Abstract
Background
Advances in immunology and cell-based therapies are creating a need to track individual cell types, such as immune cells (neutrophils, eosinophils, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, etc.) and stem cells. As the fate of administered cells remains largely unknown, nuclear imaging could determine the migration and survival of cells in patients. [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4, or [89Zr]Zr-oxine, is a radiotracer for positron emission tomography (PET) that has been evaluated in preclinical models of cell tracking and could improve on [111In]In-oxine, the current gold standard radiotracer for cell tracking by scintigraphy and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), because of the better sensitivity, spatial resolution and quantification of PET. However, a clinically usable formulation of [89Zr]Zr-oxine is lacking. This study demonstrates a 1-step procedure for preparing [89Zr] Zr-oxine and evaluates it against [111In]In-oxine in white blood cell (WBC) labelling.
Methods
Commercial [89Zr]Zr-oxalate was added to a formulation containing oxine, a buffering agent, a base and a surfactant or organic solvent. WBC isolated from 10 human volunteers were radiolabelled with [89Zr]Zr-oxine following a clinical radiolabelling protocol. Labelling efficiency, cell viability, chemotaxis and DNA damage were evaluated in vitro, in an intra-individual comparison against [111In]In-oxine.
Results
An optimised formulation of [89Zr]Zr-oxine containing oxine, polysorbate 80 and 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) was developed. This enabled 1-step radiolabelling of oxine with commercial [89Zr]Zr-oxalate (0.1–25 MBq) in 5 min and radiotracer stability for 1 week. WBC labelling efficiency was 48.7 ± 6.3%, compared to 89.1 ± 9.5% (P < 0.0001, n = 10) for [111In]In-oxine. Intracellular retention of 89Zr and cell viability after radiolabelling were comparable to 111In. There were no significant differences in leukocyte chemotaxis or DNA damage between [89Zr]Zr-oxine or [111In]In-oxine.
Conclusions, advances in knowledge and implications for patient care
Our results demonstrate that [89Zr]Zr-oxine is a suitable PET alternative to [111In]In-oxine for WBC imaging. Our formulation allows rapid, stable, high-yield, single-step preparation of [89Zr]Zr-oxine from commercially available 89Zr. This will facilitate the clinical translation of cell tracking using [89Zr]Zr-oxine.
Keywords: Zirconium-89, Cell tracking, PET, Nanomedicine, CAR-T, Cell therapy
1. Background
Recent developments in immunology and cell-based therapies are creating a need to track the migration of individual cell types. For example, neutrophils and eosinophils in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease were shown to have different distribution patterns [1–4], and there is considerable interest in tracking T-cells [5–7] and dendritic cells [8] in cancer and auto-immune diseases, or stem cells in regenerative medicine [9]. There is an emerging consensus [10,11], ac-companied by recognition by drug regulators [12], that development and trials of cell-based therapies should be accompanied by methods to determine the location, survival, proliferation and differentiation of administered cells both in animal models and human subjects. Imaging the in vivo trafficking of cells radiolabelled prior to administration is a clinically acceptable, informative, non-invasive approach that can be used in human subjects, is not limited by depth and requires no biopsy. Gamma scintigraphy, and more recently single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), with autologous leukocytes labelled with gamma-emitting radionuclides (111In, 99mTc) has been a routine part of nuclear medicine since the 1970s [13] to detect sites of infection and/or inflammation [14,15]. Further developments in cell-based therapies [9,16–19] will require detection of small lesions and low numbers of cells, as well as better quantification, all of which could be achieved by positron emission tomography (PET).
Several positron-emitting radionuclides and radiotracers have been evaluated for cell tracking. The short half-lives of 68Ga (68 min) [20] and 18F (110 min) allow tracking only over brief periods, with 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose ([18F]FDG) in particular suffering from rapid efflux and variable labelling efficiencies [21–23]. 64Cu has a longer half-life (12.7 h) and can be efficiently incorporated into cells using lipophilic tracers [6,24–26], but also suffers from rapid efflux from labelled cells. Zirconium-89 (89Zr) is a long half-life positron emitter (t1/2 = 78.4 h, β+: 23%) that could meet the need for cell tracking over longer (7 days or more), more biologically relevant periods [27]. It is commercially available for clinical use and is now commonly used for PET imaging of monoclonal antibody distribution in humans [28]. A method for using zirconium-89 for cell labelling that is highly analogous to [111In] In-oxine, has recently emerged [29–31]. [89Zr]Zr-oxine has been shown to label various cell types including tumour cell lines [27,29,30], bone marrow and dendritic cells [31–33], therapeutic T cells [34–36], and stem cells [37] as well as liposomes [38,39]. Its use to date has been in preclinical contexts only.
One of the main obstacles to the use of [89Zr]Zr-oxine-labelled cells in the clinic is its cumbersome synthesis and the absence of a simple one-step formulation (“kit”), such as exists for [99mTc]Tc-D,L-hexamethylene-propyleneamine oxime ([99mTc]Tc-HMPAO, [99mTc]Tc-exametazime). This greatly restricts its clinical translation and commercial appeal for routine use in clinical trials. Furthermore, while some studies have investigated the effect of [89Zr]Zr-oxine labelling on cell function [34,35], only one preclinical study has directly compared [89Zr]Zr-oxine to the gold standard [111In]In-oxine [30]. Here we present the first kit formulation, and a simple, good manufacturing practices (GMP)-compliant, clinically translatable protocol for using it for rapid, one-step preparation of [89Zr]Zr-oxine, [64Cu]Cu-oxine and [68Ga]Ga-oxine for radiopharmaceutical applications, which will greatly enhance access of hospitals to cell tracking by PET in clinical diagnosis and trials of cell-based therapy. We demonstrate its application in radiolabelling human white blood cells (WBC) with [89Zr]Zr-oxine following a clinical protocol and provide a direct, intra-individual comparison with [111In]In-oxine.
2. Materials and methods
Unless otherwise indicated, reagents were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich and used without further purification. 8-hydroxyquinoline was obtained in ACS reagent grade, >99% purity. No-carrier-added, GMP-grade zirconium-89 (>150 MBq/nmol; BV Cyclotron, VU Amsterdam, NL) was purchased from PerkinElmer as [89Zr]Zr-oxalate in 1 M oxalic acid. [111In]InCl3 in 0.1 M HCl was purchased from Curium, UK. [68Ga] GaCl3 was eluted with 0.1 M HCl from a TiO2-based 68Ge/68Ga generator (lGG-100, Eckert & Ziegler). Copper-64 was prepared by 64Ni(p,n)64Cu nuclear reaction on a CTl RDS 112 11 MeV cyclotron as previously described [40]. Hydroxyethylstarch (HES200/0.5) was obtained from Carbosynth. Polysorbate 80 was obtained from Alfa Aesar. pH values were measured with a SevenCompact (Mettler-Toledo, UK) pH metre. Chemotaxis plates (polycarbonate membrane, 3.2 mm diameter, 5 μm pore size; ChemoTx® #101-5) were obtained from Neuroprobe. N- formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP) was obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Antibodies were obtained from Miltenyi Biotec unless otherwise specified.
2.1. Kit formulation and quality control (QC)
Step-by-step instructions for preparing the kit formulation of [89Zr] Zr-oxine are provided in the Supplementary Material. Briefly, a solution containing 8-hydroxyquinoline (oxine; final concentration 0.5 mg/mL), HEPES (final concentration 1 M) and polysorbate 80 (final concentration 1 mg/mL) in ultrapure H2O was adjusted to pH 7.9-8.0 with aqueous NaOH. The resulting solution was filtered through a 0.2 μm membrane (Millipore), dispensed in 100 μL aliquots in sterile glass vials and stored at RT in the dark or freeze-dried and reconstituted later with 0.1–1 mL H2O. Alternative formulations were obtained by using NaHCO3 instead of NaOH, varying the amount of polysorbate 80 or substituting polysorbate 80 with EtOH (5% final concentration). [89Zr]Zr-oxalate (0.5–25 MBq, provided at 1.0–1.5 MBq/μL on reference day) in 1 M oxalic acid was added to the formulation and left at RT for 5 min before use. [89Zr]ZrCl4 was obtained by loading commercial [89Zr]Zr-oxalate onto a Sep-Pak Light Plus QMA cartridge (Waters #WAT023525), washing the cartridge with 10 mL H2O, and eluting with 500 μL of 1 M HCl [41]. The commercial [111In]In-oxine product [42] contains 50 μg 8-hydroxyquinoline, 100 μg polysorbate 80, 6 mg HEPES and 7.5 mg NaCl in a volume of 1000 μL, at a pH of 6.5–7.5. To keep labelling volumes equal to the [89Zr]Zr-oxine formulation when using [111In]In-oxine, a 10× concentrated solution (adjusted to pH 7 with 10 M NaOH) was prepared, containing 50 μg 8-hydroxyquinoline, 100 μg polysorbate 80, 6 mg HEPES and 7.5 mg NaCl in a volume of 100 μL. 111In in 0.1 M HCl (40–60 μL, 20–25 MBq) was added and left for 15 min at RT.
Product formation was confirmed by radio thin-layer chromatography (radioTLC) on instant TLC (ITLC)-SG paper (Macherey-Nagel) or Whatman no.1 paper (GE Healthcare) using 100% ethyl acetate (EtOAc) as the mobile phase. ITLC plates were read using a Mini-Scan™ radioTLC linear scanner (LabLogic Systems) equipped with a β+ probe (LabLogic B-FC-3600). Radiochemical purity of the final product was calculated as the activity associated with the [89Zr]Zr-oxine peak as a percentage of the total detected activity on the chromatogram.
To study the recovery of radiotracer from the vial, 10 μL aliquots were taken immediately after addition of [89Zr]Zr-oxalate and after 15, 30, 60, 120 min, 24, 48, 72 and 168 h. The aliquots were gammacounted 7 days after addition of [89Zr]Zr-oxalate and percentage recovery determined as the counts in each sample divided by the counts in the sample taken immediately after addition. For stability studies, samples were left at room temperature (RT) in the dark and analysed by radioTLC over 7 days. A diluted kit was obtained by further adding 900 μL H2O 5 min after addition of [89Zr]Zr-oxalate to the kit formulation.
The partition coefficient (logD) of the [89Zr]Zr-oxine and [111In]In-oxine formulations was determined by adding 10 μL (approx. 1 MBq) of each formulation to 1 mL of a 50:50 presaturated mixture of either 1-octanol and water or 1-octanol and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), then vortexing for 5 min. Phase separation was then accelerated by brief centrifugation. 100 μL were taken from each phase and gammacounted.
2.2. Cell isolation
White blood cell isolation was performed in accordance with guidelines for radiolabelling WBC with [99mTc]Tc-exametazime and [111In]In-oxine [43,44]. Briefly, peripheral venous blood (50–55 mL) was collected from healthy, male (n = 5) and female (n = 5) donors aged 22–32, in anticoagulant citrate dextrose solution A (ACD-A) blood collection tubes (BD Vacutainer #366645) using 20G needles, on two separate occasions for each donor. Cell-free plasma (CFP) was obtained by centrifuging 10–15 mL blood at 2000g for 10 min. For WBC isolation, 45 mL blood was mixed with 7 mL of HES200/0.5 (10% wt./vol. in sterile saline) and centrifuged at 8g for 45 min at room temperature. Platelets were depleted by washing the WBC layer twice with Ca2+/Mg2+-free PBS (with 10 min centrifugation at 150g). The remaining cell pellet was re-suspended in 3 mL PBS for radiolabelling.
2.3. Cell labelling: Labelling efficiency (LE), retention, viability
To WBC (1.6–4.8 × 108) resuspended in 3 mL PBS, 100 μL of optimised [89Zr]Zr(oxinate)4 formulation (50 μg oxine, 18–21 MBq 89Zr) or 100 μL of 10× concentrated [111In]In(oxinate)3 formulation (50 μg oxine, 18–24 MBq 111In) were added. Cells were incubated for 20 min at RT with gentle swirling every 5 min. As an additional control, an aliquot of WBC was incubated with PBS only. Cells were then diluted with 50 mL PBS and centrifuged at 200g for 10 min. Supernatants and cell pellets were measured in a dose calibrator (CRC-25R, Capintec). The cells were suspended in CFP or assay medium (RPMI-1640 supplemented with 1% human serum, 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin) for further experiments. Viability was assessed using the Trypan Blue dye exclusion method. Cell labelling efficiency (LE%) was calculated as:
For radiotracer retention studies, radiolabelled WBC were suspended in autologous CFP, in triplicate in a 24-well plate and incubated at 37 °C. Cells were collected after 4 h or 24 h and viability was determined as above. Cells were diluted with PBS, centrifuged at 200g for 10 min, and supernatants and pellets were measured in a dose calibrator to determine retention using the formula above.
2.4. Chemotaxis assay
After radiolabelling, cell pellets were subjected to red blood cell (RBC) lysis by hypotonic shock. Cells were resuspended in 4.5 mL cold H2O for 30 s, after which isotonicity was restored by addition of 0.5 mL 10× PBS. Lysed RBC were removed by centrifugation and the remaining WBC were resuspended in assay medium at 3.5 × 106 cells/mL. The bottom wells of a chemotaxis plate were filled with 30 μL of assay medium, with or without 10 nM fMLP. On the top wells, 20 μL of cell suspension were then plated in triplicate and incubated for 45 min at 37 °C. Remaining cells in the top wells were removed, replaced by 40 μL of 5 mM EDTA in PBS to detach cells adhering to the membrane and the plate was incubated for 30 min at 4 °C. The top wells were emptied, the plate was centrifuged at 150g for 5 min and the cells in the bottom wells were counted using a haemocytometer. The chemotaxis index (CI) was calculated by dividing the number ofWBC in the wells containing fMLP by the number of WBC in the wells containing medium only.
2.5. DNA damage
WBC labelled with [89Zr]Zr-oxine or [111In]In-oxine or treated with PBS only were suspended in assay medium, seeded onto poly-L-lysine-coated coverslips and incubated for 30 min at 37 °C. Fixation and staining for γH2AX were performed as previously described [35]. Briefly, the cells were fixed and permeabilised with 3.7% formalin, 0.5% Triton X-100 and 0.5% IGEPAL® CA-630 in PBS. Staining was performed with an anti-γH2AX (Ser139) mouse mAb (1:1600; JBW301, Merck #05-636) and goat anti-mouse AF488-IgG (1:500; Jackson ImmunoResearch #115-545-062), followed by Hoechst 33342 for nuclei staining. Slides were imaged on an Eclipse Ti-E confocal microscope (Nikon) with a Plan Apo VC 60× oil DIC N2 objective (Nikon). Ten sections (0.4 μm thickness) were imaged. At least 30 nuclei/slide were imaged (2 slides/treatment). Maximal intensity projections of z-stacks were made using ImageJ v1.51p (http://imagej.nih.gov/ij). Nuclei and γH2AX foci were counted using CellProfiler v3.1.9 (http://cellprofiler.org) to determine the average numbers of γH2AX foci per nucleus in each image.
2.6. Flow-assisted cell sorting (FACS) of89Zr-labelled WBC
89Zr-labelled WBC were stained (15 min at 4 °C) with a combination of CD45-APC-Vio770 (#130-110-773), CD3-PE (REA613, #130-113-701), CD14-APC (#130-110-578), CD19-PE-Vio770 (REA675, #130-114-173) and CD16-FITC (REA423, #130-113-954) antibodies to sort samples into neutrophils, eosinophils, monocytes, T cells and B cells, or CD45-APC-Vio770, CD2354a-FITC (REA175, #130-117-800) and CD41a-PE (REA386, #130-121-429) to sort red blood cells and platelets. Compensation settings were adjusted using beads (anti-REA MACS® Comp, #130-104-693). Samples were analysed and sorted on a FACS-Melody instrument (BD Biosciences) equipped with blue (488 nm), yellow-green (521 nm) and red (633 nm) lasers. For each cell type, a determined number of events was collected, and the fractions were gamma-counted together with activity standards to determine the absolute amount of activity per cell.
2.7. Statistical analysis
Each subject provided WBC on two separate occasions (at least 1 week apart), once for [89Zr]Zr-oxine and once for [111In]In-oxine labelling, enabling differences between groups to be evaluated by Student’s two-tailed, paired t-test or Wilcoxon’s matched pairs signed-rank test, as appropriate. When additional factors were considered, analysis was performed using a repeated-measures Mixed Model (MM) in Prism v8.2 (GraphPad Software Inc.), with Tukey’s correction for multiple pairwise comparisons unless otherwise specified. Exact significance values are reported in each figure.
3. Results
3.1. QC method development
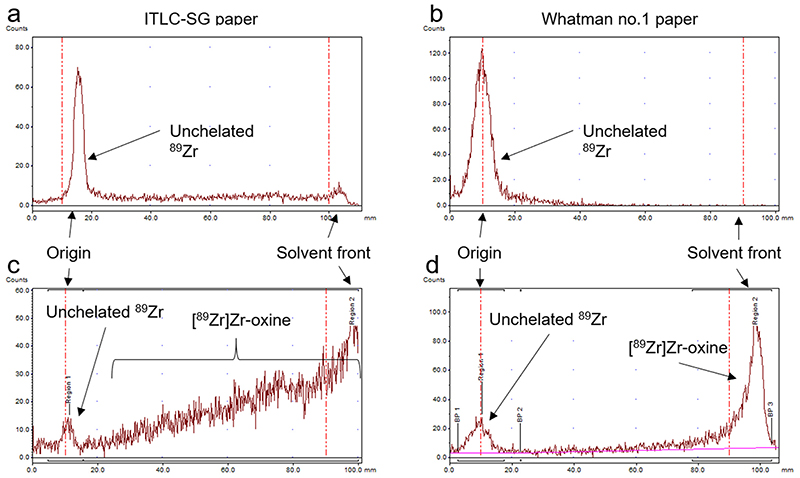
To evaluate the radiochemical yield of [89Zr]Zr-oxine, we optimised a simple radiopharmaceutical QC method. Initial measures by radioTLC on silica-gel impregnated glass fibre (ITLC-SG) using ethyl acetate showed no migration of unchelated 89Zr (Rf = 0, Fig. 1a), whereas [89Zr]Zr-oxine frequently showed marked streaking (Fig. 1c), possibly because the interaction of silanol groups with 89Zr leads to the dissociation of the metastable [89Zr]Zr-oxine complex during migration. Therefore, ITLC-SG is not an acceptable support for the QC of this radiotracer. In contrast, TLC on Whatman no. 1 paper shows a clear separation between unchelated 89Zr (Rf = 0, Fig. 1b) and [89Zr]Zr-oxine (Rf = 1, Fig. 1d). A strip length of 6 cm was found to provide clear separation between the two species, with a migration time of less than 8 min (Suppl. Fig. S1).
Fig. 1.
QC method for [89Zr]Zr-oxine. Representative radiochromatograms of [89Zr]Zr-oxalate in the absence of oxine (a, b) and [89Zr]Zr-oxine (c, d), spotted on ITLC-SG strips (a, c) or Whatman no.1 paper (b, d), with 100% EtOAc as mobile phase.
3.2. Kit formulation optimisation
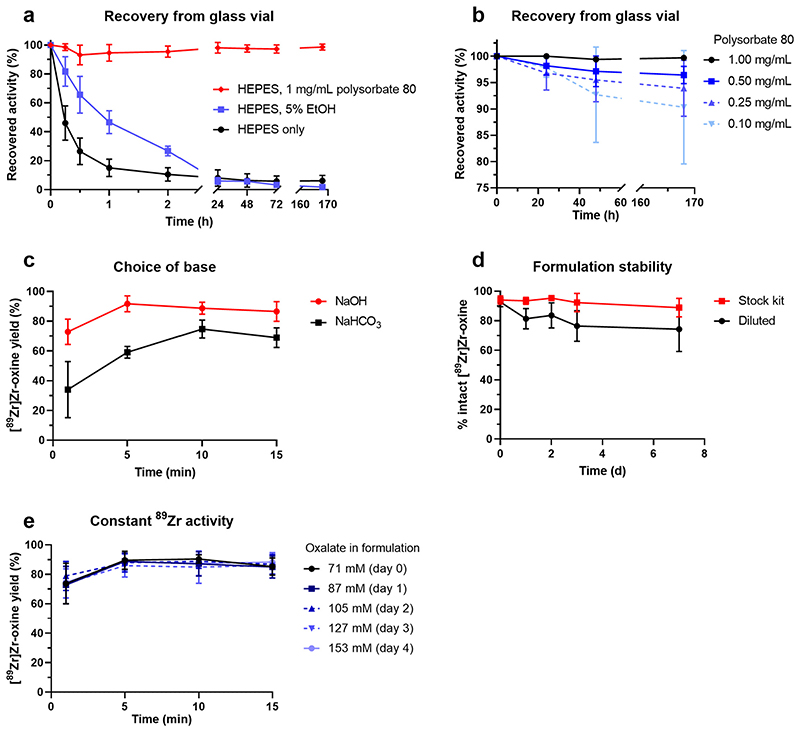
A kit formulation for [89Zr]Zr-oxine requires a base to neutralise the acidic solution of 89Zr supplied and a buffer to maintain the solution at pH 7–8. It was found that 100 μL of HEPES-buffered formulation (containing 50 μg 8-hydroxyquinoline and 52.5 μmol NaOH) was capable of buffering (pH ≥ 7.0) a maximum of 18 μL of [89Zr]Zr-oxalate solution (153 mM oxalate in final product). [89Zr]Zr-oxine formulated in 1 M HEPES buffer (pH 7.9) was found to rapidly adhere to glass vessels, with only 46% of the added activity recoverable from the vial 15 min after addition of [89Zr]Zr-oxalate. Including 5% EtOH in the solution delayed this phenomenon but did not prevent it, with 46% recoverable activity after 1 h and less than 6% after 24 h (Fig. 2a). In contrast, addition of 1 mg/mL polysorbate 80 prevented adhesion to the glass vessel and resulted in 98.7% recovery of activity up to 1 week after addition of [89Zr]Zr-oxalate (Fig. 2a, b). Reducing the concentration of polysorbate 80 resulted in minor losses of product. Replacing NaOH with NaHCO3 led to slower formation of [89Zr]Zr-oxine and reduced yields (Fig. 2c). The optimised formulation, a 100 μL solution at pH 7.9–8.0 containing 50 μg oxine, 1 M HEPES, NaOH and 1 mg/mL polysorbate 80, was stable for 7 days in concentrated format (Fig. 2d). The preparation and use of the kit formulation are schematically represented in Fig. 3. Diluting the formulation to 1 mL with H2O after addition of [89Zr]Zr-oxalate reduced the percentage of intact product from 92% to about 75% within 24–48 h. When using [89Zr]Zr-oxalate (1 Moxalic acid) as starting material, [89Zr] Zr-oxine was typically formed in 85–92% radiochemical yield (95% confidence interval, n = 15) 5 min after addition of [89Zr]Zr-oxalate (Fig. 2e). Increasing the volume of [89Zr]Zr-oxalate up to a final oxalate concentration of 153 mM to account for 89Zr decay did not affect the formation rate or final radiochemical yield of [89Zr]Zr-oxine (Fig. 2e). The percentage of “free”, unchelated oxine in a 20 MBq batch of [89Zr]Zr-oxine was calculated to be >99.86% (Supplementary Material, Table S1). The partition coefficient of the formulated [89Zr]Zr-oxine was found to be 0.80 ± 0.26 in water ([111In]In-oxine: 1.09 ± 0.03, n = 3, P = 0.18) and 0.60 ± 0.06 in PBS ([111In]In-oxine: 0.72 ±0.11, n = 3, P = 0.08; Suppl. Fig. S2).
Fig. 2. Formulation optimisation for [89Zr]Zr-oxine.
(a, b) Recovery: percentage of [89Zr]Zr-oxine remaining in solution over time when formulated in HEPES buffer only and in presence of 5% EtOHorvarying concentrations of polysorbate 80. Mean ± SDof n = 3 separate experiments. (c) Yield of [89Zr]Zr-oxine over time in HEPES buffers (pH 7.9) containing NaOH (n = 5) or NaHCO3 (n = 4), measured by radioTLC. (d) Stability: [89Zr]Zr-oxine as percentage oftotal89Zr activity in solution over 7 days, measured by radioTLC (n = 3), in original 100 pLformulation or after 10-fold dilution with H2O. (e) Formation rate and radiochemical yield of [89Zr]Zr-oxine as a function of oxalate content and 89Zr decay. [89Zr]Zr-oxalate in 1 M oxalic acid (1.1-1.5 MBq/μL on day 0, approximately 4-5 days after production in the cyclotron) was added to 20 μL aliquots of kit formulation on day of reception (day 0) and 4 subsequent days. To keep total 89Zr activity constant, increasing volumes of [89Zr]Zr-oxalate solution were added on each day, resulting in increasing concentrations of oxalate ions in the final product. Mean ± SD of n = 3 separate experiments.
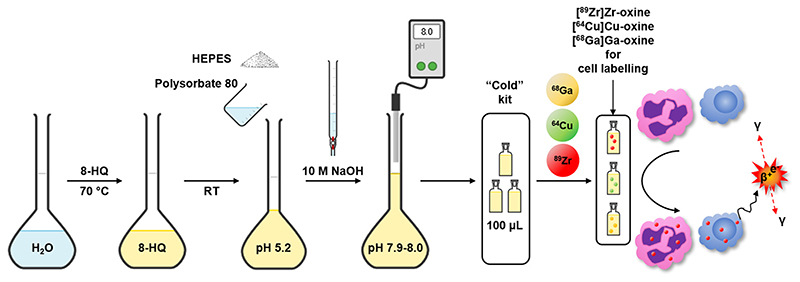
Fig. 3. Preparation and use of the kit formulation for [89Zr]Zr-oxine, [64Cu]Cu-oxine and [68Ga]Ga-oxine.
8-hydroxyquinoline is dissolved in water, followed by addition of HEPES and polysorbate 80 and pH adjustment to 7.9-8.0 with concentrated NaOH. This solution can be divided into single-use aliquots, e.g. one patient dose, and radiolabelled with commercial zirconium-89, copper-64 or gallium-68 as and when required. Alternatively, a central radiopharmacy facility could provide the radiolabelled product to the site performing the cell radiolabelling. The formulated [89Zr]Zr-oxine (or [64Cu]Cu-oxine/[68Ga]Ga-oxine) can be used to radiolabel various cell types, such as granulocytes or T-cells, without any further steps, for PET imaging.
As well as zirconium-89, the optimised oxine formulation was shown to form lipophilic complexes of oxine with gallium-68, copper-64 and indium-111 in high yield (Suppl. Fig. S3), and therefore may be useful for labelling cells or nanomedicines with these radionuclides.
3.3. Labelling efficiency and comparison with [Inin]in-oxine
A detailed standard operating procedure for labelling WBCs with the kit formulation of [89Zr]Zr-oxine is provided in the Supplementary Material. Using the optimised kit, we evaluated the labelling of human WBCs with [89Zr]Zr-oxine, in comparison with [111In]In-oxine formulated similarly to the commercial product [42]. WBCs were obtained from 10 healthy donors, following a clinical protocol for WBC labelling [44], and an intra-individual comparison of labelling with [89Zr]Zr-oxine and [111In]In-oxine was performed. In this study we have attempted to replicate real-world conditions as closely as possible, rather than standardise every single parameter (i.e. by using the same number of WBCs from each donor) or splitting WBC batches for labelling with each radiotracer. Labelling with each radiotracer was performed on separate occasions for each donor to comply with local ethical limits regarding blood donations.
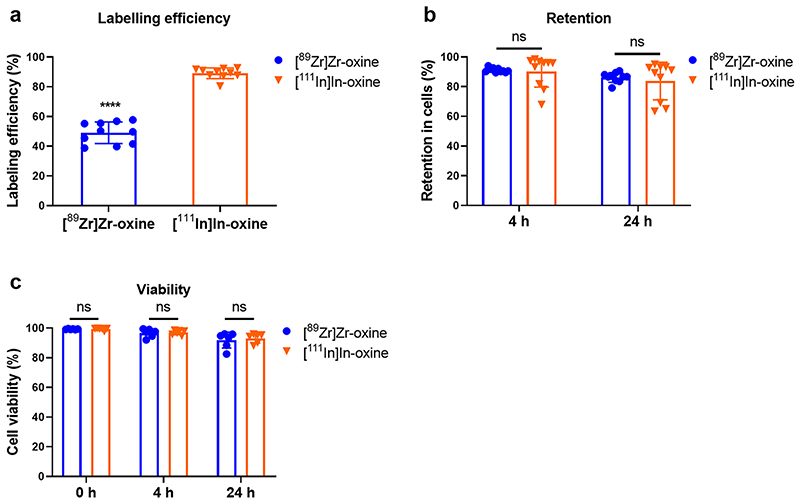
The labelling efficiency of WBCs with [89Zr]Zr-oxine was 48.7 ± 6.3%, c.f. 89.1 ± 9.5% (P <0.0001, n = 10) for [111In]In-oxine (Fig. 4a), resulting in an average activity of 32.9 ± 9.2 kBq/106 cells for [89Zr]Zr-oxine and 58.2 ± 26.1 kBq/106 cells for [111In]In-oxine. Cellular retention of 89Zr was 91.4 ± 1.4% after 4 h incubation in autologous CFP and 86.6 ± 2.9% after 24 h (Fig. 4b), and cell viability was 99.4 ± 0.3% immediately after labelling, 97.0 ± 2.3% after 4 h and 92.6 ± 4.8% after 24 h (Fig. 4c). There were no significant differences in retention or viability between [89Zr]Zr-oxine and [111In]In-oxine (P > 0.05, n = 6–10). Visual inspection of the cell preparations revealed no clumping or cells, aggregation or presence of fibrin clots.
Fig. 4. WBC radiolabelling with [89Zr]Zr-oxine and [111In]In-oxine.
(a) WBC labelling efficiency with [89Zr]Zr-oxine and [111In]In-oxine. Mean ± SD of n = 10 per group. ****P < 0.0001 (Student’s two-tailed paired t-test). (b) Retention of89Zrand 111In in WBC, 4 h and 24 h after radiolabelling. n = 10 per group, P > 0.05 (Wilcoxon’s matched pair signed-rank test). (c) Viability of 89Zr- and 111In-labelled WBC after 4 h and 24 h. Mean ± SD of n = 6 per group, Student’s two-tailed paired t-test.
The functionality of radiolabelled WBCs was tested using an in vitro chemotaxis assay, where the number of WBCs migrating in response to 10 nM fMLP was measured. The chemotaxis index of 89Zr-labelled WBCs was 2.7 ± 1.4 (n = 9), c.f. 3.4 ± 1.9 (n = 10) for 111In-labelled WBCs and 3.0 ± 1.0 (n = 10) for non-labelled WBCs (Fig. 5). There were no significant differences between the groups. Importantly, the chemotaxis indexes were all >1, demonstrating an active migration towards fMLP. There was no apparent trend relating the amount of activity per cell and the chemotaxis index (Suppl. Fig. S4).
Fig. 5. Chemotaxis of radiolabelled WBC. Cells were incubated with [89Zr]Zr-oxine, [111In]In-oxine, or vehicle only.
The chemotaxis index is the number of cells migrating towards 10 nM fMLP divided by the number of cells migrating towards vehicle, averaged from triplicates for each sample. Each point represents one donor. Bars represent the mean ± SD of n = 9, 10 and 10 individual samples. P ≥ 0.05 for all comparisons (mixed-effect analysis with Tukey’s correction for multiple comparisons).
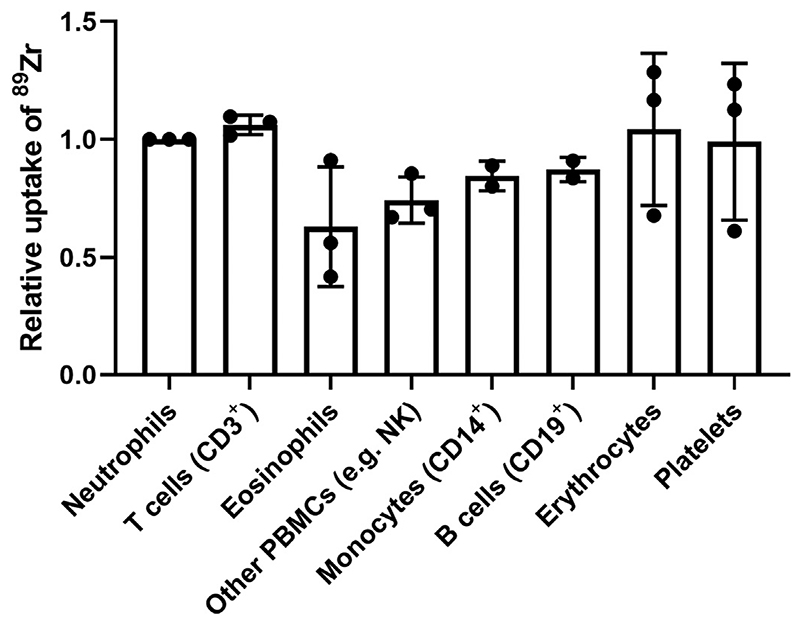
To determine whether certain subtypes of WBC had preferential uptake of [89Zr]Zr-oxine, radiolabelled WBC were stained with fluorescent monoclonal antibodies, automatically sorted and gamma-counted. For practical reasons, only a small fraction of the radiolabelled cells was sorted. There were large differences in average activity per cell (range 1–4 kBq/106 cells, Suppl. Fig. S5) between donors despite comparable labelling efficiencies (fraction of activity in cell pellet) because a fixed patient dose of [89Zr]Zr-oxine (20 MBq) was used whereas the number of WBCs isolated from each donor was highly variable. Results are therefore expressed as relative uptake of 89Zr per cell in each population (Fig. 6), taking neutrophils as reference (1.00). The relative activity of 89Zr per cell was 1.06 ± 0.04 in lymphocytes, 0.63 ± 0.25 in eosinophils, 0.74 ± 0.10 in NK cells, 0.87 ± 0.05 in B cells, 0.85 ± 0.06 in monocytes, 0.99 ± 0.33 in platelets and 1.04 ± 0.32 in erythrocytes.
Fig. 6. Relative uptake of 89Zr per cell in WBC populations after labelling mixed WBC with [89Zr]Zr-oxine.
Radiolabelled WBC were sorted by FACS and gamma-counted to determine the absolute activity per cell (>10,000 cells/sample). Data are expressed as a ratio of the activity per cell in the neutrophil population of each respective donor. Each point represents cells from an individual donor, bars represent the mean value of n = 2 or 3 donors.
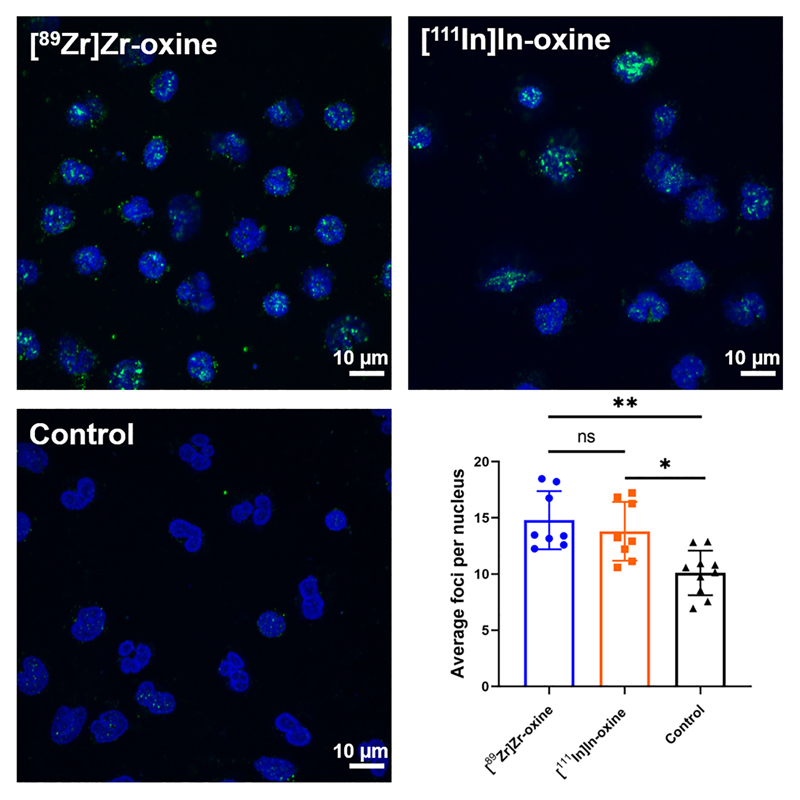
The effect of radiolabelling on DNA damage, assessed in terms of double-strand break formation, was determined by counting the number of γH2AX foci present in individual WBCs. The number of foci per nucleus was 14.8 ± 2.6 for [89Zr]Zr-oxine, 13.8 ± 2.6 for [111In]In-oxine and 10.1 ± 2.0 for unlabelled cells (Fig. 7). The differences between radiolabelled and non-radiolabelled samples were significant for both [89Zr]Zr-oxine and [111In]In-oxine, however there was no statistical difference between the two radiotracers. There was no apparent trend relating the number of foci per nucleus and the activity per cell after radiolabelling (Suppl. Fig. S6).
Fig. 7. Comparison of DNA damage induced by [89Zr]Zr-oxine and [111In]In-oxine in WBC.
Representative images (maximum intensity projections) of WBC labelled with [89Zr]Zr-oxine (top left), [111In]In-oxine (top right) or PBS only (bottom left), showing γH2AXfoci (green) and cell nuclei (blue). Scale bars represent 10 μm. Bottom right: average number of γH2AX foci per nucleus (at least 30 nuclei analysed per sample). Each point represents an individual donor, bars show the mean value of n = 8 donors. ns: P ≥ 0.05, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (mixed-effect analysis with Tukey’s correction for multiple comparisons, performed on log-transformed data).
4. Discussion
[89Zr]Zr-oxine was previously shown to be a useful cell labelling agent for PET imaging in animal models by our group and others [30–36]. In the clinic, the radiolabelling of mixed WBCs for infection imaging is one of the most common application of cell labelling, with the greatest collective experience within the nuclear medicine community. For the clinical translation of this radiotracer, we believe it is crucial to (a) simplify its synthesis to the point that it is usable with as few steps as possible by radiopharmacy operators, and (b) perform a direct comparison with the gold standard [111In]In-oxine in the clinically relevant model of radiolabelled WBCs.
Our previous synthesis of [89Zr]Zr-oxine from [89Zr]Zr-oxalate involved the use of chloroform as a solvent and subsequent evaporation and redissolution in a small amount of dimethyl sulfoxide or ethanol [29]. While relatively simple from a research perspective, this is far from ideal for the clinic as it involves several steps, requires meticulous precision during the neutralisation step and involves organic solvents (requiring further QC tests) and solvent evaporation, with an overall radiochemical yield of 60–80%. Sato et al. describe the synthesis from [89Zr]ZrCl4 [31], requiring prior conversion of the less-reactive [89Zr] Zr-oxalate [41] in which form 89Zr is typically produced [45,46] and available commercially. Leaving the conversion step to the final user results in additional manipulation, time and operator exposure, and lower activity concentration. Indeed, about 350 μLof1M hydrochloric acid are required to extract 80–90% of the [89Zr]Zr4+ from a typical anionexchange cartridge. Considering the typical batches (50–200 MBq) available commercially, this results in a large volume (35–200 μL) of 1 M hydrochloric acid to neutralise, requiring further dilution to reach isotonicity. This would result in final labelling volumes larger than recommended for WBC [44], leading to low labelling efficiencies. Furthermore, the amounts of oxine and polysorbate 80 described in that method are unnecessarily high and the process as described requires several steps. Weist et al. used unprocessed [89Zr]Zr-oxalate and a 1 M HEPES buffer, in a 2-step process [34]. However, we have demonstrated in the present work that [89Zr]Zr-oxine rapidly adheres to reaction vessels in the absence of surfactant. Socan et al. have described the on-cartridge preparation of oxine complexes of several radiometals, but reported only 64% RCY of [89Zr]Zr-oxine after 2 h, including an extraction step using n-octanol [47]. In summary, none of the published methods are suitable for clinical radiopharmacy applications. Here we present a formulation that allows rapid, stable, high-yield (≥85%) preparation of [89Zr]Zr-oxine in a single step, without further processing of commercially available zirconium-89. The commercial formulation of [111In]In-oxine [42] is or was provided in 1 mL units. In comparison, [89Zr]Zr-oxine is formulated in 100 μL units, with a 10× higher concentration of oxine and polysorbate 80 to ensure formulation stability and a 40× higher concentration of HEPES to buffer the solution because current production methods require a large amount of acid to extract [89Zr]Zr4+ from the bombardment target. Our formulation of [89Zr]Zr-oxine therefore contains the same total amount of oxine and polysorbate 80 as the [111In]In-oxine formulation, which should facilitate regulatory approval, but in a 10× lower volume. Oxalic acid is rapidly neutralised by NaOH, 1 M HEPES ensures pH buffering, and the amount of polysorbate 80 is optimised to ensure stability of the radiotracer for up to 1 week. In practice, this allows the end-user to prepare [89Zr]Zr-oxine in a single manipulation simply by transferring [89Zr]Zr-oxalate from its delivery vial, without modification, to an off-the-shelf vial (“kit”) of oxine formulation. Alternatively, it can be used as a basis for the shipping of ready-to-use, single- or multiplepatient doses of [89Zr]Zr-oxine from a central site to distant scanning centres, as has been the case previously for [111In]In-oxine. The radiolabelling agent thus prepared can be added directly to a cell suspension in a procedure analogous to that used conventionally for 111In-labelling using [111In]In-oxine, as described in the Supplementary Material. In line with conventional radiolabelling protocols, the washing step after radiolabelling ensures the amount of free oxine and unchelated zirconium-89 in the final administered product is further reduced. Sterility and endotoxin testing can be performed according to local regulations.
The labelling of WBC with [89Zr]Zr-oxine was reliable, consistently achieving 45–50% labelling efficiency with 160–480 million cells. This is significantly lower than that achieved with [111In]In-oxine in the same conditions. As the formulations of [89Zr]Zr-oxine and [111In]In-oxine both contain the same total amount of oxine, in large excess (3 orders of magnitude) compared to the amount of the respective radiometals (see Supplementary Material, Table S1), it unlikely that the difference in radiolabelling efficiencies can be explained by differences in amounts of unchelated oxine. Instead, we suggest the difference is most likely due to the physicochemical properties of each radiotracer. The partition coefficients of [89Zr]Zr-oxine in water and PBS were not significantly different from those of [111In]In-oxine, suggesting other factors are involved, such as potentially slower intracellular dissociation kinetics of [89Zr]Zr-oxine compared to [111In]In-oxine. This may lead to increased leakage of 89Zr from cells over time, and consequently increased “parasite” signal on PET scans, although in the present study we did not observe major losses nor significant differences in retention compared to [111In]In-oxine in vitro over 24 h. A previous study comparing [89Zr]Zr-oxine and [111In]In-oxine in tumour cell lines suggested the retention of 89Zr was higher than that of 111In after 24 h [30]. lf imaging cells at later time points (> 24 h) is desired, then longer radiotracer retention studies are warranted. In studies with T-cells, bone marrow cells or stem cells [32,34,35,37], significant leakage (30–60%) of [89Zr]Zr-oxine was observed over 2–3 days in vitro, with the rate of leakage slowing down after 3 days. However, preclinical PET images from the same studies suggest better in vivo retention of 89Zr than in vitro, and it has been shown that PET images can be improved by administering deferoxamine intravenously to accelerate the renal clearance of 89Zr released from radiolabelled cells [48].
Using the typical patient dose of [111In]In-oxine (approx. 20 MBq) as reference, we aimed for patient doses of [89Zr]Zr-oxine of about 9–10 MBq. Considering the sensitivity of current-generation clinical PET and SPECT scanners and the relatively low positron yield of 89Zr (23%), we estimate that 9–10 MBq of 89Zr should result in a 5-to-10-fold increase in useful counts compared to 20 MBq of 111In and therefore lead to improved image quality. Another advantage of 89Zr over 111In is that PET/CT facilitates signal quantification and will allow better determination of the cell numbers reaching the target organ. Sato et al. have recently performed dosimetry studies of 89Zr-labelled NK cells in non-human primates [48], suggesting such amounts of activity to be safe for the liver and spleen. Furthermore, their study showed good quality images in a clinical PET/CT scanner with 89Zr activities in the range of 13–44 kBq/106 cells, similar to the average activity of 32.9 kBq/106 cells achieved in the present study. Crucially, cell viability and retention of 89Zr in cells in the presence of plasma were high and comparable to those of 111In, suggesting that radiotracer leakage will be low after intravenous administration and that the PET signal will accurately reflect the location of intact cells, as previously observed in pre-clinical studies [35]. We did not perform in vivo experiments as there is no justification in this case for using unpurified human leukocytes, i.e. predominantly neutrophils, in a small animal model. Our results using flow-assisted cell sorting indicate no preferential uptake by any specific leukocyte population. In contrast, it has been shown previously that [99mTc]Tc-HMPAO accumulated preferentially in eosinophils [1], with the clinical implication that [99mTc]Tc-HMPAO WBC scans disproportionately represent the distribution of eosinophils. Our results suggest this phenomenon is not expected with [89Zr]Zr-oxine. However, because there is significant uptake in RBCs and platelets, better separation of these cells from WBC (e.g. using automated cell separators) will improve signal specificity and target-to-background ratio.
Leukocyte chemotaxis towards pathogens and inflammatory stimuli is the biological basis for WBC imaging. We found that 89Zr-labelled WBC retained their chemotactic properties in vitro, with no significant differences compared to [111In]In-oxine and unlabelled control cells. This suggests that radiolabelling with [89Zr]Zr-oxine will not affect in vivo properties of administered WBC at least within a few hours following radiolabelling and will provide clinically useful images. While both radiotracers resulted in significantly higher DNA damage compared to non-radiolabelled cells, no differences were observed between the radiotracers. Notably, our results were strengthened by the intraindividual nature of the comparison between [89Zr]Zr-oxine and [111In]In-oxine.
Considering the translational aspect of this technique, we also emphasise that WBC labelling was performed following the guidelines established for [111In]In-oxine and [99mTc]Tc-HMPAO [43,44], and thus requires no modifications from existing protocols beyond the provision of additional shielding for 89Zr.
5. Conclusions
In summary, we provide a clinically applicable, kit-based method for the simple and reliable preparation of ready-to-use [89Zr]Zr-oxine, in a single step, from commercially supplied [89Zr]Zr-oxalate and demonstrate its use in radiolabelling WBC. Our work further demonstrates that, from a cell labelling perspective, [89Zr]Zr-oxine is an appropriate PET equivalent of [111In]In-oxine, and should be investigated in the clinic not only for WBC labelling in infection diagnosis, but potentially also for upcoming trials of cell-based therapies such as CAR-T and stem cells.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ms. Ellen López Pérez and Dr. Maggie Cooper for technical assistance and advice.
Funding
This work was supported by the Wellcome EPSRC Centre for Medical Engineering at KCL [grant number WT 203148/Z/16/Z], a CRUK Multidisciplinary Project Award [grant number C48390/A21153], the KCL/ UCL Comprehensive Cancer 1maging Centre funded by CRUK and EPSRC in association with the MRC and DoH (England), the Medical Research Council Confidence in Concepts scheme, the Experimental Cancer Medicine Centre at KCL, the KHP/KCL CRUK Cancer Centre, the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre based at Guy’s and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust and KCL [grant number IS-BRC-1215-20006], the MRC Doctoral Training Programme, the Research England Confidence in Collaboration scheme and the EPSRC programme for next generation molecular imaging and therapy with radionuclides (EP/S032789/1). The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
Abbreviations
- [18F]FDG
2-deoxy-2–[18F]fluoro-D-glucose
- [99mTc]Tc-HMPAO Technetium
(99mTc) hexamethylpropyleneamine oxime
- CAR-T
chimeric antigen receptor T cell(s)
- CFP
cell–free plasma
- DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
- EDTA
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- EtOH
ethanol
- FACS
flow–assisted cell sorting
- fMLP
N–formyl–Met–Leu–Phe
- GMP
good manufacturing practice
- HEPES
4–(2–hydroxyethyl)–1–piperazineethanesulfonic acid
- HES
hydroxyethyl starch
- ITLC
instant thin-layer chromatography
- LE
labelling efficiency
- PBS
phosphate-buffered saline
- PET
positron emission tomography
- QC
quality control
- radioTLC
radio-thin-layer chromatography
- RBC
red blood cell(s)
- RT
room temperature
- SD
standard deviation
- SPECT
single-photon emission computed tomography
- WBC
white blood cell(s)
- γH2AX
gamma H2A histone family member X
Footnotes
Ethical approval
Experiments using human blood were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of King’s College London (Study Reference HR-16/ 17-3746). All donors provided written, informed consent.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Conceptualization: FM, RTMR, PB; Methodology: FM; Investigation and data analysis: FM, AK, AM; Writing – Original Draft: FM; Writing – Review & Editing: FM, AM, RTMR, PB; Funding Acquisition: RTMR, PB; Supervision: RTMR, PB. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Declaration of competing interest
FM, PJB and RTMR have submitted a patent application in relation to this article. The authors declare that they have no other competing interests.
References
- [1].Puncher MRB, Blower PJ. Autoradiography and density gradient separation of technetium-99m-Exametazime (HMPAO) labelled leucocytes reveals selectivity for eosinophils. Eur J Nucl Med. 1994;21:1175–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00182350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Ruparelia P, Szczepura KR, Summers C, Solanki CK, Balan K, Newbold P, et al. Quantification of neutrophil migration into the lungs of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38:911–9. doi: 10.1007/s00259-010-1715-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Lukawska JJ, Livieratos L, Sawyer BM, Lee T, O’Doherty M, Blower PJ, et al. Real-time differential tracking of human neutrophil and eosinophil migration in vivo. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:233–239. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.06.031. e1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Lukawska JJ, Livieratos L, Sawyer BM, Lee T, O’Doherty M, Blower PJ, et al. Imaging inflammation in asthma: real time, differential tracking of human neutrophil and eosinophil migration in allergen challenged, atopic asthmatics in vivo. EBioMedicine. 2014;1:173–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2014.10.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Sharif-Paghaleh E, Sunassee K, Tavaré R, Ratnasothy K, Koers A, Ali N, et al. In vivo SPECT reporter gene imaging of regulatory T cells. PLoS One. 2011;6:e25857. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Griessinger CM, Kehlbach R, Bukala D, Wiehr S, Bantleon R, Cay F, et al. In vivo tracking of Th1 cells by PET reveals quantitative and temporal distribution and specific homing in lymphatic tissue. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:301–7. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.113.126318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Nicol AJ, Tokuyama H, Mattarollo SR, Hagi T, Suzuki K, Yokokawa K, et al. Clinical evaluation of autologous gamma delta T cell-based immunotherapy for metastatic solid tumours. Br J Cancer. 2011;105:778–86. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Tavaré R, Sagoo P, Varama G, Tanriver Y, Warely A, Diebold SS, et al. Monitoring of in vivo function of superparamagnetic lron oxide Labelled murine dendritic cells during anti-tumour vaccination. PLoS One. 2011;6:e19662. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Paik DT, Chandy M, Wu JC. Patient and disease–specific induced pluripotent stem cells for discovery of personalized cardiovascular drugs and therapeutics. Pharmacol Rev. 2020;72:320–42. doi: 10.1124/pr.116.013003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Bulte JWM, Daldrup-Link HE. Clinical tracking of cell transfer and cell transplantation: trials and tribulations. Radiology. 2018;289:604–15. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018180449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Krekorian M, Fruhwirth GO, Srinivas M, Figdor CG, Heskamp S, Witney TH, et al. Imaging of T-cells and their responses during anti-cancer immunotherapy. Theranostics. 2019;9:7924–47. doi: 10.7150/thno.37924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].U.S. Food & Drug Administration - Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research. Guidance for industry - preclinical assessment of investigational cellular and gene therapy products. [Accessed 29 April 2020];2013 https://www.fda.gov/media/87564/download.
- [13].Segal A, Arnot R, Thakur M, Lavender J. lndium-111-labelled leucocytes for localisation of abscesses. Lancet. 1976;308:1056–8. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(76)90969-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Palestro CJ. Radionuclide imaging of musculoskeletal infection: a review. J Nucl Med. 2016;57:1406–12. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.115.157297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Signore A, Jamar F, lsrael O, Buscombe J, Martin-Comin J, Lazzeri E. Clinical indications, image acquisition and data interpretation for white blood cells and anti-granulocyte monoclonal antibody scintigraphy: an EANM procedural guideline. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018;45:1816–31. doi: 10.1007/s00259-018-4052-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Neelapu SS, Tummala S, Kebriaei P, Wierda W, Gutierrez C, Locke FL, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy — assessment and management of toxicities. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15:47–62. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Maldini CR, Ellis GI, Riley JL. CAR T cells for infection, autoimmunity and allotransplantation. Nat Rev lmmunol. 2018;18:605–16. doi: 10.1038/s41577-018-0042-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Sadek H, Olson EN. Toward the goal of human heart regeneration. Cell Stem Cell. 2020;26:7–16. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.12.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [19].Leyendecker A, Jr, Pinheiro CCG, Amano MT, Bueno DF. The use of human mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutic agents for the in vivo treatment of immune-related diseases: a systematic review. Front lmmunol. 2018:9. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [20].Welch MJ, Thakur ML, Coleman RE, Patel M, Siegel BA, Ter-Pogossian M. Gallium-68 labeled red cells and platelets: new agents for positron tomography. J Nucl Med. 1977;18:558–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [21].Forstrom LA, Mullan BP, Hung JC, Lowe VJ, Thorson LM. 18F-FDG labelling of human leukocytes. Nucl Med Commun. 2000;21:685–90. doi: 10.1097/00006231-200007000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [22].Stojanov K, de Vries EFJ, Hoekstra D, van Waarde A, Dierckx RAJO, Zuhorn IS. [18F] FDG labeling of neural stem cells for in vivo cell tracking with positron emission tomography: inhibition of tracer release by phloretin. Mol lmaging. 2012:11. doi: 10.2310/7290.2011.000217290.2011.00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Elhami E, Goertzen AL, Xiang B, Deng J, Stillwell C, Mzengeza S, et al. Viability and proliferation potential of adipose-derived stem cells following labeling with a positron-emitting radiotracer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol lmaging. 2011;38:1323–34. doi: 10.1007/s00259-011-1753-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [24].Adonai N, Nguyen KN, Walsh J, Iyer M, Toyokuni T, Phelps ME, et al. Ex vivo cell labeling with 64Cu-pyruvaldehyde-bis(N4-methylthiosemicarbazone) for imaging cell trafficking in mice with positron-emission tomography. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2002;99:3030–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.052709599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [25].Park J-J, Lee T-S, Son J-J, Chun K-S, Song I-H, Park Y-S, et al. Comparison of celllabeling methods with 124 I-FIAU and 64 cu-PTSM for cell tracking using chronic myelogenous leukemia cells expressing HSV1-tk and firefly luciferase. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2012;27:719–28. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2012.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [26].Bhargava KK, Gupta RK, Nichols KJ, Palestro CJ. In vitro human leukocyte labeling with 64Cu: an intraindividual comparison with 111In-oxine and 18F-FDG. Nucl Med Biol. 2009;36:545–9. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2009.03.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Meszaros LK, Charoenphun P, Chuamsaamarkkee K, Ballinger JR, Mullen GED, Ferris TJ, et al. 89Zr-oxine complex: a long-lived radiolabel for cell tracking using PET. [Accessed 14 January 2020];World Mol Imaging Congr. 2013 http://www.wmis.org/abstracts/2013/data/notes.htm?papers/LBAP024.htm?%27Zr-OxineComplex%3AaLong-LivedRadiolabelforCellTrackingUsingPET%27. [Google Scholar]
- [28].Jauw YWS, Menke-van der Houven van Oordt CW, Hoekstra OS, Hendrikse NH, Vugts DJ, Zijlstra JM, et al. Immuno-positron emission tomography with zirconium-89-labeled monoclonal antibodies in oncology: what can we learn from initial clinical trials? Front Pharmacol. 2016:7. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [29].Ferris TJ, Charoenphun P, Meszaros LK, Mullen GED, Blower PJ, Went MJ. Synthesis and characterisation of zirconium complexes for cell tracking with Zr-89 by positron emission tomography. Dalt Trans. 2014;43:14851–7. doi: 10.1039/C4DT01928H. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [30].Charoenphun P, Meszaros LK, Chuamsaamarkkee K, Sharif-Paghaleh E, Ballinger JR, Ferris TJ, et al. [89Zr]oxinate4 for long-term in vivo cell tracking by positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42:278–87. doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2945-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [31].Sato N, Wu H, Asiedu KO, Szajek LP, Griffiths GL, Choyke PL. 89Zr-oxine complex PET cell imaging in monitoring cell-based therapies. Radiology. 2015;275:490–500. doi: 10.1148/radiol.15142849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [32].Asiedu KO, Koyasu S, Szajek LP, Choyke PL, Sato N. Bone marrow cell trafficking analyzed by 89Zr-oxine positron emission tomography in a murine transplantation model. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:2759–68. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Asiedu KO, Ferdousi M, Ton PT, Adler SS, Choyke PL, Sato N. Bone marrow cell homing to sites of acute tibial fracture: 89Zr-oxine cell labeling with positron emission tomographic imaging in a mouse model. EJNMMI Res. 2018;8:109. doi: 10.1186/s13550-018-0463-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [34].Weist MR, Starr R, Aguilar B, Chea J, Miles J, Poku E, et al. Positron emission tomography of adoptively transferred chimeric antigen receptor T cells with Zirconium-89 oxine. J Nucl Med. 2018;59:1531–7. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.117.206714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [35].Man F, Lim L, Volpe A, Gabizon A, Shmeeda H, Draper B, et al. Mol Ther. Vol. 27. Elsevier Inc; 2019. In vivo PET tracking of 89Zr-labeled Vγ9Vδ2 T cells to mouse xenograft breast tumors activated with liposomal alendronate; pp. 219–29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [36].Watson HA, Durairaj RRP, Ohme J, Alatsatianos M, Almutairi H, Mohammed RN, et al. L-Selectin enhanced T cells improve the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2019:10. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [37].Patrick PS, Kolluri KK, Zaw Thin M, Edwards A, Sage EK, Sanderson T, et al. Lung delivery of MSCs expressing anti-cancer protein TRAIL visualised with 89Zr-oxine PET-CT. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11:256. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01770-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [38].Edmonds S, Volpe A, Shmeeda H, Parente-Pereira AC, Radia R, Baguña-Torres J, et al. Exploiting the metal-chelating properties of the drug cargo for in vivo positron emission tomography imaging of liposomal nanomedicines. ACS Nano. 2016;10:10294–307. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b05935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [39].Gawne PJ, Clarke F, Turjeman K, Cope AP, Long NJ, Barenholz Y, et al. PET imaging of liposomal glucocorticoids using 89Zr-oxine: theranostic applications in inflammatory arthritis. Theranostics. 2020;10:3867–79. doi: 10.7150/thno.40403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [40].Cooper MS, Ma MT, Sunassee K, Shaw KP, Williams JD, Paul RL, et al. Comparison of 64 cu-complexing bifunctional chelators for radioimmunoconjugation: labeling efficiency, specific activity, and in vitro/in vivo stability. Bioconjug Chem. 2012;23:1029–39. doi: 10.1021/bc300037w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [41].Pandya DN, Bhatt N, Yuan H, Day CS, Ehrmann BM, Wright M, et al. Zirconium tetraazamacrocycle complexes display extraordinary stability and provide a new strategy for zirconium-89-based radiopharmaceutical development. Chem Sci. 2017;8:2309–14. doi: 10.1039/C6SC04128K. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [42].Healthcare GE. INDIUM in 111 OXYQUINOLINE SOLUTION for the radiolabeling of autologous leukocytes. [Accessed 1 October 2019];2013 https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/pre96/019044Orig1s000lbl.pdf.
- [43].de Vries EFJ, Roca M, Jamar F, Israel O, Signore A. Guidelines for the labelling of leucocytes with 99mTc-HMPAO. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:842–8. doi: 10.1007/s00259-010-1394-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [44].Roca M, de Vries EFJ, Jamar F, Israel O, Signore A. Guidelines for the labelling of leucocytes with 111In-oxine. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:835–41. doi: 10.1007/s00259-010-1393-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [45].Deri MA, Zeglis BM, Francesconi LC, Lewis JS. PET imaging with 89Zr: from radiochemistry to the clinic. Nucl Med Biol Elsevier Inc. 2013;40:3–14. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2012.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [46].Bubenschikov Larenkov, Zhukova Makichyan, Kodina Krasnoperova. Preparation of zirconium-89 solutions for radiopharmaceutical purposes: interrelation between formulation, radiochemical purity, stability and biodistribution. Molecules. 2019;24:1534. doi: 10.3390/molecules24081534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [47].Socan A, Petrik M, Kolenc Peitl P, Krošelj M, Rangger C, Novy Z, et al. On-cartridge preparation and evaluation of 68Ga-, 89Zr- and 64Cu-precursors for cell radiolabelling. Nucl Med Biol. 2019;71:23–31. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2019.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [48].Sato N, Stringaris K, Davidson-Moncada JK, Reger R, Adler SS, Dunbar C, et al. In vivo tracking of adoptively transferred natural killer cells in rhesus macaques using 89Zirconium-oxine cell labeling and PET imaging. Clin Cancer Res. 2020 doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2897clincanres.2897.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.