Dear editors,
A novel coronavirus (COVID-19) epidemic threatens the world.1 , 2 Before this study, some studies reported cases of viral detection by RT-PCR at different timepoints throughout the disease course.3 , 4 However, these reports monitored SARS-CoV-2 in the acute phase of infection. Currently no study reported the profile of specific antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Profile of specific antibodies in patients’ blood can assist diagnosis and reflect the disease course. Here, we first studied the profile of IgM and IgG for SARS-CoV-2 from 34 COVID-19 patients.
A total of 34 hospitalized patients (admission date from Feb 1st to Feb 29th, 2020) with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection were included in this study. All enrolled patients were confirmed diagnosed of COVID-19 according to the diagnosis and treatment guideline for SARS-CoV-2 from Chinese National Health Committee (Version 5) and the interim guidance from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.5 , 6 Blood samples were obtained at different date after onset of symptoms to detect the specific antibodies to SARS-CoV-2. IgM and IgG were analyzed by chemiluminescent immunoassay according to the manufacturer's protocol (Shenzhen Yahuilong Biotechnology Co., Ltd). All data (test dates and results of IgM and IgG) were collected up to the final follow-up date (March 3rd, 2020).
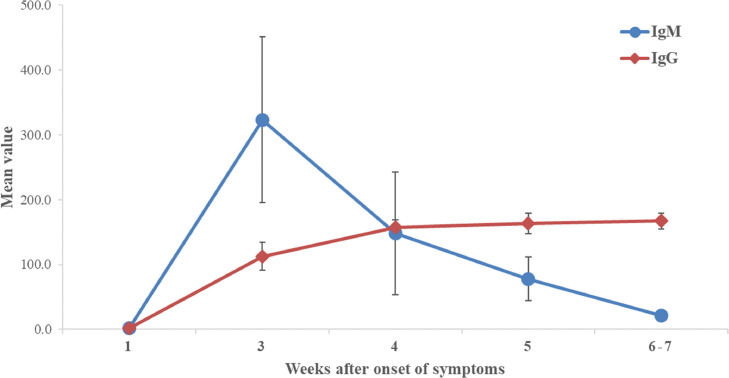
Details of demographic characteristics and test dates and results of IgM and IgG were list in Table 1 . Except for two patients (2 days and 3 days after symptoms onset), all included patients had IgM and IgG tests after 2 weeks from symptoms onset. We categorized patients by weeks according to the date of antibodies test after symptoms onset. In week 3 after symptoms onset, all patients were tested positive for IgM and IgG, with the mean value of 322.80AU/ml and 112.40AU/ml (Reference:<10AU/ml) respectively. In week 4, all the results were still positive for IgM and IgG. IgM declined while IgG continued to go up, with the mean value of 147.92AU/ml and 157.01AU/ml respectively. In week 5, however, all patients were positive for IgG, while 2 patients (16.7%) got negative results for IgM. IgM level kept going down to 78.03AU/ml and IgG continued up to 163.56AU/ml. At the end of observation (7 weeks), 2 patients (33.3%) got negative results for IgM, while all patients positive for IgG, with the mean value of 21.83AU/ml and 167.16AU/ml respectively. (Fig. 1 )
Table 1.
Characteristics of demographic and specific antibodies in COVID-19 patients (N = 34).
| Patients | Age | Gender | IgM AU/ml | IgG AU/ml | Test days, after onset | Week | Mean IgM AU/ml | SEM | Mean IgG AU/ml | SEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient1 | 82 | Female | 3.56 | 2.48 | 2 | 1 | 2.24 | 1.33 | 1.96 | 0.53 |
| Patient2 | 87 | Female | 0.91 | 1.43 | 3 | |||||
| Patient3 | 59 | Female | 122.73 | 163.85 | 14 | 3 | 322.80 | 127.65 | 112.40 | 21.43 |
| Patient4 | 72 | Male | 924 | 187.4 | 14 | |||||
| Patient5 | 32 | Female | 111.78 | 110.17 | 16 | |||||
| Patient6 | 63 | Male | 207.39 | 55.43 | 17 | |||||
| Patient7 | 69 | Male | 401.19 | 78.71 | 17 | |||||
| Patient8 | 64 | Male | 169.72 | 78.82 | 21 | |||||
| Patient9 | 65 | Female | 104.77 | 187.94 | 22 | 4 | 147.92 | 94.50 | 157.01 | 12.40 |
| Patient10 | 39 | Male | 16.63 | 152.88 | 23 | |||||
| Patient11 | 52 | Male | 89.31 | 179.18 | 23 | |||||
| Patient12 | 49 | Male | 41.55 | 128.75 | 24 | |||||
| Patient13 | 35 | Male | 62.5 | 103.89 | 27 | |||||
| Patient14 | 31 | Male | 11.26 | 193.83 | 28 | |||||
| Patient15 | 58 | Female | 709.39 | 152.57 | 28 | |||||
| Patient16 | 44 | Male | 36.57 | 190.85 | 30 | 5 | 78.03 | 33.55 | 163.56 | 15.95 |
| Patient17 | 26 | Female | 14.37 | 277.91 | 30 | |||||
| Patient18 | 57 | Male | 1.65 | 76.85 | 30 | |||||
| Patient19 | 45 | Male | 35.44 | 165.27 | 30 | |||||
| Patient20 | 62 | Female | 3.38 | 200.95 | 31 | |||||
| Patient21 | 65 | Male | 119.35 | 155.29 | 32 | |||||
| Patient22 | 83 | Male | 18.95 | 158.32 | 33 | |||||
| Patient23 | 43 | Male | 48.88 | 73.64 | 33 | |||||
| Patient24 | 53 | Male | 134.24 | 135.54 | 33 | |||||
| Patient25 | 33 | Female | 54.39 | 162.01 | 33 | |||||
| Patient26 | 64 | Male | 422.78 | 159.38 | 34 | |||||
| Patient27 | 60 | Female | 46.34 | 206.7 | 34 | |||||
| Patient28 | 73 | Male | 5.27 | 134.94 | 36 | 6–7 | 21.83 | 5.72 | 167.16 | 12.24 |
| Patient29 | 25 | Female | 15.11 | 179.23 | 36 | |||||
| Patient30 | 71 | Male | 36.11 | 184.56 | 37 | |||||
| Patient31 | 56 | Female | 34.07 | 121.08 | 37 | |||||
| Patient32 | 54 | Male | 42.28 | 216.96 | 38 | |||||
| Patient33 | 47 | Male | 11.2 | 176.73 | 38 | |||||
| Patient34 | 54 | Male | 8.75 | 156.59 | 49 |
Abbreviations: SEM, standard error of mean. *Reference of IgG and IgM are 10AU/ml.
Fig. 1.
Timeline of IgM and IgG Antibodies level to SARS-CoV-2 from the onset of symptoms.
Genomic studies have shown that SARS-CoV-2 shared around 80% identity sequencing with SARS-CoV, which caused a global epidemic with 8096 confirmed cases worldwide in 2002–2003.7 Study of case series suggested the viral nucleic acid shedding pattern of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 is different from SARS-CoV.3 For SARS-CoV, studies revealed that IgM reached the highest point within 4 weeks and was not detectable on 3 months after onset of symptoms. IgG were persistently detectable up to 24 months.8
Our results suggested that the profile of specific antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 is similar to SARS-CoV. Detectable and continuous high level of IgM indicated the acute phase of infection. Furthermore, IgM last more than a month indicating the prolonged virus replication in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. IgG responded later than IgM and persisted high in our study, indicating the humoral immune reaction to protect the body against SARS-CoV-2 virus.
The detection and profile of specific antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 will provide valuable information for rapid screening of suspects, assist diagnosis and evaluate the disease course. Furthermore, concentrated IgG antibody may be informative in vaccine development and treatment for SARS-CoV-2.
Declaration of Competing Interest
All authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
Funding
No funding resources to declare for this study.
Informed consent
Oral consent was obtained from patients involved before enrollment when data were collected retrospectively.
References
- 1.Tang J.W., TAMbyah P.A., Hui D.S. Emergence of a novel coronavirus causing respiratory illness from Wuhan, China. J. Infect. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.01.014. https://doi.org/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zunyou W., Jennifer M.G. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in china: Summary of a report of 72,314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention. JAMA. 2020 doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648. Published online February 24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zou L., Ruan F., Huang M. SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients. N Engl. J. Med. 2020 doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2001737. Published online February 19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pan Y., Zhang D.T., Yang P. Viral load of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30113-4. Published Online February 24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Interim infection prevention and control recommendations for patients with confirmed coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) or persons under investigation for COVID-19 in healthcare settings. (Update: February 21, 2020). https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/infection-control.html.
- 6.China National Health Commission Diagnosis and treatment of 2019-nCoV pneumonia in China; 2020. (Version 5) In Chinese. Published February 8Accessed March 3, 2020 http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7653p/202002/d4b895337e19445f8d728fcaf1e3e13a/files/ab6bec7f93e64e7f998d802991203cd6.pdf
- 7.Summary of probable SARS cases with onset of illness from 1 November 2002 to 31 July 2003. Geneva: World Health Organization 2004 https://www.who.int/csr/sars/country/table2004_04_21/en/.
- 8.Mo H.Y., Zeng G.Q., Ren X.L. Longitudinal profile of antibodies against SARS-coronavirus in SARS patients and their clinical significance. Respirology. 2006;11:49–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2006.00783.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]