Abstract
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) kill infected and cancerous cells. We detected transfer of cytotoxic multiprotein complexes from CTLs to target cells, termed Supramolecular Attack Particles (SMAPs). SMAPs were rapidly released from CTLs and were autonomously cytotoxic. Mass spectrometry, immunochemical analysis and CRISPR editing identified a C-terminal fragment of thrombospondin-1 as an unexpected SMAP component that contributed to target killing. Direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy resolved a cytotoxic core surrounded by a thrombospondin-1 shell of ~120 nm diameter. Cryo-Soft X-ray Tomography analysis revealed that SMAPs had a carbon-dense shell and were stored in multicore granules. We propose that SMAPs are autonomous extracellular killing entities that deliver cytotoxic cargo based on innate specificity of shell components.
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) exocytose soluble granzymes and perforin (Prf1) from secretory lysosomes (SLs) into the interface between the CTL and target, the cytotoxic immunological synapse (IS) (1–5). Prf1 forms pores in the plasma membrane of target cells that mediate entry of granzymes, such as granzyme B (Gzmb) into the target cell cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic Gzmb initiates multiple pathways leading to target cell death (6–8). Gzmb and Prf1 are stored inside SLs in condensates with serglycin (Srgn) (9, 10). There are reports that Prf1 and Gzmb may be released in particles (11–13), but their nature has remained elusive. To address this, we designed an experiment to follow putative cytotoxic particles from CMV pp65 specific human CTL clones (14) to target cells bearing pp65-HLA-A2 complexes. The CTL clones were transfected with mRNA encoding Gzmb-mCherry-SEpHluorin that concentrated in SLs. The SLs were also co-labeled with Alexa 647-wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) (15). WGA does not interact with high mannose oligosaccharides of Gzmb (16, 17) such that co-transfer of Gzmb and WGA to the target would implicate a multi-glycoprotein particle. The double-labeled CTLs were mixed with HLA-A2 positive target cells with or without the pp65 peptide and subjected to time-lapse microscopy. Within minutes of mixing, the pp65 pulsed targets contained intense double-positive puncta, whereas unpulsed target cells lacked these signals after interaction with the CTLs (Fig. 1A, Fig. S1 and Movie S1-3). We defined these multiprotein structures as supramolecular attack particles (SMAPs) and subjected them to further analysis.
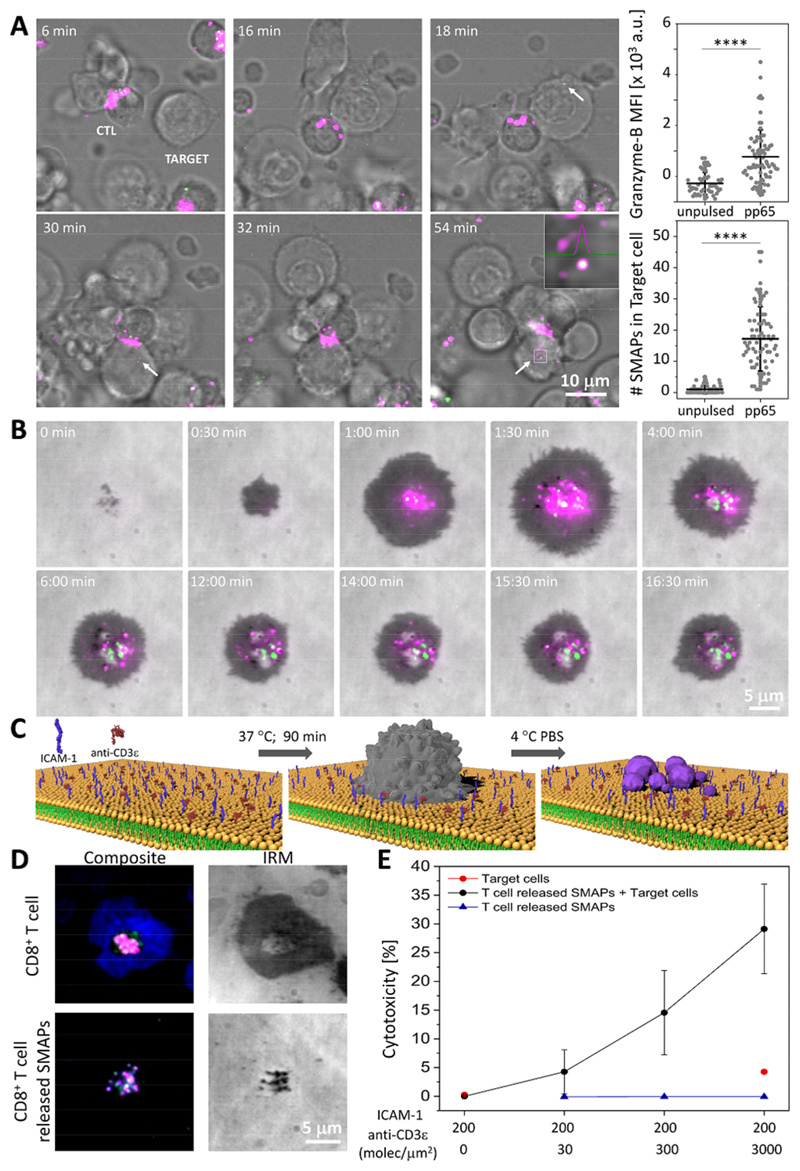
Fig. 1. SMAPs were released at the IS and displayed autonomous cytotoxicity.
(A) Time-lapse confocal images depicting the transfer of Gzmb-mCherry+ (green) and WGA (magenta) labeled SMAPs from an antigen-specific CTL clone into pp65-pulsed JY target cells (Target). Arrows and inset indicate the presence of SMAPs inside the target. Scale bar, 10 μm. Quantification of Gzmb mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) and number of double-positive particles inside the target cell in CTL conjugates with unpulsed or pulsed target cells. Each dot represents one target cell (< 50 cells). Horizontal lines and error bars represent mean ± SD from 2 independent experiments. ****, p < 0.0001 (B) Live cell imaging of SMAPs release by CD8+ T-cells transfected with Gzmb-mCherry-SEpHluorin (magenta/green) on activating SLB. IRM, interference reflection microscopy. Scale bar, 5 μm. (C) Schematic of the working model for capturing SMAPs released by activated CD8+ T-cells. CD8+ T-cells (grey) were incubated on SLB presenting activating ligands for the indicated time. Cells were removed with cold PBS leaving the released SMAPs (purple) on the SLB. Elements are not drawn to scale. (D) TIRFM images of CD8+ T-cells incubated on activating SLB in the presence of anti-Prf1 (green) and anti-Gzmb (magenta) antibodies (top panels). After cell removal, Prf1+ and Gzmb+ SMAPs remained on the SLB (bottom panels). The formation of a mature IS is indicated by an ICAM-1 ring (blue). IRM, interference reflection microscopy. Scale bar, 5 μm. (E) Target cell cytotoxicity induced by density-dependent release of SMAPs captured on SLB measured by LDH release assay. Data points and error bars represent mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments.
We first investigated the kinetics of SMAPs release. We incubated Gzmb-mCherry-SEpHluorin transfected human CD8+ T-cells on a supported lipid bilayers (SLB) coated with laterally mobile ICAM-1 and anti-CD3ε (Fig. 1B, Fig. S2) (18). Total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy (TIRFM) demonstrated that CTLs recruited acidic SLs displaying only mCherry fluorescence to the IS with activating SLB. This was rapidly followed (within 1 min) by appearance of SEpHluorin puncta in the IS (Fig. 1B, Fig. S2, Movie S4). Consistent with release of Gzmb in a SMAP, the SEpHluorin signal persisted in the IS for 20 minutes rather then dispersing.
We next determined if the SMAPs remained attached to the SLB after removal of the CTLs (Fig. 1C, Movie S5). Untransfected CTLs were incubated on the activating SLB, and either directly prepared for immunofluorescence detection of Prf1 and Gzmb or the cells were removed prior to analysis (Fig. 1D). Prf1 and Gzmb immunoreactivity were detected in the IS within 20 minutes, due to the kinetics of antibody binding (Figs. S3-4; Movies S6-9), and remained as discrete particles attached to the SLB after the CTLs were removed (Fig. 1D). The SMAPs were stable without loss of Prf1 and Gzmb for hours without fixation (Fig. S5). We next tested SMAPs for their ability to kill target cells in a cytotoxicity assay based on release of the cytoplasmic enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Target cells were killed by SLB immobilized SMAPs (Fig. 1E, black circles) after correction for “spontaneous release” of LDH by target cells (Fig. 1E, red circles). We also confirmed that SMAPs lacked LDH activity (Fig, 1E, blue triangles). Thus, SMAPs are stable after release from CTLs and can kill cells autonomously.
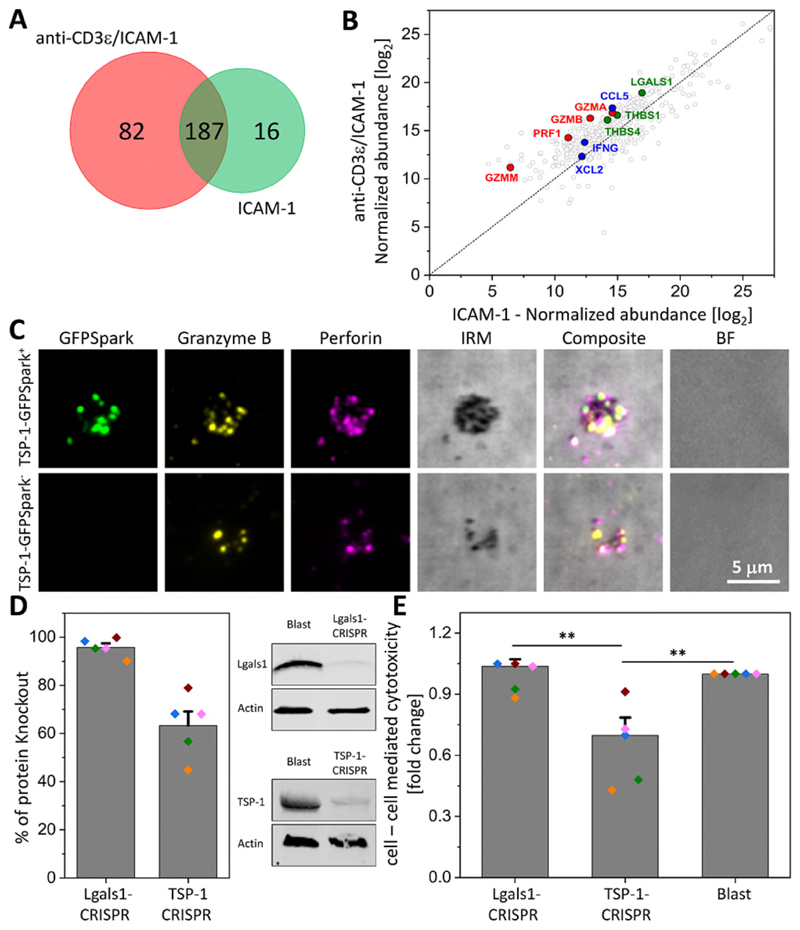
SMAPs captured on SLB were subjected to mass spectrometry (MS) analysis. We identified over 285 proteins that were consistently present in SMAPs (Fig. 2A, B). Of these, 82 were unique to SMAPs on SLB with ICAM-1 and anti-CD3ε versus ICAM-1 alone and 18 proteins were detected in a majority of experiments (Fig. S6). One peptide from Prf1 was detected in multiple experiments and multiple Gzmb peptides were identified in all experiments (Fig. S6). We also identified a number of proteins involved in cell signaling (cytokines and chemokines) (Fig. S6). The presence of Prf1 and Gzmb in SMAPs was further confirmed by SDS-PAGE and immuno-blotting (Fig S7). Plasma membrane proteins such as the phosphatase CD45 and the degranulation marker LAMP-1 (CD107a) were not detected (Fig. S7). This suggested minimal contamination with cellular membranes. LFA-1 was confirmed by immune-blotting, but not by immunofluorescence of SMAPs and thus may represent adhesion sites left on the SLB in parallel with SMAPs (19). Thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) stood out as a candidate based on its signature Ca2+ binding repeats (20, 21), which resonated with well-established Ca2+ dependent steps in CTL mediated killing (22). Live imaging of the release of SMAPs on activating SLB showed that TSP-1 and Prf1 are released together (Fig. S8; Movie S10). In addition, TIRFM on SMAPs from CTLs transfected with full length TSP-1 with a C-terminal GFPSpark revealed co-localization of the GFP signal with Gzmb and Prf1 antibody staining in the SMAPs (Fig. 2C; Fig. S9), and anti-TSP-1 antibody staining co-localized with mCherry and pHluorin signals from CTLs transfected with Gzmb-mCherry-pHluorin (Fig. S10). TSP-1-GFPSpark and Gzmb-mCherry-SEpHluorin were co-localized within cytoplasmic compartments in co-transfected CTLs (Fig. S11, Movie S11). This result suggested that SMAPs were preformed and stored in SLs. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays on soluble and SLB fractions from stimulation of primary CD8+CD57+ CTLs revealed similar levels of Gzmb and Prf1 in both fractions, but the dependence on anti-CD3ε stimulation was higher for the SLB fraction (Fig. S12). In contrast, TSP-1 was almost exclusively in the SLB fraction, and displayed significant dependence on anti-CD3ε stimulation (Fig. S12). When we analyzed TSP-1 protein by SDS-PAGE and immuno-blotting we found that CTLs and SMAPs contained not the full-length, 145 kDa species stored in platelets, but a C-terminal 60 kDa fragment under non-reducing and reducing conditions, which included the Ca2+ binding repeats (Fig. S13) (23). CRISPR/Cas9 mediated knockout of TSP-1 by 60% in CTLs reduced anti-CD3ε redirected killing of K562 cells by 30% (n = 5, p < 0.001), whereas knockout of another similarly enriched protein, galectin-1, by 90% had no effect on killing (Fig. 2D, E). While TSP-1 is associated with T cell adhesion to extracellular matrix (24), TSP-1 knockout did not alter T cell adhesion to activating SLB, but did reduce the signals for TSP-1, Prf1 and Gzmb in SMAPs (Fig S14). These results suggested that the C-terminal domain of TSP-1 was a component of SMAPs and is important in CTL mediated killing.
Fig. 2. TSP-1 was a major constituent of SMAPs and contributed to CTL killing of targets.
(A) Two-set Venn diagram showing the number of individual and common proteins identified by MS analysis of material released by CD8+ T-cells incubated on non-activating (ICAM-1) or activating (ICAM-1 + anti-CD3ε) SLB. Representative of 3 independent experiments with 8 donors. (B) Normalized abundance of the 285 proteins identified by MS in each condition. Cytotoxic proteins are highlighted in red, chemokine/cytokines in blue and adhesion proteins in green. (C) TIRFM images of SMAPs released from CD8+ T-cells transfected with TSP-1-GFPSpark (green; top row) or non-transfected cells (bottom row). Released SMAPs were further stained with anti-Gzmb (yellow) and anti-Prf1 (magenta) antibodies. IRM, interference reflection microscopy. BF, bright field microscopy. Scale bar, 5 μm. (D) Percentage of galectin-1 and TSP-1 knockout in CD8+ T-cells by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing measured from immuno-blotting analysis (left). Each colored dot represents one donor. Bars represent mean ± SEM. Representative immuno-blot for galectin-1 (Lgals1) and TSP-1 in Lgals1 and TSP-1, respectively edited CD8+ T-cells (right). CD8+ T-cells (Blast) were analyzed in parallel as a control. (E) Target cell cytotoxicity mediated by galectin-1 (Lgals1-CRISPR) or TSP-1 (TSP-1-CRISPR) gene edited CD8+ T-cells measured by LDH release assay. T cell blasts were used as a control. Bars represent mean ± SEM. **, p < 0.01. Donors are the same as in (D).
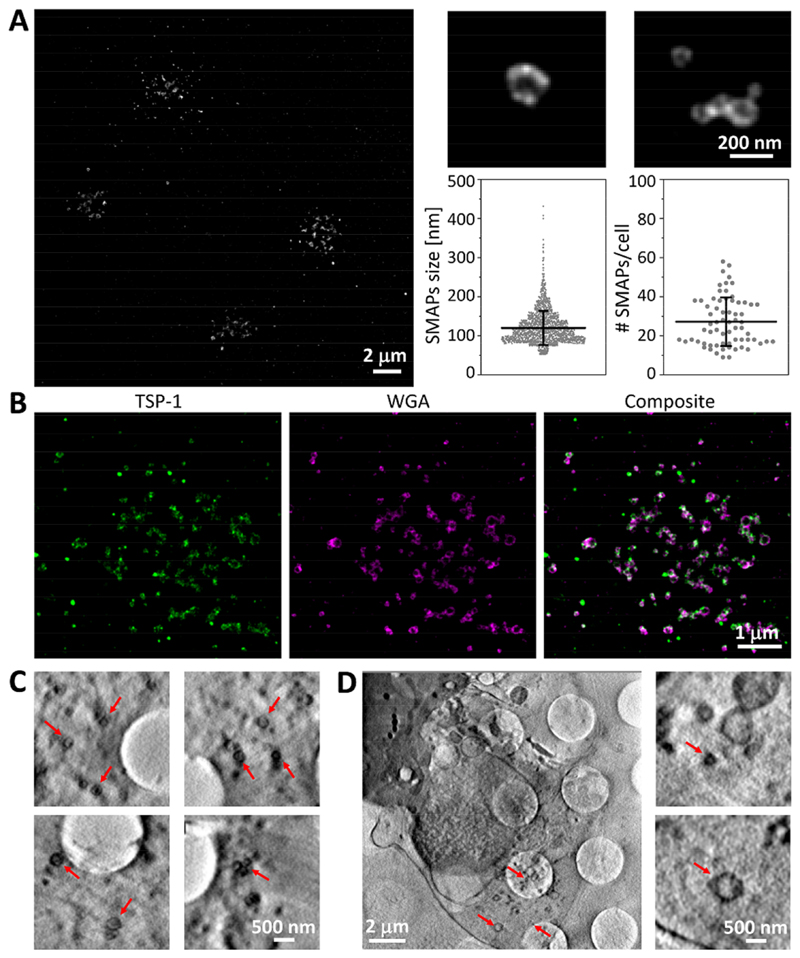
We next investigated the organization of molecules within SMAPs at 20 nm resolution by direct Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (dSTORM). SMAPs were detected with WGA in clusters of 27 ± 12 SMAPs per IS (Fig. 3A). On closer inspection, WGA staining appeared as a dense ring in the 2D projections, which indicated a spherical shell with an average diameter of 120 ± 43 nm (Fig. 3A). Many supramolecular assemblies use phospholipid bilayers as a scaffold and thus we asked if SMAPs stain with the lipophilic membrane dye DiD, which brightly stains extracellular vesicles or lipoproteins. DiD did not stain SMAPs, consistent with the paucity of membrane proteins detected in the mass spectrometry (Fig. S15). Thus, the WGA staining pattern was most consistent with a shell of glycoproteins (16), rather than a phospholipid-based membrane surrounding SMAPs. The location of TSP-1 in SMAPs was investigated by multicolor dSTORM. Strikingly, TSP-1 co-localized with WGA (59 ± 3 %) and similarly highlighted the shape of the SMAPs (Fig. 3B; Fig. S16). Thus, SMAPs from CTLs have a glycoprotein shell that includes TSP-1.
Fig. 3. SMAPs shell was rich in glycoproteins, TSP-1 and organic material.
(A) dSTORM image of SMAPs released on activating SLB by multiple cells (left; scale bar, 2 μm) and two examples of individual SMAPs (top right; scale bar, 200 nm), showing their heterogeneity in size. SMAPs were labeled with WGA. Quantification of SMAPs size and number released per cell (bottom right; n>1800 and n=67, respectively). Horizontal lines and error bars represent mean ± SD from five donors. (B) dSTORM images of SMAPs (labeled with WGA, magenta) positive for TSP-1 (green) released on activating SLB. Scale bar, 1 μm. (C) Multiple CSXT examples of released SMAPs after cell removal. Scale bar, 500 nm. (D) CSXT of CD8+ T-cells interacting with carbon coated EM grids (note grid holes in C and D) containing ICAM-1 and anti-CD3ε. Scale bar, 2 μm or 500 nm for zoomed in regions (right). Arrows indicate SMAPs.
To further investigate the structure of SMAPs, we used Cryo-Soft X-ray Tomography (CSXT), a non-destructive 3D method based on the preferential absorption of X-rays by carbon rich cellular structures within unstained, vitrified specimens with a resolution of 40 nm (25, 26). For this, CTLs were incubated on EM grids coated with ICAM-1 and anti-CD3ε. After incubation, samples were plunge-frozen with the T-cells in place or removed to leave only the SMAPs. Released SMAPs captured on the grid after cell removal (Fig. 3C; Movie S12) were readily resolved and had an average diameter of 111 ± 36 nm (Fig. S17). The slightly larger size of SMAPs by dSTORM reflects the contribution of ~9 nm based on the 2.45 nm hydrodynamic radius of WGA. The carbon dense shell observed in CSXT was consistent with the TSP-1/WGA shell observed by dSTORM. The CSXT analysis further emphasized intracellular multicore granules in the CTLs that appeared to be tightly packed with SMAPs, where the lower density cores were resolved (Movie S13). These multicore granules were associated with the basal surface of CTLs near activating grids (Fig. 3D; Movie S14), as expected (3).
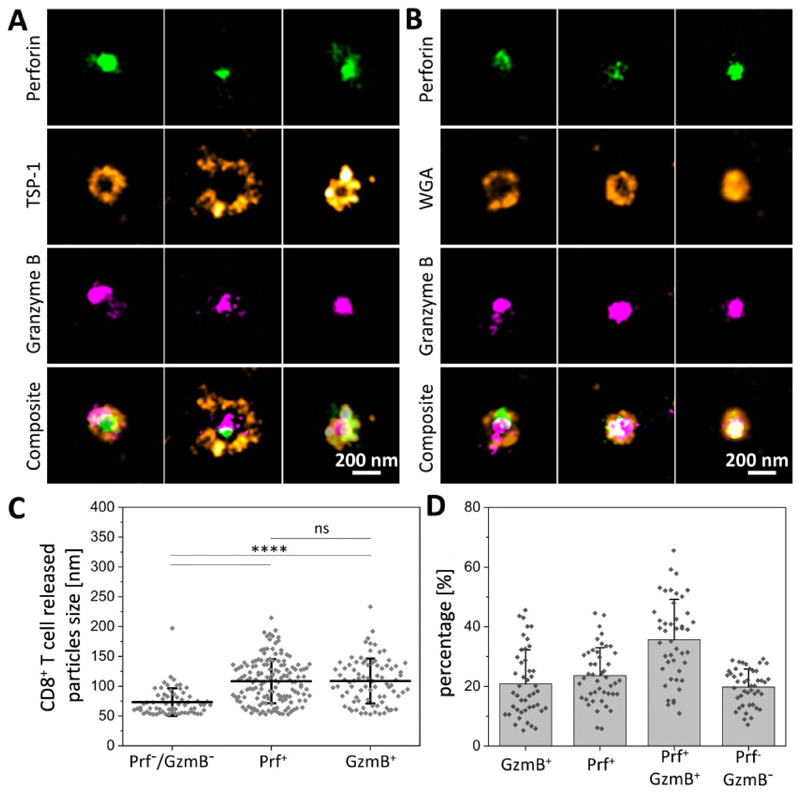
We next undertook 3-color dSTORM to determine the location of cytotoxic proteins within SMAPs. The TSP-1/WGA shell enclosed partly overlapping Prf1 and Gzmb positive areas across the 2D projection (Fig. 4A,B). We also detected Srgn in the core of SMAPs (Fig S18). Given the apparent density of material in the shell and stability of SMAPs, it was surprising that 150 kDa antibodies had access to components in the core. This is an unexpected property that will require further investigation. SMAPs containing Prf1 and/or Gzmb were bigger and more abundant than WGA+ particles devoid of cytotoxic proteins (Fig. 4C, D). Primary CD8+CD57+ CTLs and NK cells from peripheral blood also released SMAPs with Prf1, Gzmb and TSP-1 (Fig S19). These results completed our picture of SMAPs as being autonomously cytotoxic, ~120 nm in diameter with a dense shell including TSP-1, a core of Prf1, Gzmb and Srgn and surprising accessibility to antibodies.
Fig. 4. SMAPs had a TSP-1 shell and a core of cytotoxic proteins.
(A and B) dSTORM images of individual SMAPs positive for Prf1 (green), Gzmb (magenta) and TSP-1 (A, orange) or stained with WGA (B, orange). Scale bar, 200 nm. (C) Quantification of the size of cytotoxic particles based on their protein composition (n=64 for Prf1- and Gzmb- cytotoxic particles, n=149 and n=83 for Prf1+ and Gzmb+ cytotoxic particles, respectively). ****, p < 0.0001. n.s, not significant. (D) Quantification of the percentage of particles positive and negative for Prf1 or Gzmb. (C-D) Horizontal lines/bars and error bars represent mean ± SD from five donors.
CTLs can also use the ligand for the death receptor Fas (FasL) to kill targets expressing Fas (27). We only detected FasL in the CTL IS when Fas glycoprotein was incorporated in the SLB with ICAM-1 and anti-CD3ε (Fig S20). In these cases, FasL distribution in the IS was in puncta distinct from Prf1 and Gzmb. The related protein CD40L is released in a CD40 dependent manner in helper T-cell IS (28, 29). Synaptic ectosomes are a type of extracellular vesicle similar to exosomes, but generated by budding from the plasma membrane of the T-cell in the IS (29, 30). These results suggested that there were two types of cytotoxic particles released by CTLs in contact with Fas expressing targets - vesicles with FasL and SMAPs.
Our working model for SMAPs function is that they act as autonomous killing entities with innate targeting through TSP-1 and potentially other shell components. While SMAPs transferred through the IS may only impact one target, CTLs can kill without an IS using a process involving rapid contacts (14, 31). The ability of SMAPs to autonomously kill target cells may become important in situations of transient and multiple interactions where delivery might be less precise. SMAPs may have other modes of action potentially including chemoattraction through CCL5 and immune modulation through IFNγ. The TSP-1 C-terminus contains the binding site for the ubiquitous “don’t eat me” signal CD47 (32). SMAPs may thus partner with myeloid cells to ensure that any cell that cannot be killed by SMAPs is culled by phagocytosis (33).
Supplementary Material
One Sentence Summary.
Supramolecular attack particles with a dense shell and cytotoxic core are autonomous killing entities released from adaptive cytotoxic T-cells.
Acknowledgments
We thank E. Kurz, S. Valvo, L. Chen, H. Rada, M. C. Spink, M.P. Puissegur, M. Mixon, J. Love and A. Sessions for important contributions to this work; Prof. B. Alarcon, Prof. C. Baldari, Prof J. Rettig, Dr. E. Abu Shah and Dr. F. Bravo Lopes for advice.
Funding
Supported by the ERC AdG 670930 (MLD), the Wellcome Trust 100262 (MLD) and the Kennedy Trust (to MLD and BMK); the Laboratoire d’Excellence Toulouse Cancer (TOUCAN) under contract ANR11-LABX and Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer (Equipe labellisée 2018) (to SV); the Institute for Protein Innovation, and STFC and Wellcome for support of Diamond Light Source Ltd.
Footnotes
Author contributions: SB and MLD conceived study and designed experiments. SB performed experiments and analyzed data. SM and SV performed CTL clone experiments. RF and BMK acquired and analyzed Mass Spectroscopy data. MH acquired and analyzed CSXT data. SB and MLD wrote the manuscript.
Competing interests: M. Dustin and S. Balint have filed a provisional patent on SMAP isolation and engineering.
Data and materials availability: All data are available in the manuscript or the supplementary material.
References
- 1.Masson D, Tschopp J. A family of serine esterases in lytic granules of cytolytic T lymphocytes. Cell. 1987;49:679–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90544-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tschopp J, Schafer S, Masson D, Peitsch MC, Heusser C. Phosphorylcholine acts as a Ca2+-dependent receptor molecule for lymphocyte perforin. Nature. 1989;337:272–274. doi: 10.1038/337272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stinchcombe JC, Bossi G, Booth S, Griffiths GM. The immunological synapse of CTL contains a secretory domain and membrane bridges. Immunity. 2001;15:751–761. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(01)00234-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Menasche G, Feldmann J, Fischer A, de Saint Basile G. Primary hemophagocytic syndromes point to a direct link between lymphocyte cytotoxicity and homeostasis. Immunol Rev. 2005;203:165–179. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kalos M, et al. T cells with chimeric antigen receptors have potent antitumor effects and can establish memory in patients with advanced leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:95ra73. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Froelich CJ, et al. New paradigm for lymphocyte granule-mediated cytotoxicity. Target cells bind and internalize granzyme B, but an endosomolytic agent is necessary for cytosolic delivery and subsequent apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:29073–29079. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.46.29073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Keefe D, et al. Perforin triggers a plasma membrane-repair response that facilitates CTL induction of apoptosis. Immunity. 2005;23:249–262. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Law RH, et al. The structural basis for membrane binding and pore formation by lymphocyte perforin. Nature. 2010;468:447–451. doi: 10.1038/nature09518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Metkar SS, et al. Cytotoxic cell granule-mediated apoptosis: perforin delivers granzyme B-serglycin complexes into target cells without plasma membrane pore formation. Immunity. 2002;16:417–428. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(02)00286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Martina JA, et al. Imaging of lytic granule exocytosis in CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes reveals a modified form of full fusion. Cell Immunol. 2011;271:267–279. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2011.07.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Peters PJ, et al. Molecules relevant for T cell-target cell interaction are present in cytolytic granules of human T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1989;19:1469–1475. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Peters PJ, et al. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte granules are secretory lysosomes, containing both perforin and granzymes. J Exp Med. 1991;173:1099–1109. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lugini L, et al. Immune surveillance properties of human NK cell-derived exosomes. J Immunol. 2012;189:2833–2842. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bertrand F, et al. An initial and rapid step of lytic granule secretion precedes microtubule organizing center polarization at the cytotoxic T lymphocyte/target cell synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:6073–6078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218640110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kim WT, et al. Delayed reentry of recycling vesicles into the fusion-competent synaptic vesicle pool in synaptojanin 1 knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:17143–17148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.222657399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kornfeld R, Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Griffiths GM, Isaaz S. Granzymes A and B are targeted to the lytic granules of lymphocytes by the mannose-6-phosphate receptor. J Cell Biol. 1993;120:885–896. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.4.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Somersalo K, et al. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes form an antigen-independent ring junction. J Clin Invest. 2004;113:49–57. doi: 10.1172/JCI200419337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kuo JC, Han X, Hsiao CT, Yates JR, 3rd, Waterman CM. Analysis of the myosin-II-responsive focal adhesion proteome reveals a role for beta-Pix in negative regulation of focal adhesion maturation. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:383–393. doi: 10.1038/ncb2216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kvansakul M, Adams JC, Hohenester E. Structure of a thrombospondin C-terminal fragment reveals a novel calcium core in the type 3 repeats. EMBO J. 2004;23:1223–1233. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Misenheimer TM, Mosher DF. Calcium ion binding to thrombospondin 1. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:1729–1733. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.4.1729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Podack ER, Konigsberg PJ. Cytolytic T cell granules. Isolation, structural, biochemical, and functional characterization. J Exp Med. 1984;160:695–710. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Annis DS, Murphy-Ullrich JE, Mosher DF. Function-blocking antithrombospondin-1 monoclonal antibodies. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:459–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.01723.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li SS, et al. T lymphocyte expression of thrombospondin-1 and adhesion to extracellular matrix components. Eur J Immunol. 2002;32:1069–1079. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200204)32:4<1069::AID-IMMU1069>3.0.CO;2-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schneider G. Cryo X-ray microscopy with high spatial resolution in amplitude and phase contrast. Ultramicroscopy. 1998;75:85–104. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3991(98)00054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Harkiolaki M, et al. Cryo-soft X-ray tomography: using soft X-rays to explore the ultrastructure of whole cells. Emerging Topics in Life Sciences. 2018 doi: 10.1042/ETLS20170086. ETLS20170086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bossi G, Griffiths GM. Degranulation plays an essential part in regulating cell surface expression of Fas ligand in T cells and natural killer cells. Nat Med. 1999;5:90–96. doi: 10.1038/4779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Choudhuri K, et al. Polarized release of T-cell-receptor-enriched microvesicles at the immunological synapse. Nature. 2014;507:118–123. doi: 10.1038/nature12951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Saliba DG, et al. Composition and structure of synaptic ectosomes exporting antigen receptor linked to functional CD40 ligand from helper T-cells. eLife. 2019;8 doi: 10.7554/eLife.47528. 600551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cocucci E, Meldolesi J. Ectosomes and exosomes: shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2015;25:364–372. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Halle S, et al. In Vivo Killing Capacity of Cytotoxic T Cells Is Limited and Involves Dynamic Interactions and T Cell Cooperativity. Immunity. 2016;44:233–245. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.01.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mateo V, et al. CD47 ligation induces caspase-independent cell death in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat Med. 1999;5:1277–1284. doi: 10.1038/15233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Oldenborg PA, Gresham HD, Lindberg FP. CD47-signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha) regulates Fcgamma and complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 2001;193:855–862. doi: 10.1084/jem.193.7.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dustin ML, Starr T, Varma R, Thomas VK. Supported planar bilayers for study of the immunological synapse. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2007;Chapter 18 doi: 10.1002/0471142735.im1813s76. Unit 18.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bates M, Dempsey GT, Chen KH, Zhuang X. Multicolor super-resolution fluorescence imaging via multi-parameter fluorophore detection. Chemphyschem. 2012;13:99–107. doi: 10.1002/cphc.201100735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Balint S, Verdeny Vilanova I, Sandoval Alvarez A, Lakadamyali M. Correlative live-cell and superresolution microscopy reveals cargo transport dynamics at microtubule intersections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:3375–3380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219206110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lopes FB, et al. Membrane nanoclusters of FcgammaRI segregate from inhibitory SIRPalpha upon activation of human macrophages. J Cell Biol. 2017;216:1123–1141. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201608094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bates M, Huang B, Dempsey GT, Zhuang X. Multicolor super-resolution imaging with photo-switchable fluorescent probes. Science. 2007;317:1749–1753. doi: 10.1126/science.1146598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Huang B, Wang W, Bates M, Zhuang X. Three-dimensional super-resolution imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy. Science. 2008;319:810–813. doi: 10.1126/science.1153529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Malkusch S, et al. Coordinate-based colocalization analysis of single-molecule localization microscopy data. Histochem Cell Biol. 2012;137:1–10. doi: 10.1007/s00418-011-0880-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kremer JR, Mastronarde DN, McIntosh JR. Computer visualization of three-dimensional image data using IMOD. J Struct Biol. 1996;116:71–76. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1996.0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Cardona A, et al. TrakEM2 software for neural circuit reconstruction. PLoS One. 2012;7:e38011. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.