Abstract
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) is widely used as a first-line procedure for the definitive diagnosis of pancreatic solid tumor. Adverse events associated with the EUS-FNA procedure include acute pancreatitis, bleeding, infection, and duodenal perforation. Rarely, pancreatic tumors disseminate in the peritoneal cavity or seed in the gastric wall via the biopsy needle tract after EUS-FNA. Such seeding has been noted primarily in cases of adenocarcinomas and has not been associated with solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (SPN), a rare and potentially malignant tumor of the pancreas. This is the first report of a case of tumor seeding in the gastric wall after EUS-FNA of pancreatic SPN.
Keywords: endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration, solid pseudopapillary neoplasm, needle tract seeding
Introduction
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) is widely used as a first-line procedure for the definitive diagnosis of pancreatic solid tumor (1) and known to be associated with few serious complications (2-5). The rate of adverse events related to the EUS-FNA procedure is reportedly 0.98% to 3.4%, with events including acute pancreatitis, bleeding, infection, and duodenal perforation (2-5). Rarely (5, 6), pancreatic tumors disseminate in the peritoneal cavity or seed in the gastric wall via the biopsy needle tract after EUS-FNA (7-10). Such seeding has been noted primarily in cases of adenocarcinomas (5, 8, 9, 11) and has not been associated with solid pseudopapillary neoplasm (SPN), a rare and potentially malignant tumor of the pancreas (12-14).
This is the first report of a case of tumor seeding in the gastric wall after EUS-FNA of pancreatic SPN (15).
Case Report
A 78-year-old man admitted to our hospital with abdominal discomfort of 3 months' duration had undergone abdominal ultrasonography 67 months earlier that revealed a tumor in the body of the pancreas and subsequent dynamic contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) that demonstrated a hypovascular tumor 6 cm in diameter with a cystic or necrotic component and no calcification (Fig. 1). At that time, EUS-FNA was performed to confirm the diagnosis, and a biopsy specimen was obtained by puncturing through the posterior gastric wall using a 22-gauge needle 4 times with no suction. A pathological examination of the specimen suggested malignancy, so the patient underwent surgical resection of the tumor, and a final pathological diagnosis of SPN of the pancreas was obtained (Fig. 2).
Figure 1.
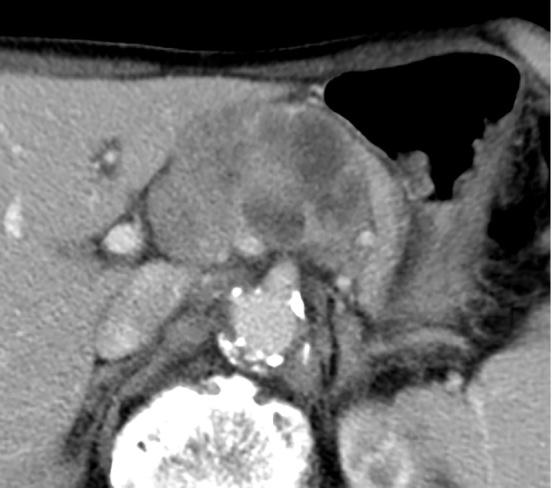
Preoperative abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography shows a hypovascular tumor 6 cm in diameter with a cystic or necrotic component in the body of the pancreas.
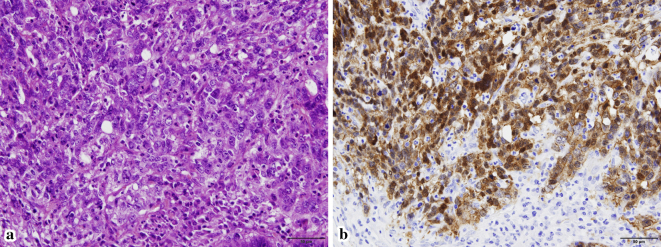
Figure 2.
Hematoxylin and Eosin staining (a, ×400) of the tumor of the body of the pancreas shows atypical tumor cells with solid growth that appear as distinct nuclear and cytoplasmic positive staining of beta-catenin on immunostaining (b, ×400)
At the current presentation, more than five years later, upper gastrointestinal endoscopy to evaluate the patient's prolonged abdominal discomfort revealed a protruding tumor in the posterior gastric wall (Fig. 3), and subsequent dynamic contrast-enhanced CT showed a hypervascular tumor 4 cm in diameter in the same location (Fig. 4). Positron emission tomography showed a mildly increased uptake of fluorodeoxyglucose by the tumor (maximum standardized uptake value: 4.7), and there was no evidence of metastasis (images not shown).
Figure 3.
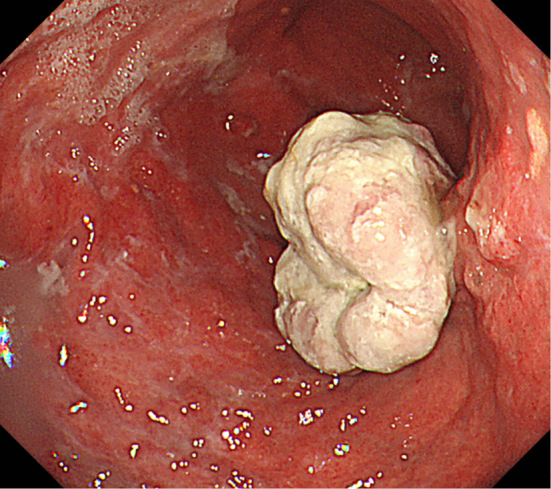
Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy reveals a protruding tumor in the posterior gastric wall.
Figure 4.
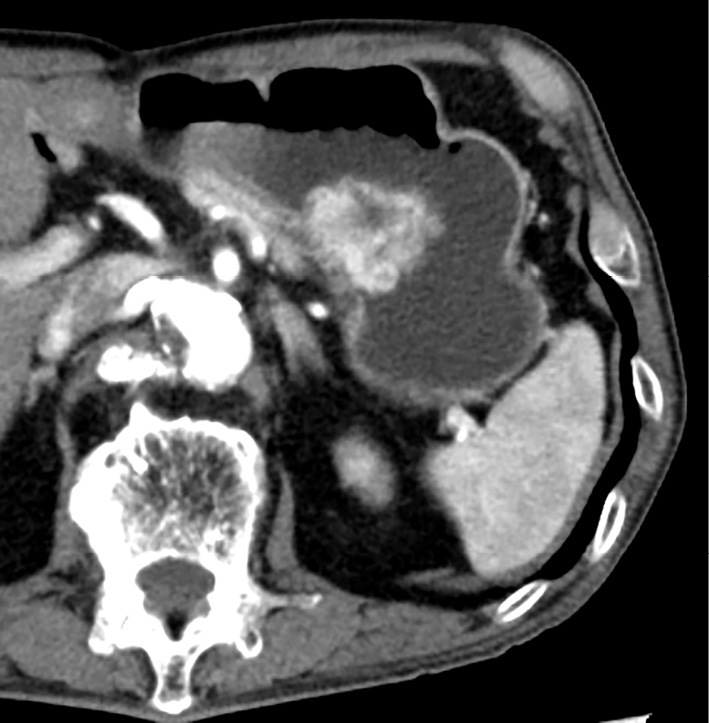
Abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography reveals a hypervascular tumor 4 cm in diameter in the posterior gastric wall.
The tumor markers (carcinoembryonic antigen and carbohydrate antigen 19-9) were within normal limits. A pathological examination of a biopsy specimen from the gastric tumor revealed atypical cells with some apoptosis that suggested malignancy; the patient therefore underwent distal gastrectomy, and the surgically resected gastric specimen revealed a well-defined solid tumor in the submucosal layer of the gastric wall. A pathological examination revealed glandular and alveolar proliferation of atypical cells and hemorrhagic changes on Hematoxylin and Eosin staining with distinct nuclear and cytoplasmic positive staining of beta-catenin on immunostaining, findings consistent with SPN (Fig. 5). Matching the location of the tumor in the gastric wall with the puncture route of the EUS-FNA performed 67 months earlier suggested that the current tumor represented seeding of the earlier tumor along the biopsy tract of EUS-FNA.
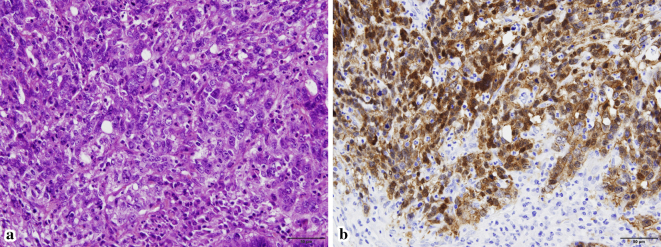
Figure 5.
Hematoxylin and Eosin staining (a, ×400) of the resected gastric tumor shows atypical tumor cells with a glandular and solid pattern. Tumor cells show distinct nuclear and cytoplasmic positive staining of beta-catenin on immunostaining (b, ×400).
Discussion
EUS-FNA is a safe procedure with a low incidence of adverse events and low risk of morbidity and mortality (2, 16). Seeding of a pancreatic tumor to the gastric wall through the biopsy needle track after EUS-FNA is uncommon but has been reported in cases of pancreatic adenocarcinoma (5, 7-9, 11, 17-19) and intraductal mucinous papillary carcinoma (10, 20).
In many cases, recurrence of needle tract seeding tends to occur at the gastric wall near the previous site of EUS-FNA puncture (16, 21, 22). Solid pseudopapillary neoplasms account for 0.1% to 2.7% of all tumors of the pancreas (12) and are 10 times more frequent in young women than in men, with an average age of occurrence of 24 years (13). There have been no reports of needle tract seeding after EUS-FNA of pancreatic SPN thus far. In our institution, EUS-FNA is usually performed to confirm the pathological diagnosis and is typically limited to atypical cases with an inconclusive imaging diagnosis. Our rare case showed SPN of the pancreatic body that seeded in the gastric wall after EUS-FNA and grew over a course of 67 months, which is much longer than the 11-month average time until recurrence of other malignant tumors in the gastric wall following EUS-FNA (7, 9-11, 17, 19, 20, 23). This may reflect the slow growth and less-aggressive nature of SPN (14). An annual follow-up with endoscopy after EUS-FNA through the gastric wall should be considered to check for gastric wall tumor seeding.
The possibility of peritoneal dissemination and gastric wall seeding of tumor cells via the puncture route has been debated. Several retrospective cohort studies showed that EUS-FNA was not associated with an increased risk of needle tract seeding (4, 8, 24). However, in previous reports (9, 18, 25) and our present case, the location of the tumor in the gastric wall matched closely with the puncture site, which supports the hypothesis of possible needle tract seeding following EUS-FNA. A larger prospective study to test this hypothesis is desirable.
Seeding of tumors after EUS-FNA occurred in the posterior gastric wall in our present case as well as all other reported cases (7, 9-11, 17, 19, 20, 23), which we attribute to puncturing being commonly performed at that site for EUS-FNA in order to achieve the shortest distance between the body and tail of the pancreas.
The differential diagnosis of gastric lesions on endoscopy and cross-sectional imaging is broad and includes a variety of epithelial and non-epithelial lesions. Based on the findings of our case, in patients who have previously undergone EUS-FNA for the evaluation of tumor of the pancreas, the differential diagnosis of gastric lesions should include seeding of the pancreatic tumor in the gastric wall after EUS-FNA.
The authors state that they have no Conflict of Interest (COI).
References
- 1. Dumonceau JM, Polkowski M, Larghi A, et al. Indications, results, and clinical impact of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided sampling in gastroenterology: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline. Endoscopy 43: 897-912, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Wang KX, Ben QW, Jin ZD, et al. Assessment of morbidity and mortality associated with EUS-guided FNA: a systematic review. Gastrointest Endosc 73: 283-290, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Katanuma A, Maguchi H, Yane K, et al. Factors predictive of adverse events associated with endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of pancreatic solid lesions. Dig Dis Sci 58: 2093-2099, 2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Yoon WJ, Daglilar ES, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Mino-Kenudson M, Pitman MB, Brugge WR. Peritoneal seeding in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas patients who underwent endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration: the PIPE Study. Endoscopy 46: 382-387, 2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Tsutsumi H, Hara K, Mizuno N, et al. Clinical impact of preoperative endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Endosc Ultrasound 5: 94-100, 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Yoon WJ, Brugge WR. The safety of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of pancreatic cystic lesions. Endosc Ultrasound 4: 289-292, 2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Kita E, Yamaguchi T, Sudo K. A case of needle tract seeding after EUS-guided FNA in pancreatic cancer, detected by serial positron emission tomography/CT. Gastrointest Endosc 84: 869-870, 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Ngamruengphong S, Xu C, Woodward TA, et al. Risk of gastric or peritoneal recurrence, and long-term outcomes, following pancreatic cancer resection with preoperative endosonographically guided fine needle aspiration. Endoscopy 45: 619-626, 2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Tomonari A, Katanuma A, Matsumori T, et al. Resected tumor seeding in stomach wall due to endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 21: 8458-8461, 2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Yamabe A, Irisawa A, Shibukawa G, et al. Rare condition of needle tract seeding after EUS-guided FNA for intraductal papillary mucinous carcinoma. Endosc Int Open 4: E756-E758, 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Paquin SC, Gariepy G, Lepanto L, Bourdages R, Raymond G, Sahai AV. A first report of tumor seeding because of EUS-guided FNA of a pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc 61: 610-611, 2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Crawford BE., 2nd Solid and papillary epithelial neoplasm of the pancreas, diagnosis by cytology. South Med J 91: 973-977, 1998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Mao C, Guvendi M, Domenico DR, Kim K, Thomford NR, Howard JM. Papillary cystic and solid tumors of the pancreas: a pancreatic embryonic tumor? Studies of three cases and cumulative review of the world's literature. Surgery 118: 821-828, 1995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Pattanshetti VM, Vinchurkar K, Pattanshetti SV. Solid pseudo papillary tumor of pancreas: presenting as acute abdomen in a female child. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol 35: 184-186, 2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Kato T, Egawa N, Kamisawa T, et al. A case of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas and tumor doubling time. Pancreatology 2: 495-498, 2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Zhu H, Jiang F, Zhu J, Du Y, Jin Z, Li Z. Assessment of morbidity and mortality associated with endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for pancreatic cystic lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Endosc 29: 667-675, 2017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Ahmed K, Sussman JJ, Wang J, Schmulewitz N. A case of EUS-guided FNA-related pancreatic cancer metastasis to the stomach. Gastrointest Endosc 74: 231-233, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Iida T, Adachi T, Ohe Y, et al. Re-recurrence after distal gastrectomy for recurrence caused by needle tract seeding during endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of a pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Endoscopy 48(S 01): E304-E305, 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Sakurada A, Hayashi T, Ono M, et al. A case of curatively resected gastric wall implantation of pancreatic cancer caused by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration. Endoscopy 47(Suppl 1 UCTN): E198-E199, 2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Hirooka Y, Goto H, Itoh A, et al. Case of intraductal papillary mucinous tumor in which endosonography-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy caused dissemination. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18: 1323-1324, 2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Sakamoto U, Fukuba N, Ishihara S, et al. Postoperative recurrence from tract seeding after use of EUS-FNA for preoperative diagnosis of cancer in pancreatic tail. Clin J Gastroenterol 11: 200-205, 2018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Yokoyama K, Ushio J, Numao N, et al. Esophageal seeding after endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of a mediastinal tumor. Endosc Int Open 5: E913-E917, 2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Chong A, Venugopal K, Segarajasingam D, Lisewski D. Tumor seeding after EUS-guided FNA of pancreatic tail neoplasia. Gastrointest Endosc 74: 933-935, 2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Ikezawa K, Uehara H, Sakai A, et al. Risk of peritoneal carcinomatosis by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration for pancreatic cancer. J Gastroenterol 48: 966-972, 2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Katanuma A, Maguchi H, Hashigo S, et al. Tumor seeding after endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of cancer in the body of the pancreas. Endoscopy 44(Suppl 2 UCTN): E160-E161, 2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]