Abstract

Practical relevance Although gait disturbance is one of the most common neurological presentations in feline medicine, the clinical approach to the paralyzed cat can be challenging. After excluding orthopedic and cardiovascular diseases that may mimic a neurological condition, the clinician has to address a long list of different diseases that may affect the spinal cord and produce paresis.

Clinical challenges In many cases a definitive cause of spinal weakness in cats is difficult to prove. Even when treatable diseases are identified, the prognosis is very much dependent on the severity of the clinical signs and their chronicity. This review sets out to describe the specific approach, diagnosis and management of cats with spinal cord disease and to outline the most common diseases responsible.
Patient group Patients of either gender and all ages and breeds can be affected by spinal cord disease.
Evidence base Many diseases affecting the spinal cord of cats, which include fibrocartilaginous embolic myelopathy, intervertebral disc disease, exogenous spinal cord trauma, spinal cord lymphosarcoma and feline infectious peritonitis, are well described in the literature. Many of these descriptions, however, have been based on case reports or series. While there have been several retrospective studies that describe the characteristics and incidence of these diseases in cats, there are no long term treatment trials or outcome studies to assist with prognostic determinations.
Neuroanatomy — an overview
Gait disturbance is one of the most common neurological presentations in veterinary medicine. 1 The main goals for the clinician approaching a patient with a gait disorder are to distinguish a neurological condition from other conditions that may mimic a neurological problem, including orthopedic or cardiovascular diseases, and to localize the lesion within the nervous system.
An understanding of basic terms used in neurology allows the clinician to describe clinical signs in a detailed way, defining conditions in order to more easily localize the neurological lesion. Specifically, when evaluating a neurological patient, the anatomic concepts of ‘upper motor neuron’ (UMN) and ‘lower motor neuron’ (LMN) are fundamental to the understanding of how the motor component of the nervous system works.
The LMN is the final common effector of movement, comprised of the peripheral nerve connecting the spinal cord to the muscles. The UMN system regulates LMN activity by inhibition; in other words, UMN ‘limits’ the LMN action. Therefore, a lesion affecting the UMN causes reduced LMN inhibition, which increases LMN activity. For this reason, normal to increased spinal reflexes (hyperreflexia) are noted on examination, in addition to increased muscular tone. A lesion of the LMN produces decreased or absent spinal reflexes (hypo- to areflexia). Neurogenic muscle atrophy is frequently detected with LMN lesions, due to lack of trophic activity of the motor neuron on the myofiber.
In neurology, an abnormal gait can be described as being due to a dysfunction of afferent or sensory pathways, resulting in ataxia, and/or due to a lesion in the efferent or motor pathways, causing an abnormality in voluntary movement (paresis/plegia).
Ataxia
An abnormality of sensory processing reduces the coordination of limb and body movements resulting in an uncoordinated gait, or ataxia. Specifically, ataxia can arise from:
Deficits in afferent (sensory) peripheral nerve or spinal cord pathways (sensory or general proprioceptive ataxia);
A vestibular disorder (vestibular ataxia);
A cerebellar disorder (cerebellar ataxia).
MULTIMEDIA
A video recording of a paralyzed cat being examined for spinal reflexor reflex function, and another recording showing a cat with moderate ambulatory tetraparesis, are included in the online version of this article doi:10.1016/j.jfms.2009.03.004
Paresis/paralysis
Paresis is defined as reduced voluntary motor function, while paralysis (or paraplegia) is complete loss of voluntary motor function (Fig 1). Voluntary motor function — ie, the ability to generate movements — should not be confused with the presence of spinal reflexes. A dysfunction of voluntary motor activity does not imply that the spinal reflexes are affected. In other words, a plegic limb can have normal reflexes (see video 1, doi:10.1016/j.jfms.2009.03.004); the reflexes will only be reduced if a spinal lesion affects the lower motor unit of the C6-T2 and L4-S3 spinal segments.
Fig 1.
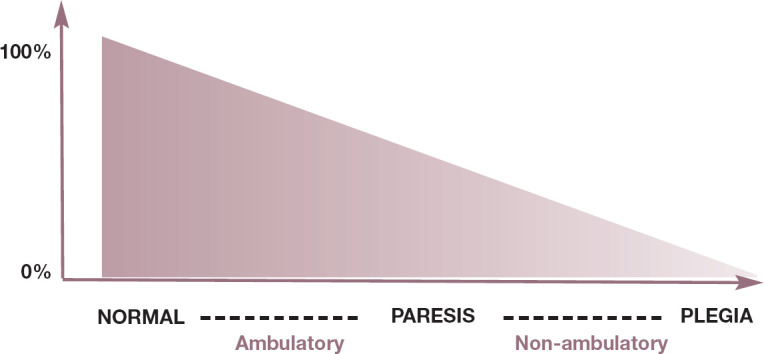
Diagram representing the definitions of paresis and plegia (x-axis) as determined by the voluntary motor function present (y-axis). The range is between 100% (normal cat) and 0% (plegia)
The term paresis encompasses mild to severe deficits of motor function; the descriptions ‘ambulatory paresis’ and ‘non-ambulatory paresis’ can help in distinguishing between the two ends of the spectrum as well as in assigning a numerical grade of motor function to the patient. Detection of voluntary movement can importantly help to define prognosis and determine the most appropriate diagnostic tests.
Further descriptive terminology such as ‘flaccid’, corresponding to decreased muscle tone and generally indicative of a LMN lesion, or ‘spastic’, defined as increased muscle tone and commonly due to an UMN lesion, can be added to the terms paresis/paralysis. Additionally the suffixes ‘mono-’ (one limb), ‘hemi-’ (two limbs on the same side), ‘para-’ (both pelvic limbs), ‘tetra-’ (all four limbs) (see video 2, doi:10.1016/j.jfms.2009.03.004) can be added to paresis/paralysis to describe which limbs are affected.
Localization of the neurological lesion
The clinical approach to a cat with a gait abnormality can be challenging. The first steps of the neurological examination involve observation of mental status, posture and gait for the presence of ataxia and/or paresis. Subsequent additional evaluation of the cat's postural reactions, which assess proprioceptive function, will allow the clinician to determine if a gait disturbance has neurological origins. The remainder of the neurological examination is mandatory to localize the responsible lesion.
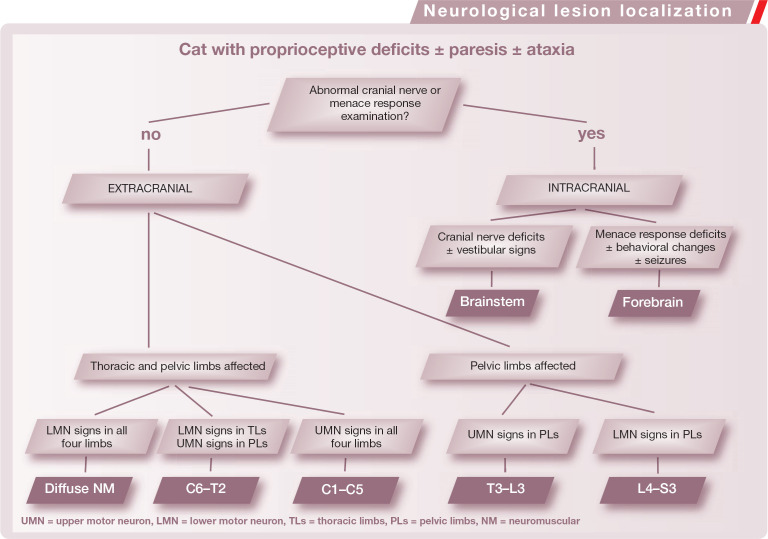
Neurological lesion localization.
To simplify the process of localization, the nervous system can be divided into two gross anatomical parts: the intracranial and the extracranial components. Clinicians should always try to localize a neurological lesion to a single part of the nervous system, which should explain each neurological sign. However, neurological signs cannot always be explained by one localization, in which case a ‘multifocal’ or ‘diffuse’ localization is suspected.
Intracranial lesions
Evaluation of cranial nerve function in addition to mental status can help to determine central nervous system (CNS) lesion localization (see box on page 362). If the menace response, cranial nerve evaluation and mental status are all normal in a cat with proprioceptive deficits and/or an alteration of gait, the lesion is likely to be extracranial. Conversely, if the menace response, cranial nerve examination or mental status are abnormal, the lesion will be intracranially located.
One of two main anatomic divisions of the intracranial compartment may be affected in a cat with proprioceptive ataxia and/or paresis and/or proprioceptive deficits: the brainstem or prosencephalon.
Brainstem localization Paresis/ataxia/proprioceptive deficits associated with cranial nerve dysfunction are usually due, at least in part, to a brainstem lesion. Mental status is usually severely affected, resulting in a depressed or obtunded status.
Prosencephalon localization A decreased menace response, seizures and/or behavioral changes suggest a prosencephalic lesion. Ataxia, paresis and decreased mental status can be present with forebrain lesions; however, if this is the case, the lesions are usually very severe resulting in increased intracranial pressure or parenchymal herniation. Otherwise, prosencephalic lesions are not responsible for obvious gait abnormalities.
Extracranial lesions
If cranial nerve examination, menace response and mental status are normal, the lesion is usually extracranial. In this case, spinal reflex evaluation must be performed to determine whether the neurological disorder is LMN or UMN in nature. Within the extracranial compartment, the two gross anatomical subdivisions are the spinal cord and the neuromuscular system (nerve roots, spinal nerves, peripheral nerves, neuromuscular junctions and muscle). Upper motor neuron lesions affect the spinal cord, and LMN lesions can affect the C6-T2 and L4-S3 segments of the spinal cord, as well as the neuromuscular system (see box on page 362).
Spinal cord localization The four segments into which the spinal cord is clinically divided (C1-C5, C6-T2, T3-L3, L4-S3) are responsible for specific neurological signs when affected by disease processes (Table 1). Asymmetry or lateralization of neurological signs needs to be carefully evaluated. Lateralized lesions affecting the brainstem, or C1-C5 or C6-T2 spinal segments, can cause hemiparesis and ipsilateral, unilateral proprioceptive deficits. Monoparesis can be observed in very lateralized lesions of the spinal cord, that are usually at the level of intumescences and may be associated with neurogenic muscle atrophy (Fig 2).
Neuromuscular localization Localization of lesions to the neuromuscular system can be very challenging as disease can affect the nerve, neuromuscular junction or muscle, separately or collectively. In general, lesions affecting the neuromuscular system can cause flaccid muscle tone, paresis, muscle atrophy, decreased spinal reflexes and, very occasionally, cranial nerve dysfunction. These lesions should affect all limbs, which helps to distinguish them from focal spinal lesions affecting the lower motor neurons. A pure sensory peripheral nerve problem causes ataxia without paresis, decreased postural reactions and decreased to absent deep and superficial sensation; while a muscular disease can cause paresis/plegia, weakness and/or stiffness, decreased spinal flexor reflexes (extensors usually intact), muscle atrophy or hypertrophy (rare) and possibly muscle pain. Decreased postural reactions can be identified with muscle disease but they reflect the reduced strength of the animal rather than being a true abnormality.
Table 1.
Neurological signs compatible with disease in the four segments of the spinal cord
| Clinical abnormality | C1-C5 spinal cord localization | C6-T2 spinal cord localization | T3-L3 spinal cord localization | L4-S3 spinal cord localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ataxia | Affects trunk and all four limbs | Affects trunk and all four limbs | Only affects the pelvic limbs | Only affects the pelvic limbs (and less commonly than with T3-L3 lesions) |
| Paresis/plegia | Hemi-, tetra- | Hemi-, tetra- | Mono- (rare), para- | Mono- (rare), para- |
| Proprioceptive deficits | In all four limbs or lateralized to one side | In all four limbs or lateralized to one side | In one (rare) or both pelvic limbs | In one (rare) or both pelvic limbs |
| Thoracic limb spinal reflexes | Intact | Reduced to absent | Intact | Intact |
| Pelvic limb spinal reflexes | Intact | Intact | Intact | Reduced to absent |
| Hyperesthesia | Cervical | Cervical | Thoracolumbar | Lumbosacral |
| Panniculus reflex | Intact | Absent/decreased motor response ipsilaterally (rare); central sensory response intact | Sometimes abnormal from approximately 1–2 vertebral lengths cranial to the lesion and caudally | Intact |
| Muscle tone | Normal to increased in all four limbs | Reduced in thoracic limbs; normal to increased in pelvic limbs | Normal to increased in pelvic limbs | Reduced in pelvic limbs |
| Others | — | Ipsilateral Horner's syndrome (rare) | Possible urinary retention and fecal incontinence | Urinary dysfunction (retention or incontinence); tail paresis; fecal incontinence; decreased perineal reflex |
Fig 2.
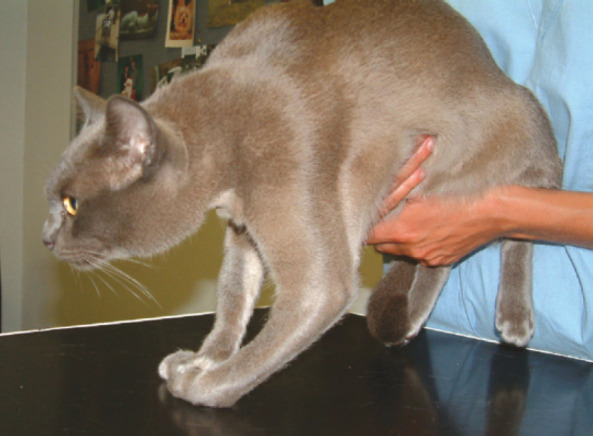
Radial nerve monoparesis in a cat secondary to trauma. There is pronounced neurogenic muscle atrophy in addition to the obvious lack of strength and extensor tone
A thorough physical examination performed before the neurological examination allows the clinician to rule out systemic conditions mimicking or actually responsible for neurological disease. Ischemia caused by aortic/iliac thromboembolism, for example, although not primarily a vascular disease affecting the nervous system, results in an ischemic neuromyopathy causing paraparesis or paraplegia.
Organising the differentials list for a spinal cord lesion
Once the lesion has been localized within the nervous system, a list of potential differential diagnoses needs to be considered in order of probability. Together with the neurological lesion localization, patient signalment, lateralization of neurological signs, presence of pain, speed of onset (acute/chronic), disease progression (signs progressive/non-progressive/improving), and response to previous therapies all need to be considered to determine the most likely differentials. 2
The mnemonic ‘VITAMIN D’ helps to ensure consideration is given to all the possible mechanisms of disease that could be responsible for neurological clinical signs. Each letter stands for one or two disease processes, the specifics of which are outlined below and in Table 2.
Table 2.
Categories of spinal cord disease and their differentials
| Category | Differentials |
|---|---|
| V Vascular | Fibrocartilaginous embolism Vascular malformations |
| I Inflammatory/infectious |
|
| T Traumatic |
|
| A Anomalous diseases |
|
| M Metabolic | Rare |
| I Idiopathic | None |
| N Neoplastic |
|
| Nutritional | Nutritional hyperparathyroidism |
| D Degenerative |
|
Major aetiologies are shown in bold
V — vascular diseases
Vascular diseases can be divided into two categories: hemorrhage, leading to hematoma formation; and ischemia, resulting from occlusion of vessel lumens by a thrombus or embolus. If severe enough, ischemia leads to the formation of infarction.3,4
Vascular diseases of the spinal cord usually cause asymmetrical signs (although bilateral disease is also common), without spinal hyperesthesia, which are peracute or acute in onset, developing in minutes or hours, and non-progressive. In general, worsening of neurological deficits has been reported in the first 24 h and stabilization and/or improvement of the neurological condition is usually observed. 5 Deterioration of clinical signs after a vascular event is due to multiple factors, including edema formation, accumulation of intracellular calcium, free radical production and secondary membrane permeability damage. 5 The final result is cellular necrosis. Deterioration of neurological signs over time may also be suggestive of an ascending/descending hemorrhagic myelomalacia. 6
I — inflammatory/infectious diseases
Inflammatory/infectious conditions can have an acute, subacute or more insidious (chronic) onset, depending on the cause. However, most of the time they are acute in onset. Neurological signs usually progress rapidly, although they can ‘wax and wane’ in the early stages. Neurological deficits can be focal or multifocal and symmetrical or asymmetrical, although more often they are asymmetrical and multifocal. 7
The most common tumor affecting the feline spinal cord is lymphosarcoma, followed by vertebral column neoplasia, meningioma and glial cell tumours.
T — traumatic diseases
Spinal trauma causes peracute/acute neurological signs, which usually remain static (nonprogressive) or improve over time; however, in the first 24–72 h worsening of the neurological signs can be noticed due to secondary spinal cord hemorrhage/ischemia or edema. 8 If there is deterioration of signs after 72 h spinal instability should be considered.
Spinal trauma sequelae such as vertebral fractures, vertebral subluxation/luxation and sacrocaudal dislocation are frequently observed in first opinion practice and can be easily diagnosed on spinal radiography.8,9 Neurological signs usually relate to a focal lesion, which might be seen on spinal radiographs; in a traumatised cat, however, there may be multiple lesions affecting the spine and/or spinal cord, including ischemia, compression, hemorrhage and laceration. 8
A — anomalous diseases
Anomalous conditions include congenital/hereditary malformations of the spinal cord or the surrounding tissues (spinal subarachnoid cyst, vertebral malformations).10,11 They are relatively uncommon in cats, and frequently asymptomatic. Most are detected at an early stage of life, with a chronic onset of neurological signs, and may become more evident over time. Congenital malformations, which can be symmetrical or asymmetrical, should be one of the differentials for a kitten/young cat.
M — metabolic diseases
Metabolic diseases causing neurological deficits compatible with spinal cord localizations are rare.
I — idiopathic diseases
There are no idiopathic diseases of the spinal cord recognized in cats.
N — neoplastic and nutritional diseases
Typically, neoplastic conditions are chronic progressive diseases, although acute and subacute onsets of neurological signs and/or spinal pain are relatively frequent. Lateralization of neurological signs is reported, depending on the lesion site.
The most common neoplasm affecting the spinal cord of cats is lymphosarcoma, followed by vertebral column neoplasia secondarily affecting the spinal cord,12–15 meningioma,14,16 and glial cell tumours14,17 (Table 2).
Age seems to be associated with the prevalence of certain tumor types: cats younger than 5 years of age are significantly more likely to be affected by lymphosarcoma, usually with a shorter duration of neurological signs and multiple spinal cord segment involvement. Asymmetry of neurological signs is also more common in cats with lymphosarcoma. Radiographs of the spine may be useful to detect lytic lesions, which are more likely to be associated with osteosarcoma (vertebral lymphosarcoma is rarely detectable radiographically).
Nutritional hyperparathyroidism should be considered as an infrequent cause of spinal cord disease in cats, 18 although dietary deficiencies have become rare due to the wide availability of balanced commercial diets. Nutritional hyperparathyroidism causes severe hypocalcemia and osteopenia, leading to spontaneous vertebral fractures. 18 Cats may also show muscle twitching and seizures. The diagnosis can be suspected from spinal radiographs showing osteopenic bone and/or pathological vertebral fractures in conjunction with low serum calcium levels and high serum parathormone levels. 18
D — degenerative diseases
Degenerative diseases are not common in cats and are typically characterized by chronic, slowly progressive clinical signs, although intervertebral disc extrusions may present acutely. 19 Degenerative conditions have a bimodal age presentation, with lysosomal storage diseases (globoid cell leukodystrophy, mucopolysaccharidosis) affecting young cats,9,20 and neuroaxonal dystrophy and disc disease affecting older cats.9,21
Neurodiagnostic investigation of spinal cord diseases in cats
Blood tests
Spinal cord diseases rarely cause alterations in hematology, biochemistry or urinalysis results. However, inflammatory disease may cause significant blood test alterations. Serum biochemistry should include, as a minimum, glucose, total protein, albumin, globulin, creatinine, urea, liver enzymes, cholesterol, total bilirubin, and creatine kinase concentrations. 22 Confirmation through serology or PCR of the presence of infectious agents, including feline coronavirus and Toxoplasma gondii, should be obtained when inflammatory/infectious conditions are suspected. Polymerase chain reaction on EDTA blood has high levels of specificity, although the sensitivity is not 100% and is not as good as testing the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Blood culture can be performed when bacterial meningoencephalitis is suspected. 22
Thoracic and abdominal radiography, and abdominal ultrasound
Radiography and ultrasonography should (like hematology and serum biochemistry) be performed in cats before advanced neurodiagnostic imaging tests, to detect any signs of potential metastatic or primary neoplastic conditions and to obtain more information about the general status of the patient before general anesthesia. Radiography and ultrasound are mandatory in any traumatized patient. 8 In addition, organ alterations can be observed in cats with inflammatory/infectious and neoplastic conditions. Ultrasound-guided biopsy of liver, kidney and lymph nodes may be performed at the same time.
Differential diagnosis: General considerations.
Age The diseases that affect the spinal cord are correlated with patient age. Congenital/inherited, inflammatory/infectious and metabolic diseases are often seen in cats younger than 2 years, while degenerative disc disease is more frequent in cats between 2 and 8 years of age. Vascular (ischemia/hemorrhage) and neoplastic diseases are observed most commonly in cats older than 8 years.
Localization Inflammatory/infectious diseases, including FIP, cryptococcosis and toxoplasmosis, often have a multifocal spinal cord distribution with the cervical segment being most commonly affected. Traumatic spinal cord diseases more commonly affect the thoracic and lumbosacral regions. Thoracic and lumbosacral spinal cord regions are also commonly affected in cats with lymphosarcoma, while neoplasia of the cord parenchyma is more prevalent in the cervical spine.
Pain Spinal pain can help to confirm the clinical localization once the neurological examination has detected the spinal cord segments affected. Pain is a feature of intervertebral disc disease, traumatic events, fracture or vertebral luxation, infectious diseases and spinal neoplasia. 9 Pain is not a feature of ischemic myelopathy, myelitis, and degenerative myelopathy (extremely rare in cats).
Asymmetry of neurological signs Asymmetrical neurological dysfunction is suggestive of neoplasia, trauma, disc disease, ischemic myelopathy and CNS inflammation.
Other non-neurological clinical signs Physical examination is essential to detect abnormalities that may be associated with the neurological disease. For example, cats with lymphosarcoma have a higher prevalence of signs such as weight loss, lethargy and anorexia. Infectious and neoplastic disease can also cause systemic clinical signs.
Survey spinal radiography, myelography and computed tomography
Spinal radiographs are indicated in most cases of vertebral column disease, especially where there is a history of trauma or where the differential diagnosis includes neoplasia. Survey spinal radiographs need to be performed in lateral and ventrodorsal positions to detect fractures, vertebral subluxation/luxation, 23 bone or disc infections, and neoplasia causing osteolysis. 14
Myelography or computed tomography (CT) myelography is required if survey spinal radiographs are normal and cord compression is suspected. 24 The benefits of myelography include rapid and economical evaluation of the whole spine. The main disadvantages are difficulties in performing and interpreting the test, and lack of sensitivity for intramedullary spinal cord lesions. In cats, the spinal cord ends more caudally than in dogs; therefore, lumbar myelography should be performed between the L6-L7 vertebrae, although it can be performed between L5-L6 as in dogs. The contrast agent used most commonly for myelography is iohexol (Omnipaque; GE Healthcare), which is injected at 0.2–0.5 ml/kg body weight. Lumbar injection has the advantages of decreasing risks of iatrogenic trauma and seizures.
Myelography in conjunction with CT image acquisition increases the specificity and sensitivity of the test, as it enables evaluation of spinal cord parenchyma and bone lesions. Computed tomography myelography can provide good tissue detail, especially of bone, and enables three-dimensional evaluation of the spinal cord and vertebrae following digital reconstruction. It is therefore particularly useful in cases of spinal trauma or when a bone tumor is suspected.
Magnetic resonance imaging
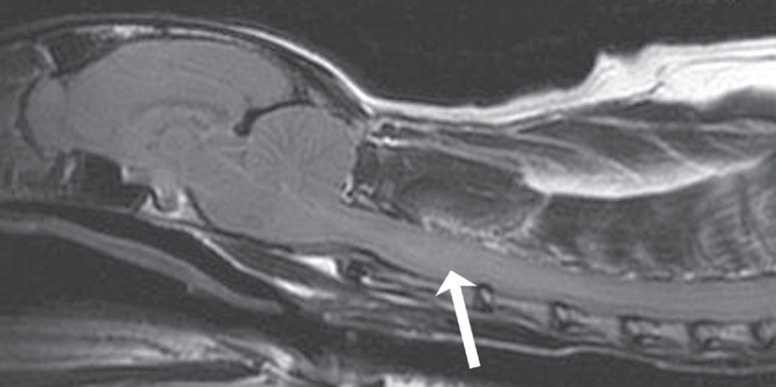
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most sensitive and specific imaging test in veterinary and human medicine for evaluation of the CNS (Fig 3). 25 Although CT has been considered for many years to have high specificity for detecting the early stages of vascular and bone disease, recent studies have shown that MRI can identify the early stages of vascular lesions and provides good bone detail, distinguishing the primary process (neoplasia/inflammation) from the associated secondary lesions (edema/hemorrhage). 26 Disadvantages of MRI include higher cost, difficulty of image interpretation and a high number of normal variants observed due to the sensitivity of the test. Evaluation of the spinal cord of cats may be problematic in low field MR magnets, so magnet field strength should be seriously considered prior to pursuing MRI.
Fig 3.
Sagittal T2-weighted FLAIR MRI scan of a feline cervical spinal cord and intracranial cavity. An indistinct intraparenchymal hyperintense lesion is noted (arrow). This is consistent with inflammation but is not absolutely specific
A recent study identified two independent factors as being predictive of whether MRI findings would be abnormal in cats with spinal cord diseases, justifying the pursuit of this modality: the severity of clinical signs and the presence of pain. 27 Cats with the most severe clinical signs (plegia with/without loss of deep pain perception) were up to 16 times more likely to have MRI abnormalities than cats with mild motor dysfunction. And cats with spinal cord pain were four times more likely to have abnormal MRI results than cats without spinal pain. Magnetic resonance imaging of the spinal cord has also recently been demonstrated to help define the prognosis in cats with spinal disease. 27
Cerebrospinal fluid analysis
Cerebrospinal fluid analysis is indicated if the differential diagnosis includes inflammatory conditions (Fig 4).7,28,29 Neoplastic conditions, primarily round cell tumors (ie, lymphosarcoma), can infrequently be diagnosed by CSF analysis. Vascular, traumatic and degenerative diseases may be associated with albuminocytologic dissociation (increased protein concentration with normal cell count), but this obviously lacks specificity. Corticosteroid administration decreases the white blood cell count and/or total protein levels; 22 therefore, evaluation of CSF in pretreated cats may give false negative results.
Fig 4.
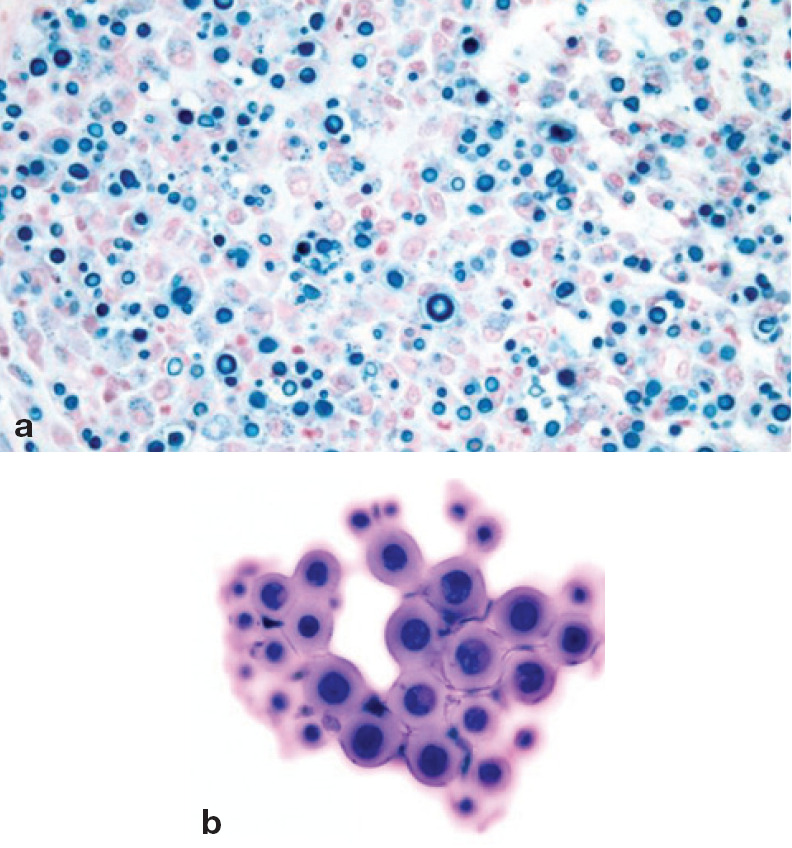
Cryptococcosis affecting the spinal cord of a cat: (a) histopathology and (b) CSF cytology. Round-shaped structures of variable size, with a thick wall, are typical of Cryptococcus neoformans, which has an affinity for the CNS of cats
Specific spinal cord diseases in cats
Fibrocartilaginous embolic myelopathy
Vascular disease, although a relatively uncommon disease type per se,30,31 is the fourth most common cause of spinal cord dysfunction in cats.9,27 Spinal cord ischemic infarction occurs due to obstruction of a spinal cord vessel by fibrocartilaginous material, thought to originate from the intervertebral disc. Many theories are reported in the literature to explain the route by which the intervertebral disc material enters the spinal cord vasculature; mild traumatic events or migration of the disc material into the spinal arteries due to persistence of a common vascular connection between the intervertebral disc and the spinal cord have been postulated.30,31
Cats with fibrocartilaginous embolic myelopathy typically present with a per-acute/acute onset of asymmetrical spinal cord-related signs, which may progress over the first 24 h. 30 Spinal palpation does not elicit pain, and any spinal cord segment may be involved, although the intumescences are most frequently affected.30–32
Definitive diagnosis relies on histopathological confirmation; 31 for this reason, ante-mortem diagnosis is reached by elimination of other causes of myelopathy. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis may detect neutrophilic pleocytosis and/or increased total protein levels. Magnetic resonance imaging is the most sensitive test for detection of ischemic infarctions and is characterized by a hyperintense signal on T2-weighted images, iso- or mildly hypointense signal on T1-weighted images and mild contrast enhancement after 3–7 days.9,32
Treatment is supportive and the prognosis is guarded, although depends on lesion localization and the severity of clinical signs. In cats that recover, improvement is seen within 2–6 weeks of disease onset. 32
Intervertebral disc disease may develop insidiously, starting with constipation, reluctance to jump, low tail carriage and spinal hyperesthesia.
Intervertebral disc disease
Intervertebral disc disease is relatively uncommon in cats, with an incidence of 0.12% of all neurological diseases.19,33 As in dogs, disc protrusions (Hansen's type II) and extrusions (Hansen's type I) have been reported in the literature, although Hansen's type I disease predominates in cats. 33 Where Hansen's type II disc disease occurs, it most commonly affects the cervical region, with bulging of the annulus fibrosus into the spinal canal. 34 However, this is often considered an incidental finding.
Disc extrusions causing neurological dysfunction are more common in the T10-S1 segments of the spine; in particular, the thoracolumbar junction (T13-L1) and L4-L6 segments.19,35–37 The reason for the greater incidence of lumbar disc disease is unknown, but the high mobility of the lumbar and lumbosacral segments may play an important role in the etiopathogenesis of spontaneous disc extrusion in this region. 19
Intervertebral disc disease occurs more frequently in middle-aged and older cats, with a mean age of onset of 7 years. 19 Neurological signs may be insidious, starting with abnormal posture, difficulty in assuming/maintaining the position to defecate (which may secondarily lead to constipation), reluctance to jump, low tail carriage and spinal pain. These signs progress to proprioceptive ataxia and paresis/plegia.
Myelography, with or without CT, is useful for localizing and evaluating the degree of spinal cord compression; however, spinal cord edema/hemorrhage and nerve root compression is better detected using MRI.19,37 Surgery (dorsal decompression/hemilaminectomy) is usually required once neurological signs are observed and can be associated with a good prognosis,19,37 although residual urinary and/or fecal incontinence has been reported. 19 In a recent study of six cats affected by lumbosacral intervertebral disc disease, clinical signs markedly improved within 2 weeks in four cats, while urinary retention and permanent urinary incontinence was reported in the remaining two cats. 36
Acute spinal cord trauma
Spinal trauma is an important cause of spinal cord dysfunction in cats. 38 The most common traumatic conditions in cats include thoracolumbar vertebral fracture and luxations, sacrocaudal (coccygeal) subluxation/luxation, traumatic ischemia and disc extrusion.8,9,23,24,39 In general, spinal trauma can be due to an event directly injuring the cord (contusion/concussion/laceration) or to a condition affecting the surrounding structures (meninges, vertebrae, intervertebral disc) with secondary compression of the spinal cord. Approximately 20% of cats with traumatic spinal injuries also have acute intervertebral disc extrusion secondary to the trauma. 23 Although all segments of the spine are susceptible to trauma, the cervicothoracic, thoracolumbar, lumbosacral and sacrocaudal (coccygeal) junctions are the most common sites of avulsion, fractures and luxation.23,40
Deep pain perception in affected limbs is the most important prognostic indicator following spinal trauma.8,24 Lack of deep pain perception associated with luxated/fractured vertebrae indicates a poor prognosis due to the functional transection of the spinal cord implied by complete sensory defects.8,24 In sacrocaudal (coccygeal) subluxation/luxation, transection of the nerves forming the caudal part of the cauda equina (pudendal and sciatic nerve roots) is frequently reported. In these patients, particular attention should be paid to the perineal reflex, deep pain sensation in genital, anal and tail structures, and the possibility of urinary and fecal incontinence (Fig 5).8,24,41
Fig 5.
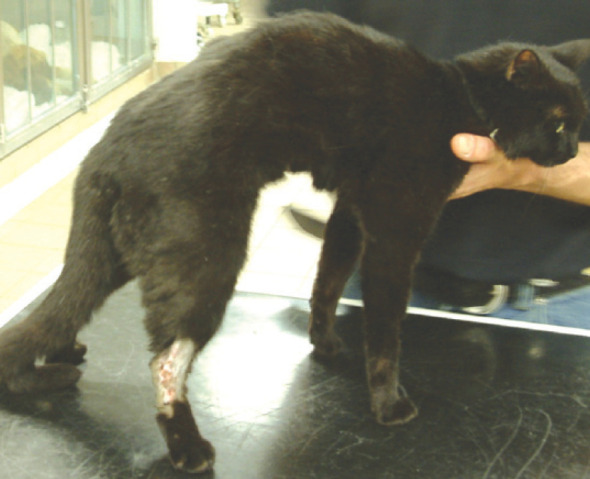
Young cat with a sacroiliac fracture following a road traffic accident. Note the hyperextended right hock and the flaccid drooped tail, which are typical of sciatic and caudal/coccygeal nerve injury, respectively
Survey spinal radiographs will assist with initial evaluation of the patient. Approximately 20% of patients with thoracolumbar fractures have a second spinal column fracture/luxation; 23 therefore, radiographs of the whole spine should be obtained in any cat with spinal trauma, 8 together with survey chest radiographs and abdominal ultrasound. Sedation may be required to ensure well positioned radiographs, but care should be taken if this is the case, due to the ensuing relaxation of the epaxial musculature and the potential for further destabilization of the spine. Advanced imaging, including myelography, CT myelography or MRI, is needed to evaluate spinal cord compression and to investigate for other lesions not visible on radiographs.8,23,24
Management of a cat with spinal trauma should focus first on systemic stabilization. 8 In a case of external trauma, such as car-associated injury, evaluation of the ‘ABC’ of trauma management (airway, breathing and circulation) is mandatory before performing a neurological examination. It is important to keep the cat immobilized; this can be achieved by securing it to a flat board, if practical or feasible. Complete blood work, or as a minimum a packed cell volume, total protein level, urea and creatinine concentration and electrolytes, should be evaluated as soon as possible.
Fluid therapy is important to maintain spinal cord perfusion. Depending on the severity of hypotension, isotonic crystalloids, hypertonic saline, colloids or blood products can be used. 8 The use of steroids is controversial in acute spinal trauma.42,43 Although routinely used in human medicine to reduce the secondary effects of ischemic and reperfusion injury lesions, 44 use of steroids in veterinary patients with spinal trauma may lead to side effects, including infections and gastrointestinal signs.45,46
When spinal instability is detected, surgical stabilization the spine is required. 24 For further information on the surgical management of spinal injury, the reader is referred to an authoritative text. 47
In cats with sacrocaudal (coccygeal) avulsion, where urinary and fecal control is normal and pudendal nerve function intact (as determined by the presence of the perineal reflex, and deep pain sensation in the anal and genital areas), the prognosis is guarded to good. The outcome, in general, for cats with spinal trauma is guarded, with one study reporting a survival rate of only 60%. 23
Lymphosarcoma is more frequently associated with the thoracic and lumbosacral spine, while the cervical segment is more frequently affected by gliomas.
Spinal cord lymphosarcoma
Lymphosarcoma has historically been considered to be the most common neoplasm affecting the spinal cord of cats and this has recently been reaffirmed by two large studies of cats with different spinal cord diseases.14,27 The tumor is especially common in young cats infected with feline leukemia virus (FeLV),48–50 but has a bimodal age distribution: 50% of cats are less than 4 years old, and 25% are between 11 and 16 years of age. 14
Lymphosarcoma tends to be associated with thoracic and lumbosacral localizations, while the cervical segment is more frequently affected by gliomas. Multifocal spinal cord localization is highly indicative of lymphosarcoma, although meningiomas can occasionally be multifocal.
Lymphosarcoma can be rapidly progressive. Being typically part of a multicentric distribution, signs of spinal cord disease are frequently associated with more systemic clinical signs, including anorexia, lethargy and weight loss.13,49,51
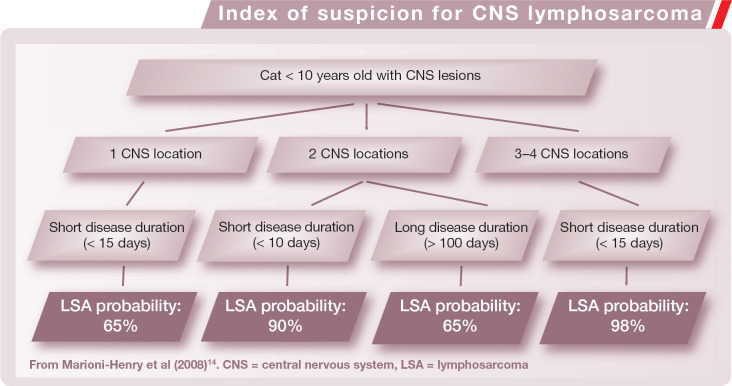
Patient age, disease onset/progression and localization of neurological signs have recently been suggested as important factors that assist with the clinical suspicion of lymphosarcoma of the CNS (see box below). 14 Definitive diagnosis of lymphosarcoma can be challenging and a thorough work-up, with complete blood work, infectious disease tests, abdominal ultrasound, chest radiography, bone marrow aspiration and lymph node aspiration, should be performed in cats in which there is a high index of suspicion.
Index of suspicion for CNS lymphosarcoma.
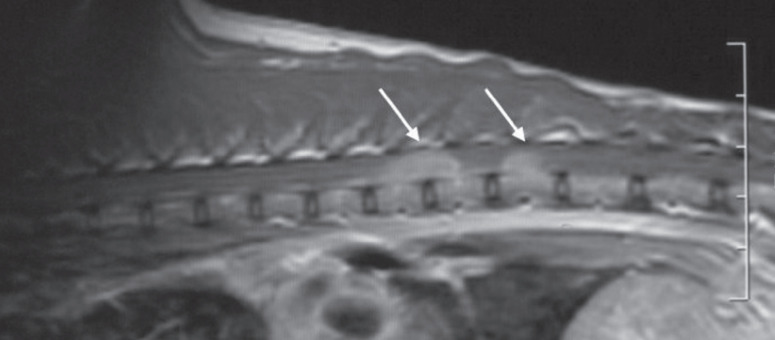
Spinal cord lymphosarcoma can be most appropriately investigated with MRI (Fig 6), 14 as well as with CSF analysis; the latter reveals neoplastic lymphocytes in almost 35% of cases (Fig 7). 48
Fig 6.
T2-weighted sagittal MRI scan of the thoracolumbar spine of a cat with spinal lymphosarcoma. Lesions (arrows) in this case are multiple, with well-defined margins and homogeneous hyperintensity. However, the imaging characteristics of spinal lymphosarcoma are too variable to be specific
Fig 7.
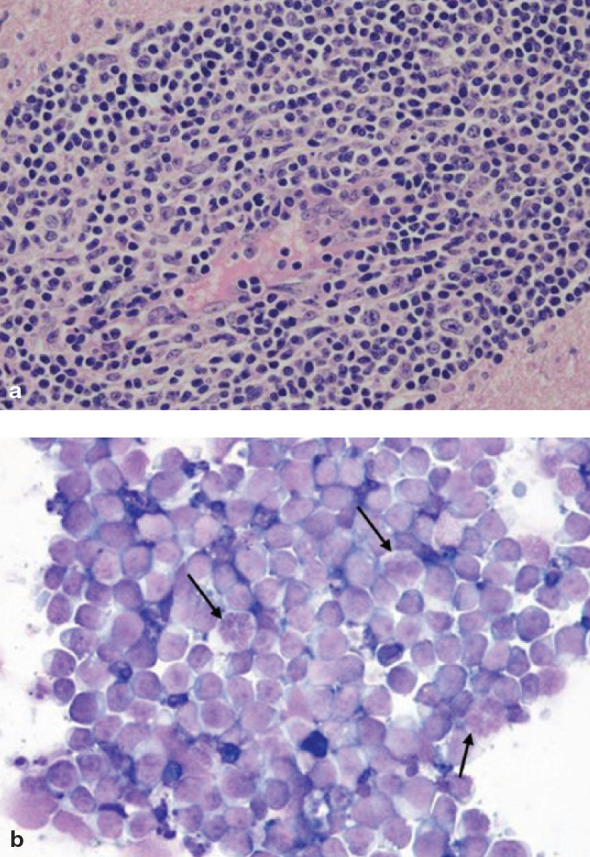
Spinal cord lymphosarcoma: (a) histopathology and (b) CSF cytology. Both images show a homogeneous population of round cells with moderate anisokaryosis. Nucleoli and high grade mitosis (arrows) are evident in the cytological preparation, while histopathology shows that neoplastic cell distribution is perivascular with vessel wall infiltration, which is suggestive of hematogenous spread
Treatment options include chemotherapy and/or surgery, although the long term prognosis in cats with paresis is considered poor. 49 A positive FeLV status in cats is also considered a negative prognostic indicator. 50
Feline infectious peritonitis
Infectious inflammatory diseases account for almost 30% of all feline spinal cord diseases and include bacterial infections, feline infectious peritonitis (FIP), cryptococcosis, toxoplasmosis, and feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) and FeLV infection.9,27,52 Feline infectious peritonitis represents almost half of the infectious inflammatory causes of myelitis in cats, although most cats with neurological FIP have intracranial signs. 53 The immune response of susceptible cats determines the resultant pathology in the CNS following infection by a mutant form of feline enteric coronavirus (FECV). 54 The dry (non-effusive) form of FIP is more frequently associated with CNS infection and causes vasculitis and pyogranulomatous inflammation of the meninges, choroid plexus and ependyma. Typically, FIP is considered a disease affecting the inner (ependyma) and outer (meninges) CNS surfaces. 55
Although cats of any age may be affected by the neurological form of FIP, young intact male cats are at a higher risk of developing the dis-ease. 9 Clinical signs of the dry form may just be neurological; however, a thorough physical examination, including fundic examination of the eye, is necessary to rule out chorioretinitis or anterior uveitis, intermittent fever and weight loss.
Definitive diagnosis requires histopathology and ante-mortem diagnosis can therefore be challenging. The most accurate test is a quantitative PCR performed on CSF and blood. Serology only confirms exposure to feline coronavirus and false negative or low titers may be observed in cats with FIP.54,56–59 However, the dry form of FIP is said to be associated with high feline corona-virus antibody titers and to be rarely associated with seronegative titers. 54 Moreover, it has been reported that high antibody titers (> 1:1600) correspond to a 94% probability of active FIP infection. 56
Advanced imaging, including CT and MRI, are essential to investigate for FIP-associated spinal cord lesions. While MRI of the intracranial form of FIP may demonstrate specific lesions, such as contrast enhancement in the ependyma and meninges, hydrocephalus and/or cerebellar herniation, 58 MRI of the spinal cord for FIP is less specific. Hydrocephalus and/or syringohydromyelia may be detected by CT as well, although MRI will show additional subtle intraparenchymal lesions. 54 Unfortunately, it has been reported that negative feline coronavirus titers in CSF and/or normal MRI findings can be observed in cats with histopathologically confirmed CNS FIP. 58
Despite supportive therapy with steroids and other immunomodulators, no treatments have been proven effective for cats with CNS FIP and the prognosis is poor, with the mortality rate exceeding 95%. 60
Ischemic neuromyopathy
Ischemic neuromyopathy is a relatively common condition in feline medicine, which tends to affect older male cats. It is frequently associated with cardiac disease (in particular, feline hypertrophic cardiomyopathy), which leads to thrombi formation and subsequent embolization of the caudal aorta or the bifurcation of the iliac arteries. Cats present with a peracute onset of paraparesis or plegia with absent or weak femoral pulses, cold and frequently cyanotic extremities, pain on muscle palpation and cardiac auscultation abnormalities.
Serum biochemistry often reveals increased creatine kinase, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, blood urea nitrogen and creatinine levels. Abdominal ultrasound focused on the aortic and iliac arteries may confirm reduced blood flow or the presence of an intraluminal thrombus. Electrocardiography is mandatory in all cats with confirmed aortic/iliac thromboembolism.
KEY POINTS.
Together with the neurological lesion localization, patient signalment, lateralization of neurological signs, presence of pain, speed of onset (acute/chronic), disease progression (progressive/non-progressive/improving), and response to previous therapies all need to be considered to determine the most likely differentials.
Spinal pain can help to confirm the clinical localization once the neurological examination has confirmed the spinal cord segments affected. Pain is a feature of intervertebral disc disease, traumatic events, fracture or vertebral luxation, infectious diseases and spinal neoplasia.
Spinal trauma is an important cause of spinal cord dysfunction in cats. The most common traumatic conditions in cats include thoracolumbar vertebral fracture and luxations, sacrocaudal (coccygeal) subluxation/luxation, traumatic ischemia and disc extrusion.
Definitive diagnosis of lymphosarcoma can be challenging and a thorough work-up with complete blood tests, infectious disease tests, abdominal ultrasound, chest radiography, bone marrow aspiration and lymph node aspiration should be performed in cats in which there is a high clinical suspicion of lymphosarcoma.
Inflammatory/infectious diseases account for almost 30% of all feline spinal cord diseases and include bacterial infections, FIP, cryptococcosis, toxoplasmosis, and FIV and FeLV infection.
Treatment needs to address the underlying cardiac disease, along with the discomfort and poor perfusion of the limbs. The prognosis depends on the primary cause of the thromboembolism as well as the severity of the neurological deficits. Most cats will die or are euthanazed due the underlying cardiomyopathy; initial survival is reported to be between 37 and 39% of cases,61,62 with a mean survival time of between 6 months 62 and 11.5 months. 61 Functional recuperation of motor and sensory pathways may occur, although a high rate of relapses is reported.61,62
References
- 1.Garosi L. The neurological examination. In: Platt S, Olby N, eds. BSAVA manual of canine and feline neurology. 3rd edn. Gloucester: BSAVA, 2004: 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Garosi L. Lesion localization and differential diagnosis. In: Platt S, Olby N, eds. BSAVA manual of canine and feline neurology. 3rd edn. Gloucester: BSAVA, 2004: 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Heyman A, Wilkinson WE, Hurwitz BJ, et al. Risk of ischemic heart disease in patients with TIA. Neurology 1984; 34: 626–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Garosi L, McConnell JF, Platt SR, et al. Results of diagnostic investigations and long-term outcome of 33 dogs with brain infarction (2000–2004). J Vet Intern Med 2005; 5: 725–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wessmann A, Chandler K, Garosi L. Ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke in the dog. Vet J 2008. June 23: Epub ahead of print [Pub Med ID: 18579421]. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Neer TM. Fibrocartilaginous emboli. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract 1992; 22: 1017–26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Singh M, Foster DJ, Child G, Lamb WA. Inflammatory cerebrospinal fluid analysis in cats: Clinical diagnosis and outcome. J Feline Med Surg 2005; 7: 77–93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Platt SR, Olby N. Neurological emergencies. In: Platt S, Olby N, eds. BSAVA Manual of canine and feline neurology. 3rd edn. Gloucester: BSAVA, 2004: 320–36. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Marioni-Henry K, Vite CH, Newton AL, Van Winkle TJ. Prevalence of diseases of the spinal cord of cats. J Vet Intern Med 2004; 18: 851–58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lujan A, Philbey AW, Anderson TJ. Intradural epithelial cyst in a cat. Vet Rec 2003; 153: 363–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Newitt A, German AJ, Barr FJ. Congenital abnormalities of the feline vertebral column. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 2008; 49: 35–41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Appel SL, Moens NM, Abrams-Ogg AC, Woods JP, Nykamp S, Bienzle D. Multiple myeloma with central nervous system involvement in a cat. J Am Vet Med Assoc 2008; 233: 743–47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Levy MS, Mauldin G, Kapatkin AS, Patnaik AK. Nonlymphoid vertebral canal tumors in cats: 11 cases (1987–1995). J Am Vet Med Assoc 1997; 210: 663–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Marioni-Henry K, Van Winkle TJ, Smith SH, Vite CH. Tumors affecting the spinal cord of cats: 85 cases (1980–2005). J Am Vet Med Assoc 2008; 232: 237–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Smoliga J, Schatzberg S, Peters J, McDonough S, DeLahunta A. Myelopathy caused by a histiocytic sarcoma in a cat. J Small Anim Pract 2005; 46: 34–38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Forterre F, Tomek A, Konar M, Vandevelde M, Howard J, Jaggy A. Multiple meningiomas: Clinical, radiological, surgical, and pathological findings with outcome in four cats. J Feline Med Surg 2007; 9: 36–43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stigen O, Ytrehus B, Eggertsdottir AV. Spinal cord astrocytoma in a cat. J Small Anim Pract 2001; 42: 306–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tomsa K, Glaus T, Hauser B, et al. Nutritional secondary hyperparathyroidismin six cats. J Small Anim Pract 1999; 40: 533–39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Muñana KR, Olby NJ, Sharp NJH, Skeen TM. Intervertebral disk disease in 10 cats. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 2001; 37: 384–89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sigurdson CJ, Basaraba RJ, Mazzaferro EM, Gould DH. Globoid cell-like leukodystrophy in a domestic longhaired cat. Vet Pathol 2002; 39: 494–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Carmichael KP, Howerth EW, Oliver JE, Klappenbach K. Neuroaxonal dystrophy in a group of related cats. J Vet Diagn Invest 1993; 5: 585–90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wamsley H, Alleman AR. Clinical pathology. In: Platt S, Olby N, eds. BSAVA manual of canine and feline neurology. 3rd edn. Gloucester: BSAVA, 2004: 35–53. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Grasmueck S, Steffen F. Survival rates and outcomes in cats with thoracic and lumbar spinal cord injuries due to external trauma. J Small Anim Pract; 45: 284–88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Voss K, Montavon PM. Tension band stabilization of fractures and luxations of the thoracolumbar vertebrae in dogs and cats: 38 cases (1993–2002). J Am Vet Med Assoc 2004; 225: 78–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Olby N, Thrall D. Neuroradiology. In: Platt S, Olby N, eds. BSAVA manual of canine and feline neurology. 3rd edn. Gloucester: BSAVA, 2004: 70–83. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lamb CR, Croson PJ, Cappello R, Cherubini GB. Magnetic resonance imaging findings in 25 dogs with inflammatory cerebrospinal fluid. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 2005; 46: 17–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gonçlves R, Platt SR, Llabrés-Díaz FJ, et al. Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging findings in 92 cats with clinical signs of spinal cord disease. J Feline Med Surg 2009; 11: 53–59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rand JS, Parent J, Percy D, Jacobs R. Clinical, cerebrospinal fluid and histological data from thirty-four cats with primary noninflammatory disease of the central nervous system. Can Vet J 1994; 35: 174–181, 292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rand JS, Parent J, Percy D, Jacobs R. Clinical, cerebrospinal fluid and histological data from twenty-seven cats with primary inflammatory disease of the central nervous system. Can Vet J 1994; 35: 103–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Abramson CJ, Platt SR, Stedman NL. Tetraparesis in a cat with fibrocartilaginous emboli. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 2002; 38: 153–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mikszewski JS, Van Winkle TJ, Troxel MT. Fibrocartilaginous embolic myelopathy in five cats. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 2006; 42: 226–33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.MacKay AD, Rusbridge C, Sparkes AH, Platt SR. MRI characteristics of suspected acute spinal cord infarction in two cats, and a review of the literature. J Feline Med Surg 2005; 7: 101–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rayward RM. Feline intervertebral disc disease: A review of literature. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol 2002; 15: 137–44. [Google Scholar]
- 34.King AS, Smith RN. Disc protrusion in the cat: Distribution of dorsal protrusion along the vertebral column. Vet Rec 1960; 72: 335–37. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kathmann I, Cizinauskas S, Rytz U, Lang J, Jaggy A. Spontaneous lumbar intervertebral disc protrusion in cats: Literature review and case presentations. J Feline Med Surg 2000; 2: 207–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Harris JE, Dhupa S. Lumbosacral intervertebral disk disease in six cats. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 2008; 44: 109–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lu D, Lamb CR, Wesselingh K, Targett MP. Acute intervertebral disc extrusion in a cat: Clinical and MRI findings. J Feline Med Surg 2002; 4: 65–68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bagley RS. Spinal fracture or luxation. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract 2000; 30: 133–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Papazoglou LG, Galatos AD, Patsikas MN, et al. High-rise syndrome in cats: 207 cases (1988–1998). Aust Vet Pract 2001; 31: 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bescalti O, Ozak A, Tong S. Management of spinal trauma in 69 cats. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr 2002; 109: 315–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Roy RR, Hodgson JA, Lauretz SD, Pierotti DJ, Gayek RJ, Edgerton VR. Chronic spinal cord-injured cats: Surgical procedures and management. Lab Anim Sci 1992; 42: 335–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hulbert RJ. Methylprednisolone for acute spinal cord injury: An inappropriate standard of care. J Neurosurg Spine 2000; 93: 1–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Short DJ, Masry WS, Jones PW. High dose methylprednisolone in the management of acute spinal cord injury –- a systematic review from a clinical perspective. Spinal Cord 2000; 38: 273–86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hall ED. The neuroprotective pharmacology of methylpred-nisolone. J Neurosurg 1992; 76: 13–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Boag AK, Otto CM, Drobatz KJ. Complications of methylpred-nisolone sodium succinate therapy in dachshunds with surgically treated intervertebral disc disease. J Vet Emerg Crit Care 2001; 11: 105–10. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rohrer CR, Hill RC, Fischer A, et al. Gastric hemorrhage in dogs given high doses of methylprednisolone sodium succinate. Am J Vet Res 1999; 60: 977–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sharp JH, Wheeler SJ. Trauma. In: Small animal spinal disorders. Diagnosis and surgery.2nd edn. Mosby: Elsevier, 2005: 281–318. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lane SB, Kornegay JN, Duncan JR, Oliver JE., Jr. Feline spinal lymphosarcoma: A retrospective evaluation of 23 cats. J Vet Intern Med 1994; 8: 99–104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Spodnick GJ, Berg J, Moore FM, Cotter SM. Spinal lymphoma in cats: 21 cases (1976–1989). J Am Vet Med Assoc 1992; 200: 373–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Vail DM, MacEwen EG. Feline lymphoma and leukemia. In: Withrow SJ, MacEwen EG, eds. Small animal clinical oncology. Philadelphia: WB Sanders, 2001: 590–611. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Noonan M, Kline KL, Meleo K. Lymphoma of the central nervous system: A retrospective study of 18 cats. Compend Contin Educ Pract Vet 1997; 19: 497–503. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Gerds-Grogan S, Dayrell-Hart B. Feline cryptococcosis: A retrospective evaluation. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 1997; 33: 118–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Legendre AM, Whitenack DL. Feline infectious peritonitis with spinal cord involvement in two cats. J Am Vet Med Assoc 1995; 167: 931–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Foley JE, Lapointe JM, Koblik P, Poland A, Pedersen NC. Diagnostic features of clinical neurologic feline infectious peritonitis. J Vet Intern Med 1998; 12: 415–23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Summers BA, Cummings JF, de Lahunta A. Veterinary neuropathology. St Louis, Missouri: Mosby-Year Book Inc, 1995: 300–7. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hartmann K, Binder C, Hirschberger J, et al. Comparison of different tests to diagnose feline infectious peritonitis. J Vet Intern Med 2003; 17: 781–90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kline KL, Joseph RJ, Averill DR. Feline infectious peritonitis with neurologic involvement: Clinical and pathological findings in 24 cats. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 1994; 30: 111–18. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Negrin A, Lamb CR, Cappello R, Cherubini GB. Results of magnetic resonance imaging in 14 cats with meningoencephalitis. J Feline Med Surg 2007; 9: 109–16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sparkes AH, Gruffydd-Jones TJ, Harbour DA. An appraisal of the value of laboratory tests in the diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 1994; 30: 345–50. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Addie DD, Paltrinieri S, Pedersen NC. Recommendations from workshops of the second international feline coronavirus/feline infectious peritonitis symposium. J Feline Med Surg 2004; 6: 125–30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Laste NJ, Harpster NK. A retrospective study of 100 cases of feline distal aortic thromboembolism: 1977–1993. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 1995; 31: 492–500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Schoeman JP. Feline distal aortic thromboembolism: A review of 44 cases (1990–1998). J Feline Med Surg 1999; 1: 221–31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]