Abstract
This study describes findings of novel coronavirus testing on pooled nasopharyngeal and bronchoalveolar lavage samples taken from patients who had negative results by routine respiratory virus testing to see if pooling samples could increase testing throughput and efficiency and facilitate early detection of community COVID-19 transmission.
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has revealed the global importance of robust diagnostic testing to differentiate severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) from other routine respiratory infections and guide appropriate clinical management. Given the limited testing capacity available in the United States early in the pandemic, individuals with a clinical syndrome consistent with COVID-19, but without travel or exposure history, were not tested.1 Therefore, it remains uncertain whether there may have been community circulation of SARS-CoV-2 prior to the identification of individuals with positive results through standard public health surveillance. Sample pooling, a strategy used for community monitoring of other infectious diseases such as trachoma, has not, to our knowledge, been deployed for the early comprehensive screening of SARS-CoV-2 in the United States.2
Methods
The Stanford Health Care Clinical Virology Laboratory serves adult and pediatric tertiary care hospitals and affiliated primary care and specialty clinics in the San Francisco Bay Area in California. We performed a retrospective study that evaluated all nasopharyngeal and bronchoalveolar lavage samples collected between January 1, 2020, and February 26, 2020, from inpatients and outpatients who had negative results by routine respiratory virus testing (respiratory pathogen or respiratory viral panels [GenMark Diagnostics] or Xpert Xpress Flu/RSV [Cepheid]) and had not been tested for SARS-CoV-2. After February 26, 2020, clinical testing for SARS-CoV-2 on individual samples was begun, as recommended by institutional policy. Nine or 10 individual samples were pooled, and screening was performed using reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction targeting the envelope (E) gene.3 Positive pools were deconvoluted and individual samples tested for both E and the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) gene for confirmation.3 This study was approved by the Stanford institutional review board. Given the deidentified nature of testing, individual patient consent was not required, as determined by the institutional review board, for this study.
Results
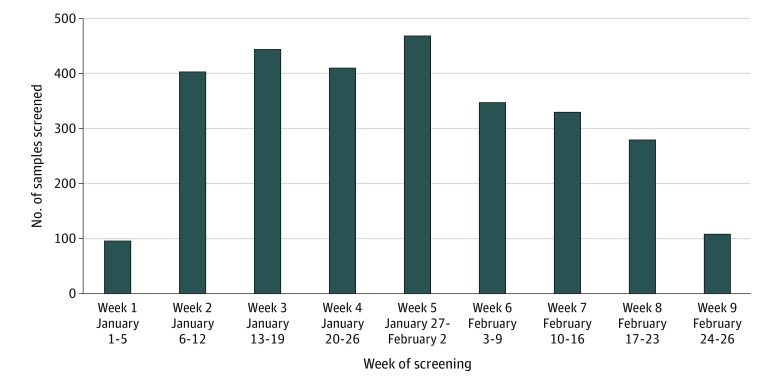
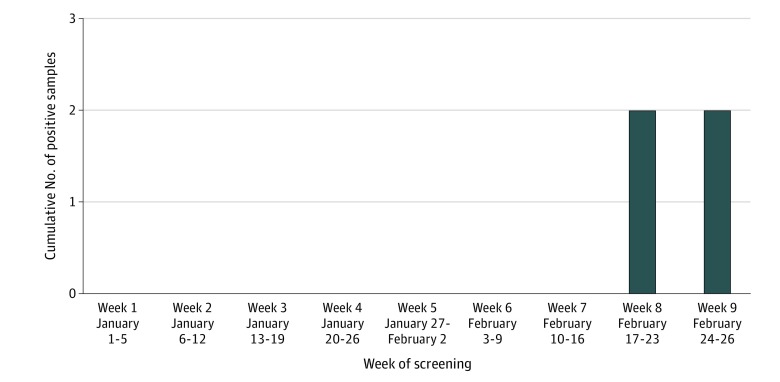
A total of 292 pools were screened, corresponding with 2740 nasopharyngeal samples and 148 bronchoalveolar lavage samples (Figure 1). The confirmed positivity rate for SARS-CoV-2 was 0.07% (2/2888) (Figure 2). The positive results were from nasopharyngeal samples collected on February 21, 2020, and on February 23, 2020. The 2 positive samples showed detection of E and RdRp. Sanger sequencing revealed 100% identity with the SARS-CoV-2 E gene. Only 1 pool showed a positive E signal that was not reproducible with testing of the individual samples of that pool.
Figure 1. Number of Samples Screened for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
Testing was performed by pooled sample screening at the Stanford Health Care Clinical Virology Laboratory over a 9-week period (January 1, 2020-February 26, 2020). Each pool included 9 to 10 individual samples that tested negative for other respiratory viruses. The number of SARS-CoV-2 samples, listed for weeks 1 through 9, were 96, 404, 444, 410, 469, 347, 330, 280, and 108. A total of 292 pools composed of 2888 individual samples were screened.
Figure 2. Cumulative Number of Positive Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Samples.
Two positive samples were identified through pooled screening during week 8. Week 9 indicates the cumulative number for the screening period. See Figure 1 caption for testing details.
Discussion
Results from this screening strategy support that the burden of disease in the San Francisco Bay Area early in the pandemic was low; less than 1% of all symptomatic individuals with negative routine testing had SARS-CoV-2 infection. The timing of the positive pools overlapped with the first 3 individuals with positive results reported from Santa Clara County, tested using criteria established by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.4,5 Thus, public health counts of individuals with SARS-CoV-2 infection indicated a reasonable estimate of overall disease burden among symptomatic individuals in this area.6 Nevertheless, the individuals identified with positive results via this screening strategy would not have met the existing testing criteria.
A pooled screening strategy was pursued to increase testing throughput, limit use of reagents, and increase overall testing efficiency at an expected slight loss of sensitivity. With only 1 false-positive reading, the strategy was specific. Due to the challenges of restricted access to diagnostic tests and kit supplies across the United States, early testing has largely been limited to symptomatic individuals fulfilling testing criteria.4 Although this approach facilitates rational use of resources, it may miss individuals in whom COVID-19 risk has not been identified.4 This study is limited in that it was performed in a single laboratory in a restricted geographical area; additional data are thus required to validate this approach on a larger scale. Furthermore, this screening strategy does not obviate the need for individual diagnostic testing, particularly as community transmission intensifies.
Strategies such as pooled screening may facilitate detection of early community transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and enable timely implementation of appropriate infection control measures to reduce spread.
Section Editor: Jody W. Zylke, MD, Deputy Editor.
References
- 1.Sharfstein JM, Becker SJ, Mello MM. Diagnostic testing for the novel coronavirus. JAMA. Published online March 9, 2020. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.3864 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ray KJ, Zhou Z, Cevallos V, et al. Estimating community prevalence of ocular Chlamydia trachomatis infection using pooled polymerase chain reaction testing. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2014;21(2):86-91. doi: 10.3109/09286586.2014.884600 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Corman VM, Landt O, Kaiser M, et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill. 2020;25(3):1-8. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Evaluating and testing persons for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Updated March 24, 2020. Accessed March 25 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-criteria.html
- 5.Santa Clara County Public Health Healthy Santa Clara County: novel coronavirus (COVID-19) data dashboard. Accessed March 25, 2020. https://www.sccgov.org/sites/phd/DiseaseInformation/novel-coronavirus/Pages/dashboard.aspx
- 6.Lipsitch M, Swerdlow DL, Finelli L. Defining the epidemiology of COVID-19—studies needed. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(13):1194-1196. Published online March 26, 2020. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2002125 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]