An outbreak caused by a novel human coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was first detected in Wuhan in December 2019,1 and has since spread within China and to other countries. Real-time RT-PCR assays are recommended for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.2 However, viral dynamics in infected patients are still yet to be fully determined. Here, we report our findings from different types of clinical specimens collected from 82 infected individuals.
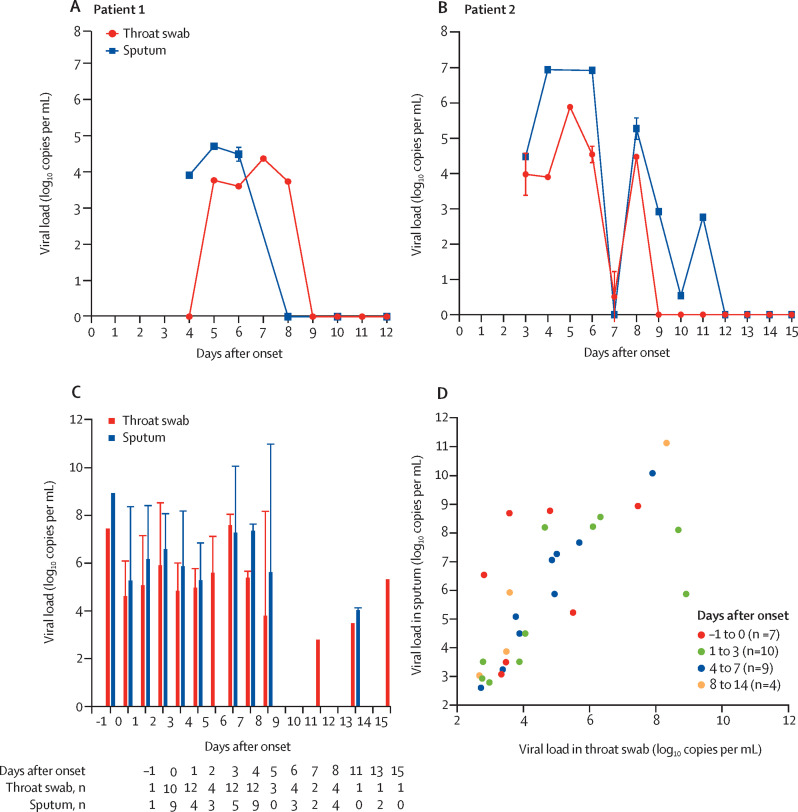
Serial samples (throat swabs, sputum, urine, and stool) from two patients in Beijing were collected daily after their hospitalisation (patient 1, days 3–12 post-onset; patient 2, days 4–15 post-onset). These samples were examined by an N-gene-specific quantitative RT-PCR assay, as described elsewhere.3 The viral loads in throat swab and sputum samples peaked at around 5–6 days after symptom onset, ranging from around 104 to 107 copies per mL during this time (figure A, B ). This pattern of changes in viral load is distinct from the one observed in patients with SARS, which normally peaked at around 10 days after onset.4 Sputum samples generally showed higher viral loads than throat swab samples. No viral RNA was detected in urine or stool samples from these two patients.
Figure.
Viral dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 in infected patients
Viral load (mean [SD]) from serial throat swab and sputum samples in patient 1 (A) and patient 2 (B). (C) Viral load (median [IQR]) in throat and sputum samples collected from 80 patients at different stages after disease onset. (D) Correlation between viral load in throat swab samples and viral load in sputum samples.
We also studied respiratory samples (nasal [n=1] and throat swabs [n=67], and sputum [n=42]) collected from 80 individuals at different stages of infection. The viral loads ranged from 641 copies per mL to 1·34 × 1011 copies per mL, with a median of 7·99 × 104 in throat samples and 7·52 × 105 in sputum samples (figure C). The only nasal swab tested in this study (taken on day 3 post-onset) showed a viral load of 1·69 × 105 copies per mL. Overall, the viral load early after onset was high (>1 × 106 copies per mL). However, a sputum sample collected on day 8 post-onset from a patient who died had a very high viral load (1·34 × 1011 copies per mL). Notably, two individuals, who were under active surveillance because of a history of exposure to SARS-CoV-2-infected patients showed positive results on RT-PCR a day before onset, suggesting that infected individuals can be infectious before them become symptomatic.
Among the 30 pairs of throat swab and sputum samples available, viral loads were significantly correlated between the two sample types for days 1–3 (R2=0·50, p=0·022), days 4–7 (R2=0·93, p<0·001), and days 7–14 (R2=0·95, p=0·028).
From 17 confirmed cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection with available data (representing days 0–13 after onset), stool samples from nine (53%; days 0–11 after onset) were positive on RT-PCR analysis. Although the viral loads were less than those of respiratory samples (range 550 copies per mL to 1·21 × 105 copies per mL), precautionary measures should be considered when handling faecal samples.
Acknowledgments
We declare no competing interests. This work was supported by the Theme-based Research Scheme (UGC, Hong Kong).
Contributor Information
Leo L M Poon, Email: llmpoon@hku.hk.
Quanyi Wang, Email: bjcdcxm@126.com.
References
- 1.Lu R, Zhao X, Li J. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet. 2020 doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8. published online Jan 30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.WHO Laboratory testing for 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in suspected human cases. Interim guidance. Jan 17, 2020. https://www.who.int/publications-detail/laboratory-testing-for-2019-novel-coronavirus-in-suspected-human-cases-20200117
- 3.Chu DKW, Pan Y, Cheng SMS. Molecular diagnosis of a novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) causing an outbreak of pneumonia. Clin Chem. 2020 doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvaa029. published online Jan 31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Peiris JS, Chu CM, Cheng VC. Clinical progression and viral load in a community outbreak of coronavirus-associated SARS pneumonia: a prospective study. Lancet. 2003;361:1767–1772. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13412-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]