Graphical abstract
Compound (1S,2S)-16b exhibited antiviral activity against Influenza A H3N2 subtype (EC50 = 20 μM—visual CPE score; EC50 = 18 μM—MTS method; MCC >100 μM, CC50 >100 μM) in Madin Darby canine kidney cell cultures (MDCK), and (1S,2S)-16k against vesicular stomatitis virus and respiratory syncytial virus in HeLa cells (EC50 = 9 and 12 μM, respectively). Moreover, (1R,2S)-16l showed activity against both herpes simplex viruses (HSV-1, HSV-2) in HEL cell cultures (EC50 = 2.9 and 4 μM, respectively) and feline herpes virus in CRFK cells (EC50 = 4 μM) but at the same time it exhibited cytotoxicity toward uninfected cell (MCC ⩾ 4 μM). Several compounds (1S,2S)-16i–l and (1R,2S)-16f–l inhibited proliferation of L1210, CEM as well as HeLa cells with IC50’s in the 4–50 μM range.

Keywords: Cycloaddition; 1,2,3-Triazoles; Phosphonates; Nucleotide analogues; Antiviral; Cytostatic
Abstract
The efficient synthesis of a new series of polyhydroxylated dibenzyl ω-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)alkylphosphonates as acyclic nucleotide analogues is described starting from dibenzyl ω-azido(polyhydroxy)alkylphosphonates and selected alkynes under microwave irradiation. Selected O,O-dibenzylphosphonate acyclonucleotides were transformed into the respective phosphonic acids. All compounds were evaluated in vitro for activity against a broad variety of DNA and RNA viruses and for cytostatic activity against murine leukemia L1210, human T-lymphocyte CEM and human cervix carcinoma HeLa cells. Compound (1S,2S)-16b exhibited antiviral activity against Influenza A H3N2 subtype (EC50 = 20 μM—visual CPE score; EC50 = 18 μM—MTS method; MCC >100 μM, CC50 >100 μM) in Madin Darby canine kidney cell cultures (MDCK), and (1S,2S)-16k was active against vesicular stomatitis virus and respiratory syncytial virus in HeLa cells (EC50 = 9 and 12 μM, respectively). Moreover, compound (1R,2S)-16l showed activity against both herpes simplex viruses (HSV-1, HSV-2) in HEL cell cultures (EC50 = 2.9 and 4 μM, respectively) and feline herpes virus in CRFK cells (EC50 = 4 μM) but at the same time it exhibited cytotoxicity toward uninfected cell (MCC ⩾ 4 μM). Several other compounds have been found to inhibit proliferation of L1210, CEM as well as HeLa cells with IC50 in the 4–50 μM range. Among them compounds (1S,2S)- and (1R,2S)-16l were the most active (IC50 in the 4–7 μM range).
1. Introduction
Infectious diseases caused by different microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi and viruses, are still a problem of human civilization. Among all pathogenic microorganisms viruses are notorious, the most active and probably the most dangerous because they penetrate into cells, evolve rapidly and interfere with the genetic material of the host. Despite current achievements in the development of antiviral drugs,1, 2 there is still a need for new compounds with an unique mechanism of action and limited side-effects.
The successful search for acyclic nucleoside analogues started when acyclovir [9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine] was described as an antiherpesvirus agent.3 Soon after, a few other acyclic nucleoside or acyclic nucleoside phosphonate analogues became available as antiviral compounds, namely, ganciclovir, cidofovir, tenofovir, adefovir, etc.4, 5
Attempts to improve the solubility of compounds in aqueous media resulted in synthesis of hydroxylated analogues of nucleosides such as ganciclovir as well as other nucleoside mimetics shown on Figure 1.4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 The interest in investigation of hydroxylated nucleosides has also been stimulated by a previous discovery of extreme potency of the naturally accessible d-eritadenine 2,7, 8 which acts as an inhibitor of S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine hydrolase (SAHH). This enzyme has earlier been shown to be an attractive target for poxviruses, (−)RNA viruses such as paramyxovirus and rhabdovirus, and (±)RNA viruses such as reovirus.15, 16 Consequently, (2′S)-9-(2′,3′-dihydroxypropyl)adenine 3 10 and other N(9)-substituted adenines and guanines possessing polyhydroxyalkyl chains have been obtained (Fig. 1 ).
Figure 1.

Examples of hydroxylated nucleoside analogues.
Among various structural modifications of nucleosides/nucleotides 1,2,3-triazole analogues have been of special interest. The applicability of a 1,2,3-triazole ring as a replacement of sugar17, 18, 19 or nucleobase moieties17, 19, 20, 21 as well as an additional linker between a phosphonoalkyl unit and a nucleobase has been widely explored22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28 including our achievements.29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35 Recently, several acyclic 1,2,3-triazolyl analogues of nucleosides/nucleotides with nucleobases attached via the methylene group at the C4 in the 1,2,3-triazole moiety have been obtained and some of them showed promising biological activity (Fig. 2 ). While (1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)nucleosides 9–11 were found to be inactive against selected viruses,22, 23 the phosphonomethyl-12 (n = 1; B = Thy, Ade) and phosphonoethyl(1,2,3-triazoles) 12 (n = 2; R = Thy, Ura) showed moderate activity against hepatitis C virus (HCV).25 Recently, we succeeded in the synthesis of 1-(3-phosphonopropyl)-1,2,3-triazole 13 substituted with benzoylbenzuracil via a methylene linker which exhibited activity against herpes simplex virus-1 (KOS), herpes simplex virus-2 (G) and feline herpes virus.33 Moreover, the 1-(3-amino-3-phosphonopropyl)-1,2,3-triazole analogue (R)-14 having 3-acetylindole as a modified nucleobase showed moderate activity toward vesicular stomatitis virus.35
Figure 2.

Examples of known 1,2,3-triazolyl analogues of nucleosides/nucleotides.
In continuation of our research program towards 1,2,3-triazole nucleoside analogues,14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21 and taking into account the known biological activity of hydroxylated nucleoside analogues as well as the antiviral activity of 13 and 14 and the cytostatic properties of 15, 1,2,3-triazoles 16 and 17 possessing dibenzyloxyphosphono(polyhydroxy)alkyl residues have been designed (Fig. 3 ). We assumed that incorporation of additional hydroxyl groups into an alkyl side-chain would assure better solubility and perhaps improve biological activity of 1,2,3-triazoles 16 and 17 in comparison with analogous compounds having unfunctionalised aliphatic moieties.33
Figure 3.

Structures of the designed nucleotide phosphonate analogues 16 and 17.
2. Results and discussion
2.1. Chemistry
Enantiomerically pure (1R,2S)- and (1S,2S)-azidophosphonates 18 were obtained from l-ascorbic acid,36, 37 whereas for the synthesis of (1S,2R,3S)- and (1S,2R,3R)-azidophosphonates 19 38 tartaric acid and l-isoascorbic acid were used, respectively, as a source of chirality.
The 1,2,3-triazoles (1R,2S)- and (1S,2S)-16 were synthesised by the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of the corresponding (1R,2S)- and (1S,2S)-azidophosphonates 18 with N-propargyl nucleobases 20 (N 9-propargyladenine 20a,23 N 1-propargylthymine 20b,23 N 1-propargyluracil 20c,39 N 4-acetyl-N 1-propargylcytosine 20d 40) and several propargylated nucleobase mimetics 20 (N 1-propargyl-6-azauracil 20e,41 3-acetyl-N-propargylindole 20f,42 N 1-propargyltheobromine 20g,43, 44 N 7-propargyltheophylline 20h,45 8-chloro-N 7-propargyltheophylline 20i,46 N-propargyl-2-pyridone 20j,47 N 3-benzoyl-N 1-propargyluracil 20k 33, 48 and N 3-benzoyl-N 1-propargylquinazolin-2,4-dione 20l 33).
According to a standard protocol the regioselective formation of respective 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazoles was secured by the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of azides with terminal alkynes in the presence of a catalytic amount of Cu(I) at room temperature.49, 50 However, under these conditions more than 3 days were required to complete the reaction of (1S,2S)- and (1R,2S)-azidophosphonates 18 with N-propargyl nucleobases 20. To accelerate the reaction the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition was performed under microwave irradiation. Under these conditions the full conversion of azidophosphonates 18 into 1,2,3-triazoles 16 was observed at 40–45 °C within 20 min (Scheme 1 ).
Scheme 1.

Reagents and conditions: (a) CuSO4 × 5H2O (0.05 equiv), sodium ascorbate (0.1 equiv), H2O·EtOH (1:1), MW, 40–45 °C, 20 min.
In a similar way, employing (1S,2R,3S)- and (1S,2R,3R)-azidophosphonates 19 the corresponding 1,2,3-triazoles (1S,2R,3S)- and (1S,2R,3R)-17 were successfully obtained (Scheme 2 ).
Scheme 2.
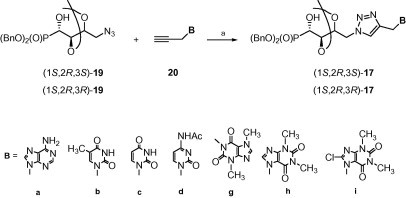
Reagents and conditions: (a) CuSO4 × 5H2O (0.05 equiv), sodium ascorbate (0.1 equiv), H2O·EtOH (1:1), MW, 40–45 °C, 20 min.
The compounds (1R,2S)- and (1S,2S)-16 as well as (1S,2R,3S)- and (1S,2R,3R)-17 were obtained in good yields after purification by column chromatography on silica gel.
Selected dibenzyl phosphonates (1S,2S)-16 were subjected to hydrogenation in the presence of 10% Pd–C in aqueous methanol37 to give the respective phosphonic acids 21 in good yields (Scheme 3 ).
Scheme 3.
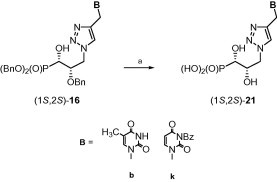
Reagents and conditions: (a) H2, 10% Pd–C, MeOH·H2O, 24 h.
Structures of all new compounds were confirmed on the basis of 1H, 13C, 31P NMR and IR spectra data as well as by elemental analysis.
2.2. Antiviral activity and cytotoxicity evaluation
All the synthesised phosphonates (1R,2S)- and (1S,2S)-16 and (1S,2R,3S)- and (1S,2R,3R)-17 as well as the phosphonic acids (1S,2S)-21b and (1S,2S)-21k were evaluated for their antiviral activities against a wide variety of DNA and RNA viruses, using the following cell-based assays: (a) human embryonic lung (HEL) cells: herpes simplex virus-1 (KOS), herpes simplex virus-2 (G), herpes simplex virus-1 (TK ACVr KOS), vaccinia virus and vesicular stomatitis virus, cytomegalovirus (AD-169 strain and Davis strain), varicella-zoster virus (TK+ VZV strain OKA and TK− VZV strain 07-1); (b) CEM cell cultures: human immunodeficiency virus [HIV-1 and HIV-2]; (c): Vero cell cultures: para-influenza-3 virus, reovirus-1, Sindbis virus, Coxsackie virus B4, Punta Toro virus; (d) HeLa cell cultures: vesicular stomatitis virus, Coxsackie virus B4 and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV); (e) Crandell-Rees Feline Kidney (CRFK) cell cultures: feline corona virus (FIPV) and feline herpes virus (FHV); (f) Madin Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cell cultures: influenza A virus H1N1 subtype (A/PR/8), influenza A virus H3N2 subtype (A/HK/7/87) and influenza B virus (B/HK/5/72). Ganciclovir, cidofovir, acyclovir, brivudin, (S)-9-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)adenine [(S)-DHPA], Hippeastrum hybrid agglutinin (HHA), Urtica dioica agglutinin (UDA), dextran sulfate (molecular weight 5000, DS-5000), ribavirin, oseltamivir carboxylate, amantadine and rimantadine were used as the reference compounds. The antiviral activity was expressed as the EC50: the compound concentration required to reduce virus plaque formation (VZV) by 50% or to reduce virus-induced cytopathogenicity by 50% (other viruses).
The cytotoxicity of the tested compounds toward the uninfected host cells was defined as the minimum cytotoxic concentration (MCC) that causes a microscopically detectable alteration of normal cell morphology. The 50% cytotoxic concentration (CC50), causing a 50% decrease in cell viability was determined using a colorimetric 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium (MTS) assay system.
It was established that compound (1S,2S)-16b containing a 1,2,3-triazole moiety substituted at C4′ with thymine exhibited antiviral activity against Influenza A H3N2 subtype (EC50 = 20 μM by visual CPE score; EC50 = 18 μM by MTS score; MCC >100 μM, CC50 >100 μM) in Madin Darby canine kidney cells (MDCK). On the other hand, compound (1S,2S)-16k with N 3-benzoyluracil showed antiviral activity against vesicular stomatitis virus (EC50 = 9 μM) and respiratory syncytial virus (EC50 = 12 μM) in HeLa cells which favourably compares with the data for ribavirin (EC50 = 17 and 5 μM, respectively). Moreover, compound (1R,2S)-16l containing the N 3-benzoylbenzuracil moiety showed activity against both herpes simplex viruses (HSV-1, HSV-2) in HEL cell cultures (EC50 = 2.9 and 4 μM, respectively) and feline herpes virus in CRFK cells (EC50 = 4 μM) but at the same time it exhibited cytotoxicity toward uninfected cell cultures (MCC ⩾ 4 μM). Moreover, compound (1S,2S)-16e was slightly active against both TK+ VZV and TK VZV strains (EC50 = 63.7 and 70 μM, respectively), whereas (1S,2R,3R)-17i showed activity against the TK+ VZV strain only (EC50 = 55.7 μM).
2.3. Evaluation of cytostatic activity
The cytostatic activity of the tested compounds was defined as the 50% cytostatic inhibitory concentration (IC50), causing a 50% decrease in cell proliferation and was determined against murine leukaemia L1210, human lymphocyte CEM and human cervix carcinoma HeLa cells.
The inhibitory effect of the series of dibenzyl (1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)alkylphosphonates against the proliferation of murine leukemia (L1210), human T-lymphocyte (CEM) and human cervix carcinoma cells (HeLa) are shown in Table 1 . Several compounds were endowed with a cytostatic activity at compound concentrations below 50 μM [i.e., (1S,2S)-16i–l and (1R,2S)-16f–l] toward tested tumor cell lines, namely, L1210,CEM and HeLa. Among all tested compounds, 1,2-dihydroxypropylphosphonates (1S,2S)- and (1R,2S)-16l, both having N 3-benzoylbenzuracil as a modified nucleobase, were the most potent and showed cytostatic activity between 4 and 7 μM toward the tested tumor cell lines (Table 1).
Table 1.
Inhibitory effect of tested compounds against the proliferation of murine leukemia (L1210), human T-lymphocyte (CEM) and human cervix carcinoma cells (HeLa)
| Compound | Nucleobase (B) | IC50a (μM) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEM | L1210 | HeLa | ||
| (1S,2S)-16a | Adenine | 78 ± 15 | 66 ± 6.4 | 81 ± 21 |
| (1S,2S)-16b | Thymine | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (1S,2S)-16c | Uracil | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (1S,2S)-16d | N4-Acetylcytosine | 169 ± 9.9 | 153 ± 35 | >200 |
| (1S,2S)-16e | 6-Azauracil | 71 ± 11 | 78 ± 7.8 | 64 ± 18 |
| (1S,2S)-16f | 3-Acetylindole | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (1S,2S)-16g | Theobromine | 82 ± 0.7 | 71 ± 8.5 | 78 ± 17 |
| (1S,2S)-16h | Theophylline | 71 ± 0.7 | 71 ± 9.2 | 79 ± 0.7 |
| (1S,2S)-16i | 8-Chlorotheophylline | 27 ± 2.1 | 70 ± 42 | >200 |
| (1S,2S)-16j | 2-Pyridon | 90 ± 0.7 | 63 ± 22 | 45 ± 2.1 |
| (1S,2S)-16k | N3-Benzoyluracil | 21 ± 2 | 26 ± 12 | 76 ± 21 |
| (1S,2S)-16l | N3-Benzoylbenzuracil | 4.7 ± 0.6 | 4.1 ± 1.8 | 7.1 ± 4.3 |
| (1S,2S)-21b | Thymine | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (1S,2S)-21k | N3-Benzoyluracil | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (1R,2S)-16a | Adenine | 76 ± 11 | 46 ± 40 | 80 ± 6.4 |
| (1R,2S)-16b | Thymine | 83 ± 2.8 | 85 ± 9.9 | 64 ± 25 |
| (1R,2S)-16c | Uracil | 91 ± 6.4 | 86 ± 18 | 66 ± 12 |
| (1R,2S)-16d | N4-Acetylcytosine | 82 ± 3.5 | 96 ± 11 | 160 ± 57 |
| (1R,2S)-16e | 6-Azauracil | 81 ± 2.8 | 71 ± 13 | 122 ± 35 |
| (1R,2S)-16f | 3-Acetylindole | 16 ± 3.5 | 15 ± 4.2 | 13 ± 2.8 |
| (1R,2S)-16g | Theobromine | 68 ± 6.4 | 58 ± 15 | 76 ± 9.2 |
| (1R,2S)-16h | Theophylline | 72 ± 9.9 | 56 ± 13 | 83 ± 9.9 |
| (1R,2S)-16i | 8-Chlorotheophylline | 25 ± 1.4 | 22 ± 0.7 | 86 ± 4.2 |
| (1R,2S)-16j | 2-Pyridon | 101 ± 6.4 | 76 ± 2.8 | 28 ± 19 |
| (1R,2S)-16k | N3-Benzoyluracil | 21 ± 1 | 21 ± 1 | 57 ± 33 |
| (1R,2S)-16l | N3-Benzoylbenzuracil | 4.7 ± 0.1 | 4.7 ± 0.3 | 5.1 ± 3.2 |
| (1S,2R,3S)-17a | Adenine | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (1S,2R,3S)-17b | Thymine | >200 | 139 ± 46 | 107 ± 37 |
| (1S,2R,3S)-17c | Uracil | >200 | >200 | 118 ± 16 |
| (1S,2R,3S)-17d | N4-Acetylcytosine | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (1S,2R,3S)-17g | Theobromine | 142 ± 40 | 145 ± 0 | >200 |
| (1S,2R,3S)-17i | 8-Chlorotheophylline | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (1S,2R,3R)-17a | Adenine | 140 ± 49 | 98 ± 3.5 | ⩾167 |
| (1S,2R,3R)-17b | Thymine | >200 | 122 ± 21 | ⩾200 |
| (1S,2R,3R)-17c | Uracil | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (1S,2R,3R)-17d | N4-Acetylcytosine | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (1S,2R,3R)-17g | Theobromine | 115 ± 4.2 | 86 ± 2.1 | >200 |
| (1S,2R,3R)-17h | Theophylline | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| (1S,2R,3R)-17i | 8-Chlorotheophylline | 51 ± 1.4 | 58 ± 9.9 | 85 ± 3.5 |
| 5-Fluorouracil | 18 ± 5 | 0.33 ± 0.17 | 0.54 ± 0.12 | |
50% Inhibitory concentration or compound concentration required to inhibit tumor cell proliferation by 50%.
2.3.1. Structure–activity relationship studies
As far as cytostatic properties are considered, within a series of hydroxylated (1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)nucleotide analogues 16 and 17, compounds 16 containing three-carbon phosphonoalkyl chain are more cytostatic toward the tested tumor cell lines when compared with four-carbon phosphonates 17 having the same nucleobases (16a vs 17a, 16c vs 17c, 16d vs 17d, 16g vs 17g, 16i vs 17i). Moreover, the configurations at stereogenic centres have slight or negligible impact on the cytostatic properties of (1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)nucleotides [(1S,2S)-16 vs (1R,2S)-16 and (1S,2R,3S)-17 vs (1S,2R,3R)-17)]. Among the series of 1,2-dihydroxypropylphosphonates 16, both stereoisomers substituted with the N 3-benzoylbenzuracil moiety [(1S,2S)-16l and (1R,2S)-16l] were the most potent to inhibit the proliferation of L1210, CEM as well as HeLa cells, whereas their N 3-benzoyluracil counterparts (1S,2S)-16k and (1R,2S)-16k showed significantly lower inhibitory activity. The removal of the N 3-benzoyl group from uracil resulted in complete loss of activity for (1S,2S)-16c and further decrease in potency for (1R,2S)-16c. Functionalisation of the alkyl chains in the analogues equipped with the N 3-benzoylbenzuracil moiety significantly improved cytostatic activity of 1-hydroxy-2-benzyloxypropylphosphonates (1S,2S)-16l and (1R,2S)-16l when compared with the slightly active 1-hydroxypropyl- and 2-hydroxypropylphosphonates33 and the inactive propylphosphonate 13.33 As could be expected highly polar phosphonic acid (1S,2S)-21k showed no cytostatic activity while much more lipophilic O,O-dibenzyl ester (1S,2S)-16k was moderately active.
Analogous structure–antiviral activity relationship studies on a series of (1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)nucleotide analogues 16 and 17 were performed. Thus, 1-hydroxy-2-benzyloxypropylphosphonate (1R,2S)-16l, which contains a N 3-benzoylbenzyuracil residue, showed promising antiviral activity against herpes simplex viruses (HSV-1, HSV-2) in HEL cell cultures (EC50 = 2.9 and 4 μM, respectively) and feline herpes virus in CRFK cells (EC50 = 4 μM), whereas its N 3-benzoyluracil and uracil analogues (1R,2S)-16k and (1R,2S)-16c, respectively, appeared inactive. This trend well correlates with our previous observations on structurally analogous (1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)nucleotides having an unsubstituted phosphonopropyl chain, since compound 13 was the most active against HSV-1, HSV-2 (EC50 = 17 μM) and against feline herpes virus (EC50 = 24 μM).33 Furthermore, the stereochemistry of the aliphatic chain substituted with hydroxyl groups is essential for activity since analogue (1S,2S)-16l showed no activity. On the other hand, the significant activity toward vesicular stomatitis virus and respiratory syncytial virus in HeLa cell cultures was observed for compound (1S,2S)-16k containing an N 3-benzoyluracil unit (EC50 = 9 and 12 μM, respectively) since analogous compounds (1S,2S)-16l (B = N 3-benzoylbenzuracil) and (1S,2S)-16c (B = uracil) were inactive against these viruses. Again, stereochemistry of an aliphatic fragment appeared important and resulted in lack of activity for (1R,2S)-16k.
3. Conclusions
Dibenzyl ω-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)alkylphosphonates (1S,2S)- and (1R,2S)-16 as well as (1S,2R,3S)-17 and (1S,2R,3R)-17 were efficiently synthesised as acyclic nucleotide analogues. The phosphonic acids (1S,2S)-21b and (1S,2S)-21k were synthesised from O,O-dibenzylphosphonate acyclonucleotides (1S,2S)-16b and (1S,2S)-16k by hydrogenolysis. All synthesised esters and acids were tested in vitro for activity against a broad variety of DNA and RNA viruses and for cytostatic activity against murine leukemia L1210, human T-lymphocyte CEM and human cervix carcinoma HeLa cells. Antiviral activity against Influenza A H3N2 subtype (EC50 = 20 μM—visual CPE score; EC50 = 18 μM—MTS; MCC >100 μM, CC50 >100 μM) in Madin Darby canine kidney cell cultures (MDCK) has been observed for phosphonate (1S,2S)-16b, whereas (1S,2S)-16k was found active against vesicular stomatitis virus and respiratory syncytial virus in HeLa cell cultures (EC50 = 9 and 12 μM, respectively). Compounds (1S,2S)-16i–l and (1R,2S)-16f–l inhibited proliferation of L1210, CEM as well as HeLa cells with IC50’s in the 4–50 μM range. Especially, (1S,2S)- and (1R,2S)-16l consistently inhibited tumor cell proliferation in the lower micromolar range (IC50 = 4–7 μM), irrespective of the nature of the tumor cell line.
4. Experimental section
1H NMR were taken in CDCl3 or CD3OD on the following spectrometers: Varian Mercury-300 and Bruker Avance III (600 MHz) with TMS as an internal standard; chemical shifts δ in ppm with respect to TMS; coupling constants J in Hz. 13C NMR spectra were recorded for CDCl3,CD3OD or DMSO-d6 solutions on a Varian Mercury-300 and Bruker Avance III (600 MHz) spectrometer at 75.5 and 150.5 MHz, respectively. 31P NMR spectra were taken in CDCl3 or CD3OD on Varian Mercury-300 and Bruker Avance III at 121.5 and 242 MHz.
IR spectral data were measured on an Infinity MI-60 FT-IR spectrometer. Melting points were determined on a Boetius apparatus and are uncorrected. Elemental analyses were performed by the Microanalytical Laboratory of this Faculty on a Perkin Elmer PE 2400 CHNS analyzer. Polarimetric measurements were conducted on an Optical Activity PolAAr 3001 apparatus.
The following adsorbents were used: column chromatography, Merck silica gel 60 (70–230 mesh); analytical TLC, Merck TLC plastic sheets silica gel 60 F254. TLC plates were developed in chloroformmethanol solvent systems. Visualization of the spots was effected with iodine vapours. All solvents were purified by methods described in the literature.
All microwave irradiation experiments were carried out in a microwave reactor Plazmartonika RM 800. The reaction carried out in 50 mL-glass vials.
4.1. General procedure for the preparation of 1,2,3-triazoles
To a solution of azidophosphonate (1.00 mmol) in EtOH (1 mL) and H2O (1 mL) were added CuSO4 × 5H2O (0.05 mmol), sodium ascorbate (0.10 mmol) and alkynes (1.00 mmol). The suspension was microwave irradiated in the microwave reactor (Plazmatronika RM 800, 800 W) at 40–45 °C for 20 min. After cooling the solvent was removed by vacuum evaporation. The residue was suspended in chloroform (5 mL) and filtered through a layer of Celite. The solution was concentrated in vacuo and the crude product was purified on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol mixtures (50:1, 20:1 or 10:1, v/v) to give the desired 1,2,3-triazoles.
4.2.1. (1S,2S)-Dibenzyl 3-{4-[(6-aminopurin-9-yl)methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl]}-2-benzyloxy-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1S,2S)-16a
Yield: 86%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 25.6 (c 1.15 in DMSO); mp: <200 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3389, 2984, 2872, 1643, 1604, 1245, 1025, 749, 698 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 8.25 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.86 (s, 1H), 7.64 (s, 1H), 7.30–7.22 (m, 10H, Haromat), 7.19–7.11 (m, 3H, Haromat), 7.06–6.98 (m, 2H, Haromat), 6.16 (br s, 2H, NH2), 5.37 (AB, J = 15.3 Hz, 1H, CHaHb-Ade), 5.32 (AB, J = 15.3 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb-Ade), 5.03 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 4H, 2×POCH2Ph), 4.61 (dd, J = 14.1 Hz, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.54 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.47 (dd, J = 14.1 Hz, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.25 (dddd, J = 7.8 Hz, J = 7.2 Hz, J = 5.1 Hz, J = 3.0 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.15 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 3.96 (dd, J = 11.1 Hz, J = 3.0 Hz, 1H, H-1), 2.16 (br s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR (151 Hz, DMSO-d 6): δ = 156.4, 153.0, 149.8, 143.0, 141.0, 137.9, 137.1 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, Cipso), 137.0 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, Cipso), 129.3, 129.0, 128.9, 128.8, 128.7, 128.4, 128.3, 128.2, 128.1, 127.5, 125.1, 119.1, 78.7 (d, J = 3.3 Hz, C-2), 73.0, 68.0 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, POC), 67.8 (d, J = 162.2 Hz, PC), 67.3 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, POC), 50.9 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, C-3), 38.4; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.49 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C32H33N8O5P: C, 59.99; H, 5.19; N, 17.49. Found: C, 60.12; H, 5.19; N, 17.21.
4.2.2. (1S,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(5-methyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1S,2S)-16b
Yield: 76%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 11.8 (c 0.77 in CHCl3); mp: 145–147 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3290, 3031, 2827, 1682, 1604, 1220, 1023, 754, 698 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 8.77 (br s, 1H, NH), 7.70 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.33–7.27 (m, 11H, 10Haromat, 1H, CH3C CH), 7.23–7.18 (m, 3H, Haromat), 7.12–7.07 (m, 2H, Haromat), 5.09–4.97 (m, 4H, 2×POCH2Ph), 4.89 (AB, J = 14.4 Hz, 1H, CHaHb-Thy), 4.83 (AB, J = 14.4 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb-Thy), 4.58 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.57 (dd, J = 13.8 Hz, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.49 (dd, J = 13.8 Hz, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.32–4.24 (m, 1H, H-2), 4.19 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 3.90 (dd, J = 12.0 Hz, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.80 (br s, 1H, OH), 1.83 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 164.5, 151.2, 141.9, 140.1, 136.9, 135.9 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 135.8 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 128.7, 128.6, 128.5, 128.3, 128.2, 128.2, 128.1, 127.9, 125.5, 111.3, 75.5, 73.9, 68.8 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, POC), 68.3 (d, J = 162.6 Hz, PC), 50.8 (d, J = 10.1 Hz, C-3), 43.0, 12.6; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 22.85 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C32H34N5O7P: C, 60.85; H, 5.43; N, 11.09. Found: C, 60.96; H, 5.20; N, 11.30.
4.2.3. (1S,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(3,4-dihydro-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1S,2S)-16c
Yield: 74%; white solid [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v) and appropriate fractions were crystallized from methanol diethyl ether mixture]; [α]D 20 34.1 (c 1.50 in DMSO); mp: 178–180 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3251, 2931, 2830, 1706, 1242, 1023, 750, 700 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 9.43 (s, 1H, NH), 7.68 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.40 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, HC CH), 7.33–7.27 (m, 10H, Haromat), 7.22–7.19 (m, 3H, Haromat), 7.10–7.07 (m, 2H, Haromat), 5.64 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, HC=CH), 5.10–5.01 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.94 (AB, J = 14.1 Hz, 1H, CHaHb-Ura), 4.90 (AB, J = 14.1 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb-Ura), 4.59 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.57 (dd, J = 13.8 Hz, J = 5.1 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.48 (dd, J = 13.8 Hz, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.30–4.23 (m, 1H, H-2), 4.19 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 3.90 (brd, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.40 (br s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO-d 6): δ = 164.1 (s, C O), 151.2 (s, C O), 145.8, 142.8, 138.1, 137.2 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, Cipso), 137.1 (d, J = 6.2 Hz, Cipso), 128.9, 128.9, 128.6, 128.5, 128.4, 128.3, 128.2, 128.1, 127.9, 125.1, 101.7, 78.7 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, C-2), 73.0, 67.9 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, POC), 67.8 (d, J = 162.2 Hz, PC), 67.3 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, POC), 50.8 (d, J = 9.9 Hz, C-3), 42.8; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 22.98 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C31H32N5O7P: C, 60.29; H, 5.22; N, 11.34. Found: C, 60.06; H, 5.03; N, 11.37.
4.2.4. (1S,2S)-Dibenzyl 3-{4-[(N4-acetylamino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-2-benzyloxy-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1S,2S)-16d
Yield: 78%; white solid [crystallized from methanol–diethyl ether mixture]; [α]D 20 0.8 (c 1.41 in CHCl3); mp: 168–171 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3276, 3033, 2837, 1720, 1660, 1220, 1025, 796, 700 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 10.22 (br s, 1H, NH), 8.23 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.82 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, HC CH), 7.51 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, HC CH), 7.32–7.22 (m, 10H, Haromat), 7.18–7.07 (m, 5H, Haromat), 5.18–4.97 (m, 6H, 2 × POCH2Ph, CH2-Cyt), 4.85–4.75 (m, 2H, H-3a, H-3b), 4.48 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.35–4.28 (m, 1H, H-2), 4.23 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 3.99 (dd, J = 12.0 Hz, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.47 (br s, 1H, OH), 2.14 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 171.4, 162.7, 155.6, 148.5, 141.4, 137.3, 136.1 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, Cipso), 135.9 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 128.7, 128.6, 128.2, 128.1, 128.0, 127.8, 127.7, 126.9, 97.1, 77.5, 73.6, 68.8 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, POC), 68.7 (d, J = 162.6 Hz, PC), 68.5 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, POC), 50.1 (d, J = 11.1 Hz), 44.9, 24.6; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.63 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C33H35N6O7P: C, 60.18; H, 5.36; N, 12.76. Found: C, 60.00; H, 5.13; N, 12.91.
4.2.5. (1S,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(3,5-dioxo-1,2,4-triazin-2-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1S,2S)-16e
Yield: 93%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 20.3 (c 1.15 in CHCl3); mp: 68–70 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3262, 3033, 2908, 1730, 1673, 1216, 1022, 769, 698 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 11.07 (br s, 1H, NH), 7.67 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.35–7.25 (m, 11H, 10Haromat, 1H, HC N), 7.21–7.14 (m, 3H, Haromat), 7.07–7.03 (m, 2H, Haromat), 5.13–5.07 (m, 6H, 2 × POCH2Ph, CH2), 4.57 (dd, J = 13.8 Hz, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.52 (d, J = 10.5 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.50 (dd, J = 13.8 Hz, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.33–4.26 (m, 1H, H-2), 4.12 (d, J = 10.5 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 3.92 (dd, J = 11.1 Hz, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.07 (br s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 155.6, 149.5, 141.5, 136.9, 135.8 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 135.6 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 134.8, 128.6, 128.6, 128.3, 128.2, 128.1, 128.0, 127.9, 125.7, 77.5, 73.9, 68.9 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, POC), 68.3 (d, J = 162.6 Hz, PC), 50.7, 34.6; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.34 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C30H31N6O7P: C, 58.25; H, 5.05; N, 13.59. Found: C, 58.21; H, 4.82; N, 13.36.
4.2.6. (1S,2S)-Dibenzyl 3-{4-[(3-acetyl-1H-indol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-2-benzyloxy-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1S,2S)-16f
Yield: 82%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 3.7 (c 1.08 in CHCl3); mp: 163–165 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3148, 3063, 3031, 2881, 1645, 1216, 1014, 739, 695 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 8.83–8.34 (m, 1H), 7.79 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.35–7.11 (m, 17H, Haromat), 6.98–6.94 (m, 2H, Haromat), 5.36 (s, 2H, CH2), 5.06–4.95 (m, 5H, 2 × POCH2Ph, OH), 4.53 (dd, J = 13.8 Hz, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.48 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 3.80 (dd, J = 13.8 Hz, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.93 (dddd, J = 8.1 Hz, J = 7.5 Hz, J = 4.8 Hz, J = 3.3 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.06 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 3.87 (dd, J = 11.1 Hz, J = 3.3 Hz, 1H, H-1), 2.45 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 193.1, 142.8, 136.7, 136.4, 135.8 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, Cipso), 135.6 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, Cipso), 134.8, 128.6, 128.4, 128.2, 128.1, 128.0, 126.4, 123.7, 123.6, 122.8, 122.7, 117.5, 109.8, 77.4, 74.0, 68.7 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, POC), 68.3 (d, J = 162.0 Hz, PC), 51.0 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, C-3), 42.4, 27.7; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 22.74 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C37H37N4O6P: C, 66.86; H, 5.61; N, 8.43. Found: C, 67.02; H, 5.91; N, 8.27.
4.2.7. (1S,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(3,7-dimethyl-2,6-dioxopurin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1S,2S)-16g
Yield: 86%; yellow pale oil [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 10.8 (c 1.95 in CHCl3); IR (film): = 3267, 3011, 2931, 2893, 1707, 1663, 1253, 1024, 753, 698 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.60 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.42 (s, 1H), 7.34–7.12 (m, 15H, Haromat), 5.28 (s, 2H, CH2), 5.09–4.96 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.56 (dd, J = 13.8 Hz, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.55 (d, J = 10.2 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.42 (dd, J = 13.8 Hz, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.24–4.12 (m, 1H, H-2), 4.21 (d, J = 10.2 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 3.93 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.87 (dd, J = 11.4 Hz, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.52 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.93 (br s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 154.6, 151.1, 148.6, 143.4, 141.8, 137.0, 135.9 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, Cipso), 135.8 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, Cipso), 128.6, 128.5, 128.4, 128.3, 128.2, 128.1, 128.0, 127.9, 124.9, 107.8, 77.5, 74.0, 68.5 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 162.0 Hz, PC), 68.2 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, POC), 50.5 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, C-3), 31.6, 33.7, 29.9; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 22.96 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C34H36N7O7P: C, 59.56; H, 5.29; N, 14.30. Found: C, 59.28; H, 5.42; N, 14.44.
4.2.8. (1S,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(1,3-dimethyl-2,6-dioxopurin-7-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1S,2S)-16h
Yield: 95%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 2.0 (c 0.95 in CHCl3); mp: 167–169 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3362, 3242, 3140, 2951, 2883, 1705, 1659, 1219, 1018, 745, 697 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.78 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.77 (s, 1H), 7.35–7.05 (m, 15H, Haromat), 5.53 (AB, J = 15.0 Hz, 1H, CHaHb), 5.49 (AB, J = 15.0 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb), 5.09–4.97 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.56 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.55 (dd, J = 13.8 Hz, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.46 (dd, J = 13.8 Hz, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.27 (dddd, J = 8.4 Hz, J = 6.6 Hz, J = 5.4 Hz, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.19 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 3.84 (dd, J = 12.0 Hz, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.55 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.35 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.97 (br s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 155.2, 151.4, 148.7, 141.9, 141.4, 138.8, 135.8 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 135.7 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 128.6, 128.6, 128.5, 128.3, 128.2, 128.1, 128.0, 127.9, 125.1, 106.4, 77.4 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, C-2), 74.0, 68.6 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, POC), 68.5 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, POC), 68.3 (d, J = 162.2 Hz, PC), 50.9 (d, J = 12.1 Hz, C-3), 41.5, 29.9, 28.1; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 22.86 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C34H36N7O7P: C, 59.56; H, 5.29; N, 14.30. Found: C, 59.71; H, 4.97; N, 14.15.
4.2.9. (1S,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(8-chloro-1,3-dimethyl-2,6-dioxopurin-7-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1S,2S)-16i
Yield: 91%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 3.8 (c 1.05 in CHCl3); mp: 163–165 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3302, 3011, 2953, 2893, 1706, 1668, 1216, 1045, 753, 698 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.74 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.34–7.06 (m, 15H, Haromat), 5.58 (AB, J = 15.3 Hz, 1H, CHaHb), 5.57 (AB, J = 15.3 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb), 5.09–4.96 (m, 4H, 2×POCH2Ph), 4.57 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.55 (dd, J = 14.1 Hz, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.45 (dd, J = 14.1 Hz, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.32–4.24 (m, 1H, H-2), 4.17 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 3.84 (br d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.51 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.39 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.80 (br s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 154.2, 151.0, 147.0, 141.3, 138.8, 138.7, 135.6 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 135.5 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 128.4, 128.0, 127.9, 127.8, 127.7, 125.1, 107.2, 77.2 (s, C-2), 73.8; 68.6 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, POC), 68.0 (d, J = 163.4 Hz, PC), 50.8 (d, J = 10.6 Hz, C-3), 40.8, 29.8, 28.0; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 22.73 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C34H35ClN7O7P: C, 56.71; H, 4.90; N, 13.62. Found: C, 56.48; H, 5.12; N, 13.81.
4.2.10. (1S,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-1-hydroxy-3-{4-[(2-oxopyridin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}propylphosphonate (1S,2S)-16j
Yield: 96%; brown oil [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 9.2 (c 0.90 in CHCl3); IR (film): ν = 3067, 3007, 2913, 2894, 1658, 1217, 1025, 754, 695 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.72 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.55 (dd, J = 6.3 Hz, J = 1.3 Hz, 1H, Haromat), 7.35–7.09 (m, 16H, Haromat), 7.52 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H, Haromat), 6.15 (dt, J = 8.1 Hz, J = 1.3 Hz, 1H, Haromat), 5.14 (AB, J = 14.4 Hz, 1H, CHaHb), 5.13 (AB, J = 14.4 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb), 5.09–4.98 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.56 (dd, J = 13.8 Hz, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.52 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.43 (dd, J = 13.8 Hz, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.27 (ddd, J = 9.0 Hz, J = 5.4 Hz, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.20 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 3.84 (ddd, J = 11.4 Hz, J = 9.0 Hz, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 3.40 (dd, J = 9.0 Hz, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H, H-1); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 162.2, 142.3, 139.3, 137.7, 136.8, 135.8 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 135.7 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 128.5, 128.5, 128.4, 128.4, 128.2, 128.1, 128.0, 127.9, 125.4, 106.2, 77.3 (d, J = 4.9 Hz, C-2), 73.9, 68.4 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, POC), 68.1 (d, J = 162.9 Hz, PC), 68.0 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, POC), 50.5 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, C-3), 44.3; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 22.96 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C32H33N4O6P: C, 63.99; H, 5.54; N, 9.33. Found: C, 64.26; H, 5.81; N, 9.11.
4.2.11. (1S,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(3-benzoyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1S,2S)-16k
Yield: 77%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 16.4 (c 1.10 in CHCl3); mp: 113–114 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3418, 3088, 2924, 1748, 1704, 1663, 1235, 1021, 739, 698 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.89–7.86 (m, 1H, Haromat), 7.87 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, HC CH), 7.63–7.55 (m, 2H, Haromat), 7.58 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.47–7.40 (m, 2H, Haromat), 7.33–7.26 (m, 11H, Haromat), 7.23–7.20 (m, 3H, Haromat), 7.10–7.07 (m, 2H, Haromat), 5.76 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, HC CH), 5.08–5.00 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.92 (s, 2H, CH2), 4.57 (dd, J = 14.0 Hz, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.58 (d, J = 10.9 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.45 (dd, J = 14.0 Hz, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.28–4.20 (m, 1H, H-2), 4.19 (d, J = 10.9 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 3.88 (dd, J = 11.1 Hz, J = 3.2 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.10 (br s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 168.4 (s, C O), 162.1 (s, C O), 149.5 (s, C O), 143.8, 136.5, 135.6 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 135.5 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 135.0, 131.2, 130,2, 129.0, 128.6, 128.5, 128.5, 128.3, 128.1, 128.0, 125.1, 102.3, 74.0, 68.6 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, POC), 68.3 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, POC), 68.2 (d, J = 161.9 Hz, PC), 50.7 (d, J = 10.4 Hz, C-3), 43.2;31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 22.20 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C38H36N5O8P: C, 63.24; H, 5.03; N, 9.70. Found: C, 62.97; H, 4.88; N, 10.02.
4.2.12. (1S,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(3-benzoyl-2,4-dioxoquinazolin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1S,2S)-16l
Yield: 82%; white solid [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 −6.4 (c 3.85 in CHCl3); mp: 136–138 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3430, 3269, 3032, 2957, 2894, 1750, 1702, 1664, 1607, 1480, 1390, 1249, 755, 673 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 8.18 (dd, J = 7.9 Hz, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.95–7.91 (m, 2H, 2 × o-CH), 7.85 (br d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.73 (ddd, J = 7.9 Hz, J = 7.0 Hz, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.66–7.60 (m, 1H, p-CH), 7.59 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.49–7.43 (m, 2H, 2 × m-CH), 7.34–7.25 (m, 11H), 7.20–7.13 (m, 3H), 7.03–7.00 (m, 2H), 5.36 (AB, J AB = 15.9 Hz, 1H, CH aHb), 5.34 (AB, J AB = 15.9 Hz, 1H, CHa H b), 5.08–4.96 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.54 (d, J = 10.9 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.53 (dd, J = 14.3 Hz, J = 5.3 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.40 (dd, J = 14.3 Hz, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.14–4.06 (m, 1H, H-2), 4.12 (d, J = 10.9 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 3.86 (dd, J = 11.2 Hz, J = 2.9 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.00 (br s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 168.6 (s, C O); 161.1 (s, C O); 149.5 (s, C O); 142.4 (s, HC C); 140.3; 136.7; 136.2; 135.9 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, Cipso), 135.8 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, Cipso), 135.1, 131.7, 130,5, 129.2, 128.9, 128.7, 128.7, 128.6, 128.4, 128.2, 128.2, 128.1, 125.1, 123.8, 115.6, 115.2, 77.0 (d, J = 1.3 Hz), 74.1, 68.6 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 161.9 Hz, PC), 68.3 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, POC), 50.9 (d, J = 11.7 Hz, C-3), 38.9; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 22.09 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C42H38N5O8P: C, 65.36; H, 4.96; N, 9.07. Found: C, 65.63; H, 5.18; N, 9.02.
4.2.13. (1R,2S)-Dibenzyl 3-{4-[(6-aminopurin-9-yl)methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl]}-2-benzyloxy-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1R,2S)-16a
Yield: 70%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 20.0 (c 0.68 in DMSO); mp: 85–88 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3408, 3289, 3115, 2924, 2888, 1668, 1600, 1244, 1020, 754, 697 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 8.32 (s, 1H), 8.00 (s, 1H), 7.67 (s, 1H), 7.32–7.22 (m, 10H, Haromat), 7.21–7.13 (m, 3H, Haromat), 7.02–6.98 (m, 2H, Haromat), 6.16 (br s, 2H, NH2), 5.41 (s, 2H, CH2-Ade), 5.09–4.96 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.70 (dd, J = 14.7 Hz, J = 3.9 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.64 (dd, J = 14.7 Hz, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.39 (AB, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.27 (AB, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 4.11 (dddd, J = 8.4 Hz, J = 6.0 Hz, J = 5.4 Hz, J = 3.9 Hz, 1H, H-2), 3.99 (dd, J = 8.4 Hz, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H, H-1), 2.06 (br s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR (151 Hz, DMSO-d 6): δ = 156.5, 153.0, 149.8, 142.9; 141.0, 138.6, 137.8 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, Cipso), 137.6 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, Cipso), 129.3, 128.8, 128.6, 128.6, 128.5, 128.4, 128.2, 128.1, 127.9, 127.5, 125.1, 119.1, 78.7 (d, J = 10.8 Hz, C-3), 71.7; 68.0 (d, J = 4.7 Hz, POC), 67.3 (d, J = 4.7 Hz, POC), 67.1 (d, J = 161.8 Hz, PC), 40.6, 38.4; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 24.32 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C32H33N8O5P × H2O: C, 58.35; H, 5.36; N, 17.01. Found: C, 58.38; H, 5.14; N, 17.06.
4.2.14. (1R,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(5-methyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1R,2S)-16b
Yield: 76%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 5.3 (c 1.20 in CHCl3); mp: 72–74 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3277, 3061, 2927, 2855, 1680, 1216, 1012, 739, 696 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 9.51 (s, 1H, NH), 7.79 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.39–7.22 (m, 11H, 10 × Haromat, 1H × CH3C CH), 7.22–7.17 (m, 3H, Haromat), 7.09–7.05 (m, 2H, Haromat), 5.02 (dd, J = 12.3 Hz, J = 8.1 Hz, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.91 (AB, J = 14.7 Hz, 1H, CHaHb-Thy), 4.86 (AB, J = 14.7 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb-Thy), 4.79 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 3.0 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.58 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.50 (br s, 1H, OH), 4.38 (AB, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.33 (AB, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 4.15 (dddd, J = 8.1 Hz, J = 6.3 Hz, J = 6.0 Hz, J = 3.0 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.20 (dd, J = 8.4 Hz, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H, H-1), 1.87 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 164.7, 151.2, 141.7, 140.3, 136.7, 135.9 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, Cipso), 135.8 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, Cipso), 128.6, 128.6, 128.5, 128.3, 128.2, 128.2, 128.1, 128.1, 128.0, 125.6, 111.2, 77.4, 72.6, 68.5 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, POC), 67.6 (d, J = 160.3 Hz, PC), 50.2 (d, J = 7.4 Hz), 43.0, 12.5; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 22.85 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C32H34N5O7P: C, 60.85; H, 5.43; N, 11.09. Found: C, 61.06; H, 5.23; N, 11.22.
4.2.15. (1R,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1R,2S)-16c
Yield: 92%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 6.3 (c 1.23 in CHCl3); mp: 73–75 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3241, 3033, 2891, 2826, 1680, 1214, 1029, 750, 700 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 9.48 (s, 1H, NH), 7.76 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.47 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H, HC=CH), 7.31–7.23 (m, 10H, Haromat), 7.22–7.18 (m, 3H, Haromat), 7.10–7.05 (m, 2H, Haromat), 5.66 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H, HC=CH), 5.04 (dd, J = 11.4 Hz, J = 8.1 Hz, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.98 (AB, J = 14.4 Hz, 1H, CHaHb-Ura), 4.88 (AB, J = 14.4 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb-Ura), 4.79 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 3.0 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.61 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.41 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.33 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 4.41 (dddd, J = 8.7 Hz, J = 6.9 Hz, J = 6.0 Hz, J = 3.0 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.00 (dd, J = 8.7 Hz, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H, H-1), 1.88 (br s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 164.2 (s, C O), 151.1 (s, C O), 144.5, 141.5, 136.7, 135.9 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, Cipso), 135.8 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, Cipso), 128.8, 128.7, 128.6, 128.4, 128.3, 128.2, 128.2, 128.1, 125.7, 102.7, 77.4, 72.7, 68.7 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, POC), 68.7 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, POC), 67.5 (d, J = 147.4 Hz, PC), 50.3 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, C-3), 43.2; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.40 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C31H32N5O7P: C, 60.29; H, 5.22; N, 11.34. Found: C, 60.56; H, 5.14; N, 11.58.
4.2.16. (1R,2S)-Dibenzyl 3-{4-[(N4-acetylamino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-2-benzyloxy-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1R,2S)-16d
Yield: 75%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +20.1 (c 0.96 in CHCl3); mp: 82–84 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3256, 3033, 2937, 2854, 1720, 1660, 1222, 1025, 744, 697 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 10.96 (br s, 1H, NH), 8.88 (s, 1H, HC5′), 8.05 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H, HC CH), 7.44 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H, HC CH), 7.33–7.08 (m, 15H, Haromat), 5.41 (d, J = 14.4 Hz, 1H, CHaHb-Cyt), 5.08–4.80 (m, 5H, 2 × POCH2Ph, H-3a), 4.89 (d, J = 14.4 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb-Cyt), 4.76 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.73 (AB, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.39 (AB, J = 10.8 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 4.10 (dddd, J = 9.3 Hz, J = 8.7 Hz, J = 3.3 Hz, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H, H-2), 3.93 (br d, J = 9.3 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.07 (br s, 1H, OH), 2.18 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 171.4, 162.9, 155.6, 149.1, 141.3, 137.0, 136.0 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, Cipso), 128.6, 128.5, 128.4, 128.3, 128.2, 128.0, 127.9, 127.0, 97.0, 77.4, 72.3, 68.5 (d, J = 4.3 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 4.3 Hz, POC), 66.9 (d, J = 161.2 Hz, PC), 48.9, 44.6, 24.9; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 27.48 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C33H35N6O7P: C, 60.18; H, 5.36; N, 12.76. Found: C, 59.87; H, 5.44; N, 12.82.
4.2.17. (1R,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(3,5-dioxo-1,2,4-triazin-2-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1R,2S)-16e
Yield: 91%; colorless oil [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 2.3 (c 1.42 in CHCl3); IR (film): ν = 3242, 3033, 2907, 1730, 1673, 1241, 998, 740, 696 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 11.41 (br s, 1H, NH), 7.68 (s, 1H, HC5’), 7.31 (s, 1H, HC N), 7.29–7.21 (m, 10H, Haromat), 7.20–7.16 (m, 3H, Haromat), 7.09–7.03 (m, 2H, Haromat), 5.13 (AB, J = 14.7 Hz, 1H, CHaHb), 5.10 (AB, J = 14.7 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb), 5.06–4.98 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.71 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 3.3 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.60 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.39 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.27 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 4.14 (dddd, J = 9.3 Hz, J = 6.3 Hz, J = 6.3 Hz, J = 3.3 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.01 (dd, J = 8.4 Hz, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.00 (br s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 155.7, 149.3, 141.3, 136.8, 135.9 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 135.8 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 128.5, 128.4, 128.3, 128.1, 128.0, 127.9, 127.8, 125.7, 77.4, 72.7, 68.7 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, POC), 68.5 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, POC), 67.7 (d, J = 162.9 Hz, PC), 50.4, 34.7; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 24.40 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C30H31N6O7P: C, 58.25; H, 5.05; N, 13.59. Found: C, 58.52; H, 5.08; N, 13.67.
4.2.18. (1R,2S)-Dibenzyl 3-{4-[(3-acetyl-1H-indol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-2-benzyloxy-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1R,2S)-16f
Yield: 91%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +7.7 (c 1.09 in CHCl3); mp: 133–135 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3224, 3033, 2891, 1643, 1231, 1012, 749, 695 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 8.40–8.36 (m, 1H), 7.81 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.37–7.11 (m, 17H, Haromat), 6.96–6.93 (m, 2H, Haromat), 5.39 (s, 2H, CH2), 5.30–4.96 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.66 (dd, J = 14.5 Hz, J = 3.4 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.53 (dd, J = 14.5 Hz, J = 6.7 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.35 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.14 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 4.12–4.06 (m, 2H, H-2, OH), 3.93 (dd, J = 8.9 Hz, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H, H-1), 2.47 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 193.2, 142.4, 136.6, 136.4, 135.7 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 135.6 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 135.0, 128.5, 128.3, 128.0, 127.9, 127.8, 126.4, 123.9, 123.5, 122.7, 122.6, 117.3, 109.8, 77.8, 72.0, 68.5 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, POC), 67.6 (d, J = 161.8 Hz, PC), 50.5, 42.3, 27.6; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.68 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C37H37N4O6P: C, 66.86; H, 5.61; N, 8.43. Found: C, 66.73; H, 5.49; N, 8.53.
4.2.19. (1R,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(3,7-dimethyl-2,6-dioxopurin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1R,2S)-16g
Yield: 80%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +9.9 (c 0.91 in CHCl3); mp: 72–74 °C; IR (KBr): = 3260, 3011, 2951, 2894, 1707, 1663, 1223, 1022, 753, 699 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.61 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.48 (s, 1H), 7.32–7.24 (m, 10H, Haromat), 7.22–7.19 (m, 3H, Haromat), 7.14–7.09 (m, 2H, Haromat), 5.29 (s, 2H, CH2), 5.02 (dd, J = 13.2 Hz, J = 8.4 Hz, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.67 (dd, J = 14.7 Hz, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.58 (dd, J = 14.7 Hz, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.40 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.29 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 4.16 (dddd, J = 9.6 Hz, J = 6.6 Hz, J = 6.3 Hz, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H, H-2), 3.95 (dd, J = 9.6 Hz, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.94 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.52 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.93 (br s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 154.6, 151.1, 148.8, 143.2, 141.6, 137.0, 136.0 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, Cipso), 135.8 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, Cipso), 128.6, 128.5, 128.3, 128.2, 128.1, 128.0, 127.8, 125.0, 107.5, 78.1 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, C-2), 72.8, 68.5 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, POC), 67.9 (d, J = 161.8 Hz, PC), 50.4 (d, J = 4.7 Hz, C-3), 36.1, 33.7, 29.8; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 24.09 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C34H36N7O7P × H2O: C, 58.03; H, 5.44; N, 13.93. Found: C, 58.35; H, 5.26; N, 13.87.
4.2.20. (1R,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(1,3-dimethyl-2,6-dioxopurin-7-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1R,2S)-16h
Yield: 91%; colorless oil [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +2.8 (c 1.05 in CHCl3); IR (film): ν = 3243, 2953, 2893, 1703, 1660, 1212, 998, 746, 697 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.80 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.47 (s, 1H), 7.35–7.25 (m, 10H, Haromat), 7.23–7.15 (m, 3H, Haromat), 7.06–7.02 (m, 2H, Haromat), 5.52 (s, 2H, CH2), 5.09–4.97 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.70 (dd, J = 14.1 Hz, J = 3.3 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.61 (dd, J = 14.1 Hz, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.44 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.25 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 4.14 (dddd, J = 9.3 Hz, J = 6.6 Hz, J = 5.7 Hz, J = 3.3 Hz, 1H, H-2), 3.97 (dd, J = 8.4 Hz, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H, H-1); 3.60 (br s, 1H, OH), 3.54 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.33 (s, 3H, CH3), 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 155.2; 151.4; 148.7; 141.9; 141.4, 136.8, 135.8 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, Cipso), 135.6 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, Cipso), 128.6, 128.5, 128.4, 128.2, 128.0, 127.9, 127.8, 125.1, 106.4, 77.4 (s, C-2), 72.6, 68.6 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, POC), 67.4 (d, J = 147.2 Hz, PC), 50.4 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, C-3), 41.5, 29.9, 28.1; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.91 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C34H36N7O7P: C, 59.56; H, 5.29; N, 14.30. Found: C, 59.82; H, 5.13; N, 14.22.
4.2.21. (1R,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(8-chloro-1,3-dimethyl-2,6-dioxopurin-7-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1R,2S)-16i
Yield: 85%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +3.3 (c 1.35 in CHCl3); mp: 69–71 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 32662, 3010, 2952, 2863, 1706, 1663, 1214, 994, 744, 698 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.77 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.34–7.25 (m, 10H, Haromat), 7.24–7.14 (m, 3H, Haromat), 7.07–7.01 (m, 2H, Haromat), 5.58 (s, 2H, CH2), 5.09–4.96 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.70 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 3.3 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.59 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.40 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.24 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 4.19–4.09 (m, 1H, H-2), 3.97 (dd, J = 9.0 Hz, J = 6.0 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.67 (br s, 1H, OH), 3.51 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.32 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 154.2, 151.0, 147.0, 141.3, 138.8, 136.7, 135.6 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, Cipso), 135.6 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, Cipso), 128.6, 128.5, 128.2, 128.0, 127.9, 127.8, 127.7, 125.1, 107.2, 77.4 (s, C-2), 72.8, 68.5 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, POC), 67.8 (d, J = 161.4 Hz, PC), 50.8 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, C-3), 41.0, 29.8, 28.0; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.85 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C34H35ClN7O7P: C, 56.71; H, 4.90; N, 13.62. Found: C, 56.72; H, 4.72; N, 13.53.
4.2.22. (1R,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-1-hydroxy-3-{4-[(2-oxopyridin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}propylphosphonate (1R,2S)-16j
Yield: 81%; brown oil [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +4.5 (c 0.78 in CHCl3); IR (film): ν = 3267, 3067, 2953, 2890, 1657, 1216, 1024, 751, 695 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.77 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.60–7.54 (m, 1H, Haromat), 7.31–7.23 (m, 11H, Haromat), 7.22–7.13 (m, 3H, Haromat), 7.07–7.02 (m, 2H, Haromat), 6.53–5.58 (m, 1H, Haromat), 6.14 (dt, J = 6.9 Hz, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H, Haromat), 5.17 (br s, 1H, OH), 5.12 (s, 2H, CH2), 5.06–4.98 (m, 4H, 2×POCH2Ph), 4.72 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 3.3 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.59 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.42 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.26 (d, J = 11.1 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 4.14 (dddd, J = 9.3 Hz, J = 6.6 Hz, J = 5.4 Hz, J = 3.3 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.06–4.01 (m, 1H, H-1); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 162.2, 142.3, 139.9, 137.8, 136.0, 135.9 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, Cipso), 135.8 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, Cipso), 128.5, 128.4, 128.3, 128.2, 128.1, 128.0, 125.4, 106.2, 77.6 (s, C-2), 72.9, 68.5 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, POC), 67.7 (d, J = 162.3 Hz, PC), 50.4 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, C-3), 44.3; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 24.51 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C32H33N4O6P: C, 63.99; H, 5.54; N, 9.33. Found: C, 63.75; H, 5.33; N, 9.46.
4.2.23. (1R,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(3-benzoyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1R,2S)-16k
Yield: 81%; colorless oil [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +3.4 (c 3.77 in CHCl3); IR (film): ν = 3410, 3260, 2924, 2853, 1748, 1705, 1664, 1237, 740, 697 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.90–7.86 (m, 2H), 7.68–7.56 (m, 3H), 7.47–7.42 (m, 2H, Haromat), 7.33–7.26 (m, 11H, Haromat), 7.24–7.18 (m, 2H, Haromat), 7.08–7.05 (m, 2H, Haromat), 5.78 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H, HC CH), 5.08–5.00 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.96 (s, 2H, CH2), 4.67–4.62 (m, 2H, H-3b, H-3a), 4.42 (AB, J AB = 11.3 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.28 (AB, J AB = 11.3 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 4.17–4.07 (m, 1H, H-2), 3.91 (dd, J = 8.7 Hz, J = 5.8 Hz, 1H, H-1), 1.80 (br s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 168.7 (s, C O), 162.3 (s, C O), 149.8 (s, C O), 144.2, 136.7, 135.9 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, Cipso), 135.8 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, Cipso), 135.1, 131.5, 130,5, 129.2, 128.7, 128.7, 128.6, 128.5, 128.2, 128.2, 102.7, 75.5 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, C-2), 68.6 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, POC), 68.5 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, POC), 67.7 (d, J = 161.8 Hz, PC), 50.5 (d, J = 3.9 Hz, C-3), 43.1; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.31 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C38H36N5O8P: C, 63.24; H, 5.03; N, 9.70. Found: C, 63.17; H, 5.33; N, 9.57.
4.2.24. (1R,2S)-Dibenzyl 2-benzyloxy-3-{4-[(3-benzoyl-2,4-dioxoquinazolin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1-hydroxypropylphosphonate (1R,2S)-16l
Yield: 88%; white solid [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +2.9 (c 2.34 in CHCl3); mp: 145–147 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3418, 3277, 2925, 2855, 1749, 1702, 1665, 1608, 1480, 1391, 1249, 754, 691 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 8.17 (dd, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.95–7.91 (m, 2H, 2 × o-CH), 7.86 (br d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (ddd, J = 8.8 Hz, J = 7.3 Hz, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.61 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.64–7.38 (m, 1H, p-CH), 7.47–7.41 (m, 2H, 2 × m-CH), 7.30–7.23 (m, 11H), 7.16–7.08 (m, 3H), 7.00–6.96 (m, 2H), 5.34 (s, 2H, CH2), 5.00 (t, 4H, J = 8.3 Hz, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.67 (dd, J = 14.5 Hz, J = 3.1 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.54 (dd, J = 14.5 Hz, J = 6.9 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.37 (AB, J AB = 11.2 Hz, 1H, OCHaHbPh), 4.17 (AB, J AB = 11.2 Hz, 1H, OCHa HbPh), 4.14–4.06 (m, 1H, H-2), 3.98 (dd, J = 8.9 Hz, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H, H-1), 1.85 (br s, 1H, OH); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 168.6 (s, C O); 161.1 (s, C O); 149.5 (s, C O); 142.4 (s, HC C); 140.3; 136.7; 136.2; 135.9 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, Cipso), 135.8 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, Cipso), 135.0, 131.7, 130.5, 129.2, 128.9, 128.7, 128.6, 128.4, 128.2, 128.1, 128.1, 125.3, 123.8, 115.6, 115.3, 77.6 (d, J = 4.8 Hz), 72.9, 68.5 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, POC), 68.0 (d, J = 161.4 Hz, PC), 50.4 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, C-3), 38.9; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.37 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C42H38N5O8P: C, 65.36; H, 4.96; N, 9.07. Found: C, 65.17; H, 5.18; N, 8.87.
4.2.25. (1S,2R,3S)-Dibenzyl 4-{[4-(6-amino-purin-9-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2,3-trihydroxy-2,3-O-isopropylidenebutylphosphonate (1S,2R,3S)-17a
Yield: 83%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 21.7 (c 1.12 in DMSO); mp: 193–195 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3233, 3187, 2957, 2925, 1646, 1216, 1047, 996, 777, 698 cm−1; 1H NMR (CD3OD, 600 MHz): δ = 8.25 (s, 1H, N CH), 8.21 (s, 1H, HCN), 8.00 (s 1H, HC5′), 7.407.32 (m, 10H, 2xC6H5), 5.55 (s, 2H, HC CCH 2), 5.185.08 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH 2Ph), 4.74 (dd, J = 14.5 Hz, J = 2.9 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.64 (dd, J = 14.5 Hz, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.50 (dt, J = 6.8 Hz, J = 2.9 Hz, 1H, H-3), 4.17 (dd, J = 8.9 Hz, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H, H-1), 4.06 (dt, J = 6.8 Hz, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H, H-2), 1.32 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.14 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CD3OD): δ = 156.4, 153.0, 149.8, 142.9, 141.1, 137.1 (d, J = 5.7 Hz, Cipso), 137.0 (d, J = 5.5 Hz, Cipso), 128.8, 128.6, 128.6, 128.2, 128.1, 125.1, 119.1, 110.1 (s, C(CH3)2), 77.5 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, C-3), 76.8 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, C-2), 67.9 (d, J = 162.7 Hz, C-1), 67.9 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, COP), 67.4 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, COP), 52.3 (s, C-4), 38.4 (s, HC C— CH2 —N), 27.2 (s, CH3), 27.2 (s, CH3); 31P NMR (CD3OD, 242 MHz): δ = 22.57 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C29H33N8O6P: C, 56.13; H, 5.36; N, 18.06. Found: C, 55.87; H, 5.24; N, 17.85.
4.2.26. (1S,2R,3S)-Dibenzyl 4-{[4-(5-methyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2,3-trihydroxy-2,3-O-isopropylidenebutylphosphonate (1S,2R,3S)-17b
Yield: 83%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 11.5 (c 1.12 in DMSO); mp: 194–195 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3238, 3034, 2957, 2823, 1682, 1214, 1057, 745, 695 cm−1; 1H NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz): δ = 8.58 (br s, 1H, NH), 7.80 (s 1H, HC5′), 7.427.38 (m, 11H, 2 × C6H5, HC C), 5.155.08 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH 2Ph), 4.96 (AB, J AB = 15.0 Hz, 1H, CH aHb), 4.94 (AB, J AB = 15.0 Hz, 1H, CHa H b), 4.75 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.58 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 6.4 Hz, 1H, H-4a), 4.50 (dt, J = 2.6 Hz, J = 6.4 Hz, 1H, H-3), 4.15 (dt, J = 7.6 Hz, J = 6.4 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.05 (dt, J = 7.6 Hz, J = 5.3 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.40 (dd, J = 12.6 Hz, J = 5.3 Hz, 1H), 1.95 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.38 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.22 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO-d 6): δ = 164.7 (s, C O), 151.2 (s, C O), 142.8 (s, HC C —CH3), 141.6, 137.1 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, Cipso), 137.0 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, Cipso), 128.9, 128.6, 128.6, 128.2, 128.1 (Caromat), 125.1, 110.1 (s, C(CH3)2), 109.4 (s, HC CCH3), 77.4 (d, J = 8.0 Hz), 76.8 (d, J = 8.0 Hz), 68.0 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, POC), 67.9 (d, J = 162.7 Hz, PC), 67.5 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, POC), 52.3 (s, C-4), 42.6, 27.2, 12.4; 31P NMR (CDCl3, 242 MHz): δ = 21.48 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C29H34N5O8P: C, 56.95; H, 5.60; N, 11.45. Found: C, 56.92; H, 5.53; N, 11.28.
4.2.27. (1S,2R,3S)-Dibenzyl 4-{[4-(2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2,3-trihydroxy-2,3-O-isopropylidenebutylphosphonate (1S,2R,3S)-17c
Yield: 85%; yellow pale powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 28.3 (c 1.07 in CH3OH); mp: 157–159 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3231, 3061, 2891, 2826, 1675, 1226, 1052, 996, 737, 696 cm−1; 1H NMR (CD3OD, 600 MHz): δ = 7.95 (s 1H, HC5′), 7.70 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H, HC CH), 7.427.32 (m, 10H, 2 × C6H5), 5.68 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, HC CH), 5.175.09 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH 2Ph), 5.06 (AB, J AB = 15.3 Hz, 1H, CH aHb), 5.03 (AB, J AB = 15.3 Hz, 1H, CHa H b), 4.76 (dd, J = 14.5 Hz, J = 2.9 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.65 (dd, J = 14.5 Hz, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.52 (ddd, J = 7.2 Hz, J = 6.3 Hz, J = 2.9 Hz, 1H, H-3), 4.20 (dt, J = 8.8 Hz, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H, H-1), 4.10 (dt, J = 7.3 Hz, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H, H-2), 1.35 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.24 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CD3OD): δ = 165.2 (s, C O), 151.2 (s, C O), 145.4 (s, N-CH CH) 142.2, 136.3 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, Cipso), 136.2 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, Cipso), 128.2, 128.2, 128.2, 127.9, 127.8 (Caromat), 125.1, 110.3 (s, C(CH3)2), 101.3 (s, NCH CH), 77.0 (d, J = 8.4 Hz), 76.6 (d, J = 8.6 Hz), 68.5 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, COP), 68.2 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, COP), 67.9 (d, J = 165.3 Hz, C-1), 52.0 (s, C-4), 42.5 (s, HC C— CH2 —N), 25.9 (s, CH3), 25.7 (s, CH3); 31P NMR (CD3OD, 242 MHz): δ = 22.60 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C28H32N5O8P: C, 56.28; H, 5.40; N, 11.72. Found: C, 56.42; H, 5.21; N, 11.70.
4.2.28. (1S,2R,3S)-Dibenzyl 4-{[4-(N4-acetylamino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2,3-trihydroxy-2,3-O-isopropylidenebutylphosphonate (1S,2R,3S)-17d
Yield: 89%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 18.7 (c 0.92 in DMSO); mp: 167–168 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3395, 3306, 3136, 3065, 2999, 1714, 1672, 1223, 1059, 966, 797, 742 cm−1; 1H NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz): δ = 10.15 (br s, 1H, NH), 8.48 (s 1H, HC5′), 8.15 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, HC CH), 7.51 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, HC CH), 7.467.32 (m, 10H, 2 × C6H5), 6.64 (br s, 1H), 5.32–5.10 (m, 6H, 2 × POCH2Ph, HC CCH2), 4.86 (dd, J = 14.1 Hz, J = 1,9 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.60 (dd, J = 14,1 Hz, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H, H-4a), 4.52 (dt, J = 8.8 Hz, J = 1.9 Hz, 1H, H-3), 4.184.11 (br m, 1H), 4.023.98 (m, 1H), 2.25 (s, 3H, NHC(O)CH3), 1.45 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.40 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO-d 6): δ = 171.4 (s, C O), 163.0, 155.5 (s, C O), 150.5, 142.4, 137.1 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, Cipso), 137.0 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, Cipso), 128.9, 128.6, 128.6, 128.2 (Caromat), 125.4, 110.2 (s, C(CH3)2), 95.9, 77.5 (d, J = 8.3 Hz), 76.9 (d, J = 8.3 Hz), 68.0 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, POC), 67.9 (d, J = 162.6 Hz, CP), 67.5 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, POC), 52.3 (s, C-4), 44.9 (s, HC C— CH2 —N), 27.3 (s, C-CH3), 27.2 (s, C-CH3), 24.8 (s,CH3C(O)); 31P NMR (CDCl3, 242 MHz): δ = 23.14 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C30H35N6O8P: C, 56.42; H, 5.52; N, 13.16. Found: C, 56.62; H, 5.53; N, 12.97.
4.2.29. (1S,2R,3S)-Dibenzyl 4-{[4-(3,7-dimethyl-2,6-dioxopurin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2,3-trihydroxy-2,3-O-isopropylidenebutylphosphonate (1S,2R,3S)-17g
Yield: 88%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 9.3 (c 1.96 in CHCl3); mp: 187–188 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3275, 3012, 2998, 2965, 1708, 1663, 1218, 1023, 757, 693 cm−1; 1H NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz): δ = 7.70 (s 1H, HC5′), 7.48 (s, 1H, NCH N), 7.407.25 (m, 10H, 2 × C6H5), 5.35 (AB, J AB = 14.5 Hz, 1H, CH aHb), 5.33 (AB, J AB = 14.5 Hz, 1H, CHa H b), 5.185.05 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH 2Ph), 4.69 (dd, J = 14.5 Hz, J = 2.9 Hz, 1H, H-4a), 4.60 (dd, J = 14.5 Hz, J = 5.8 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.50 (ddd, J = 7.6 Hz, J = 5.8 Hz, J = 2.9 Hz, 1H, H-3), 4.13 (dt, J = 10.6 Hz, J = 5.5 Hz, 1H, H-1), 4.05 (dt, J = 7.6 Hz, J = 5.5 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.00 (s, 3H, NCH3), 3.58 (s, 3H, NCH3), 3.29 (dd, J = 12.9 Hz, J = 5.5 Hz, 1H), 1.36 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.24 (s, 3H, CH3), 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 154.8 (s, C O), 151.3 (s, C O), 148.9, 143.3, 141.6, 136.0 (d, J = 5.3 Hz, Cipso), 135.9 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, Cipso), 128.6, 128.6, 128.5, 128.5, 128.2, 128.0 (Caromat), 124.9, 110.3 (s, C(CH3)2), 107.7, 76.7 (d, J = 7.8 Hz), 76.6 (d, J = 3.9 Hz), 68.6 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, COP), 68.6 (d, J = 162.3 Hz, C-1), 68.5 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, COP), 51.9 (s, C-4), 35.9 (s, HC C— CH2), 35.9 (s, CH3), 33.6 (s, CH3), 29.7 (s, CH3), 26.9 (s, CH3), 26.8(s, CH3); 31P NMR (CDCl3, 242 MHz): δ = 21.64 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C31H36N7O8P: C, 55.94; H, 5.45; N, 14.73. Found: C, 55.73; H, 5.43; N, 14.69.
4.2.30. (1S,2R,3S)-Dibenzyl 4-{[4-(8-chloro-1,3-dimethyl-2,6-dioxopurin-7-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2,3-trihydroxy-2,3-O-isopropylidenebutylphosphonate (1S,2R,3S)-17i
Yield: 92%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 22.8 (c 1.09 in CHCl3); mp: 208–209 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3229, 3010, 2998, 2982, 1704, 1667, 1236, 1063, 778, 693 cm−1; 1H NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz): δ = 7.82 (s 1H, HC5′), 7.387.26 (m, 10H, 2 × C6H5), 5.67 (AB, J AB = 14.5 Hz, 1H, CH aHb), 5.64 (AB, J AB = 14.5 Hz, 1H, CHa H b), 5.185.06 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH 2Ph), 4.70 (dd, J = 14.5 Hz, J = 2.9 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.64 (dd, J = 14.5 Hz, J = 5.7 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.50 (ddd, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 5.8 Hz, J = 2.9 Hz, 1H, H-3), 4.13 (dt, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H, H-1), 4.03 (dt, J = 7.6 Hz, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H, H-2), 3.56 (s, 3H, NCH3), 3.41 (s, 3H, NCH3), 3.14 (dd, J = 13.0 Hz, J = 5.2 Hz, 1H), 1.36 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.21 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 154.4 (s, C O), 151.3, 147.4, 141.5, 139.1, 135.9 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, Cipso), 128.6, 128.6, 128.3, 128.0 (s, Caromat), 125.1, 110.3 (s, C(CH3)2), 107.4, 76.4 (d, J = 5.7 Hz), 76.3 (d, J = 8.5 Hz), 68.7 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, COP), 68.6 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, COP), 68.5 (d, J = 162.0 Hz, C-1), 51.9 (s, C-4), 41.0 (s, HC C— CH2), 29.9 (s, CH3), 28.0 (s, CH3), 26.9 (s, CH3), 26.8 (s, CH3); 31P NMR (CDCl3, 242 MHz): δ = 21.35 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C31H35ClN7O8P: C, 53.18; H, 5.04; N, 14.01. Found: C, 53.15; H, 4.83; N, 13.90.
4.2.31. (1S,2R,3R)-Dibenzyl 4-{[4-(6-amino-purin-9-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2,3-trihydroxy-2,3-O-isopropylidenebutylphosphonate (1S,2R,3R)-17a
Yield: 81%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +21.8 (c 1.43 in DMSO); mp: 100–102 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3324, 3185, 2987, 1646, 1602, 1219, 1053, 1009 cm−1; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 8.31 (s, 1H, HC N), 8.02 (s, 1H, N CH), 7.79 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.37–7.23 (m, 10H, 2 × C6H5), 6.48 (s, 2H, NH2), 5.44 (s, 2H, HC—C—CH2), 5.19–5.08 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.99 (dd, J = 14.2 Hz, J = 1.5 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.54–4.50 (m, 2H), 4.42–4.36 (m, 1H), 4.20 (dt, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.33 (br s, 1H, OH), 1.41 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.27 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 155.6, 152.7, 149.6, 141.9, 140.6, 136.1 (d, J = 5.5 Hz, Cipso), 135.0 (d, J = 5.5 Hz, Cipso), 128.6, 128.5, 128.5, 128.5, 128.0, 128.0 (Caromat), 124.1, 119.1, 110.1 (s, C(CH3)2), 76.4 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, C-3), 75.6 (s, C-2), 68.5 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, COP), 68.4 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, COP), 66.3 (d, J = 163.0 Hz, C-1), 50.9 (s, C-4), 38.6 (s, HC C— CH2 —N), 27.9 (s, CH3), 25.5 (s, CH3); 31P NMR (243 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.84 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C29H33N8O8P: C, 56.13; H, 5.36; N, 18.06. Found: C, 56.15; H, 5.34; N, 17.97.
4.2.32. (1S,2R,3R)-Dibenzyl 4-{[4-(5-methyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2,3-trihydroxy-2,3-O-isopropylidenebutylphosphonate (1S,2R,3R)-17b
Yield: 89%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +10.2 (c 1.02 in CHCl3); mp: 126–127 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3225, 3063, 2988, 2819, 1680, 1456, 1218, 1051, 966 cm−1; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 8.94 (s, 1H, NH), 7.76 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.40–7.29 (m, 11H, 2 × C6H5, HC C), 5.18–5.07 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 5.00 (dd, J = 14.2 Hz, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.98 (AB, JAB = 15.0 Hz, 1H, CHaHb), 4.94 (AB, JAB = 15.0 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb), 4.58–4.52 (m, 1H, H-3), 4.46 (dt, J = 8.7 Hz, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.42 (dd, J = 14.2 Hz, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H, H-4a), 4.24 (br s, 1H, OH), 4, 13 (dt, J = 8.7 Hz, J = 5.5 Hz, 1H, H-1), 1.63 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.42 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.25 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 164.3 (s, C O), 151.2 (s, C O), 141.9 (s, HC C —CH3), 140.3, 136.1 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, Cipso), 136.0 (d, J = 5.6 Hz, Cipso), 128.6, 128.6, 128.6, 128.5, 128.1, 128.0 (Caromat), 124.7, 111.2 (s, C(CH3)2), 110.1 (s, HC CCH3), 76.5 (d, J = 12.3 Hz, C-3), 75.5 (s, C-2), 68.6 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, POC), 66.5 (d, J = 162.2 Hz, PC), 50.9 (s, C-4), 42.8, 27.9, 25.5, 12.2; 31P NMR (243 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.36 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C29H34N5O8P: C, 56.95; H, 5.60; N, 11.45. Found: C, 57.10; H, 5.51; N, 11.33.
4.2.33. (1S,2R,3R)-Dibenzyl 4-{[4-(2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2,3-trihydroxy-2,3-O-isopropylidenebutylphosphonate (1S,2R,3R)-17c
Yield: 93%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +29.4 (c 1.18 in CHCl3); mp: 155–156 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3221, 3012, 2825, 1688, 1241, 1052 cm−1; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 9.23 (s, 1H, NH), 7.78 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.57 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, HC C— H), 7.40–7.33 (m, 10H, 2 × C6H5), 5.70 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, HC C—H), 5.18–5.08 (m, 5H, 2 × POCH2Ph, OH), 5.10 (AB, JAB = 15.0 Hz, 1H, CHaHb), 4.90 (AB, JAB = 15.0 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb), 4.98 (dd, J = 14.2 Hz, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.58–4.52 (m, 1H, H-3), 4.46 (dt, J = 8.9 Hz, J = 6.2 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.42 (dd, J = 14.2 Hz, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H, H-4a), 4,14 (dt, J = 8,9 Hz, J = 5,5 Hz, 1H, H-1), 1.44 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.30 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 164.0 (s, C O), 151.2 (s, C O), 144.5 (s, N—CH CH), 141.6, 136.1 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, Cipso), 136.0 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, Cipso), 128.6, 128.6, 128.5, 128.5, 128.1, 128.0 (Caromat), 124.8, 110.1 (s, C(CH3)2), 102.6 (s, NCH=CH), 76.4 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, C-3), 75.5 (s, C-2), 68.6 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, COP), 68.4 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, COP), 66.4 (d, J = 162.6 Hz, C-1), 50.9 (s, C-4), 43.0 (s, HC C— CH2 —N), 28.0 (s, CH3), 25.5 (s, CH3); 31P NMR (243 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.43 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C28H32N5O8P: C, 56.28; H, 5.40; N, 11.72. Found: C, 56.42; H, 5.23; N, 11.91.
4.2.34. (1S,2R,3R)-Dibenzyl 4-{[4-(N4-acetylamino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2,3-trihydroxy-2,3-O-isopropylidenebutylphosphonate (1S,2R,3R)-17d
Yield: 95%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +30.7 (c 0.75 in CHCl3); mp: 107–108 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3227, 2986, 2936, 1721, 1663, 1494, 1219, 1051, 966 cm−1; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 8.30 (s, 1H, HC5′), 8.08 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, H-C=CH), 7.55 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, HC C— H), 7.45–7.30 (m, 10H, 2 × C6H5), 6.70 (br s, 1H, N—H), 5.25 (dd, J = 14.1 Hz, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 5.19–5.07 (m, 6H, 2 × POCH2Ph, HC C—CH2), 4.98–4.95 (m, 2H, H-3, OH), 4.84 (dd, J = 14.1 Hz, J = 10.2 Hz, 1H, H-4a), 4.63 (ddd, J = 10.3 Hz, J = 7.7 Hz, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.20 (dt, J = 10.3 Hz, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H, H-1), 2.26 (s, 3H, C(O)CH 3), 1.49 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.38 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 171.6 (s, C O), 163.4, 155.5 (s, C O), 149.4, 140.9, 136.3 (d, J = 5.5 Hz, Cipso), 136.1 (d, J = 5.5 Hz, Cipso), 128.5, 128.4, 127.8, 127.6 (Caromat), 125.4, 110.4 (s, C(CH3)2), 97.1, 77.1 (d, J = 14.5 Hz, C-3), 75.1 (s, C-2), 68.8 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, POC), 68.4 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, POC), 66.4 (d, J = 163.0 Hz, C-1), 50.3 (s, C-4), 45.4 (s, HC C— CH2 —N), 28.1 (s, C— CH3), 25.8 (s, C— CH3), 24.7 (s,CH3C(O)); 31P NMR (243 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 25.31 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C30H35N6O8P: C, 56.42; H, 5.52; N, 13.16 Found: C, 56.33; H, 5.44; N, 13.02.
4.2.35. (1S,2R,3R)-Dibenzyl 4-{[4-(3,7-dimethyl-2,6-dioxopurin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2,3-trihydroxy-2,3-O-isopropylidenebutylphosphonate (1S,2R,3R)-17g
Yield: 96%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +7.7 (c 0.95 in CHCl3); mp: 93–95 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3418, 3287, 2938, 1708, 1662, 1455, 1220, 1039, 997 cm−1; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.78 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.48 (s, 1H, N = CH—N), 7.38–7.21 (m, 10H, 2 × C6H5), 5.41 (br s, 1H, OH), 5.30 (AB, JAB = 14.5 Hz, 1H, CHaHb), 5.27 (AB, JAB = 14.5 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb), 5.12–5.03 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.95 (dd, J = 14.2 Hz, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.57–4.52 (m, 1H, H-3), 4.49 (dt, J = 9.1 Hz, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.36 (dd, J = 14.2 Hz, J = 9.6 Hz, 1H, H-4a), 4.17 (dt, J = 9.1 Hz, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.93 (s, 3H, N—CH3), 3.52 (s, 3H, N—CH3), 1.39 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.26 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 154.8 (s, C O), 151.3 (s, C O), 148.3, 143.3, 141.6, 136.1 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, Cipso), 136.0 (d, J = 6,3 Hz, Cipso), 128.6, 128.5, 128.5, 128.4, 128.0, 127.9 (Caromat), 124.4, 109.9 (s, C(CH3)2), 107.7, 76.5 (d, J = 12.4 Hz, C-3), 75.6 (s, C-2), 68.4 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, COP), 68.3 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, COP), 66.5 (d, J = 161.8 Hz, C-1), 50.4 (s, C-4), 36.0 (s, HC C— CH2), 33.6 (s, CH3), 29.7 (s, CH3), 27.9 (s, CH3), 25.5 (s, CH3); 31P NMR (243 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.73 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C31H36N7O8P: C, 55.94; H, 5.45; N, 14.73 Found: C, 56.07; H, 5.20; N, 15.02.
4.2.36. (1S,2R,3R)-Dibenzyl 4-{[4-(1,3-dimethyl-2,6-dioxopurin-7-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2,3-trihydroxy-2,3-O-isopropylidenebutylphosphonate (1S,2R,3R)-17h
Yield: 94%; colorless oil [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +122.1 (c 1.70 in CHCl3); IR (film): ν = 3097, 2948, 2865, 1707, 1664, 1222, 1029, 997, 745, 644 cm−1; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.91 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.83 (s, 1H, N CH—N), 7.38–7.30 (m, 10H, 2 × C6H5), 5.63 (AB, JAB = 15.0 Hz, 1H, CHaHb), 5.60 (AB, JAB = 15.0 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb), 5.17–5.06 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.96 (dd, J = 14.2 Hz, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.55–4.52 (m, 1H, H-3), 4.45 (dt, J = 8.6 Hz, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.38 (dd, J = 14.2 Hz, J = 9.7 Hz, 1H, H-4a), 4.11 (dt, J = 8.7 Hz, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.66 (br s, 1H, OH), 3.59 (s, 3H, N—CH3), 3.43 (s, 3H, N—CH3), 1.45 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.30 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 155.4 (s, C O), 151.6 (s, C O), 148.9, 141.9, 141.5, 135.9 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, Cipso), 135.9 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, Cipso), 128.6, 128.6, 128.6, 128.0, 127.9 (Caromat), 124.7, 110.1 (s, C(CH3)2), 106.5, 76.4 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, C-3), 75.5 (s, C-2), 68.6 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, COP), 68.4 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, COP), 65.5 (d, J = 162.0 Hz, CP), 50.8 (s, C-4), 41.5, 29.8 (s, CH3), 27.9 (s, CH3), 27.9 (s, CH3), 25.5 (s, CH3); 31P NMR (242 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.14 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C31H36N7O8P: C, 55.94; H, 5.45; N, 14.73 Found: C, 55.75; H, 5.68; N, 14.55.
4.2.37. (1S,2R,3R)-Dibenzyl 4-{[4-(8-chloro-1,3-dimethyl-2,6-dioxopurin-7-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2,3-trihydroxy-2,3-O-isopropylidenebutylphosphonate (1S,2R,3R)-17i
Yield: 94%; white powder [chromatographed on a silica gel column with chloroform–methanol (50:1, 20:1, 10:1, v/v)]; [α]D 20 +17.0 (c 1.37 in CHCl3); mp: 194–196 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3279, 2992, 2954, 2895, 1706, 1663, 1541, 1378, 1217, 997 cm−1; 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 7.89 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.37–7.29 (m, 10H, 2 × C6H5), 5.65 (AB, JAB = 15.2 Hz, 1H, CHaHb), 5.62 (AB, JAB = 15.2 Hz, 1H, CHa Hb), 5.15–5.04 (m, 4H, 2 × POCH2Ph), 4.96 (dd, J = 14.2 Hz, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H, H-4b), 4.91 (br s, 1H, OH), 4.57–4.52 (m, 1H, H-3), 4.49 (dt, J = 8.9 Hz, J = 6.4 Hz, 1H, H-2), 4.37 (dd, J = 14.2 Hz, J = 9.8 Hz, 1H, H-4a), 4.12 (dt, J = 9.1 Hz, J = 5.8 Hz, 1H, H-1), 3.54 (s, 3H, N—CH3), 3.39 (s, 3H, N—CH3), 1.41 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.28 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 154.5 (s, C O), 159.3, 147.4 (s, C O), 141.5, 139.1, 135.9 (Cipso), 128.6, 128.6, 128.5, 128.1, 127.9 (s, Caromat), 124.7, 110.0 (s, C(CH3)2), 107.4, 76.3 (d, J = 12,2 Hz, C-3), 75.6 (s, C-2), 68.6 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, COP), 68.4 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, COP), 66.5 (d, J = 161.6 Hz, C-1), 50.6 (s, C-4), 41.0 (s, HC C— CH2), 29.8 (s, CH3), 28.0 (s, CH3), 27.9 (s, CH3), 25.5 (s, CH3); 31P NMR (243 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 23.46 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C31H35ClN7O8P: C, 53.18; H, 5.04; N, 14.01. Found: C, 53.28; H, 4.81; N, 14.28.
4.3. Synthesis of phosphonic acid 21b and 21k (general procedure)
The dibenzyl phosphonates (1S,2S)-16b and (1S,2S)-16k (1 mmol) were dissolved in methanol (10 mL) and water (2 mL) and 10% Pd–C (10 mg) was added. The suspension was stirred under hydrogen atmosphere at room temperature for 48 h. The catalyst was filtered through a layer of Celite and the aqueous solution was concentrated in vacuo to give pure phosphonic acids 21b and 21k.
4.3.1. (1S,2S)-3-{4-[(5-Methyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2-dihydroxypropylphosphonic acid (1S,2S)-21b
Yield: 87%; white powder; [α]D 20 18.3 (c 1.85 in DMSO); mp: 240–243 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3290, 2833, 1680, 1614, 1225, 1020 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CD3OD): δ = 8.05 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.55 (d, J = 1.1 Hz, 1H, CH3C CH), 5.02 (s, 2H, CH2), 4.67 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 3.8 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.52 (dd, J = 14.4 Hz, J = 9.6 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.32–4.25 (m, 1H, H-2), 3.76 (dd, J = 10.8 Hz, J = 4.1 Hz, 1H, H-1), 1.84 (d, J = 1.1 Hz, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 164.7, 151.2, 142.5, 141.6, 124.8, 109.3, 70.6, 68.6 (d, J = 164.2 Hz, PC), 53.2 (d, J = 5.6 Hz), 42.6, 12.4; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CD3OD): δ = 18.47 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C11H16N5O7P × H2O: C, 34.84; H, 4.78; N, 18.47. Found: C, 35.02; H, 5.00; N, 14.20.
4.3.2. (1S,2S)-3-{4-[(3-benzoyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl}-1,2-dihydroxypropylphosphonic acid (1S,2S)-21k
Yield: 89%; white powder; [α]D 20 17.6 (c 3.42 in DMSO); mp: 130–132 °C; IR (KBr): ν = 3323, 2830, 1701, 1698,1230, 1025, 762, 689 cm−1; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CD3OD): δ = 8.03 (s, 1H, HC5′), 7.97–7.95 (m, 2H, Haromat), 7.85 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, HC CH), 7.75–7.68 (m, 1H, Haromat), 7.60–7.54 (m, 2H, Haromat), 5.84 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, HC CH), 5.15 (s, 2H, CH2), 4.72 (dd, J = 13.9 Hz, J = 3.8 Hz, 1H, H-3a), 4.50 (dd, J = 13.9 Hz, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H, H-3b), 4.31–4.22 (m, 1H, H-2), 3.78 (dd, J = 10.5 Hz, J = 4.1 Hz, 1H, H-1); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CD3OD): δ = 170.0 (s, C O), 162.7 (s, C O), 149.9 (s, C O), 147.0, 141.8, 136.0, 131.6, 130.5, 125.0, 101.4, 70.6 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, C-2), 68.9 (d, J = 157.7 Hz, PC), 53.3 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, C-3), 43.4; 31P NMR (121.5 MHz, CD3OD): δ = 21.53 ppm. Anal. Calcd for C17H18N5O8P × H2O: C, 43.50; H, 4.30; N, 14.92. Found: C, 43.72; H, 4.55; N, 15.16.
4.4. Antiviral activity assays
The compounds were evaluated against the following viruses: herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) strain KOS, thymidine kinase-deficient (TK−) HSV-1 KOS strain resistant to ACV (ACVr), herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) strains Lyons and G, varicella-zoster virus (VZV) strain Oka, TK− VZV strain 07−1, human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) strains AD-169 and Davis, vaccinia virus Lederle strain, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) strain Long, vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), Coxsackie B4, Parainfluenza 3, Influenza virus A (subtypes H1N1, H3N2), influenza virus B, Reovirus-1, Sindbis, Reovirus-1, Punta Toro, human immunodeficiency virus type 1 strain IIIB and human immunodeficiency virus type 2 strain ROD. The antiviral, other than anti-HIV, assays were based on inhibition of virus-induced cytopathicity or plaque formation in human embryonic lung (HEL) fibroblasts, African green monkey cells (Vero), human epithelial cells (HeLa) or Madin-Darby canine kidney cells (MDCK). Confluent cell cultures in microtiter 96-well plates were inoculated with 100 CCID50 of virus (1 CCID50 being the virus dose to infect 50% of the cell cultures) or with 20 plaque forming units (PFU) (VZV) in the presence of varying concentrations of the test compounds. Viral cytopathicity or plaque formation was recorded as soon as it reached completion in the control virus-infected cell cultures that were not treated with the test compounds. Antiviral activity was expressed as the EC50 or compound concentration required to reduce virus-induced cytopathogenicity or viral plaque formation by 50%.
4.5. Anti-HIV activity assays
Inhibition of HIV-1(IIIB)- and HIV-2(ROD)-induced cytopathicity in CEM cell cultures was measured in microtiter 96-well plates containing ∼3 × 105 CEM cells/mL infected with 100 CCID50 of HIV per milliliter and containing appropriate dilutions of the test compounds. After 4–5 days of incubation at 37 °C in a CO2-controlled humidified atmosphere, CEM giant (syncytium) cell formation was examined microscopically. The EC50 (50% effective concentration) was defined as the compound concentration required to inhibit HIV-induced giant cell formation by 50%.
4.6. Cytostatic activity assays
All assays were performed in 96-well microtiter plates. To each well were added (5–7.5) × 104 tumor cells and a given amount of the test compound. The cells were allowed to proliferate for 48 h (murine leukemia L1210 cells) or 72 h (human lymphocytic CEM and human cervix carcinoma HeLa cells) at 37 °C in a humidified CO2-controlled atmosphere. At the end of the incubation period, the cells were counted in a Coulter counter. The IC50 (50% inhibitory concentration) was defined as the concentration of the compound that inhibited cell proliferation by 50%.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude to Mrs. Małgorzata Pluskota, Mrs. Leentje Persoons, Mrs. Frieda De Meyer, Mrs. Lies Van den Heurck, Mr. Steven Carmans, Mrs. Anita Camps and Mrs. Lizette van Berckelaer for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by the National Science Centre under Decision DEC-2011/01/D/NZ4/01276. The virological part of this work was supported by the KU Leuven (GOA no. 10/014).
References and notes
- 1.Herdewijn P. Wiley-VCH; Weinheim: 2008. Modified Nucleosides in Biochemistry, Biotechnology and Medicine. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chu C.K. Elsevier B.V; Amsterdam: 2003. Antiviral Nucleosides: Chiral Synthesis and Chemotherapy. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schaeffer H.J., Beauchamp L., De Miranda P., Elion G.B., Bauer D.J., Collins P. Nature. 1978;272:583. doi: 10.1038/272583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Martin J.C., Smee D.F., Verheyden J.P.H. J. Org. Chem. 1985;50:755. [Google Scholar]
- 5.De Clercq E. Med. Res. Rev. 2013;33:1278. doi: 10.1002/med.21283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lin T.-S., Liu M.-C.h. Tetrahedron Lett. 1984;25:905. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kamiya T., Saito Y., Hashimoto M., Seki H. Tetrahedron Lett. 1969;10:4729. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(01)97969-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kamiya T., Saito Y., Hashimoto M., Seki H. Tetrahedron. 1972;28:899. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(01)97969-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Votruba I., Holý A. Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 1982;47:167. [Google Scholar]
- 10.De Clercq E., Descamps J., De Somer P., Holý A. Science. 1978;200:563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.De Clercq P., Holý A. J. Med. Chem. 1979;22:510. doi: 10.1021/jm00191a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Holý A., Votruba I., De Clercq E. Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 1985;50:245. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Slama K., Holý A. Acta Entomol. Bohemoslav. 1988;85:94. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wróblewski A.E., Karolczak W. Tetrahedron. 2003;59:6075. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wolfe M.S., Borchardt R.T. J. Med. Chem. 1991;34:1521. doi: 10.1021/jm00109a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.De Clercq E. Adv. Virus Res. 1993;42:1. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Amblard F., Cho J.H., Schinazi R.F. Chem. Rev. 2009;109:4207. doi: 10.1021/cr9001462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nájera C., Sansano J.M. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009;7:4567. doi: 10.1039/b913066g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tron G.C., Pirali T., Bilington R.A., Canonico P.L., Sorba G., Genazzani A.A. Med. Res. Rev. 2008;28:278. doi: 10.1002/med.20107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Saito Y., Escuret V., Durantel D., Zoulim F., Schinazi R.F., Agrofoglio L.A. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003;11:3633. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(03)00349-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Holý A., Dvořáková H., Jindřich J., Masojídková M., Buděšínský M., Balzarini J., Andrei G., De Clercq E. J. Med. Chem. 1996;39:4073. doi: 10.1021/jm960314q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lazrek H.B., Taourirte M., Oulih T., Lebtoumi M., Barascut J.L., Imbach J.L. Nucleosides Nucleotides. 1997;16:1115. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lazrek H.B., Taourirte M., Oulih T., Barascut J.L., Imbach J.L., Pannecouque C., Witrouw M., De Clercq E. Nucleosides, Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 1949;2001:20. doi: 10.1081/NCN-100108325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Diab S.A., Hienzch A., Lebargy C., Guillarme S., Pfund E., Lequeux T. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009;7:4481. doi: 10.1039/b912724k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Elayadi H., Smietana M., Pannecouque Ch., Leyssen P., Neyts J., Vasseur J.-J., Lazrek H.B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010;20:7365. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.10.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ganesan M., Muraleedharan K.M. Nucleosides, Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2010;29:91. doi: 10.1080/15257771003597709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Koszytkowska-Stawińska M., Mironiuk-Puchalska E., Rowicki T. Tetrahedron. 2012;68:214. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Koszytkowska-Stawińska M., Sas W. Tetrahedron. 2013;69:2619. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Głowacka I.E., Balzarini J., Wróblewski A.E. Nucleosides, Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2012;31:293. doi: 10.1080/15257770.2012.662611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Głowacka I.E., Balzarini J., Wróblewski A.E. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2013;346:278. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201200421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Głowacka I.E., Balzarini J., Wróblewski A.E. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2013;346:677. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201300156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Piotrowska D.G., Balzarini J., Głowacka I.E. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012;47:501. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.11.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Głowacka I.E., Balzarini J., Wróblewski A.E. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013;70C:703. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.10.057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Głowacka I.E., Balzarini J., Wróblewski A.E. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2014 doi: 10.1002/ardp.201300468. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Głowacka I.E., Balzarini J., Piotrowska D.G. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2014 doi: 10.1002/ardp.201300471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wróblewski A.E., Głowacka I. E. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 2002;13:989. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wróblewski A.E., Głowacka I.E. Pol. J. Chem. 1895;2005:79. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wróblewski A.E., Głowacka I.E. Tetrahedron. 2005;61:11930. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Alvarez R., Velázquez S., San-Félix A., Aquaro S., De Clercq E., Perno C.-F., Karlsson A., Balzarini J., Camarasa M.J. J. Med. Chem. 1994;37:4185. doi: 10.1021/jm00050a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lindsell W.E., Murray Ch., Preston P.N., Woodman T.A.J. Tetrahedron. 2000;56:1233. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Krim J., Taourirte M., Engels J.W. Molecules. 2012;17:179. doi: 10.3390/molecules17010179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Pérez-Serrano L., Casarrubios L., Dominguez G., González-Pérez P., Pérez-Castells J. Synthesis. 1810;2002:13. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Waer, M. J. A.; Herdewijn, P. A. M. M.; Pfleiderer, W. E. Immunosupressive effects of 8-substituted xanthine derivatives. US7, 253, 176 B1 2007.
- 44.Casaschi A., Grigg R., Sansano J.M. Tetrahedron. 2000;56:7553. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Daly J.W., Padgett W.L., Shamim M.T. J. Med. Chem. 1986;29:1305. doi: 10.1021/jm00157a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Himmelsbacg, F.; Mark, M.; Eckhardt, M.; Langkopf, E.; Maier, R. Xanthine derivatives, the preparation thereof and use as pharmaceutical compositions. US2002/198205; 2002 (A1).
- 47.Casaschi A., Grigg R., Sansano J.M. Tetrahedron. 2001;57:607. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lee Y.-S., Kim B.H. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002;12:1395. doi: 10.1016/s0960-894x(02)00182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Tornøe C.W., Christensen C., Meldal M. J. Org. Chem. 2002;67:3057. doi: 10.1021/jo011148j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rostovtsev V.V., Green L.G., Fokin V.V., Sharpless K.B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2002;41:2596. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20020715)41:14<2596::AID-ANIE2596>3.0.CO;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


