An 83-year-old man with positive fecal occult blood test results underwent colonoscopy, which revealed a 15-mm-diameter laterally spreading tumor surrounded by multiple diverticula at the ascending colon (Figs. 1 and 2). The lesion was a nongranular-type laterally spreading tumor, and the Japanese Narrow-Band Imaging Expert Team classification was type 2A, meaning no evidence of invasion; therefore, we performed endoscopic resection instead of surgery.
Figure 1.
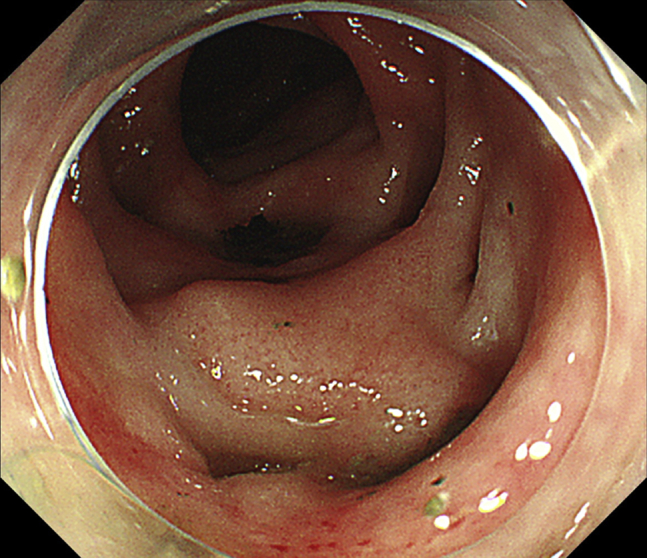
Endoscopic image showing the tumor surrounded by diverticula.
Figure 2.
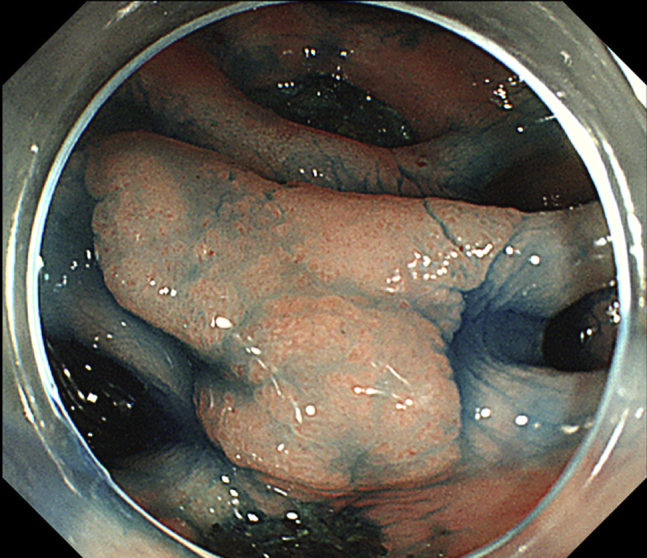
Endoscopic image showing the tumor well demarcated with indigo carmine.
Conventional EMR of the tumor surrounded by diverticula with the use of submucosal saline solution injection would have been difficult because the appropriate lifting up by submucosal injection is difficult, and snaring including adjacent diverticula would have resulted in perforations. Furthermore, endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for tumors adjacent to diverticula carries a high risk of perforation, and performing ESD on such lesions demands highly advanced skills, although we have reported success with the use of ESD for colonic polyps involving a diverticulum.1,2 Underwater EMR was developed and described by Binmoeller et al3 in 2012. We previously reported the usefulness of this procedure with a high en bloc resection rate for intermediate-sized colorectal polyps4; therefore, we performed underwater EMR for this lesion (Video 1, available online at www.VideoGIE.org). We here report the first case, to our knowledge, of a colonic adenoma surrounded by diverticula treated with underwater EMR.
We used a magnifying colonoscope (Evis PCF-Q260ZAI; Olympus Medical Systems, Tokyo, Japan). Air was evacuated from the affected segment of the lumen and infused water until the lumen was completely full, after which we performed hot-snare polypectomy without submucosal injection, using a SnareMaster (15 mm; Olympus Medical Systems) (Fig. 3). A high-frequency electrical generator (Vio 300D; Erbe Elektromedizin, Tübingen, Germany) was used with the following settings: endocut Q mode: effect 3, duration 2, interval 4. We resected the lesion en bloc in 2 minutes without perforation and completely closed the mucosal defect with clips (Figs. 4 and 5). No adverse events occurred, and the patient experienced no postoperative abdominal pain or fever requiring antibiotics. On pathologic examination, the lesion was a tubular adenoma, high-grade in part, with negative margins (Fig. 6).
Figure 3.
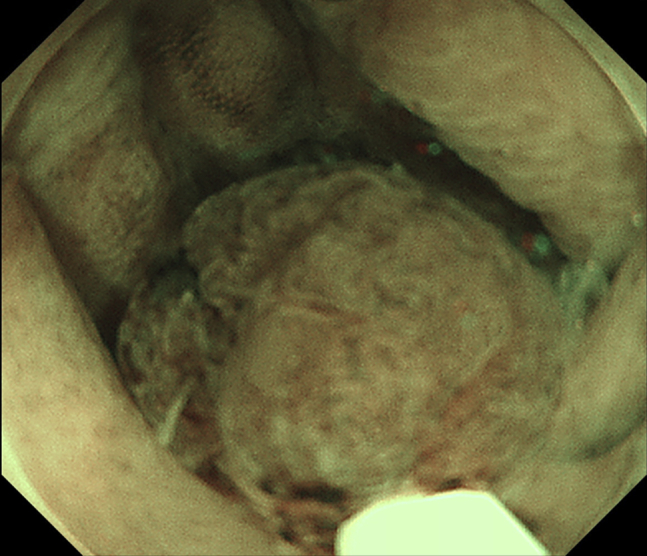
Endoscopic image showing the polyp snared underwater.
Figure 4.
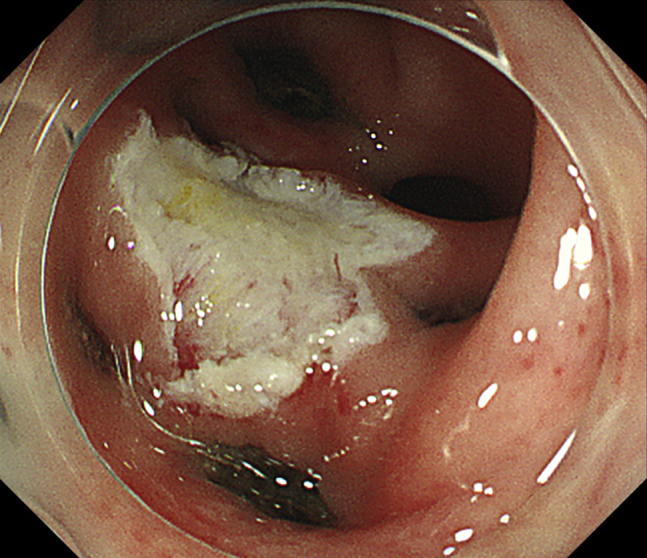
Endoscopic image showing completed underwater EMR.
Figure 5.
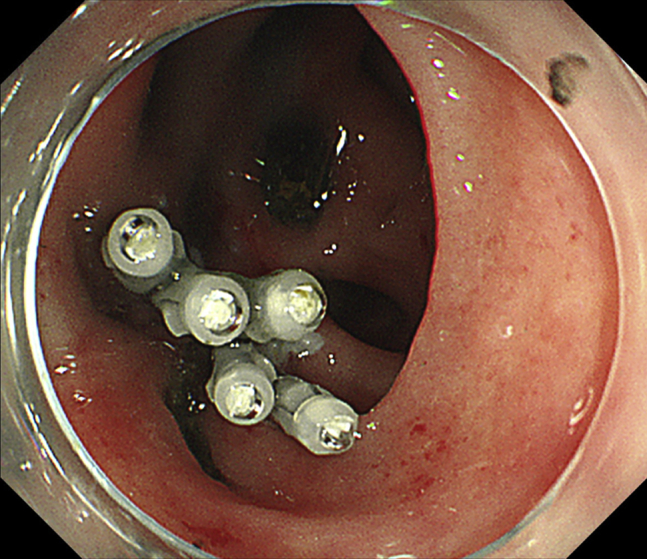
Endoscopic image showing complete closure of the defect with clips.
Figure 6.

Photograph of the specimen after it was resected en bloc in 2 minutes.
Disclosure
All authors disclosed no financial relationships relevant to this publication.
Footnotes
If you would like to chat with an author of this article, you may contact Dr Shichijo at shichijiyou-tky@umin.ac.jp.
Supplementary data
Underwater EMR of the colonic adenoma surrounded by diverticula.
References
- 1.Shichijo S., Matsuno K., Takeuchi Y. Pulley traction-assisted colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection affords good visibility of submucosal layer. VideoGIE. 2018;3:358–360. doi: 10.1016/j.vgie.2018.08.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Shichijo S., Yamasaki Y., Takeuchi Y. Case of colonic adenoma involving a diverticulum resected by a traction-assisted endoscopic submucosal dissection technique. Dig Endosc. 2017;29:729–730. doi: 10.1111/den.12904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Binmoeller K.F., Weilert F., Shah J. "Underwater" EMR without submucosal injection for large sessile colorectal polyps (with video) Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75:1086–1091. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.12.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yamashina T., Uedo N., Akasaka T. Comparison of underwater vs conventional endoscopic mucosal resection of intermediate-size colorectal polyps. Gastroenterology. 2019;157:451–461.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Underwater EMR of the colonic adenoma surrounded by diverticula.


