Fig. 1.
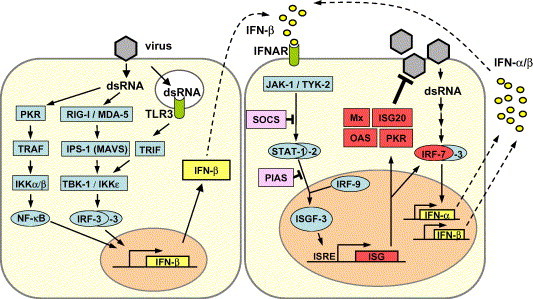
Type I IFN induction, signaling and action. Left panel: dsRNA, a characteristic by-product of virus replication, leads to activation of the transcription factors NF-κB, IRF-3 and AP-1 (not shown). The cooperative action of these factors is required for full activation of the IFN-β promoter. IRF-3 is phosphorylated by the kinases IKKε and TBK-1 which in turn are activated by the RNA-sensing complex of RIG-I, MDA5 and IPS-1/MAVS. A second signaling pathway involves endosomal TLR-3 and TRIF. Right panel: Newly synthesized IFN-β binds to the type I IFN receptor (IFNAR) and activates the expression of numerous ISGs via the JAK/STAT pathway. IRF-7 amplifies the IFN response by inducing the expression of several IFN-β subtypes. SOCS and PIAS are negative regulators of the JAK-STAT pathway. Mx, ISG20, OAS and PKR are examples of proteins with antiviral activity. For details see text.
