancer progression (Hanahan and Weinberg, 2000). By contrast, some large DNA viruses (for example, herpesviruses) are able to elicit cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase to limit the competition between the virus and the host for cellular DNA replication resources. Retroviruses, which also replicate in the nucleus, are also associated with cell cycle perturbations. For example, the Vpr protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is responsible for inducing cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase, when the expression of the viral genes is optimal (Hrimech et al., 2000, He et al., 1995). Increasingly, RNA viruses, whose primary site of replication is the cytoplasm, have also been observed to alter the host cell cycle. In the coronavirus family, infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) induces a G2/M-phase arrest in infected cells that favors viral replication (Dove et al., 2006), while mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) replication and some severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) proteins induce cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase (Chen and Makino, 2004, Yuan et al., 2005).
Newcastle disease virus (NDV) belongs to the genus Avulavirus in the family Paramyxoviridae. It is a single-stranded, negative-sense, enveloped RNA virus and causes respiratory diseases and death in poultry. NDV has also attracted much interest in cancer viro-therapy, as it can selectively infect and kill human cancer cells (Mansour et al., 2011). NDV induces apoptosis in cancer cells by activating the mitochondrial pathway (Elankumaran et al., 2006, Molouki et al., 2010). Cross talk between apoptosis and the cell cycle occurs as a result of the overlap in their regulatory mechanisms; however, the effects of NDV infection on the cell cycle are unknown.
In this study, we examined the potential effects of NDV infection on cell cycle progression. NDV replication induced cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase, and this ability was shared among different strains of NDV. We also analyzed viral protein expression and viral titers to evaluate whether cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase produces favorable conditions for viral replication. The findings reported here indicate that cell cycle regulation may be a common strategy exploited by NDV during infection to promote virus proliferation.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Virus and cells
The NDV velogenic strain Herts/33 and the lentogenic strain La Sota were obtained from the Chinese Institute of Veterinary Drug Control (IVDC) (Beijing, China). Viral titers were determined by plaque assay titration on DF-1 cells and were expressed as the tissue culture infective dose of 50 (TCID50) per milliliter. The viruses were inactivated with UV light irradiation (0.36J).
2.2. Infection
For cell cycle analysis, HeLa cells were infected with NDV at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of one. After 1 h, the cells were cultured in complete medium at 37 °C and harvested at various times post infection (p.i.) for cell cycle and western blot analyses. For comparison of viral protein expression and progeny virus production in different cell cycle phases, cells were infected with NDV at an MOI of 0.1. After 1 h, a medium was added to maintain cells in different cell-cycle phases. Sixteen hours after infection, the cells were harvested and nucleocapsid protein (NP) protein expression was detected by western blotting. The viral titer in the supernatant was determined by the plaque forming assay on DF-1 cells.
2.3. Synchronization of cells
Cell cultures at 80% confluency were synchronized in the G0 phase by serum deprivation. Approximately 5 × 105 cells/well were plated in a six-well plate and maintained in FBS-free medium for 48 h. For G1 phase arrest, cells were seeded at approximately 5 × 105 cells/well in six-well plates and treated with N-butyrate (B5887; Sigma, Saint Louis, MO, USA) at 3 mM for 20 h. For G2 phase arrest, cells were seeded at 5 × 105 cells/well and treated with 100 μM genistein (G6649; Sigma, Saint Louis, MO, USA) for 48 h. For M phase arrest, cells were seeded at 5 × 105 cells per well in six-well plates and treated with nocodazole (M1404; Sigma, Saint Louis, MO, USA) at 50 ng/ml for 10 h.
2.4. BrdU incorporation and flow cytometry analysis
For cell cycle analysis, two-color flow-cytometric analysis was used for accurate determination of the cell cycle profile. Mock-infected and infected cells were pulsed with bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU [B5002; Sigma, Saint Louis, MO, USA] 10 μM to approximately 1 × 106 cells) for 1 h prior to harvesting with trypsin. Cells were fixed with ice-cold 70% ethanol at 4 ℃ overnight and then treated with 2 N HCl containing 0.5% Triton X-100 for 30 min. Residual acid was neutralized by incubating the cell suspension with 0.1 M sodium borate (pH 8.5) for 2 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated with anti-BrdU-FITC solution (anti-BrdU-FITC antibody [556028; BD Biosciences Pharmingen, San Diego, CA, USA] in a 1:5 dilution) at 4 ℃ overnight. The cell suspension was incubated with propidium iodide (PI) staining solution in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (50 μg/ml PI [Sigma, Saint Louis, MO, USA] and 200 μg/ml RNase [Beyotime, Shanghai, China]) for 30 min at 37 ℃ and then analyzed with a FACSCalibur Flow Cytometer (Beckman, Mississauga, ON, Canada) and FlowJo software.
2.5. Transfection and plasmid, small interfering RNA
When the cells were grown to 70–80% confluent, plasmid DNA was transfected using Lipofectamine 3000 reagent according to the manufacture's protocol. 16 h post-transfection, cells were infected with NDV. PXJ40F plasmid was constructed and preserved in out lab (Liao et al., 2016). Specific sets of small interfering RNA (siRNA) for CHOP as well as nonsense sequence used as scrambled siRNA were purchased from GenePharma (Shanghai China).
2.6. Western blot analysis and antibodies
Cells were lysed in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 6.8], 2% SDS, 10% glycerol, 5% 2-mercaptoethanol, and 0.01% bromophenol blue), and the amount of protein in each sample was determined with the bicinchoninic acid assay (Beyotime, Shanghai, China). Ten to twenty micrograms of total cellular protein from each sample were subjected to SDS-PAGE. Proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) and proteins were detected with corresponding primary and secondary antibodies. Blots were performed using an enhanced chemiluminescence detection kit (Thermo Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). Primary antibodies were: anti-phospho-Rb (Ser 795) (Sigma-Aldrich, MO, USA), anti-cyclin D1 (Cell Signaling Technology [CST], MA, USA), anti-cyclin E1 (CST, MA, USA), anti-P21 (Santa Cruz Biotechology, CA, USA), anti-P27 (Santa Cruz Biotechology, CA, USA), anti-P53 (CST, MA, USA), anti-PERK/ p-PERK (Abcam, MA, USA), anti- eIF2α/ p- eIF2α, anti-ATF4 and anti-CHOP (CST, MA, USA). A mouse monoclonal antibody against the NDV NP protein was prepared in our laboratory for use in these experiments. Actin was detected with a mouse anti-actin monoclonal antibody (Sigma-Aldrich, MO, USA). Horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-rabbit or -mouse secondary antibodies were purchased from Jackson ImmunoResearch (West Grove, PA, USA).
2.7. Statistical and densitometry analysis
Statistical probabilities were determined using the Student's t-test. Results are presented as means and standard deviations (SD) of three experiments. P values of < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Representative western blots are shown for one of the three independent experiments. Band density was evaluated and quantified for each protein using Image J software.
3. Results
3.1. Infection with replication-competent NDV results in an accumulation of cells in the G0/G1 phase
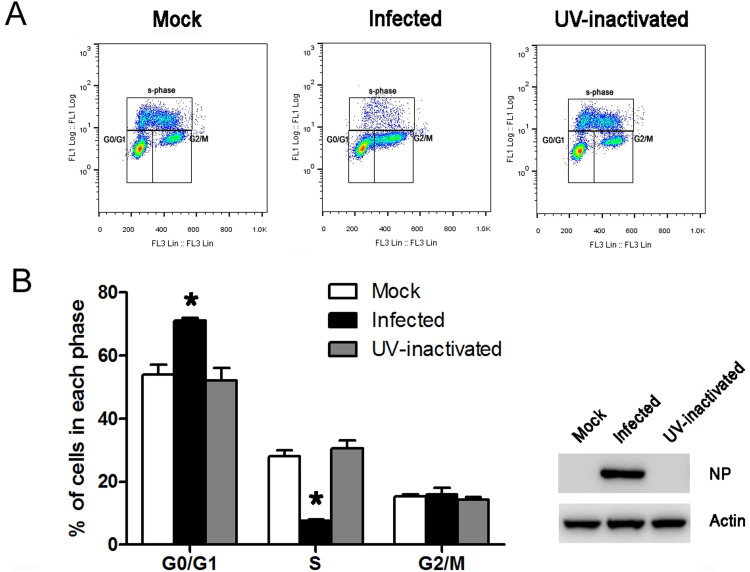
To investigate the effect of infection with NDV on cell cycle profiles and to determine whether the replication of NDV is necessary for specific cell cycle anomalies, asynchronously growing cells were mock-infected or infected with intact virus or UV-inactivated NDV for 24 h and then analyzed by flow-cytometry. HeLa cells were used in these experiments, as they are permissive for NDV infection and have been used as a model cell type to study virus-cell interactions. Representative cell cycle profiles and histograms are shown in Fig. 1. An obvious accumulation of cells in the G0/G1 phase was evident in NDV-infected cells when compared with mock-infected cells (Fig. 1A). Further analysis of the plots using Prizm (Fig. 1B) revealed that the proportion of cells in each of the G0/G1, S, and G2/M phases were similar in the mock-infected cells and cells infected with UV-inactivated virus (Fig. 1). UV inactivation of NDV was confirmed by the absence of the N protein in the cells treated with the UV-inactivated NDV at 24 h post infection (Fig. 1C). Thus, we concluded that NDV infection resulted in G0/G1 cell cycle arrest, but the arrest was dependent on virus replication.
Fig. 1.
NDV-induced G0/G1 phase accumulation depends on the presence of replication-competent virus. (A) Asynchronously growing HeLa cells were mock infected (Mock), infected with UV-inactivated virus (UV), or infected with NDV at an MOI of 1. At 24 h post-infection, cells were pulsed with 10 μM BrdU for 1 h prior to harvest and then collected by trypsinization. Cells were fixed, stained with anti-BrdU antibody and propidium iodide, and analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Representative histograms of flow cytometry data are shown. Statistical significance was determined by comparisons between Mock (white) and NDV (black) or UV (gray) cells. *P < 0.05. (C) To ensure that UV-inactivated virus was incapable of replication, viral NP proteins from Mock, NDV, and UV cells were examined by western blotting. Data are presented as mean ± SD for three independent experiments.
3.2. Entry of NDV-infected cells into the S phase is prevented
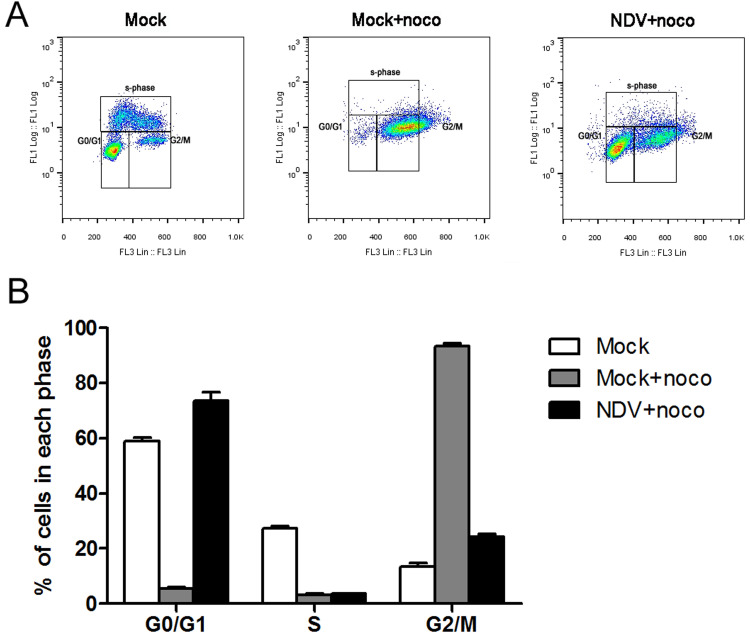
This accumulation of cells in the G0/G1 phase was further investigated by adding nocodazole (which is known to block cell cycle progression in the G2/M phase through disruption of mitotic spindles) to cells to induce G2/M-phase arrest. HeLa cells were treated with nocodazole at 8 h post infection, after the expression of the viral proteins had already occurred. Cells were harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry after another 16 h. The mock-infected cells progressed normally through G0/G1 to G2/M phase but stopped at the G2/M phase because of the mitotic block. Only 2.3% of the mock-infected cells remained in the G0/G1 phase after 16 h of nocodazole treatment. However, more than 60% of the NDV-infected cells stayed in G0/G1 phase, indicating that fewer cells stayed in the G2/M phase when compared to the mock-infected cells ( Fig. 2A and B). Therefore, NDV infection appeared to induce a G0/G1 phase accumulation by preventing cell cycle entry into the S phase, rather than influencing late-phase cell progression from the M into the G1 phase.
Fig. 2.
NDV infection prevents cell entry into S phase. (A) HeLa cells were mock-infected (mock) or infected with NDV at an MOI of 1 (infected). At 8 h post-infection, cells were treated with nocodazole (noco) at 50 ng/ml. After 16 h of noco treatment, the cells were pulsed with 10 μM BrdU for 1 h prior to harvest and then collected by trypsinization. The cells were fixed, stained with anti-BrdU antibody and propidium iodide, and then analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Representative histograms of flow cytometry data are shown. Data are presented as mean ± SD for three independent experiments.
3.3. NDV infection induces G0/G1 arrest in different cell lines and different strains
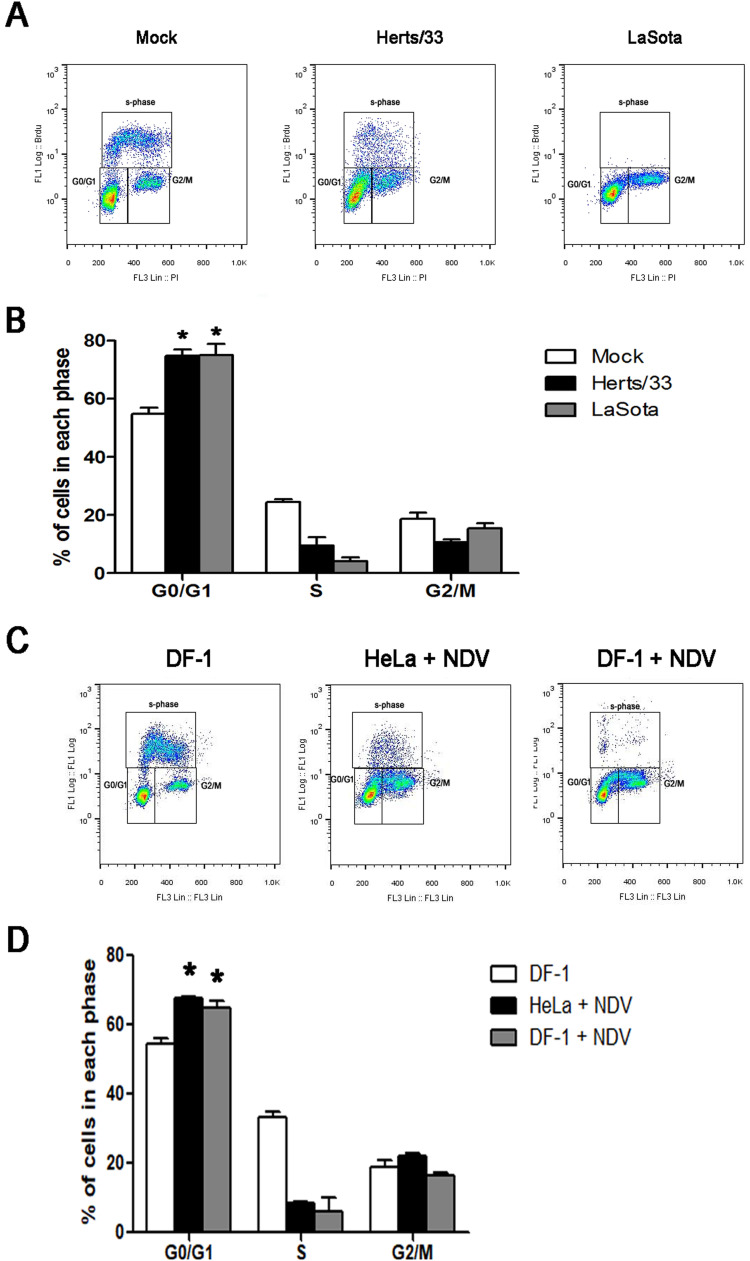
Different NDV strains were tested for their ability to induce G0/G1 arrest by infecting HeLa cells with 1 MOI of Herts/33 strain and La Sota strain. The cells infected with La Sota exhibited G0/G1 accumulation with the same profile seen following infection with Herts/33 ( Fig. 3A and B). Infection of DF-1 cells with NDV also resulted in G0/G1 arrest, (Fig. 3C and D). These experiments suggest that arrest of the host cell cycle in the G0/G1 phase may be a common strategy for NDV strains.
Fig. 3.
Cell cycle regulation effects in different strains and different cell line. (A) Cells were mock-infected or infected with Herts/33 (NDV) or La Sota (NDV) at an MOI of 1. At 24 h post-infection, the cells were pulsed with 10 μM BrdU for 1 h prior to harvest and then collected by trypsinization. The cells were fixed, stained with anti-BrdU antibody and propidium iodide, and analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Representative histograms of flow cytometry data are shown. Statistical significance was determined by comparisons between mock-infected and Herts/33-infected or La Sota-infected. (C) DF-1 cells and HeLa cells were mock-infected or infected with Herts/33 (NDV) at 1of MOI. At 24 h post-infection, cells were pulsed with 10 μM BrdU for 1 h prior to harvest and then collected by trypsinization. The cells were fixed, stained with anti-BrdU antibody and propidium iodide, and analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) Representative histograms of flow cytometry data are shown. Statistical significance was determined by comparisons between DF-1 cells and HeLa cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD for three independent experiments. *P < 0.05.
3.4. NDV replication is favored in cells synchronized in G0/G1-phase
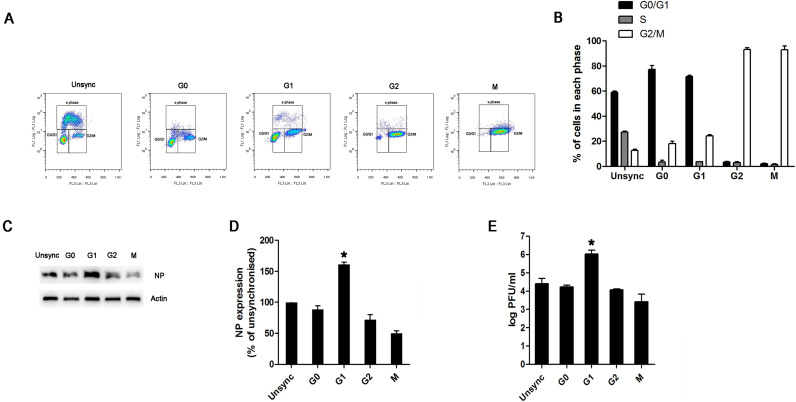
The benefit of a cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase was not clear in terms of viral replication. Therefore, we compared the replication of NDV in infected cells synchronized into the G1 phase with other cells synchronized in the G0, G2, and M-phase or unsynchronized, using viral NP expression and viral progeny titers as surrogates for viral replication. As shown in Fig. 4A–B, 78% of the cells were blocked in the G0 phase among the G0-phase-synchronized cells, 72% of the cells were blocked in the G1 phase among G1-phase-synchronized cells, and 59% of the cells were in G0/G1 phase among the normal unsynchronized cells. When G2 synchronization was considered, 92% of the cells were in the G2/M phase, with < 5% of the cells in G0/G1 phase. For M synchronization, 93% of the cells were in the G2/M phase, with < 3% of the cells in G0/G1 phase. Cells were then simultaneously infected with NDV at a low MOI of 0.1. After 16 h, the expression level of viral NP protein was significantly higher in G1-phase-synchronized cells than those synchronized in the G0, G2, or M phases or in asynchronous cells (Fig. 4C-D). Analysis of progeny viral production at 16 h post infection indicated a greater viral production in the G1-phase-synchronized cells (~1.09 × 106 PFU/ml) than in progeny virus in the G0 (~1.70 × 104 PFU/ml), G2 (~1.00 × 104 PFU/ml), and M (~2.63 × 103 PFU/ml) phases or in asynchronous cells (~2.57 × 104 PFU/ml) (Fig. 4E). This result matched the pattern of viral protein expression levels, indicating a likely benefit to viral replication in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle.
Fig. 4.
G1-phase synchronization promotes viral replication. (A–B) Synchronized cells were treated by serum starvation (G0) for 48 h, treated with 3 mM N-butyrate (G1) for 20 h, treated with 100 µm genistein (G2) for 48 h, or treated with 50 ng/ml nocodazole (M) for 12 h. (A) The synchronized cells were pulsed with 10 μM BrdU for 1 h prior to harvest and then collected by trypsinization. The cells were fixed, stained with anti-BrdU antibody and propidium iodide, and then analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Representative histograms of flow cytometry data are shown. (C–E) The synchronized and unsynchronized cells were infected with NDV at an MOI of 1 for 1 h. After infection, the medium was restored to maintain the respective cell cycle synchronization status. An additional 16 h later, cells were harvested and analyzed. (C) The expression of NP was determined by western blotting. (D) The levels of NP from three experiments were quantified with ImageJ software and normalized against the results of actin. (E) NDV progeny in the supernatant were titrated by a plaque assay on DF-1 cells, and quantitative analysis data, in PFU/ml, are shown. Data are presented as mean ± SD for three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by comparisons between unsynchronized and different groups of synchronized cells. *P < 0.05.
3.5. Key molecules regulating the cell cycle in NDV-infected cells
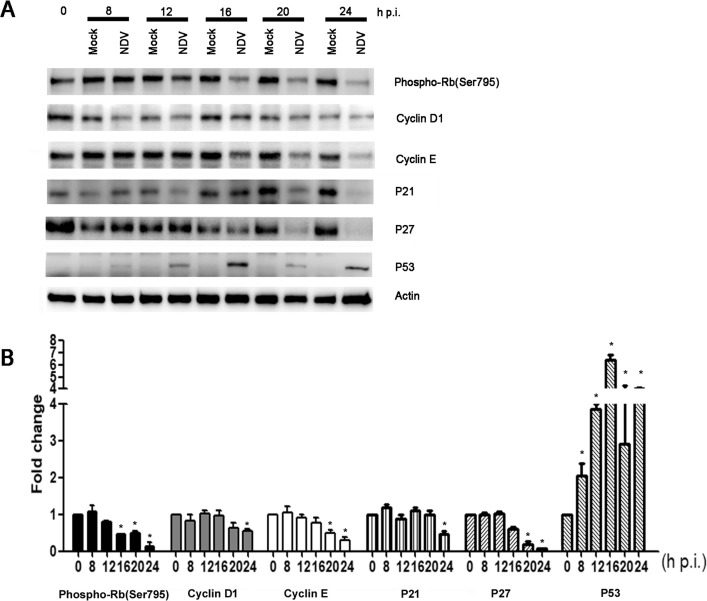
Many host molecules are involved in regulation of the G1/S transition, including cyclin-Cdk complexes, pRb, and CKI molecules (He et al., 2010). We identified the signaling pathway and key molecules responsible for NDV-induced cell cycle arrest by examining the expression profiles of host G1/S transition proteins. HeLa cells were infected with NDV and harvested at 8, 12, 16, 20, and 24 h post infection. Intracellular proteins were extracted and subjected to western blotting using specific antibodies.
Among the molecules investigated, we examined the phosphorylation status of Rb, a key regulator of cell cycle progression from the G0/G1 phase to the S phase. Fig. 5 shows a marked decrease in the amount of hyper-phosphorylated Rb after infection. Rb is a downstream regulatory protein of the cyclin–Cdk pathway, so the expression profiles of various cyclins and CKIs were also examined. A significant decrease in cyclin E and cyclin D1 was noted in NDV-infected cells compared to mock-infected cells (Fig. 5A and B). The protein expression pattern indicated a significant decrease in the expression of proteins associated with cell cycle progression from the G0/G1 to the S phase in NDV-infected cells. Unexpectedly, instead of increase, a significant decrease was noted in both p21 and p27 expression, although a significant increase occurred for P53 in NDV-infected cells compared to mock-infected cells (Fig. 5A and B). This result suggests that NDV-induced cell cycle arrest did not involve the activation of P21 or P27.
Fig. 5.
NDV infection induces the down regulation of phosphorylated Rb and cyclin E. (A) At the indicated times post-infection (p.i.), mock-infected and NDV-infected cells were collected for western blot analysis of phosphorylated Rb, cyclin D1, and cyclin E. The data shown are from one of three experiments. (B) The protein amounts in panel A were quantified using ImageJ software. The ratio of protein (normalized to the actin loading control) in NDV-infected samples to that in mock-infected samples was calculated. The data are presented as mean ± SD for three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by comparison to the corresponding value at 0 h p.i., *P < 0.05.
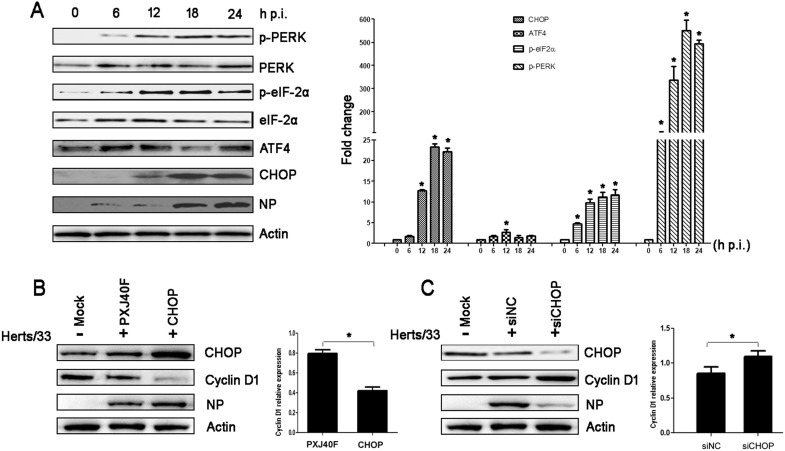
3.6. CHOP is involved via PKR activation in the decrease in cyclin D1 induced by NDV infection
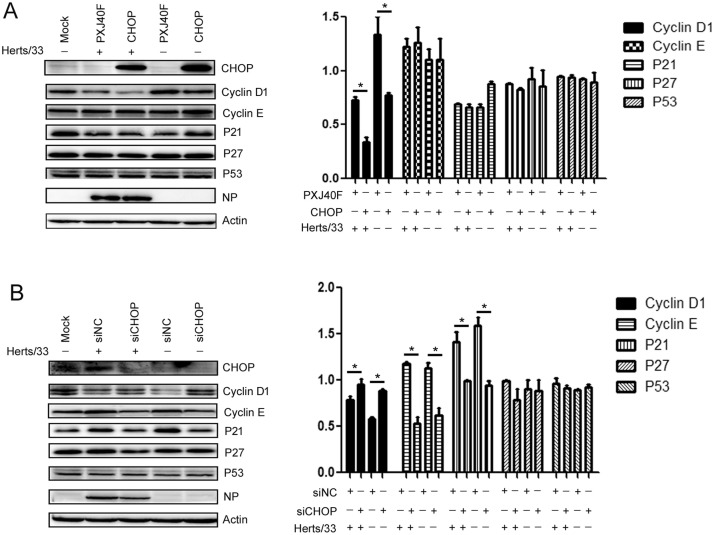
A previous report (Liao et al., 2016) from our lab showed that NDV infection activates the PERK/ eIF2α cascade and inhibits protein translation of the host cells, while viral protein NP levels increase. C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) is a downstream effector of PKR/ eIF2α/ATF4 and is also known as “growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible gene 153” (GADD153). Therefore, we hypothesized that CHOP might be involved in the attenuation of cyclin D1 and cyclin E expression. In order to address this question, we determined the activation of PERK/eIF2 α signaling cascade at different time point post-infection. Coincided with our previous report (Liao et al., 2016), NDV infection activated the PERK/ eIF2α signaling cascade by exhibiting increased phosphorylation of PERK and eIF-2α, as well as the increased level of CHOP expression. ( Fig. 6A). Importantly, exogenous expression of CHOP in HeLa cells by transfection of the PXJ40F-CHOP significantly enhanced the decreasing of cyclin D1 expression resulted by NDV infection (Fig. 6B). In contrast to overexpression, silencing the expression of CHOP by transfection of siCHOP prevented the decreasing of cyclin D1 induced by NDV infection (Fig. 6C). However, overexpression of CHOP had no significant effect on cyclin E, P21, P27 and P53 (Supplementary Fig. 1A). Although silencing of CHOP expression by siCHOP decreased cyclin E and P21 levels (Supplementary Fig. 1B), the reason that overexpression of CHOP had no effect on cyclin E and P21, and the final effect of CHOP knockdown-induced cyclin E and P21 decrease, require further study. These results suggested that NDV infection activated the PERK/ eIF2α/CHOP pathway, thereby involving this pathway in the G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest via downregulation of cyclin D1.
Fig. 6.
NDV infection regulates the protein expression of cyclin D1 and promotes virus replication by the PKR-CHOP pathway. (A) HeLa cells were mock-infected or infected with Herts/33 for 6, 12, 18 or 24 h. (Left) The cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by western blotting with antibodies against p-PERK, PERK, p-eIF2α, eIF2α, ATF4, NDV NP protein and actin. (Right) The intensities of p-PERK, p-eIF2α, ATF4, and CHOP were determined by densitometry, normalized to actin and shown as fold changes compared to mock infected. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with PXJ40-CHOP or PXJ40F and infected with Herts/33 at 16 h post-transfection. (Left) The cell lysates (12 h p.i.) were prepared and analyzed by western blotting with antibodies against CHOP, cyclin D1, NDV NP protein and actin. (Right) The intensities of cyclin D1were determined by densitometry, normalized to actin and shown as fold changes (PXJ40F-CHOP: PXJ40F). (C) HeLa cells were transfected with siCHOP or negative control siRNA (siNC) and infected with Herts/33 at 48 h post-transfection. (Left) The cell lysates (12 h p.i.) were prepared and analyzed by western blotting with antibodies against CHOP, cyclin D1, NDV NP protein and actin. (Right) The intensities of cyclin D1were determined by densitometry, normalized to actin and shown as fold changes (siCHOP: siNC). The data are presented as mean ± SD for three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by comparison to the corresponding value of control treatment, *P < 0.05.
4. Discussion
NDV is an avian paramyxovirus with significant oncolytic activity in tumor cells, and the mechanisms of NDV-mediated oncolysis have been investigated extensively. In this study, we explored the effect of NDV infection on host cell cycle progression. BrdU incorporation and FACS analyses demonstrated that NDV infection increased the percentage of cells in the G0/G1 phase, which prevented the cells from entering the S phase. This accumulation depended on infection with replication-competent NDV, as UV-inactivated NDV failed to induce a G0/G1 phase arrest. We hypothesized that an arrest in the G0/G1 phase by NDV infection could create a more favorable environment for NDV replication. Both NDV NP protein production and progeny viral production were highest in cells synchronized in the G1 phase. This benefit can be explained by a number of hypotheses, including increased efficiencies of transcription, translation, and viral assembly. This indicates that the G1 phase of the cell cycle provides a beneficial environment for NDV replication. However, the exact mechanism needs further study.
Cyclin D1-Cdk4/6 complexes regulate G1 phase progression through phosphorylation of the downstream retinoblastoma (Rb) protein (Blomen and Boonstra, 2007). When Rb is in the hypo-phosphorylated form, it is active and represses cell cycle progression by binding and inhibiting E2F transcription factors, which are responsible for transcription of genes important for DNA synthesis (Vermeulen et al., 2003, Bagga and Bouchard, 2014). Consistent with the cell cycle profile data, NDV replication inhibited Rb hyper-phosphorylation. A significant decrease in cyclin D1 was seen in NDV-infected cells, but the amounts of the CKIs p21Cip1and p27Kip1 decreased unexpectedly, even with an increase in P53 expression in the infected cells. Therefore, the NDV-induced inhibition of Rb hyper-phosphorylation and G1/S progression did not appear to be a result of the activation of these CKIs.
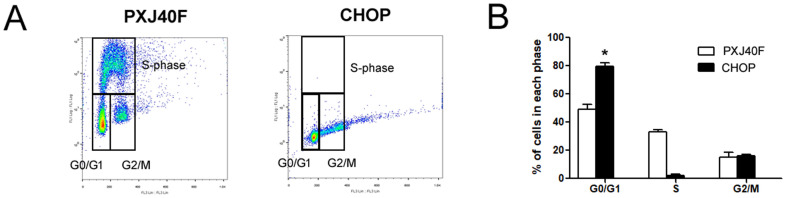
The reduced levels of both cyclin D1 and cyclin E in infected cells might have reduced the formation of cyclin D1-Cdk4/6 complexes and cyclin E-Cdk2 complexes, which are important for S-phase entry. The reduced levels of these complexes could then lead to insufficient pRb hyper-phosphorylation, thereby inhibiting cell cycle progression in the G0/G1 phase. Some reports have indicated that NDV infection can result in a general decrease in cellular protein synthesis (Liao et al., 2016) and the inhibition of translation may contribute to the decreased levels of cyclin D1 and cyclin E. Moreover, NDV infection reportedly will activate the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 cascade and inhibit protein translation in the host cells. As a downstream effector, CHOP plays an important role in the regulation of apoptosis. In this study, we showed that the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP signal pathway was activated in the cells upon NDV infection. Overexpression of CHOP significantly enhanced the reduction of cyclin D1, whereas inhibition of CHOP expression by siCHOP transfection reversed the NDV-induced cyclin D1 decrease. In addition to the effect on cyclin D1 level, overexpression of CHOP could sufficiently induce the accumulation of cells in G0/G1 phase (Supplementary Fig. 2), which further proved the involvement of CHOP in NDV infection-induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. Given that CHOP is implicated in apoptosis (Maytin et al., 2001, Yamaguchi and Wang, 2004), our results suggest a novel role of CHOP as a link between apoptosis and cell cycle arrest induced by NDV infection.
Funding
This work was supported by the key projects of Chinese Natural Sciences Foundation (31530074 and 31372421) and The National Key Research & Development Program of China (NO.2018YFD050103).
Footnotes
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.virol.2018.05.005.
Appendix A. Supplementary material
Fig. 1.
Overexpression of CHOP had no significant effect on cyclin E, P21, P27 and P53 levels, while knockdown of CHOP expression reduced cyclinE and P21 levels. (A) HeLa cells were transfected with PXJ40F-CHOP or PXJ40F and infected or mock infected with Herts/33 at 16 h post-transfection. (Left) The cell lysates (12 h p.i.) were prepared to analyze by western blot. (Right) The intensities of cyclin D1, cyclin E, P21, P27 and P53 were determined by densitometry, normalized to actin and shown as fold changes. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with siCHOP or negative control siRNA and infected or mock infected with Heres/33 at 48 h post-transfection. (Left) The cell lysates (12 h p.i.) were prepared and analyzed by western blot. (Right) The intensities of cyclin D1, cyclin E, P21, P27 and P53 were determined by densitometry, normalized to actin and shown as fold changes. The data are presented as mean ± SD for three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by comparison to the corresponding value of control treatment, * P < 0.05.
Fig. 2.
Overexpression of CHOP led to an accumulation of cells in the G0/G1 phase. HeLa cells were transfected with PXJ40F-CHOP or PXJ40F, and cultured for 24 h. (A) Cells were pulsed with 10 μM BrdU for 1 h prior to harvest and then collected by trypsinization. The cells were fixed, stained with anti-BrdU antibody and propidium iodide, and analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Representative histograms of flow cytometry data are shown. Statistical significance was determined by comparison between PXJ40F transfected cells and PXJ40F-CHOP transfected cells, *P < 0.05.
References
- Bagga S., Bouchard M.J. Cell cycle regulation during viral infection. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014;1170:165–227. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0888-2_10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomen V.A., Boonstra J. Cell fate determination during G1 phase progression. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2007;64:3084–3104. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7271-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C.J., Makino S. Murine coronavirus replication induces cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase. J. Virol. 2004;78:5658–5669. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.11.5658-5669.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S.J., Balmanno K., Garner A., Millar T., Taverner C., Todd D. Regulation of cell cycle re-entry by growth, survival and stress signaling pathways. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2000;28:233–240. doi: 10.1042/bst0280233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dove B., Brooks G., Bicknell K., Wurm T., Hiscox J.A. Cell cycle perturbations induced by infection with the coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus and their effect on virus replication. J. Virol. 2006;80:4147–4156. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.8.4147-4156.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elankumaran S., Rockemann D., Samal K.S. Newcastle disease virus exerts oncolysis by both intrinsic and extrinsic caspase-dependent pathways of cell death. J. Virol. 2006;80:7522–7534. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00241-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Weinberg R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81683-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J.V., Brooks G. The mammalian cell cycle: an overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005;296:113–153. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-857-9:113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He J., Choe S., Walker R., Di Marzio P., Morgan D.O., Landau N.R. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 viral protein R (Vpr) arrests cells in the G2 phase of the cell cycle by inhibiting p34cdc2 activity. J. Virol. 1995;69(11):6705–6711. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.11.6705-6711.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He Y., Xu K., Keiner B., Zhou J., Czudai V., Li T., Chen Z., Liu J., Klenk H.D., Shu Y.L., Sun B. Influenza A virus replication induces cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase. J. Virol. 2010;84:12832–12840. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01216-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrimech M., Yao X.J., Branton P.E., Cohen E.A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpr-mediated G(2) cell cycle arrest: vpr interferes with cell cycle signaling cascades by interacting with the B subunit of serine/threonine protein phosphatase 2A. EMBO J. 2000;19:3956–3967. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.15.3956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Jiang H., Gomez-Manzano C., Rivera-Molina Y., Lang F.F., Conrad C.A., Fueyo J. Oncolytic adenovirus research evolution: from cell-cycle checkpoints to immune checkpoints. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015;13:33–39. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2015.03.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao Y., Gu F., Mao X., Niu Q., Wang H., Sun Y., Song C., Qiu X., Tan L., Ding C. Regulation of de novo translation of host cells by manipulation of PERK/PKR and GADD34-PP1 activity during Newcastle disease virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2016;97:867–879. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin G.Y., Lamb R.A. The paramyxovirus simian virus 5 V protein slows progression of the cell cycle. J. Virol. 2000;74:9152–9166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.19.9152-9166.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A.S., Weinberg R.A. Functional inactivation of the retinoblastoma protein requires sequential modification by at least two distinct cyclin-cdk complexes. Mol. Cell Biol. 1998;18:753–761. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.2.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour M., Palese P., Zamarin D. Oncolytic specificity of Newcastle disease virus is mediated by selectivity for apoptosis-resistant cells. J. Virol. 2011;85:6015–6023. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01537-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maytin E.V., Ubeda M., Lin J.C., Habener J.F. Stress-inducible transcription factor CHOP/gadd153 induces apoptosis in mammalian cells via p38 kinase-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Exp. Cell Res. 2001;267:193–204. doi: 10.1006/excr.2001.5248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molouki A., Hsu Y.T., Jahanshiri F., Rosli R., Yusoff K. Newcastle disease virus infection promotes Bax redistribution to mitochondria and cell death in HeLa cells. Intervirology. 2010;53:87–94. doi: 10.1159/000264198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obaya A.J., Sedivy J.M. Regulation of cyclin-Cdk activity in mammalian cells. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2002;59:126–142. doi: 10.1007/s00018-002-8410-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinson T., Henno L., Toots M., Ustav M., Ustav M., Jr. The cell cycle timing of human papillomavirus DNA replication. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0131675. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohaly G., Korf K., Dehde S., Dornreiter I. Simian virus 40 activates ATR-Delta p53 signaling to override cell cycle and DNA replication control. J. Virol. 2010;84:10727–10747. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00122-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafer K.A. The cell cycle. Vet. Pathol. 1998;35:461–478. doi: 10.1177/030098589803500601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C.J. G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell. 1994;79:551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C.J., Roberts J.M. CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev. 1999;13:1501–1512. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.12.1501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen K., Van Bockstaele D.R., Berneman Z.N. The cell cycle: a review of regulation, deregulation and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 2003;36:131–149. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2184.2003.00266.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Wang H.G. CHOP is involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis by enhancing DR5 expression in human carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:45495–45502. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406933200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan X., Shan Y., Zhao Z., Chen J., Cong Y. G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis induced by SARS-CoV 3b protein in transfected cells. Virol. J. 2005;2:66. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-2-66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]