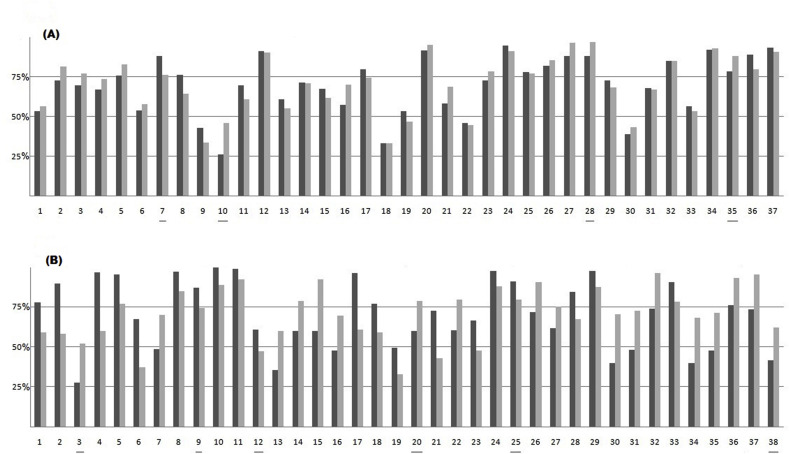
Fig. 2.
Analysis of the amino acid diversity in the 75 pairs of homologous overlapping genes. Each pair of columns shows: i) the percent amino acid identity between the protein encoded by the upstream frame of the overlap and that encoded by the homolog (dark column); ii) the percent amino acid identity between the protein encoded by the downstream frame of the overlap (shifted of one nucleotide 3′ with respect to the upstream frame) and that encoded by the homolog (gray column). The horizontal line separates well-conserved homologous pairs (aa identity >50%) from not well-conserved homologous pairs (aa identity <50%). (A) Subset of the 37 overlapping genes under symmetric evolution. (B) Subset of the 38 overlapping genes under asymmetric evolution. The numbering of overlapping genes is in accordance with that given in Supplementary Table S1. The underlined numbers indicate the overlaps in which the pattern of symmetric evolution (4 cases out of 37) or that of asymmetric evolution (6 cases out of 38) was not confirmed by chi-square analysis of the nucleotide diversity.