Figure 1.
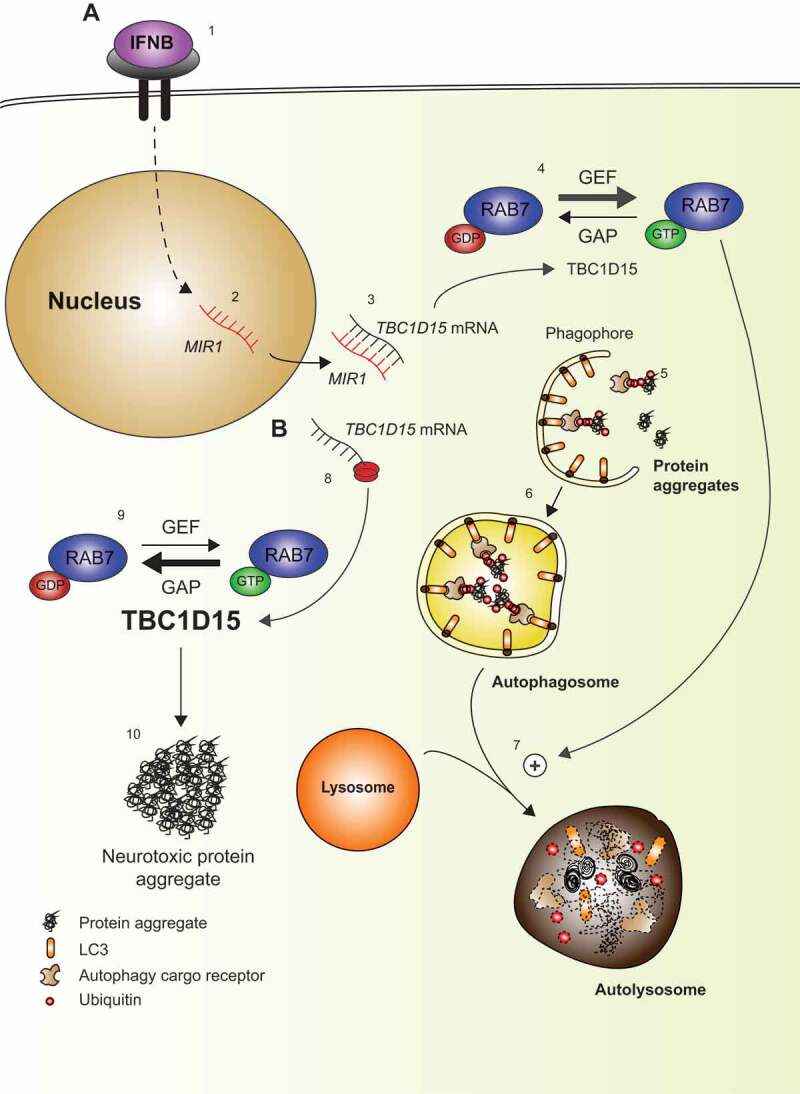
Schematic overview. (A) IFNB binds to IFNAR1/IFN-α/β-receptor and activates downstream signaling (1) including transcription of MIR1 (2), which binds to the 3ʹ UTR of TBC1D15 and thereby repress its translation (3). TBC1D15 is a GTPase activating protein (GAP), which shuts down the activity of RAB7 by promoting GDP-binding. Thus, with low levels of TBC1D15, the abundance of active GTP-bound RAB7 will be favored due to guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity (4). Protein aggregates are targeted by autophagy cargo receptors and subsequently couple to LC3-II in the phagophore membrane (5), which eventually forms a vesicular autophagosome (6). The autophagosomes fuse with lysosomes for clearance of the protein aggregates in a process promoted by active RAB7 (7). (B) If TBC1D15 translation is increased, e.g., by low MIR1 (8) this shuts down RAB7 activity (9), and under stress conditions neurotoxic protein aggregates will form due to reduced autophagy (10).
