Dear Editor
The mortality rate COVID-19 has been reported One study showed that out of 99 infected patients, 57 (58%) were hospitalized, 31 (31%) were discharged, and 11 (11%) had died [1].Shortly after the emergence of the disease in Iran, many people were infected and unfortunately died, and many others were also recovered and discharged from hospitals. The main purpose of this study was to evaluate new clinical experiences and assess the clinical and paraclinical features of patients deceased due to COVID-19 in Shahid Mostafa Khomeini Hospital of Ilam in March 2020.
In this cross-sectional descriptive-analytic study, clinical archives of patients diagnosed with and deceased due to COVID-19 in ShahidMostafa Khomeini Hospital of Ilam (Iran) were evaluated in March 2020.
The first part of the tool included patients’ demographic variables, the second part was related to clinical symptoms, and the third part included blood and biochemical laboratory tests, the final section of the data gathering tool was related to the results of chest CT scan and their interpretation.
From February 3, 2020 to3/9/2020, 56 patients were hospitalized in the Mustafa Khomeini Hospital of Ilam. Out of these, 4 including 3 (75%) women and 1 (25%) man died of COVID-19. The patients’ mean age was 63 ± 6.37 years, and the mean hospital stay was 3.25 ± 2.5days.
The patients’ details of CT scan results have been illustrated in Fig. 1a, Fig. 1b, Fig. 1c, Fig. 1d (a–d) . Real time PCR results were positive in all the patients.
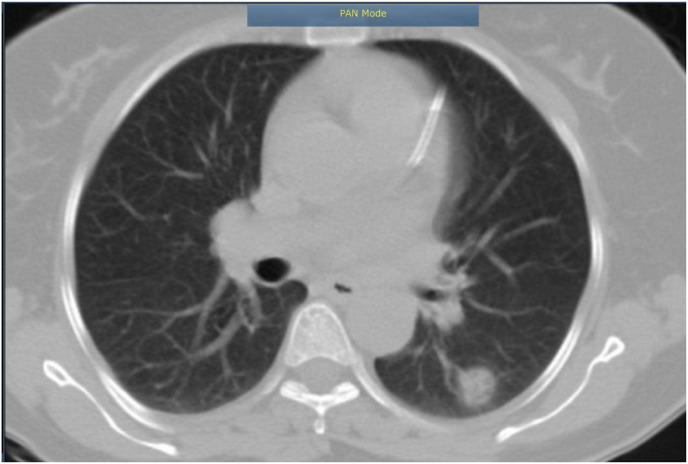
Fig. 1a.
There is round area of ground glass opacity in superior segment of LLL, it can highly suggestive for COVID-19, further essay is recommended. The bronchial system is visualized to have normal caliber with no sign of peribronchial infiltration. No abnormal dilatation of bronchial system or bronchiectasis is noted. Unfortunately due to lack of contrast evaluation of mediastinum can notpossible. Bony thorax and soft tissue structures are apparently normal in anatomic configuration and density.
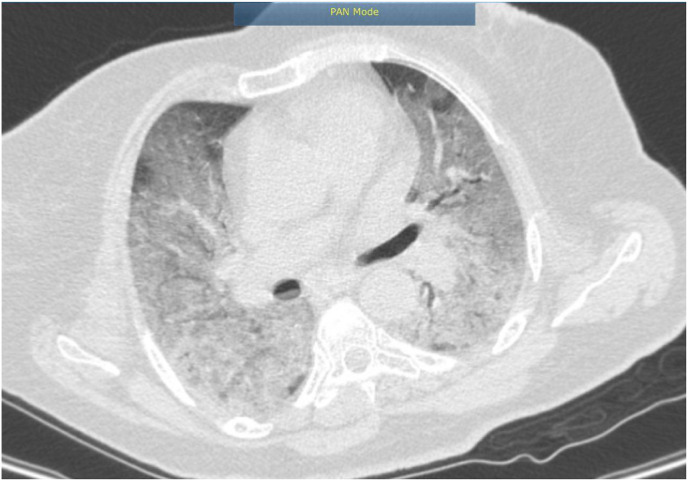
Fig. 1b.
Widespread diffuse ground glass opacity are noted in both lung more dominant in lower lobes, finding are highly suggestive of viral/atypical pneumonia including COVID -19 with resultant ARDS, COVID-19 essay and clinical correlation is recommended pneumothorax in left hemithorax is noted, there is no sign of interstitial lung disease.
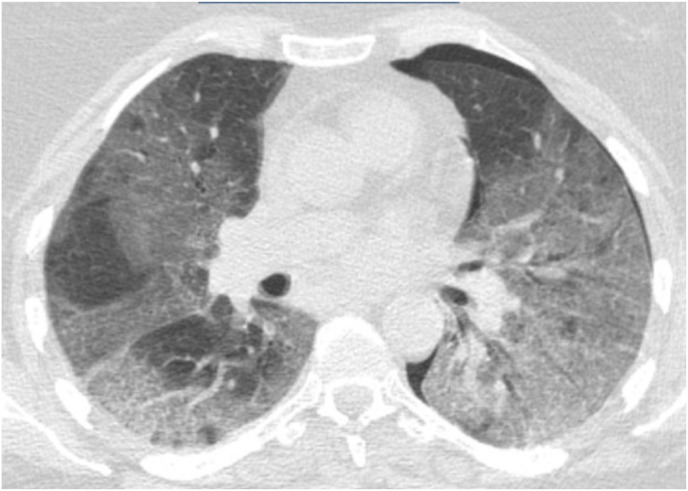
Fig. 1c.
Widespread diffuse ground glass opacity are noted in both lung more dominant in lower lobes, finding are highly suggestive of viral/atypical pneumonia including COVID -19 with resultant ARDS, COVID -19 essay and clinical correlation is recommended pneumothorax in left hemithorax is noted, there is no sign of interstitial lung disease.
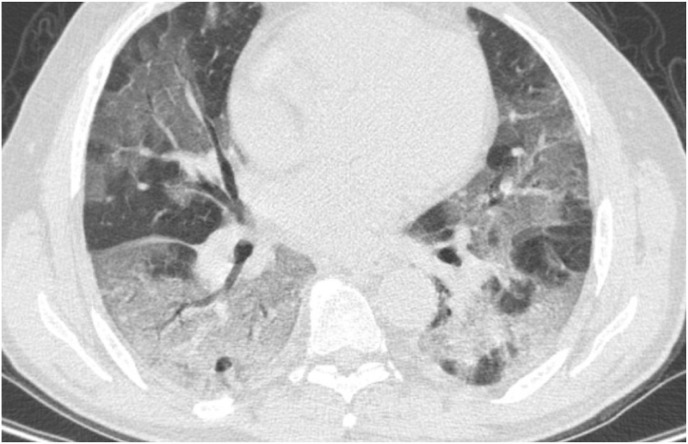
Fig. 1d.
Diffuse ground glass opacity in both lungs mostly in peripheral spaces with extension to central parts associated with patchy consolidation in both lower lobes, in favor of viral pneumonia, COVID-19.There is a calcification area measuring about 19.5*10.7 mm in RUL.
Specialists should consider biochemical conditions such as sodium and potassium disorders and previous histories of heart failure, diabetes and hypertension when visiting patients who are suspicious to have COVID-19. In fact, physicians should not overlook other clinical symptoms in the shadow of COVID-19. Another new clinical experience was that CRP might be negative in patients with COVID-19. Therefore, CRP is not a sensitive marker in this condition. Late referral of patients can increase mortality rate while those who timely visited the hospital had better response to treatment. Finally, many subjects had actually negative results for COVID-19, but they had fear of the virus indicating an exaggerated rate of panic of the disease.
The bronchial systems are visualized to have normal caliber with no sign of peribronchial infiltration or bronchiectasis.
According to the official report of ShahidMostafa Khomeini Hospital of Ilam, 56 patients with the definitive diagnosis of COVID-19 were admitted to the hospital until October 3, 2020. Of these, four patients succumbed to the disease complications representing a mortality rate of 7.14%.
Regarding CT results, patients with COVID-19 showed complete involvement of lungs and considerable damage to the pulmonary tissue. Consistent with our results, Nanshan Chen et al., in 2020 also reported widespread pulmonary involvement and extensive tissue damage in patients with COVID-19 [1]. These observations show that CT scan can be a suitable diagnostic procedure for COVID-19.
Declaration of competing interest
We declare that we have no competing interests.
Acknowledgments
The Research Ethics Committee of Ilam University of Medical Sciences (IR.MEDILAM.REC.1398.212) approved this research.
Reference
- 1.Chen Nanshan, Zhou Min, Dong Xuan, Qu Jieming, Gong Fengyun, Han Yang, Qiu Yang, Wang Jingli, Liu Ying, Yuan Wei, Xia Jia’an, Ting Yu, Zhang Xinxin, Zhang Li. Pidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel corona virus pneumonia in Wuhan, China:a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395:507–513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]